Agronomists, gardeners and summer residents know how to preserve plant seedlings and crops in early spring and during frosts. For these purposes, they use covering material for beds, roses, strawberries, etc. This material allows you to protect plants and crops from temperature extremes and other negative effects of cold weather.
A few decades ago, ordinary or reinforced polyethylene film was the main and practically the only covering material. The film protects plants from the cold, but has several disadvantages. Polyethylene does not allow air and moisture to pass through, so the plants have to be regularly watered and ventilated. Also, frost and snow loads negatively affect the durability of such a film. It usually lasts only a couple of seasons, or even one.
|
|
Polyethylene
Polyethylene is perhaps the most popular material among gardeners and gardeners. The scope of its use is very large (greenhouses, hotbeds, beds in spring, etc.). However, with the advent of more modern and technologically advanced materials on the market, it gradually began to lose ground. One of the main disadvantages of polyethylene is that it does not breathe, that is, by covering it with roses or any other culture, you cut off oxygen. A typical situation is when plants are burned under polyethylene. Positive qualities - wear resistance, ability to retain heat, cheapness. Such covering material for roses for the winter can be used in emergencies and with caution.


Answers to questions from gardeners
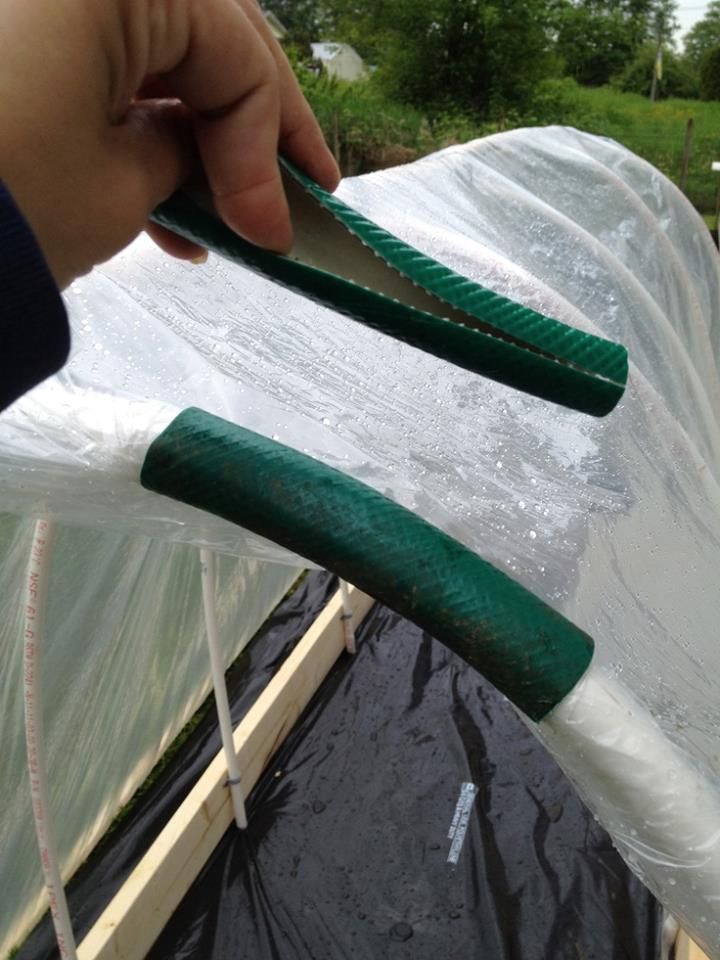


For attaching the covering material to the frame, cuttings of the old hose are useful. Question # 1: How to properly secure the Spunbond to the greenhouse frame?
The covering material is easily pinned to the wooden frame with a construction stapler. You can connect individual pieces of Spunbond to each other with double-sided tape, special construction tape or Velcro stitched along the edges. A hot glue gun or ordinary plastic film, laid between the overlapping layers of Spunbond and ironed with a hot iron, will firmly glue the joints. As a last resort, the edges of the canvases can simply be sewn with synthetic (not cotton) threads.
Tip # 2: To prevent the non-woven fiber from spilling out from damage by nails, screws or stapling staples, it is recommended to attach the Spunbond to the frame through a protective pad.
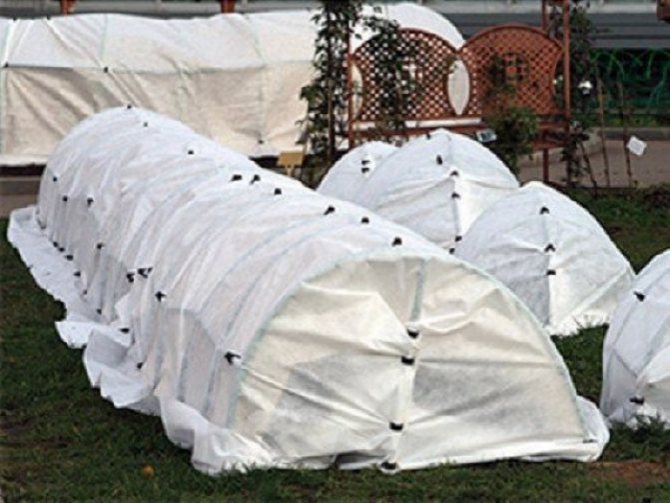


It is convenient to fasten the Spunbond on the arches of the greenhouse or greenhouse with clothespins or plastic clips. Question # 2: For what period is the spanbond's service life calculated?
The thinner the covering material, the shorter the period of its operation, on average it is 3-4 seasons. With careful use and proper storage, the service life can be extended to 5-6 years. At the end of use, the canvas is cleaned of debris, if necessary, rinsed in water, but do not twist. Repeatedly used material is recommended to be disinfected with a weak solution of potassium permanganate or any fungicides. If it is heavily soiled, the cloth is washed with an ordinary detergent by hand and even in a washing machine, but without spinning. Then the water is allowed to drain, the material is well dried and stored folded. The storage location must be dry and protected from the sun.
Rate the quality of the article. Your opinion is important to us:
Shelter technology
The technology is simple.The pre-prepared rose bushes are twisted and tied up in the form of arches (not too high) to the arches pre-installed on the garden bed. Then roofing material is laid, and polyethylene is placed on top. It is important to press down on the edges of the material to limit the access of moisture. The main purpose of any shelter is to create an air cushion inside where warm air will circulate. In the spring, the shelter is removed gradually: first, the end sides are opened so that the roses do not get blocked, and when the heat comes, the bushes are completely released.
Purchased


Covering materials for roses for the winter, manufactured industrially, have a different composition, price, quality. Agrotextiles are sold in rolls or in pieces of a certain format. Covering properties are determined by density, it is measured in g / m². The higher the value, the more reliable the protection.
Lutrasil
Lightweight durable material for long-term use. Multiple seasons can be used. Lutrasil benefits:
- allows air to pass through;
- there is no greenhouse effect under it;
- the canvas does not get wet.
To protect the flower garden from frost, white lutrasil with a density of 60 g / m² is best suited. Roses are covered with material folded in 2 layers.
A less dense material (30-50 g / m²) can be used to cover bushes. It is folded into 3-4 layers. A running meter of lutrasil costs from 25 to 50 rubles. Covers are sewn on erect, thick shoots from covering material with their own hands. Flexible varieties of roses are bent to the ground, leaving a gap to the ground (10-20 cm), arcs are placed, a non-woven cloth is thrown. On the sides it is fixed with hairpins, bricks, boards.
Geotextile
Geotextiles have long been used in industrial rose gardens in the Moscow region. The canvas is sewn from 3 layers, covering large areas with it. All varieties of roses under it hibernate well without hilling. Group plantings are covered in one piece. For standard and climbing types of roses, they sew covers.
The canvas is laid on arches or supports, this allows you to distribute the snow load. Leaves are removed from the bushes and bent down. The soil is covered with mulch from a mixture of dry sawdust and horse manure.


Geotextiles are used in construction and landscape design. It is composed of polymer fibers. It is sold in rolls of different widths. Ready-made geotextile covers are available at gardening stores. Material pluses:
- strength;
- durability;
- frost resistance;
- environmental friendliness;
- air and water permeability;
- no condensation.
Read also Money tree planting an appendix
Polyethylene film
The attitude to the film as a means of protection against frost among flower growers is not unambiguous. There are negative reviews, but many use it successfully. In regions with harsh winters, thick snow cover, roses winter well under a cover made of plastic wrap. The air cushion under it protects the roots and shoots of roses from freezing.
Spunbond
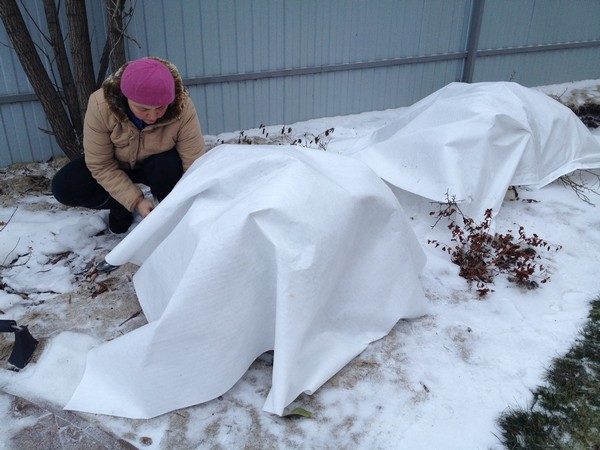


This material can be used for several seasons. It allows water and air to pass through. The cost of spunbond is not high, which makes it affordable. It is used for winding single bushes of the standard type, pulled on frames made of plastic (metal) arcs, bars, willow rods.
Spunbond is used in 2-3 layers, only white with a density:
Sackcloth
Jute bags or polypropylene sugar bags are a budget option for sheltering roses for the winter. They are put on separately growing bushes. Dry leaves are poured inside, the bottom is fixed with twine and spud with earth. Vegetable nets are filled with dry fallen leaves, used as a heater.
Construction Materials


The materials left over after the construction of summer cottages, a country house may come in handy. Boards, bars go to the construction of shields, houses. Roofing material is laid on the ground before shoots are put on it. Sheets of slate are used to build huts for roses. Trunk circles are mulched with expanded clay.
Improvised means
Various materials at hand are used to fix the covering material:
- ropes;
- twine;
- pegs made of wood or reinforcement;
- welding electrodes instead of staples;
- pieces of wire;
- boards;
- bricks.
Spruce branches
Lapnik is not available to everyone. It is used by those who live near a coniferous forest. It is not very suitable for hiding large rose gardens; you need a lot of it. To protect low-growing rose bushes from frost, you need to create a layer of branches at least 30 cm thick.
A shelter made of spruce branches must be covered with snow, and a covering material should be pulled over it if there is no snow. You can close roses with spruce branches when the daytime temperature drops to -6 ° C.
Leaves
In the fall, there are enough leaves in any garden. They can be used for frost protection if the trees are healthy. You can only fall asleep rose bushes with dry material. Wet leaves provoke the development of fungal diseases in roses.
Leaves will fly apart without additional cover. To fix them around the bush, cardboard boxes, nets, fine-mesh plastic mesh, wood shields, and other materials at hand are used.
Sawdust
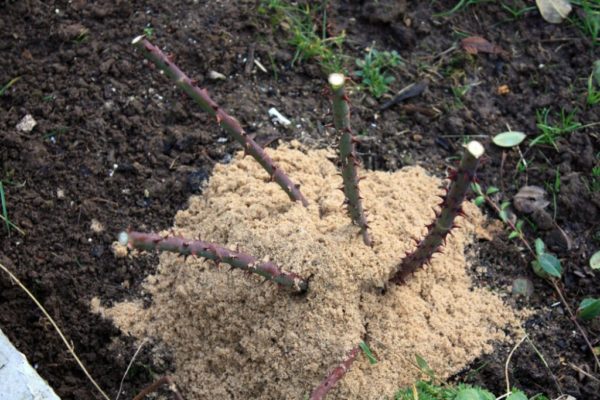


Sawdust is best used by combining them with other types of shelters (shields, covering material). They are more suitable for regions with harsh winters, where thaws are rare. Not all sawdust is suitable for covering a flower garden. Can not use:
- fine fraction;
- furniture waste containing chemicals.
It is better to use coniferous sawdust with a size of 10 mm or more as a covering material. They are less caked, hygroscopic, and have antiseptic properties. They insulate with sawdust in different ways:
- the trunk circle is covered, shields are placed over the bushes, they are covered with film;
- they do not fill the nets tightly with sawdust, put them under the lashes, put arcs on top, throw covering material;
- in the northern regions, shields are placed over low bushes with a house, on top of them they are filled with a thick layer of sawdust.
Humus
This organic material will not protect the aerial part of the flower from frost. It is used for mulching the soil, it protects it from freezing, increases fertility. Humus is mixed with dry sawdust to loosen it up.
Spunbond
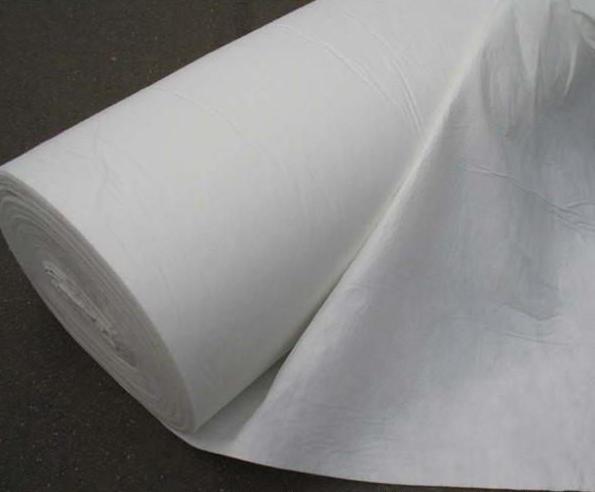


Spunbond is a non-woven covering material (including for winter roses), which has become a good alternative to the usual polyethylene. Its main advantage is its excellent price / functionality ratio. Spunbond is able to create a favorable light regime for the plant (black, opaque, on the contrary, helps to fight weeds), protecting it from the scalding rays of the sun, which is important for roses in early spring. It quickly and easily passes air and moisture without retaining it, prevents insects and rodents from penetrating the bushes, is wear-resistant and can be used for several seasons. Spunbond tolerates temperatures as low as -55 ° C.
This covering material for roses for the winter prices (reviews about it are very positive) are very affordable. It can be used in many different ways. For bush plants, you first need to build a frame made of wood or put arcs, and then lay spunbond on top. It is also very convenient for climbing roses, which do not need to be removed from the supports, but it is enough to wrap it with material and fix it with clothespins or a construction stapler. It is almost impossible to bend the standard species to the ground, so they should be wrapped up. You can make an impromptu bag of non-woven material, or just carefully wrap it around the trunk of the plant, and gently fasten it with a soft rope on top.
Spundbond is highly rated according to reviews. Gardeners note that it is reliable, easy to handle (storage, assembly, drying) and efficient. Rose bushes and other plants hibernate well, in addition, after winter, a cloth of material can be used for other purposes in the garden.
What to make arches for sheltering roses.Air dry shelter
Let's not reinvent the wheel, but turn our eyes to the past. Even our grandmothers, by trial and error, came to the conclusion that roses winter more successfully in low dry shelters with an air gap. So this method got its name - air-dry shelter (APU). Let's remember how it was ...
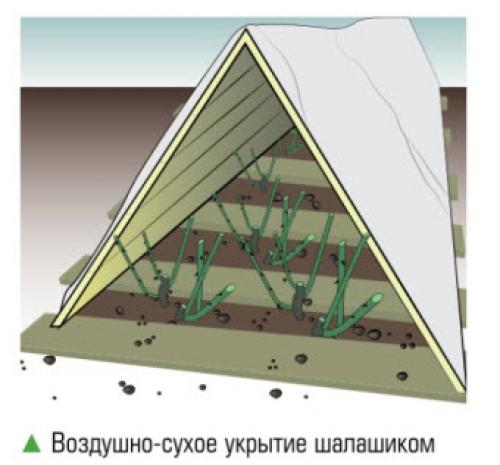

In the years of total deficit and in the absence of any other choice, the roses were covered with building materials that were at hand at that moment, most often they were boards, roofing material and film. The first step was to build wooden frames. These could be both rectangular shapes with a flat roof, and frame houses or huts. A prerequisite is strength, since they must withstand the weight of roofing material and snow. The frames were overlapped with sheets of roofing material, and to protect them from rain and moisture, a film was laid on top - hence the name of the method. Since these materials do not allow air to pass through, the sides or vents were necessarily left open before the first frost. With the onset of stable subzero temperatures, they were carefully and tightly closed. In the spring, the order of opening and airing began with the opening of the ends.


Over the years, the APU method has established itself as the most reliable and effective. However, over the past time, it has undergone significant transformations. Only the general principle has remained unchanged - the construction of frame houses and huts is still at its core. And with the advent of a huge variety of garden tools and modern covering materials, the arrangement of shelters for roses has become much simpler, easier and, importantly, faster. The quality and functionality of shelters has also noticeably improved: they have become more reliable in terms of wintering and more convenient in construction. Consider some of the most popular and uncomplicated shelter methods and their features.
First of all, let me remind you: in order to see the luxurious flowering of roses in the middle lane, it is necessary to preserve the entire ground part of the bushes, or rather, their shoots along the entire length. So, roses need to be covered for the winter. You need to think about the future shelter and the method of its construction even at the stage of planting, namely, in which direction you will bend the bushes (this is especially important when planting climbing and standard roses). You should also calculate the length and width of future shelters, their shape, provide with a margin of space for the construction of frames.
The easiest way is to build a long rectangular shelter no wider than 1.5 m.
Therefore, it is more convenient to plant roses not as single bushes or tapeworms, but in arrays in one or two rows or in a checkerboard pattern. Rosaries of a wide, irregular, round or curved shape with smooth turns will require more careful skill in the construction of frames, they will not be the most convenient to maintain, and the construction will take you more time.


Geotextile
Timely covering roses for the winter with covering material is a necessary measure if you want to save the plants until next year. In recent years, geotextiles have become very popular. Initially, it was created for the construction industry, however, due to its structure and properties, it has become indispensable in horticulture. Geotextiles are perfect for protecting plants from mold, frost and rodents. Advantages of the material: strength (not subject to decay), the ability to pass air and moisture, allowing excess condensate to evaporate, affordability.
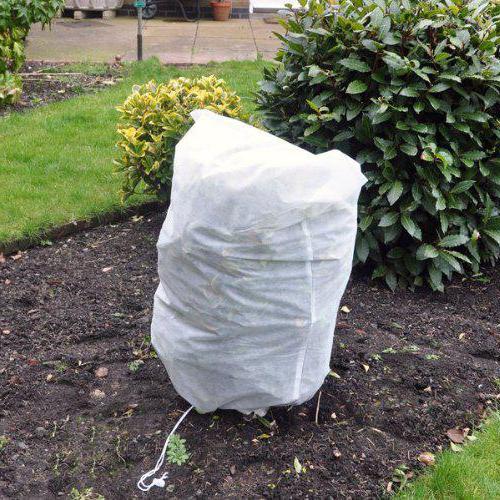


Shelter technology is similar to that of a spunbond and is described above. In horticulture, it is best to use geotextiles with a density of 200 g per sq.m. Now in stores you can buy material not only for a cut, but also ready-made bags for sheltering roses and other shrubs.
Features of the use of different types of Spunbond
Black spunbond is used to get rid of weeds, regulate soil temperature and moisture. White - to protect plants from bad weather, frost and heat.Depending on the technical characteristics, different Spunbond modifications are used for different types of garden work:
- white (with a density of 17 g / m² and 30 g / m²) - light, hygroscopic, transmits sunlight well, used to protect plants from bad weather and frost down to -3 ° C;
- white (42 g / m²) - with sufficient thermal insulation and light transmission, serves to cover the beds on arcs, create tunnel greenhouses and light greenhouses, withstands frosts down to -8 ° C;
- white (60 g / m²) - high density, used in the construction of greenhouses, for winter wrapping of plants for use in windy areas;
- black (50 and 60 g / m²) - used for mulching and rapid heating of the soil;
- black and white two-layer - combines the properties of a covering and mulching cloth: the black layer inhibits weeds, the white one protects the roots from overheating;
- red-white and red-yellow - to protect garden and horticultural crops from adverse weather conditions;
- foil - activates growth processes by reflecting the sun's rays on the plant;
- laminated - does not allow moisture and air to pass through;
- reinforced - a modernized material of increased strength for enhanced protection of plants from temperature extremes, weeds, pests, construction of greenhouses and greenhouses.
Lutrasil
A popular covering material for roses for the winter, reviews of which are mostly positive. It is made using a technology similar to the production of spunbond, and therefore has similar characteristics. Positive qualities: durability, ease of storage (it is enough to dry, roll up and remove), eco-friendly, moisture and air permeable, affordable. Varies with density. To shelter roses before winter, use material with an indicator of 60 g per square meter. m. As for the comparison with spunbond, then lutrasil loses to him only in terms of resistance to ultraviolet radiation. Shelter technology is similar.
Varieties of nonwovens


It is convenient to cover roses for the winter with ready-made protective covers made of non-woven fabric. Spunbond is produced under different brands: Lutrasil, Agrotex, Agrolux, Spunbel, Agril. In fact, these are the same material, differing in some details.
- Lutrasil is a high quality German material with good breathability, no greenhouse effect. Unlike Spunbond, it is less resistant to solar radiation.
- Agrospan is a domestic material with an increased (up to 5 years) service life due to the special Agrolight stabilizer.
- Agril is a French material with a high quality UV stabilizer. Has 5 density categories.
- Spunbel is a material of Belarusian production, has increased strength. Available in 5 density options.
- AgroSUF is a Russian material with a smooth homogeneous structure. The designation SUF indicates the presence of ultraviolet stabilizers in the fabric, which neutralize the effect of sunlight.
- Agrotex - has a wide assortment. In addition to standard rolls and cut-off panels, the Russian company produces ready-made shelters: protective covers, near-trunk circles, inter-row strips, etc.
Spruce branches and dry foliage


Dry leaves, formed in abundance in the fall, as well as reliable coniferous spruce branches - a traditional covering material for roses for the winter, considered one of the best. It is not expensive, although you will have to set aside time for a trip to the forest, and it is environmentally friendly, helping to protect plants not only from frost, but also from annoying rodents that can destroy everything in their path. Pine or spruce branches perfectly protect from cold wind, freezing rain, sleet and create an ideal space inside the shelter with excellent ventilation. Under its cover, sharp temperature drops are smoothed out and the detrimental effect of winter sunlight is reduced.
But, like any materials, spruce branches have their drawbacks.Firstly, the harvesting of branches is allowed only from trees that have already been felled in certain places or a sanitary cleaning zone. Secondly, if the forest is far away, then it will be problematic to stock up on spruce branches. Thirdly, it is possible to bring various pests or diseases along with the branches to the site. Therefore, walking through the forest, you need to carefully look at the trees from which you are going to take spruce branches.
How to mulch plants?
Here are the main materials used for this:
- sawdust;
- needles;
- sackcloth;
- brushwood;
- straw;
- Construction Materials;
- spruce branches;
- peat.
Check out the advantages and disadvantages of these plant shelters.
Sackcloth
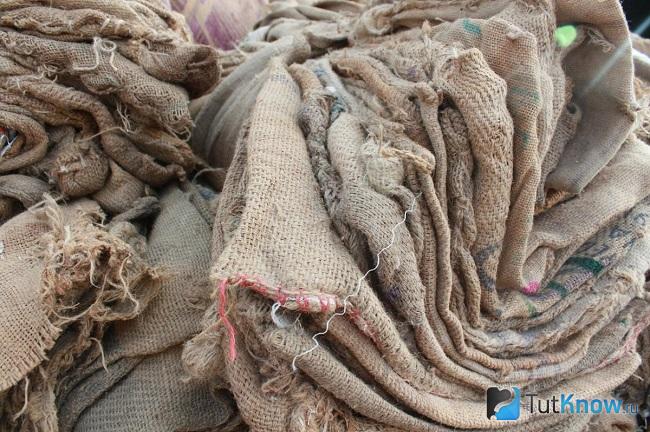


Insulation for plants has been made from it since ancient times. With this material:
- tying tree trunks;
- cover roses, hydrangeas;
- shade conifers so that they do not get sunburn.
These are the disadvantages of this material - burlap allows moisture. If it gets wet and freezes, it will become an ice carapace for plants. Under the burlap, ventilation is not very good and the crops covered with it can vomit, rot, and mold. Therefore, such a shelter is justified in a region where there is dry snow and there are no winter thaws.
Sawdust


Sawdust is an excellent thermal insulation material. But it is better not to cover the whole plant with them, but only the near-stem circle, covering the above-ground part. Some put sawdust in bags and thus insulate crops.
You can use only natural sawdust from wood, and not various by-products, such as chipboard.
It is necessary to mulch the plants only with dry sawdust, as wet preyut. If the shelter is not dry, moisture gets under the crops, then the sawdust should be positioned so that they do not touch the plant trunks. It is better to use large sawdust, they do not absorb moisture as well as small ones.
Sawdust acidifies the soil, so it is better to mulch the soil with them under crops that prefer acidic soil. For example, covering the hydrangea for the winter with such material will be justified. She prefers just such lands.
Under the sawdust, the soil will thaw longer in the spring. Therefore, if it is necessary for the plant to wake up in time after winter, it is better to remove them in the spring.
Peat


One of the most successful materials that will allow you to insulate plants for the winter, covering them as if with a feather bed. After all, peat is light and warm under it. Even if it gets wet, it does not retain moisture for a long time.
But like sawdust, peat makes the soil more acidic. Therefore, for crops that like neutral or alkaline, you need to add a little ash or lime, dolomite flour, chalk.
Construction Materials


Some people use these wooden boxes as a winter material. But first you need to mulch the plant, and put such a box on top. To prevent water from penetrating, the container is covered with foil. But it is necessary to create ventilation systems.
Other building materials are also used:
- slate;
- trimming boards;
- roofing material.
A frame is built from boards or boxes, but it only traps the snow, and in order to insulate crops, you need to put burlap or non-woven material on this base. A kind of roof is built from slate or roofing material, not forgetting to make ventilation.
Lapnik


Plants are also covered with it. Plus, it will protect them from mice. But it is better not to cover in this way crops that like alkaline soils. The crumbling needles will make the earth more acidic in this place.
It is important to properly harvest spruce branches so as not to break the law. It can be cut, for example, from a fallen tree, but not from a growing tree. It is better to photograph this object so that you can prove where the spruce branches came from. The same applies to planned tree felling.
Foliage


Dry foliage is a good material for insulating roots and lower parts of plants.But if the tree is affected by fungal diseases, such foliage is not suitable.
In the spring, it is difficult to remove foliage from under the plants, so it is better to pour it into vegetable nets, to insulate crops in this way, making at the same time a small art object.
You can make a shelter for plants by taking:
- stakes;
- twine;
- dry leaves;
- mesh;
- roofing material.
Stakes are placed around the plant. Foliage bags are applied to them. Roofing material is placed on top to protect the pet from precipitation. Then it will be well ventilated and the plant will not get wet.
Straw


If you can get some straw, take advantage of this. This material is well suited for warming plants and sheltering beds for the winter. In order to thaw the soil here in time in spring, you need to remove this shelter early enough.
You can make from straw a semblance of a wigwam, a hut, a statue, a scarecrow, so that the shelter of plants for the winter is elegant. But strengthen such an art object well so as not to be blown away by the winds.
Now you can reliably protect the plants in the country, and the shelters will look unusual and picturesque! In the video below 5 myths about sheltering plants for the winter:
Shelter technology with spruce branches
Before winter, roses are covered gradually, in several stages. The trimming procedure is required regardless of whether you are using spruce branches or synthetic nonwoven fabric. With a sharp pruner, the shoots of roses are cut to a height of 40-50 cm, no more. Then all the leaves are removed, covered with earth after the first frost and sprinkled with peat. When the air temperature drops below zero (-6-7 ° C), rose bushes are covered with pine spruce branches and dry leaves on top.
The use of spruce or pine twigs is allowed even for sheltering climbing roses. For this, the shoots do not need to be removed from the support, they are simply wrapped in branches, securing the latter with soft ropes.
Protecting garden plants in winter
Exotic plants and luxurious rose bushes look great on a suburban area, but during the harsh Russian winter they will definitely need help to resist the frost.
Do all garden greens require protection from the cold?
Gardening experts recommend covering all plants with USD winter hardiness of 5 units or more with special covers.
To find out the winter hardiness of a particular plant, you can use a special reference book or search for the necessary information on the Internet.


Mandatory protection is required for such types of garden plants as:
- Roses (except for park roses);
- Evergreens (rhododendrons, juniper, boxwood, holly, privet, cypress);
- Plants from the southern regions (lavender, grapes);
- Perennial garden flowers and flowering shrubs;
- Any seedlings in pots (including seedlings of winter-hardy plants such as spruce, cedar and pine).
Depending on the country of origin and winter hardiness indicators, plants deprived of protection in the spring may miss part of their crown or freeze completely.
The most common construction for protecting garden plants from the cold is the combination of a rigid pyramid frame and covering material.
To create the frame, wooden rods or lightweight structures made of plastic or metal are used, and spruce branches, newspapers, burlap, mats, reed or straw mats, as well as modern geotextile can be used as a covering material.
Covering material for roses for the winter: price
It is impossible to give accurate information on prices, perhaps only indicative ones. The indicator largely depends on the manufacturer, region and even the season.
The price of polyethylene (popularly called "greenhouse film") depends on its density. So, the material of the highest grade costs from 10-15 rubles per running meter. Reinforced polyethylene is more expensive - an average of 40-45 rubles.
The price of non-woven synthetic material is higher. For spunbond with a density of 17, 42, 60 g / sq. m with a canvas size of 3.2x10 will have to pay, respectively, about 170, 330, 455 rubles.
Prices for geotextiles are approximately in the same range. Canvas density 200 g / sq. m costs 22-50 rubles per square meter.
Rose and winter hardiness


Winter hardiness of roses depends on the species. Some varieties in the Middle Lane can not be covered for the winter. In the Moscow region and other regions of the Central strip, modern hybrid forms of the Rugosa rose winter without problems.
Canadian park roses are distinguished by their high frost resistance:
- Adelaide Hoodless;
- Prairi Joy;
- Winnipeg Parks;
- Hope of Humanity.
Climbing roses are popular among gardeners. Some varieties tolerate frosts down to -30 ° C (Alchemist, Hendel), others freeze out when the thermometer drops to -7 ° C. Climbing roses of continuous flowering require a good shelter for the winter:
- Lagoon;
- Parade;
- Paul Scarlet.
Most hybrid tea varieties do not withstand frosty winters, they are easier to grow in the southern regions. They require compulsory shelter if the temperature drops to -20 ° C in winter. Floribunda roses are frost-hardy, but in Siberia and the Urals they are sheltered for the winter.
When buying a seedling, it is necessary to specify the frost resistance zone (USDA). There are 13 of them and each has its own minimum temperature value. She is shown without taking into account the shelter. In the presence of a covering layer, roses can withstand frosts 5-10 ° lower than indicated in the recommendation.
Preparing roses for winter: features
The process of preparing any plant for winter, including roses, is not as simple as it seems at first glance. First, you need to carry out sanitary and preparatory measures, and only at the final stage is a covering material for roses required. How to cover roses for the winter correctly? The question is relevant for both a novice gardener and a more experienced one.
First, you need to determine if the plant is ready for winter. If a rose bush has red-colored shoots in September, this is a sign of active growth. The plant is not ready for winter, has not accumulated the required amount of carbohydrates, and the shoots are not yet lignified. Rose needs help. To do this, the bushes are fed with phosphorus fertilizers, pinch the growing point and remove the faded buds.
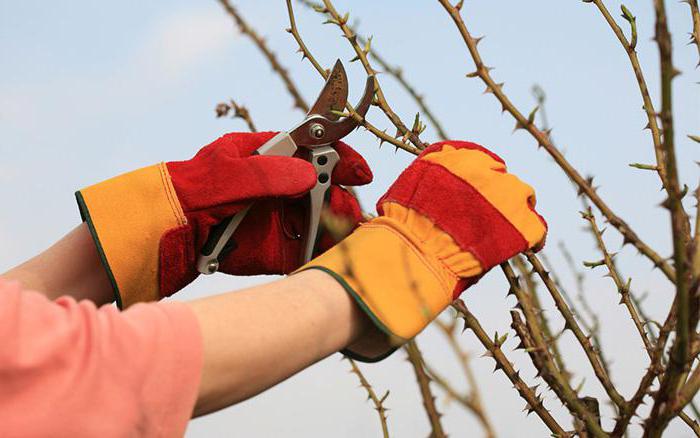


Secondly, from the beginning of September, the loosening of the soil around the roses and the process of plant formation should be stopped. This is required to prevent the stimulation of the growth of shoots from dormant buds. In late October - early November, all leaves are removed from the plant. This is done in order to prevent them from rotting under cover in winter.
Thus, before making the cover of roses for the winter with a covering material, the features of the latter should be carefully studied. And weigh all the positive and negative points.
Pre-winter preparation
In a previous publication, I stopped at the fact that roses in the dry season of Indian summer must be tied and bent to the ground. The unripe tops of scrubs and clays, English, ground cover and musk roses are preliminarily cut, blooming shoots with buds are removed.
Roses in the dry season of Indian summer must be tied and bent to the ground. Photo by the author
For the convenience of shelter, hybrid tea roses and floribundas are shortened to 40 cm. In climbing roses, ramblers, part of the shoots is cut out, leaving 7-8 of the strongest, which will bloom next year. They are laid on some dry surface - a sheet of plywood, boards, spruce branches.
Before covering them thoroughly, they first cover them with a film so that they do not get wet from the rains. Before bending, they are sprayed with a 4% solution of ferrous sulfate (not to be confused with copper!) - This is an effective anti-decay agent. Usually a standard package of 200 g is diluted per 5 liters of water. Moreover, not only the plants themselves are processed, but also the land around.
From the rose garden, diseased leaves that have fallen (a source of diseases) are carefully removed and sent to the fire. We leave all the rest of the foliage, contrary to the existing recommendations to remove it. I strongly object to this procedure. And that's why.Firstly, in the presence of a large rose garden, where sometimes at least a hundred roses grow, this is simply physically impossible to do.
The leaves of roses continue to participate in the process of photosynthesis. Photo by the author
Second: when pruning leaves, it is easy to damage the delicate skin of the shoots, where the infection will penetrate. But most importantly, the leaves of roses continue to participate in the process of photosynthesis, providing everything the roots of plants need. This continues even in a shelter with scant rays of light that penetrate there (if a translucent lutrasil was used). To deprive them of this opportunity is to weaken the plants.
It has been noticed that those roses that have lost their leaves as a result of black spot disease hibernate much worse and die more often. Therefore, the main task is to preserve the leaves to the last. And in the spring they will disappear by themselves, and you will calmly collect them.
Save the leaves to the last. Photo by the author






















