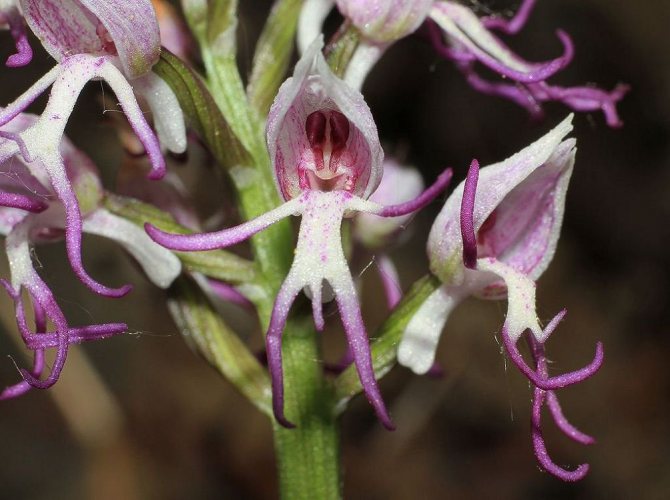
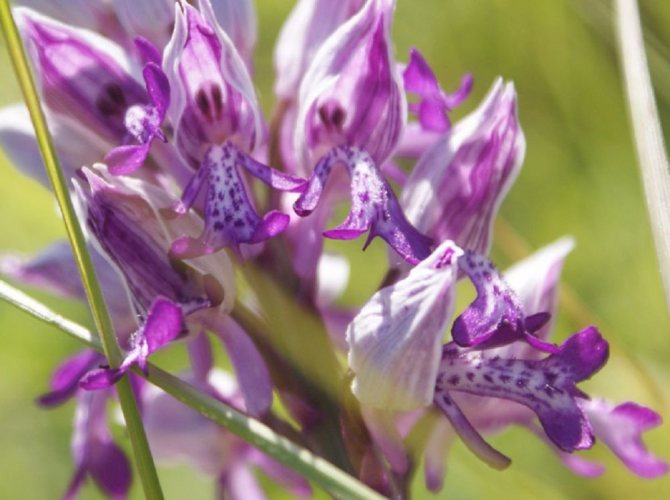
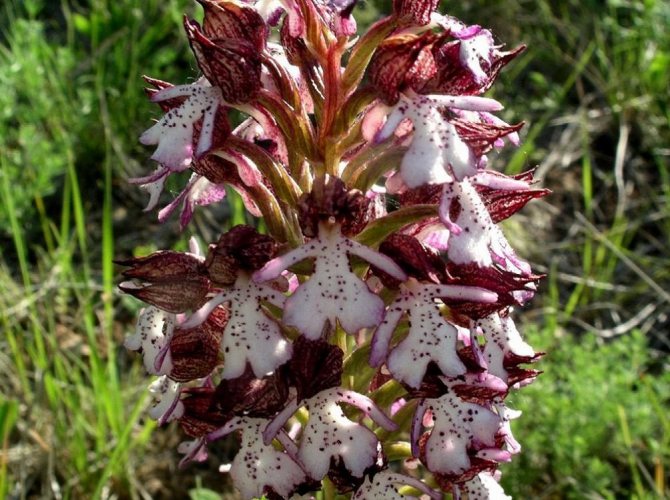
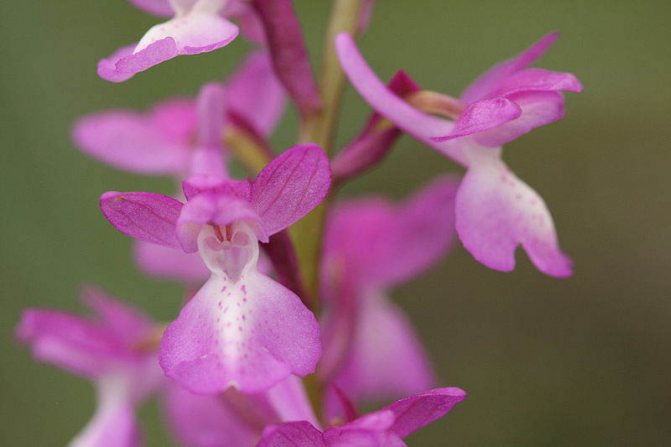
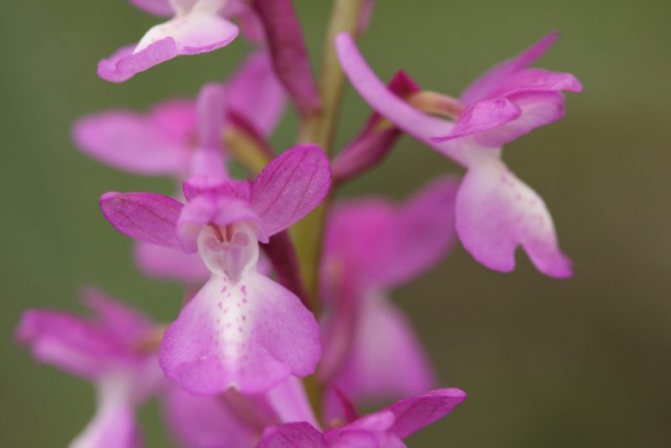
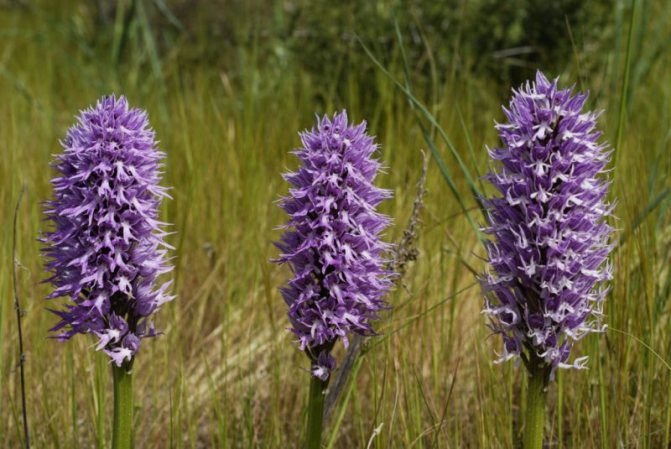
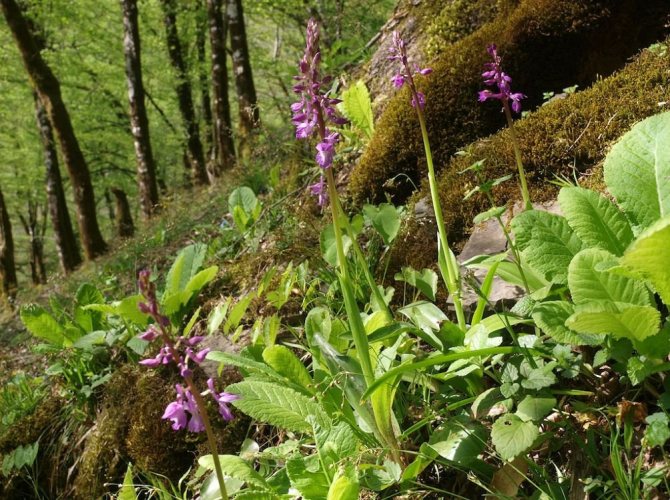
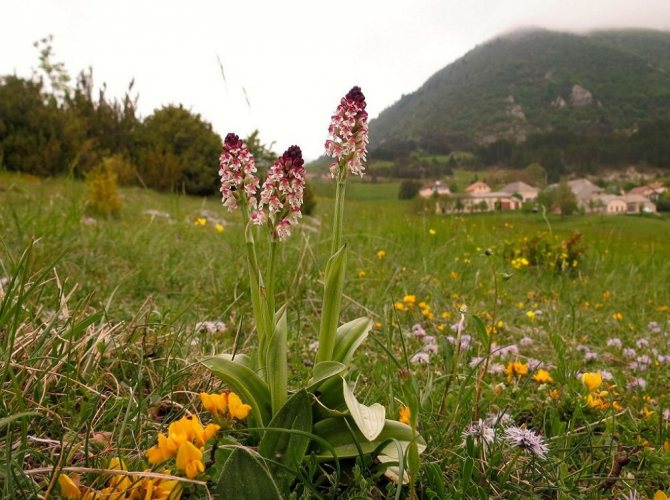
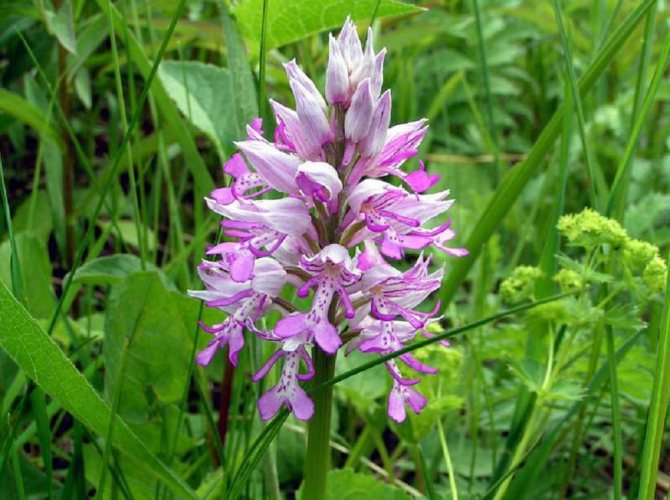
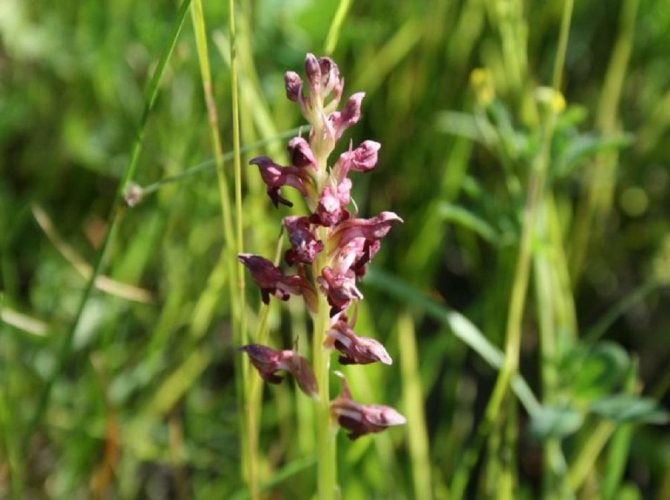
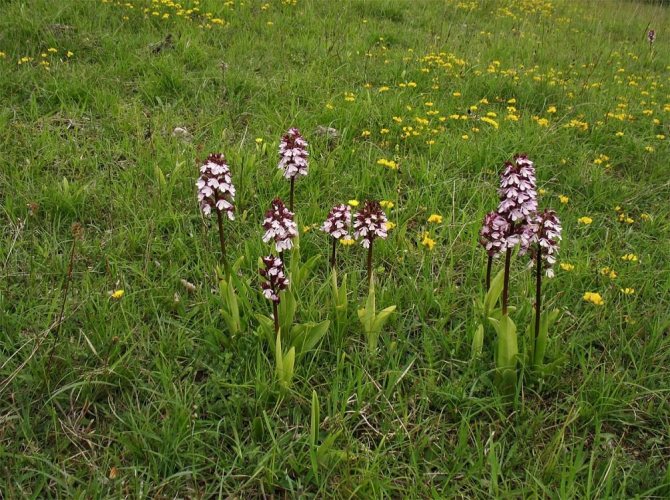
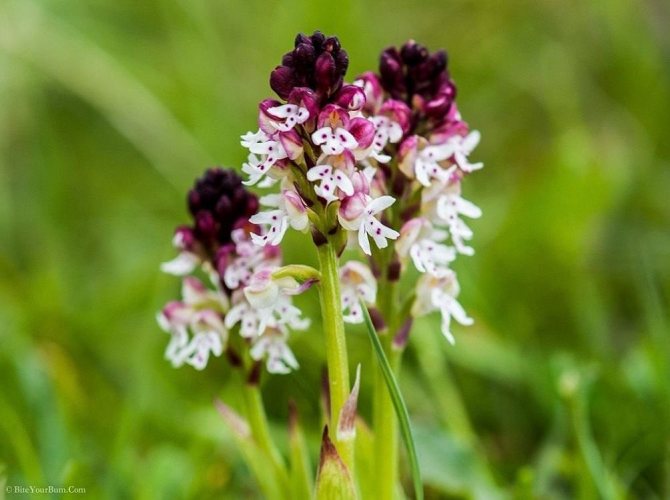
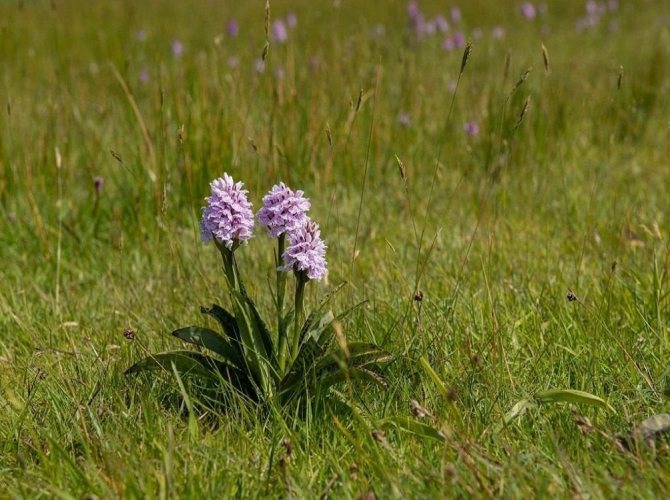
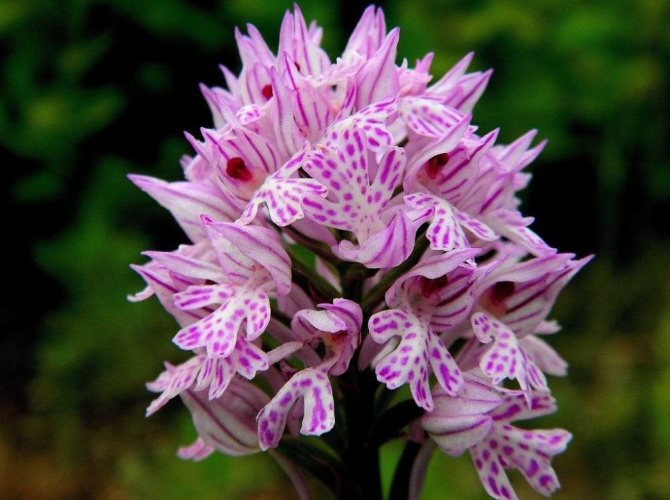
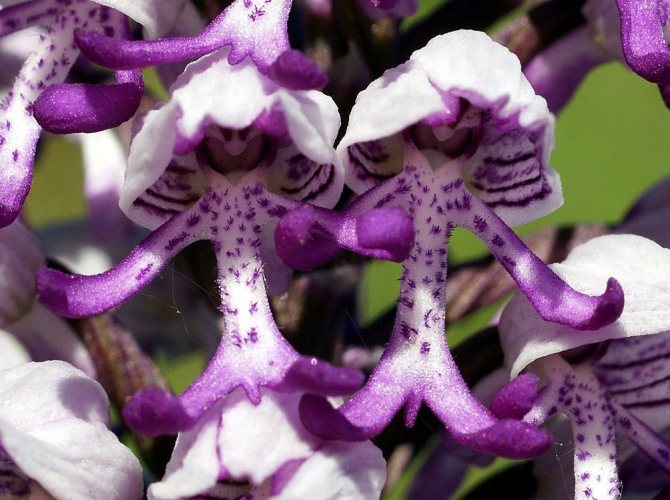
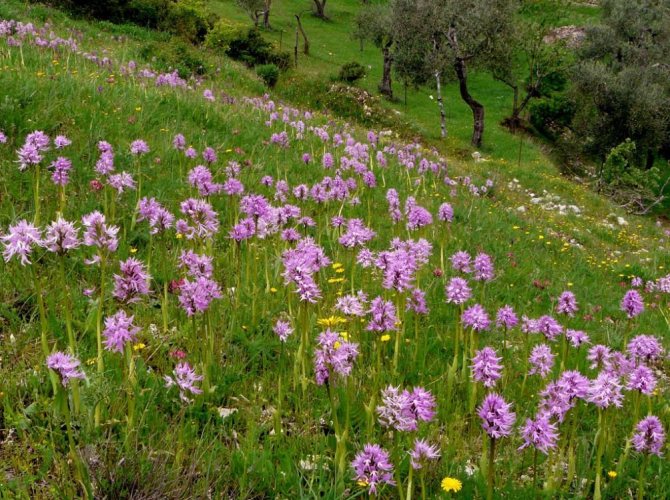
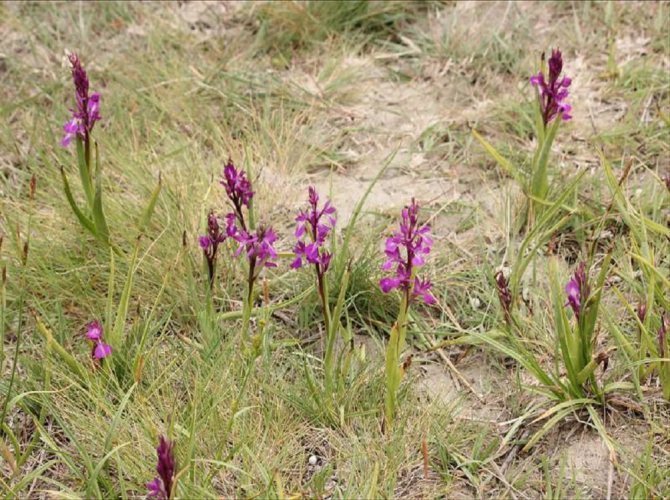
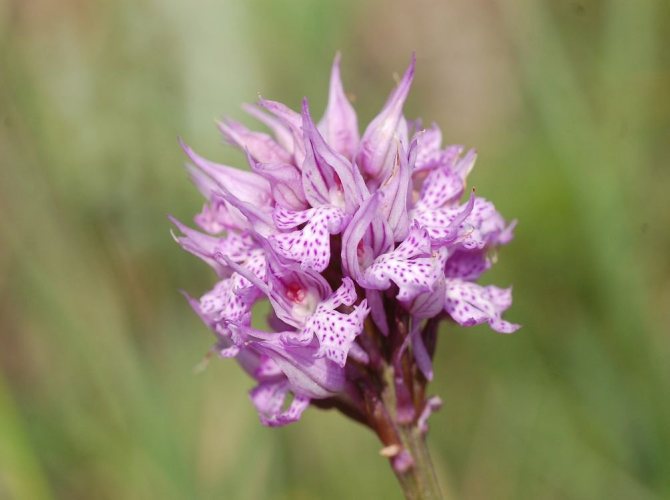
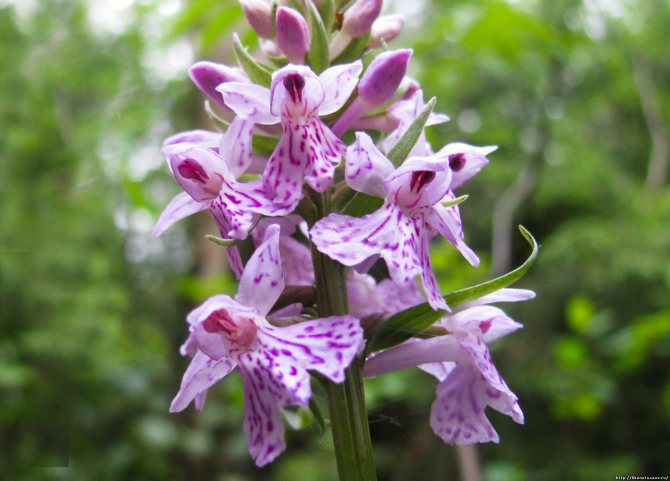
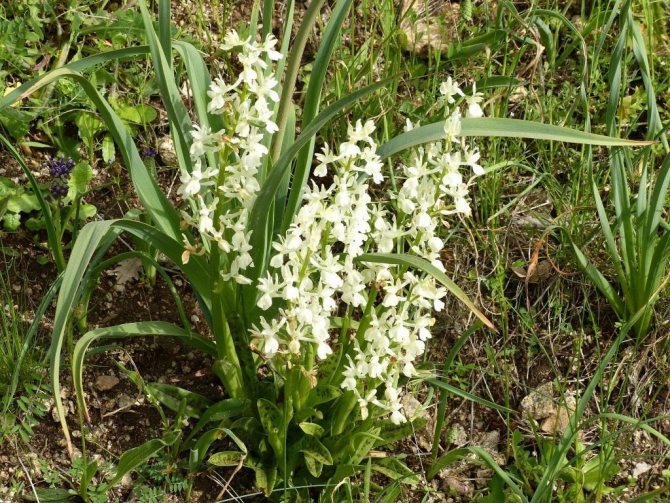
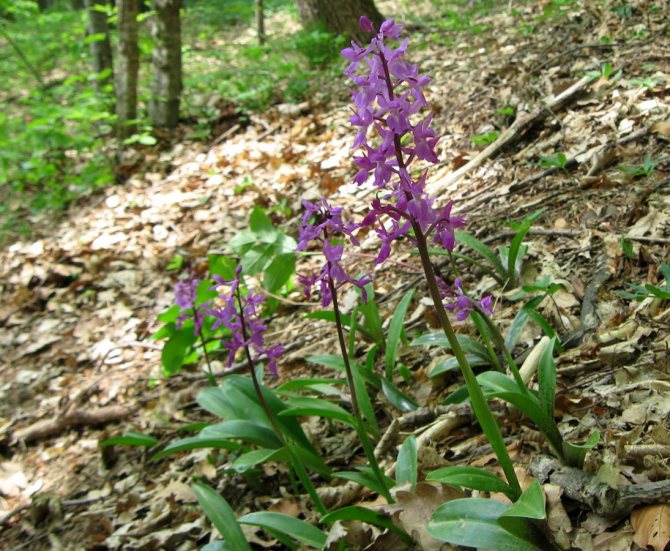
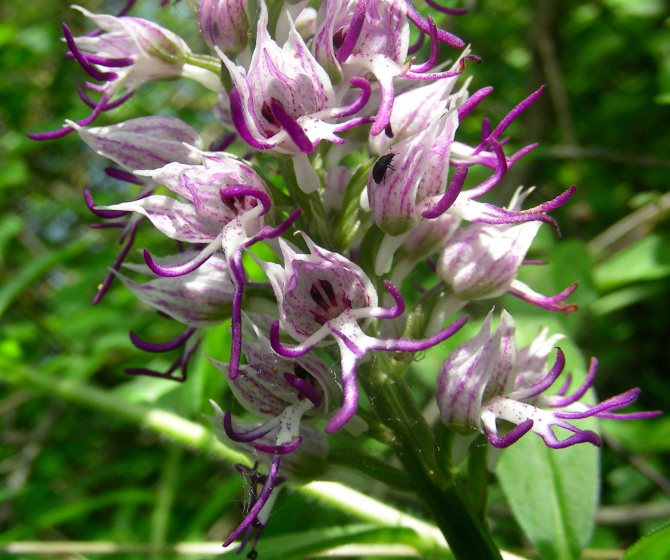
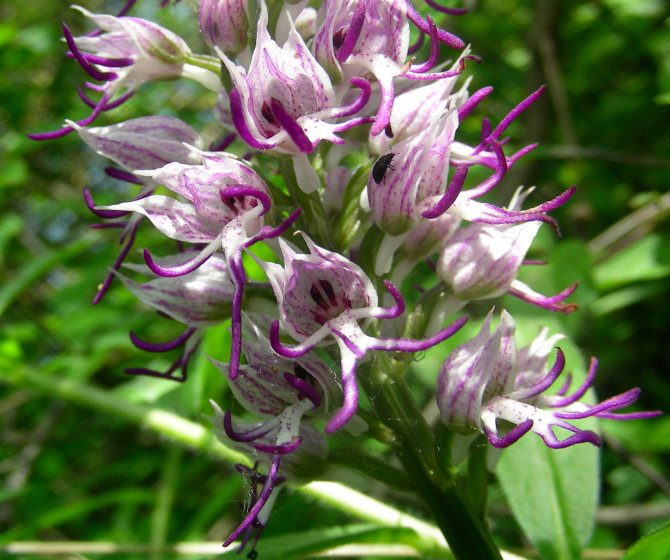
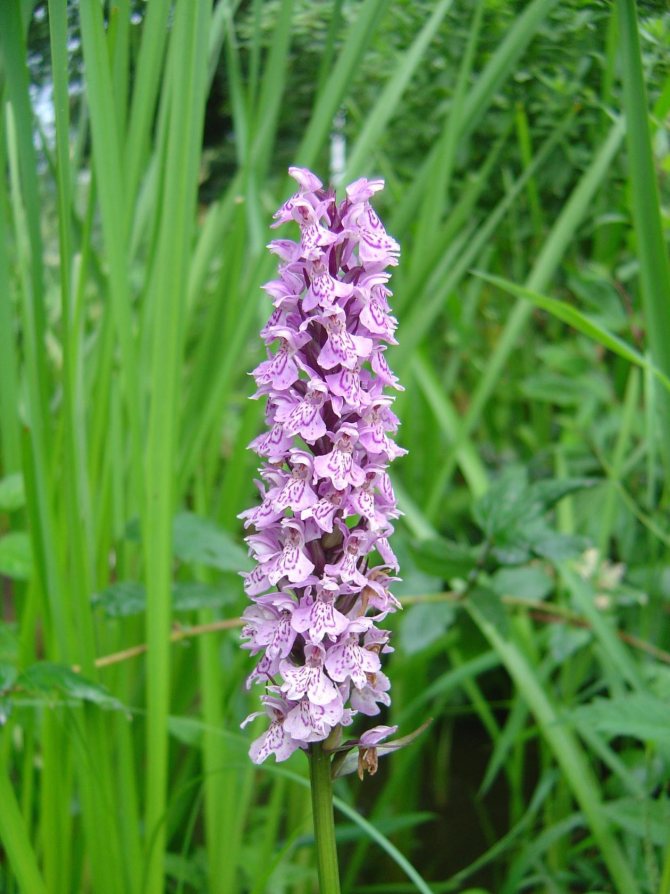
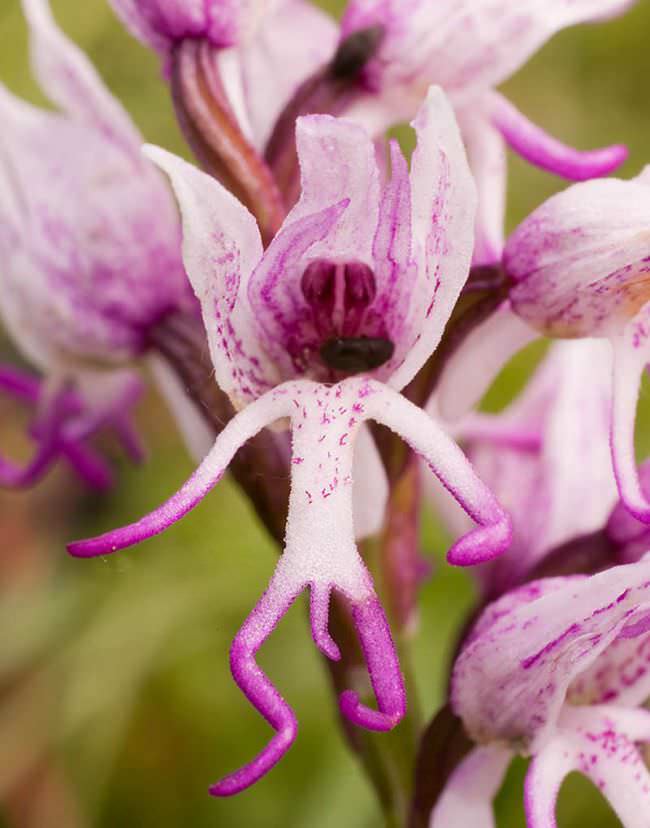
Orchis is a perennial herb with highly decorative buds and many medicinal properties. It is thanks to its benefits that the orchis has been destroyed for decades and is now included in the Red Book as an endangered plant. Growing it in your own garden, you can not only enrich the flower garden, but also take care of the preservation of rare flora. The orchis has many popular names, among them “dog tongues”, “core”, “vymechko”, “cuckoo's tears”, “wild orchid”. It is distributed in the temperate zone of the entire northern hemisphere. The plant prefers a cold climate, it grows on rich calcareous soils of forest edges and damp foothills.
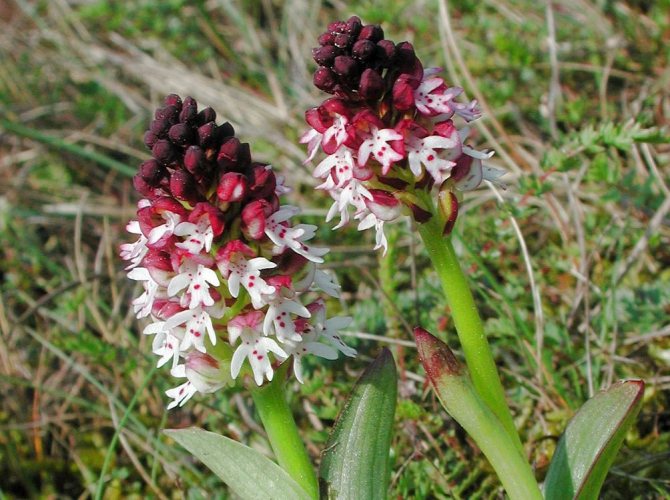

Orchis: Treating Diseases
In folk medicine, orchis root mucus is most often used, which is used for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, catarrh of the upper respiratory tract, and for poisoning with poisonous substances. The mucus of the plant is known for its anti-inflammatory agents, which makes it possible to treat acute and chronic respiratory diseases in young children.
The plant is also used to treat the following diseases:
- BPH;
- Chronic prostatitis;
- Colitis and gastritis;
- Diabetes;
- Ulcers of the stomach and duodenum;
- Impotence;
- Inflammation of the oral mucosa;
- Radiculitis;
- Pneumonia;
- Tuberculosis;
- Bronchitis;
- Nervous exhaustion;
- Physical exhaustion;
- Diseases of the female genital organs;
- Beli;
- Various poisoning.
The mechanism of action of orchis on male strength
For the treatment of sexual impotence, it is important that there is a complex effect on the causes that led to its occurrence. This property is possessed by the orchis. For an erection, it is useful due to its ability to positively influence the composition of blood, hematopoiesis and its flow to the pelvic organs.
The antibacterial properties of the phytoncides contained in the orchis protect against inflammation of the prostate and slow down the aging process of genital tissues, which directly affects the preservation of potency.
The tonic effect on the male body as a whole gives strength and confidence in its solvency.
Where does the orchis grow?
Orchis is a common plant. In total, about 100 species are known, but some of them are on the verge of extinction. There are about 40 species of orchis growing in Russia, of which the male is the most famous. It has properties to restore male potency.
Different types of plants prefer different habitats. For example, the helmeted orchis grows on forest edges, clearings and damp meadows. It can also be found in North Africa and America, the Canary Islands and the Caucasus.
The plant is mainly distributed in Siberia and Russia. The orchis tolerates high terrain well, climbs into the mountains to an altitude of 1800 m. In the southern regions, digging the plant is strictly prohibited.
Wild Orchid Care
Spotted orchis does not like waterlogged soils. When feeding, it is important to ensure that the plant does not get fresh manure. It is recommended to mulch the soil, the best option for this is needles.


If the orchis grows in a sunny area, it is worth watering. The rest of the plant is unpretentious, does not require much care, and is not susceptible to pests and diseases. Loves semi-wild parts of the garden.
Propagated by division of the root, seeds, sometimes self-sowing. Dislikes weeds.It endures winter without shelter.
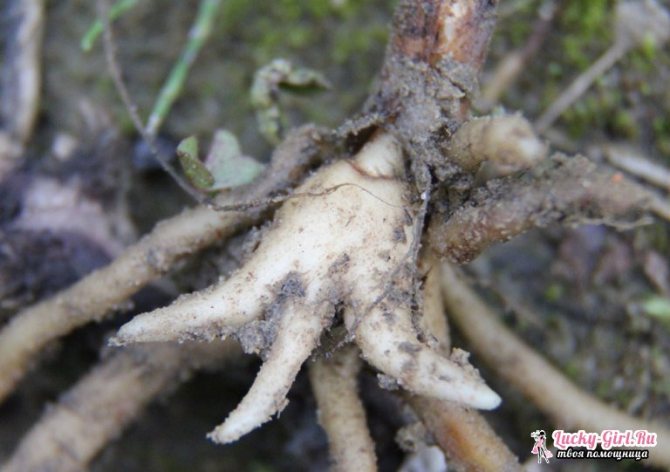
Orchis root in medicine
In medicine, only young roots are used. They are dug up with a shovel, cleaned of soil and skin, washed with running cold water. For some time immersed in boiling water, then dried in a suspended state.
The roots contain mineral salts, essential oils, a lot of mucus, starch, glycosides, proteins and vitamins. A slimy broth is often boiled from tubers to treat inflammatory diseases of the stomach and intestines, it is also used for coughing, sore throat and mouth. External use of a mucous broth is effective for tumors and abscesses. Orchis root is recommended for men with impotence, prostate adenoma and chronic prostatitis.
When using the broth, the dosage should be observed in order to avoid the side effect - excessive arousal. For external use, the tuber of the plant is pounded in a mortar, mixed with pork fat and steamed in milk. This remedy is used for abscesses, toothache, to enhance hair growth.


The use of the root of the plant helps patients with tuberculosis, people who have suffered severe bleeding and suffering from intestinal catarrh. Older orchis helps maintain strength. Preparations from the root of the herb help in case of poisoning with poison from scorpions, bees, snakes, intoxication - chemical and bacterial toxins.
In addition, the roots of some plant species can be eaten.
Video: Medicinal properties of orchis
A detailed story about the orchis from the Herb World canal:
Nature has prepared a lot of medicinal herbs for humans, and the orchis in this collection is far from the last comrade in importance. Make friends with him, even if there is complete order with your masculine strength. From time to time, indulging in a cup or two of healing milk with a miracle root for general health promotion will not hurt anyone.
In the article, we discuss orchis - medicinal properties and contraindications, types and descriptions of the plant, recipes for various diseases and areas of application. You will learn how to collect and harvest tubers, recipes for decoction for impotence, colds and diarrhea, what diseases the yarrist helps to treat.


The people have always had a special attitude to the orchis plant, it is not without reason that it has a lot of alternative names - cuckoo tears, dog tongues, udders, Ivan's hands, core, wild orchid. The sorcerers used the double tubers of the flower for love spells and arousing sensuality. The peasants used a pair of stems with roots in ancient rituals, where nepotism, funerals and the resurrection of the cuckoo doll were played out. The Itelmens say that swimming at sunrise in the waters of the lake, on the shores of which the orchis blooms, helps to gain eternal youth and beauty.
The saddest and most emotional story associated with the cuckoo flower tells of a mother offended by her ungrateful sons. The woman, drenched in the rain, fell seriously ill and fell ill, but the boys threw her in bed without even giving her water. Only in the evening, tired of the fun walk, the children returned home, where an unprecedented miracle awaited them. Sick mother, not wanting to stay with them any longer, turned into a bird and flew out the window, shedding bitter tears as she flew. Since then, where the cuckoo drops tear-drops, beautiful orchis flowers sprout there.
Orchis: application
- Decoction for poisoning and gastrointestinal diseases. Pour in 1 tsp. chopped root 200 ml of hot milk or water. Leave the mixture for 30 minutes. The result should be a thick jelly-like mass, which must be applied orally 2 times a day, half an hour before meals. To soften the taste, you can add a little honey to the finished broth.
- Infusion for diarrhea in children. Pour 120 g of root with 500 ml of water. Insist 1 tsp. Give infusion to children every hour for 1 tsp.
- Cooking slime. Grind orchis tubers into powder and cover with water (1: 100).First, the powder is diluted in 10 parts of water, then the rest of the liquid is added. Shake the mixture for 15 minutes until a thick, homogeneous mass is obtained. Ready mucus is consumed 3 times a day for 1 tsp. while eating. She is good at helping men with sexual dysfunction, diarrhea and dysentery. You can make enemas from the prepared mucus by adding a decoction of flaxseed (1 tsp. Flax seeds per 1 tbsp. Boiling water).
- Fortifying drink. Mix 30 g of plant root, 30 g of potato starch, 100 g of sugar. Add 30 ml of water. When the mixture looks like thick sour cream, pour in 1 tbsp. milk and put the drink on low heat. Boil the mixture for about 5 to 10 minutes. The finished drink is poured into glasses, sprinkled with cinnamon, cloves or nutmeg.
- External use. Mix the crushed powder with any fat until a homogeneous ointment is formed. The resulting mass is applied to the sore spot and wrapped with a sterile bandage. The remedy is excellent for abscesses, ulcers, toothache and alopecia.
- In the treatment of impotence. Pour in 2 tsp. root 1 tbsp. boiling water. Put the mixture on fire and simmer for 10 minutes over low heat. The finished broth is infused for 30 minutes, after which they filter and drink 1/3 tbsp. 3 times a day.
- With inflammation of the prostate gland. Grind 100 g of dried flowers into powder, pour 1 liter of olive oil and leave for 2 weeks in a dark and warm place. Then strain and take 1 tsp for inflammation of the prostate gland. 2 times a day before meals.
Orchis is a useful medicinal plant that has practically no contraindications for use. It can be used by children, pregnant and lactating women. Orchis effectively copes with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth, strengthens the immune system and helps with abscesses. In any case, it is recommended to consult a doctor when using the plant.
Maintaining a harmonious relationship between man and nature is one of the most important tasks today. Hence, the significant attention of society to the protection of natural objects, including the flora. It is necessary to preserve the entire variety of plants - all species without exception that grow both in a specific territory and on the planet as a whole. The degree of threat of extinction of various plant species is far from the same. Rare plant species listed in the Red Book are especially in need of protection.
Such rare plants disappearing from nature include orchis spotted
(Orchis maculata L., or Dactylorchis maculata, or Dactylorchiza maculata) from the Orchid family (Orchidaceae). The generic name Orchis means "orchid", and the specific maculata ("spotted") is given to the plant due to the fact that its lanceolate leaves are covered with brownish-brown spots. For the spotting of the leaves, the people called this wild orchid “
cuckoo tears
».
Spotted orchis is a perennial herb with finger-divided roots thickened in the form of tubers (hence its name Dactylorchis - “finger orchid
»).
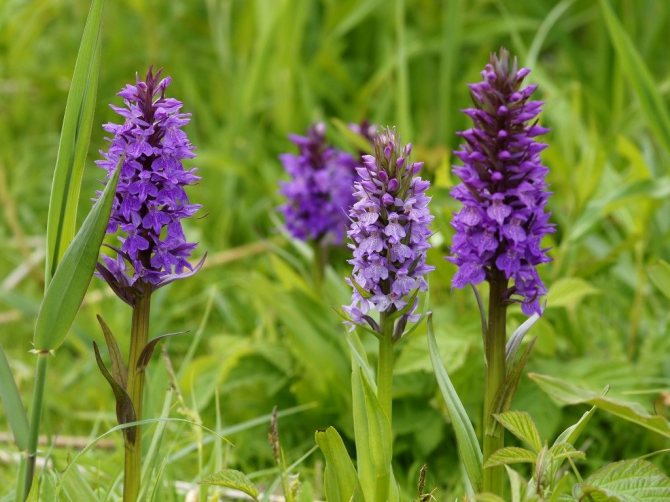
Spotted orchis is widespread almost throughout the territory of Russia (except for the regions of the Far North), Belarus, and Ukraine. The orchid grows in wet meadows and swamps, on the edges of forests and forest glades, in river and stream valleys, in moist spruce forests, among thickets of bushes. This orchid prefers clay soils that retain moisture better.
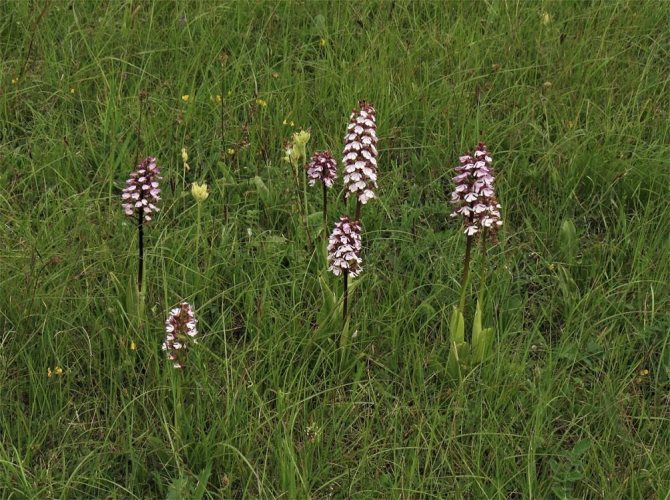
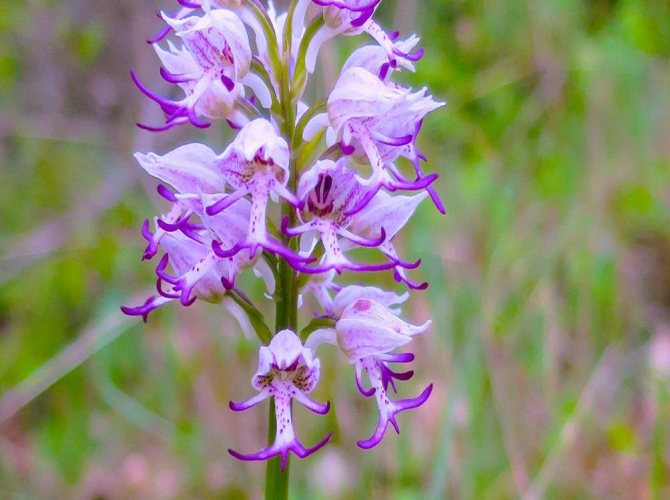
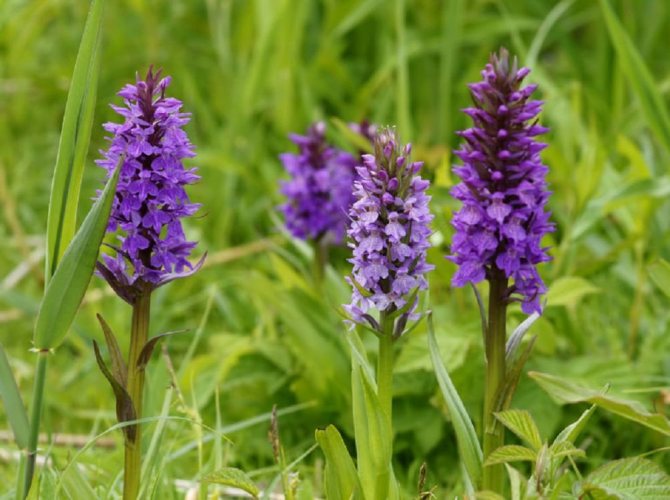
In the wild, plant heights vary greatly (from 15 cm to 60 cm) depending on growing conditions. Leaves of orchis spotted linear-lanceolate; they taper into a petiole or cover the stem. A simple leafy stem of an orchid ends with a long peduncle with a spike-shaped inflorescence bearing numerous flowers. The flower has a three-lobed lip with purple spots; the spur is conical-cylindrical. The color of the flowers of the spotted orchis ranges from light purple to purple.But in our area, this orchid has only two varieties of color.
Spotted orchis blooms in June-July, seeds ripen in August (capsule fruit with many small seeds). In nature, this orchid reproduces extremely slowly, mainly vegetatively - by dividing the plant. Seed reproduction of orchis is difficult, since its seeds germinate in the soil only in the case of symbiosis with a fungus of a certain race. Therefore, seedlings of orchid seedlings are single, although the orchis produces a huge number of seeds annually.
Due to the development of new lands by man, as well as in dry years, there are fewer and fewer orchis in nature. In order to preserve and increase these beautiful plants, there is only one way out - to transfer wild orchids to the category of cultivated plants, to multiply them en masse for decorative and medicinal purposes and to return these rare plants to nature. What I am doing. Orchis tolerate transplantation perfectly.
Many years ago a frail orchis plant settled in my garden. The new favorable growth conditions affected him very quickly. A year later, the saved plant was transformed beyond recognition. Its stems have become three times higher and thicker, dense cylindrical "ears" of huge inflorescences with numerous elegant flowers have formed on them. Even the color of the flowers has become extraordinary, more saturated and bright. Moreover, I did not water this plant additionally and never fed it with any fertilizers. Such a radical transformation of the orchid happened only because the orchis began to grow in the fertile loose soil of the garden, without weeds - it had enough nutrition and moisture, there was no competition for survival.
The orchis is very winter-hardy and does not need shelter for the winter. It is gratifying that this beautiful orchid never gets sick with anything. The only care for it on my part is pruning the aerial part with the beginning of its drying (approximately at the end of August), when the plant loses its decorative effect, and its seeds have already spilled out.
Over the years of cultivation in the garden, the orchis has grown and multiplied significantly. Many young orchids sprout and grow on my own among the clematis plantings. Most likely, orchis seeds got there along with particles of soil on the soles of shoes. I believe that the orchid seeds germinated successfully there due to the fact that when planting clematis, I introduced a large amount of compost compost into the planting pits, which was not completely rotted; and more - I water clematis abundantly in the summer. In such a loose, moist, fertile soil, a huge number of compost earthworms live. Perhaps it was the worms that created that favorable microflora in which the fungi necessary for the germination of orchid seeds settled.
The spectacularly blooming orchis growing in a group make for a wonderful sight.
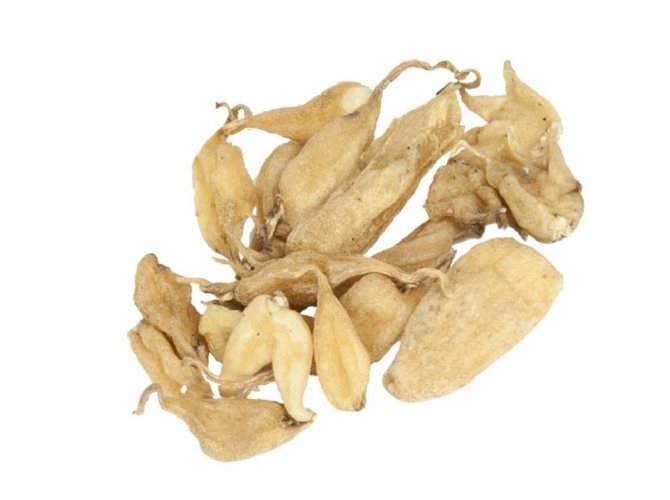
However, the spotted orchis has long been valued not only as an ornamental plant, but also as a medicinal plant: its tubers, called salep
.
The root system of the orchis is fibrous; the nutrients formed by the roots pass into the juicy storing root tuber. In spring and summer, the stored nutrients of the orchid are spent on the development of the aerial part, flowering and seed formation, so the root tuber is gradually depleted and dies off. But since spring, a new subsidiary storage tuber is formed in the axil of the base of the orchis leaf. It overwinters and serves for the development and reproduction of the plant next year. The tubers of the spotted orchis are usually two to three-fingered, slightly compressed. So many valuable substances accumulate in the tubers of this orchid that if they are eaten, then the energy contained in them is enough for the normal functioning of the human body during the day! Although the orchis tubers cannot boast of their taste - they taste like ordinary grass ...
The Persians used the nutritional properties of the orchis tubers when they conquered new lands. They dug up and stored a large number of root tubers of this plant. In the absence of the usual food on long campaigns, the warriors could do without food for a long time, using only chopped orchid tubers along with water or milk.
For medical purposes, only young tubers of the spotted orchis are used. They are dug out during flowering or immediately after the plant has faded (when the flower arrow has not yet disappeared). Orchid tubers are peeled, strung on a string and immersed in boiling water for several minutes to prevent further germination. Then the tubers are air-dried by hanging them on strings.
Salep contains mucus (47-50%), starch (27-31%), dextrin (13%), pentosans, methylpentosans, sucrose (1%), bitter substances, essential oil. Mucus is composed primarily of mannan (a high molecular weight polysaccharide).
Spotted orchis is used as a stimulant for impotence, as an antidote for poisoning with cauterizing poisons. Due to the mucus content, salep has enveloping properties - this is important in the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory tract, thanks to which the inflamed tissues are protected from excessive irritants. Salep is used for stomach and duodenal ulcers, ulcerative colitis, hemorrhoids and other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, with dystrophy, with exhaustion, with loss of strength due to prolonged illness.
Salep mucus is isolated immediately before use: the tubers of the spotted orchis are crushed, poured with hot water (200 ml of boiling water is taken for 2 g of dried root tubers) and shaken for 10-15 minutes. The resulting mucus is stored in a cool place for no more than 2-3 days. This gelatinous mass is consumed 1 teaspoon 3 times a day (along with cereals, broths, milk and other products). Or they take salep mucus for 2-3 days, several times a day for a tablespoon (before each meal and at night before bedtime). For children, this dose should be reduced depending on age and weight.
The mucous mass obtained from salep does not have any taste or smell. Therefore, this healing agent is successfully used to treat sick children, as well as in surgery, in ear-nose-throat clinics (especially for severe “tubal” patients). This mucus is also recommended for setting enemas (50 ml of mucus is taken for one therapeutic enema).
Salep mucus should not be used in conjunction with tannin and other astringent substances, as it will precipitate. Salep has no contraindications and side effects.
As a stimulant
for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases and poisoning:
take 3-10 g of spotted orchis tubers per 180 water. Grind 3-5 g of tubers, pour 0.2 cups of cold water, gradually add boiling water to 1.5-2 cups, stirring for 10-15 minutes, until mucus is obtained. Take salep mucus before meals, 3-4 times a day for 2-6 tbsp. spoons.
For catarrh of the large intestines and catarrh of the bladder:
powder of orchis spotted tubers is diluted in cold water 1:10, then 90 parts of boiling water or milk are added and shaken again until a thick, uniform mass is obtained.
With diarrhea and dysentery:
use an aqueous emulsion of spotted orchis. The tubers powder is diluted 1:10 in cold water, then 90 parts of boiling water are added and shaken again until a thick, uniform mass is obtained. A decoction of flaxseed is added to the emulsion (1 teaspoon per glass of boiling water) and then the cooled mixture is used for enemas.
As a means to maintain strength
in decrepit old people, in tuberculosis patients and other patients, in those who have suffered heavy and prolonged bleeding (including hemorrhoids), in people who have lost strength and health after difficult experiences.In the tubers of spotted orchis, relatively small in volume, a powerful concentrate of nutrients accumulates. Taken in an amount appropriate to the characteristics of the disease, the spotted orchis quickly restores strength in an exhausted and sick person.
In Bulgaria, salep is used as an enveloping anti-inflammatory agent for acute and chronic diseases of the respiratory tract, for gastrointestinal catarrh, for dysentery (especially in young children) in the form of an infusion: 3 g of tubers per 250 ml of boiling water, leave for 15 minutes. Adults with diarrhea drink the infusion hot, and children are given it cooled down.
In Austrian medicine, spotted orchis tubers are used for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Salep preparations are prepared in pharmacies.
Every week, for 10 years, for our 100,000 subscribers, an excellent selection of relevant materials about flowers and garden, as well as other useful information.
Subscribe and receive!
cuckoo tears, five-finger, cuckoo, zozulin
Pharmacy name: Salep tubers or mucus Part used: daughter tubers Harvesting time: June-August
Description of the plant
Orchis is a herbaceous perennial from the Orchid family. It is fed by rhizomes with paired, oblong tubers, which are often compared to male testicles. Erect stems 10-50 cm long at the base are hidden by a leaf rosette. Oval or broadly lanceolate leaves sit on the shoot. The upper leaves have small petioles. Sometimes there are small dark spots at the base of the olive green leaf plate.
In April-August, the stem lengthens and turns into a bare simple peduncle with a dense spike-shaped inflorescence 7-9 cm long. Small orchid-like flowers are painted in lilac-pink or cherry color. A helmet is formed from the upper petals, and the lower ones form a three-lobed lip with a spur. The base of the lip is covered with dark dots. The flowers exude a subtle sweetish aroma with hints of vanilla and honey. A single bud blooms for 7-10 days until insects pollinate it. Immediately after the pollen enters the ovary, the petals wither. Dry seed pods with very small dark seeds soon ripen.
Recipes: Spotted Orchis
Broth: 3-10 g per 200 ml; 1-2 st. spoons 3-4 times a day.
Enema: 2 teaspoons of salep for 2 cups of boiling water (after wetting the powder with cold water), add a quarter of a teaspoon of crushed flaxseed.
Preparation of mucus: a teaspoon of chopped tubers is poured into 100 ml of cold boiled water, then gradually, stirring constantly, boiling water is added (the total volume is brought to 1.5-2 cups). Store in the refrigerator for no more than 2 days. Take 1-3 tbsp. l. 3-4 times daily before meals.
Orchis is a medicinal plant that is used in many folk recipes.
It has an enveloping, anticonvulsant, expectorant, tonic and hematopoietic effect.
The roots and flowers of this plant have a unique biochemical composition, due to which preparations based on them are used to treat many diseases.
The orchis grows in the Caucasus and Crimea, in Western Europe, Ukraine, Russia and Belarus.
Despite its widespread distribution, it is listed in the Red Book.
The amazing healing properties of the plant led to uncontrolled collection and almost complete destruction.
Collection, procurement and storage
Many orchis species are protected by law and included in the Red Book. You cannot harvest them in the wild, but you can grow a plant from seeds in your garden.


Procurement is a basic and important step.
Tubers need to be harvested when the orchis is in bloom. You can do this right after the end of flowering. It is at this time that the largest amount of healing substances accumulates in the tubers.
They can be washed well and doused with boiling water.Raw materials are dried in the shade in a ventilated area, but not in the sun. Well-dried tubers are slightly translucent. They can be stored in cardboard boxes or linen bags for up to 6 years.
Beneficial features
The medicinal properties of this plant have been known for a long time. For example, in Turkey, the traditional drink made from the crushed roots of orchis - salep - has been prepared since the days of the Ottoman Empire.
Then the drug was considered the best aphrodisiac and was used to cure male impotence.
Young tubers of the plant are used as a medicine. They are harvested from July to August, just after the end of the flowering period.
Orchis tubers include:
- mucus - 50%;
- resins and essential oils;
- protein substances - 5%;
- dextrin - 13%;
- starch - 27%;
- glycosides;
- mineral salts;
- sucrose - 1.5%;
- oxalic calcium.
The aerial parts of the orchis are less useful, however, they are also used in medicine: for example, dried and crushed flowers of the plant are part of herbal preparations that increase potency.
Benefits for men
It has been proven that the normal potency of a man depends on a number of factors. It is important in general to maintain normal physical and mental health, the healing properties of orchis for men are:
- in the elimination of toxins from the body;
- normalization of the hormonal system;
- strengthening and tonic action;
- stimulating hematopoiesis processes;
- protection from irritation of tissues that have undergone inflammation;
- improving the regeneration of the skin.
What diseases does it treat
Decoctions and tinctures from fresh or dried orchis root are used to treat:
The powder, made from dried orchis root, is a natural contraceptive.
To avoid unwanted pregnancy, women take it a couple of hours before the intended intercourse. Such a contraceptive drug is completely harmless.
Orchis medicines are an excellent general tonic. They are used to restore the body's defenses after serious illness, severe bleeding or nervous exhaustion.
Orchis mucus is also suitable for external use: compresses from it quickly eliminate swelling, felon, carbuncles and abscesses.
For cosmetic purposes, it is used to treat scalp diseases and accelerate hair growth.
Title [edit | edit code]
The Latin name comes from ancient Greek. ὄρχις (testicle
) due to a pair of testicle-like tubers.
There is, by Etymological Dictionary of the Russian Language
Max Vasmer, several assumptions about the origin of the Russian name of the plant: according to one of them, the root of this plant was used as a love potion -
yatrov flower
; in another way - the name is associated with the dialectal Stavropol-Caucasian word
yatro
(
egg
); in the third case, the dictionary refers to the opinion of V.I.Dahl, who connected
orchis
from
nucleus
(from
core
) [2] .
Like many other plants [3], for example, the shake and the two-leaved, the orchis is also called “cuckoo tears” or “tears” [4].
Types and application in traditional medicine
There are about 100 orchis species. However, few have healing properties:
Orchis male
... The roots of the plant contain essential oils and mucus. These substances help in the treatment of:
- gastritis,
- cystitis,
- convulsions and paralysis,
- eliminate cough and toothache,
- treat inflammatory processes.
They also cope well with diseases of the respiratory organs - bronchitis and pneumonia.
No less popular are fortifying agents prepared on the basis of orchis. They are used for nervous exhaustion, as well as to increase potency.
Orchis
... For medicinal purposes, fresh and dried tubers of this plant are used.Preparations based on them have a general strengthening effect on the body and increase potency.
Orchis spotted
... The tubers of this plant contain a lot of useful substances - mucus, sucrose, starch, pentosan, methylpentosan, dextrin.
Orchis spotted root powder is used to treat inflammatory processes in the upper respiratory tract and gastrointestinal diseases.
The rest of the orchis species are grown for decorative purposes.
Reproduction
Most orchis species are propagated by seed. In favorable conditions, the plant produces abundant self-seeding. However, seeds can only germinate if special fungi are present in the soil. Often, when sowing at home, the land is taken from the place where wild orchis grow in the clearing. The seeds can be sown all year round. Try to distribute them evenly in a container with moist nutrient soil. The container is covered with foil and placed in a well-lit place with a temperature of + 18 ... + 24 ° C. Seedlings emerge slowly and unevenly. The germination process takes 1-3 months.
When the seedlings grow several leaves, they are carefully planted in separate pots. In order not to damage the roots, each plant is transplanted with a large clod of earth. Until spring, seedlings are grown in greenhouse conditions; in April-May, on sunny warm days, hardening is carried out. Orchis are planted in open ground only at the end of May, when frosts have passed. The distance between seedlings should be 10-15 cm.
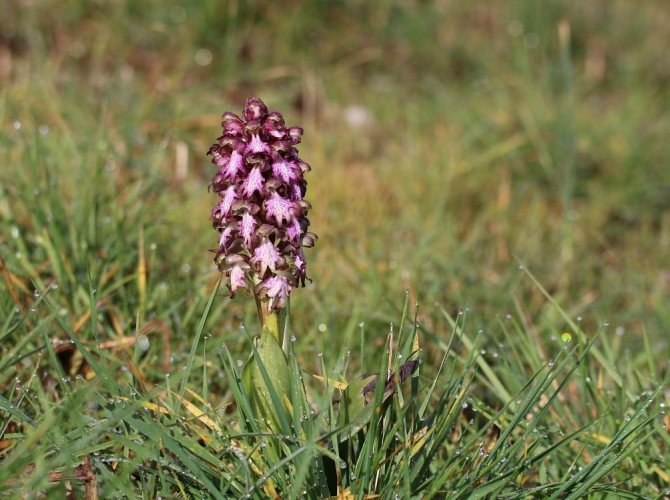


The simplest is the reproduction of orchis by tubers. In autumn, when the ground part of the plant withers, it is cut off. The tubers are dug up and carefully separated. They are immediately planted in new holes. In this case, part of the land from the old place must be transferred along with the tuber.
Interestingly, tubers grow as they separate, so this propagation method can be carried out during the summer. The first time the tuber is separated when buds appear. It is very important to be careful not to damage the stem and rhizome. Further, the separation is repeated every 25-30 days. The resulting tuber is planted in a new place. You should not wait for flowering soon. Within 3-5 years, only a leaf rosette is formed and a rhizome develops. Only after that, with proper care, flowering begins.
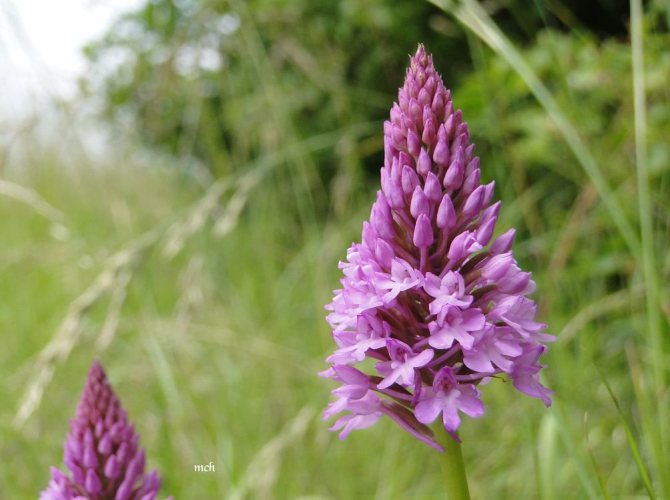


Root based recipes
To get the most out of the plant, you need to use young, freshly dug roots. They are harvested during the period when flowering ends.
If the root is not used immediately, it is cleaned of dirt and skin, rinsed thoroughly with water, doused with boiling water, cut and dried.
And so it turns out - a valuable medicinal raw material.
It is stored in dry ventilated rooms, away from exposure to sunlight, in cans with tight lids.
The shelf life is up to 6 years.
From sexual impotence
For sexual impotence, alcoholic tinctures of orchis root will help. Ingredients:
- half a loaf of rye bread;
- 1.5 tbsp. l. pounded orchis roots;
- 500 ml of cognac alcohol.
All ingredients are mixed and sent to a dark, dry place. The composition is insisted for about 2 months. After that, it is filtered, the thick is burned and again added to the tincture. The resulting mixture is infused for another 2 months. The drug is taken orally for 1 tsp. daily (before meals). But you need to drink the tincture with caution: exceeding the dosage will lead to excessive sexual arousal.
Orchis Root Powder Healing Paste
prepared using the following ingredients:
The powder is poured with hot milk and shaken until the mixture in consistency resembles a thick jelly. Then wine is added there. The resulting portion of the composition is eaten during the day for 3-4 visits.
From prostatitis
For the treatment of prostatitis or prostate adenoma
an infusion of several medicinal herbs is made. Ingredients:
- 10 chopped walnuts;
- 6 tbsp. l. powder from orchis tubers, lemon balm leaves, mallow seeds;
- 1.5 liters of hot water.
All ingredients are mixed, poured with boiling water and insisted for 2 hours. The finished preparation is filtered and the entire volume is drunk during the day.
For inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system
1. Orchis mucus, which has an enveloping and expectorant effect, is easy to make. To do this, take:
Powder of orchis root is poured with water and then shaken. The resulting liquid is allowed to brew for an hour, honey is added to improve the taste and taken twice a day, 100 ml before meals.
This simple remedy has not only an anti-inflammatory effect: it strengthens the body, increases immunity and tones up.
2. Water decoction of orchis helps with poisoning. It is used as an emergency aid for diarrhea or vomiting. Ingredients:
- 3 g orchis root powder;
- 400 ml boiling water.
Mix the ingredients, bring to a boil and keep on low heat, stirring constantly, for 8-10 minutes. Then the broth is infused for half an hour and taken three times a day, 100 ml before meals.
For external use
A topical product is made from the following ingredients:
- orchis root powder;
- milk;
- pork fat.
The powder is mixed with milk and lard to form a dense texture mixture.
This remedy, applied to the affected area in the form of cakes, eliminates toothache, abscesses and felon, and when rubbed into the scalp, it accelerates hair growth.
General tonic
In the East, a vitamin drink is prepared from the root of the orchis, which is considered almost an "elixir of eternal youth" - salep. Ingredients:
- 100 ml of cold water;
- 2 tbsp. l. pounded orchis root;
- 1 liter of hot milk;
- pinch of cinnamon (optional)
Powder from orchis root is poured with cold water, heated milk is added and the drink is shaken until it acquires the consistency of jelly. To improve the taste, you can add a pinch of cinnamon there. It is drunk every morning, before meals.
Sometimes sugar is added to salep, but in this case, the benefits of the drink are significantly reduced.
Taxonomy [edit | edit code]
A characteristic feature of the species of the genus Orchis
that is, many of them form interspecific hybrids, which testifies to the relative youth of the orchid family, and also to the fact that the processes of speciation in it are continuing [6]. Morphological differences of representatives of genera
Orchis
,
Anacamptis
and
Neotinea
in their modern understanding, they are rather indistinct, changeable and require detailed clarifications [6]. The traditional understanding of this genus in the "broad sense", which is still widespread in Russian literature, presupposed its broad understanding, with the inclusion in it of most of the species now considered as part of the genera
Anacamptis
Rich. and
Neotinea
Rchb.f. [7] According to the molecular phylogenetic studies of the genus
Orchis
, some of the species that previously belonged to it were transferred to genera
Anacamptis
and
Neotinea
... So to kind
Anacamptis
translated:
Anacamptis coriophora
,
Anacamptis fragrans
,
Anacamptis laxiflora
,
Anacamptis morio
,
Anacamptis palustris
,
Anacamptis picta
,
Anacamptis morio
subsp.
picta
, Anacamptis coriophora subsp.
nervulosa
... To the family
Neotinea
translated:
Neotinea tr> [6].
The proposed taxonomic changes were perceived ambiguously by the scientific community. The main reason for the negative reaction is the difficulty of selecting clear diagnostic signs for childbirth in the "new understanding". If the genus Neotinea
s.l. morphologically homogeneous, then childbirth
Orchis
and
Anacamptis
s.l. so heterogeneous that it is problematic to find clear differences between them [7].
The healing power of flowers
Orchis flowers are used relatively rarely in folk recipes, since they do not even have half the healing properties of the root of the plant.
However, the oil infusion of orchis flowers is used in the treatment of inflammation of the prostate gland.
- 50 g of dried orchis flowers;
- 0.5 l of olive oil.
The flowers are crushed in a mortar to a powder state, poured with olive oil and sent to a dark, warm room for 2 weeks.
Then the infusion is filtered and consumed twice a day for 1 tsp. before eating.
Places of growth of the spotted fingernail
Spotted fingernail, or cuckoo tears, is an amazing plant belonging to the orchid family.Currently, it is distributed in the forest zones of Europe, some regions of Asia. As for Russia, such a flower grows in the north-west and north, as well as in the central non-chernozem regions, in the east of Siberia. A favorite habitat is deciduous and coniferous forests with good moisture.


This genus includes about thirty species. Only twenty of them are found in our latitudes. Earlier, the spotted fingernail was unjustifiably referred to as orchis. And only in the seventies, botanists were able to isolate the plant into a completely separate genus.
Possible contraindications
Preparations based on orchis root are safe.
They can be consumed by babies, the elderly and even pregnant women (after consulting a doctor).
All men can take medicinal decoctions and infusions from orchis root to maintain male health and increase potency, but the dosage must be selected by the doctor.
With uncontrolled intake of orchis, excessive sexual arousal occurs.
Orchis flowers have a slightly higher number of contraindications: they can aggravate indigestion, especially when combined with preparations containing tannin.
Efficiency
Avicenna himself argued that drugs containing orchis are most effective for increasing potency. He called them the best aphrodisiacs. With their help, you can increase the attraction to the opposite sex, and cuckoo tears are also effective for the prevention of diseases that reduce potency.
Tinctures and decoctions based on the roots and, sometimes, orchis flowers fight not only with somatic causes, but also eliminate the factors that provoke psychogenic impotence.
Products containing orchis allow a man to:
- enhance libido;
- increase sexual stamina;
- become more active in the sexual sphere;
- increase the tone of the reproductive system;
- avoid urological pathologies and hemorrhoids;
- restore the normal functioning of the nervous system;
- increase the body's resistance to overwork; shocks and stressful situations;
- get rid of anxiety and nervousness before sexual intercourse;
- remove persistent fears and memories of past failures.
Preparing the landing site
Since in its natural habitat, orchis is found in meadows and glades, the conditions of artificial cultivation must be brought as close as possible to them. The planting site should be sunny with no shade. The soil is required neutral, as nutritious and loose as possible.


The growth of wild orchids on excessively wet and waterlogged soil is excluded. To prepare the suburban area for the appearance of the orchis, sand and peat are introduced into the land allocated for it, in proportions of 1: 2: 1.
The culture does not require the introduction of additional mineral compositions, but it gratefully responds to feeding with humus, followed by abundant flowering.
Pests and diseases
Despite their "orchid" nature, orchis are amazingly resistant plants. They are resistant to all types of fungal diseases and pests. But they have no natural protection from slugs. Snails, slugs and other leaf beetles adore this exotic plant. And around the orchis plantings, it is better to place special traps or lay out straw circles.


Dremlik orchis (Orchis morio) is now known as the Anacamptis morio species.
Features of the herb
Orchis is a patent. In other words, such a plant tries to avoid being adjacent to competitive types of grasses. If this could not be avoided, then it occupies less fertile land. In this regard, orchis are found only in single specimens or in small numbers and rather rarely form large clusters.
The plant in question is well adapted to the transfer of unfavorable natural conditions.Due to the accumulated substances in underground organs, it can wait for their changes for several years.
The population of orchis is not affected by hay-making and forest visits in summer. However, cattle grazing turns out to be fatal for them.


Medicinal types
Orchis, the medicinal properties and contraindications of which will be described in detail below, has quite a few varieties. But only 4 species of this plant have healing properties. Each of the species is used in the treatment of various diseases.
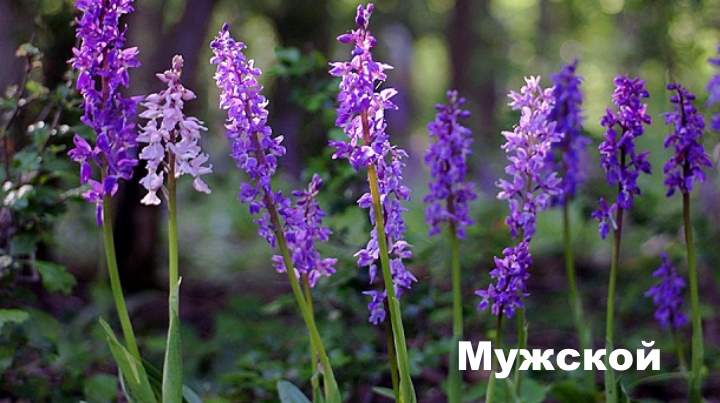
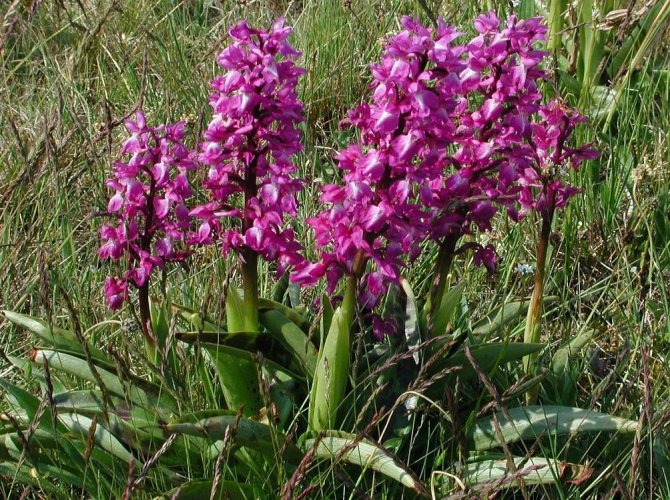
Orchis male
This species is found in the west of Russia up to the Urals, in the Caucasus and in Ukraine.
It adapts well to various types of soil in deciduous forests, does not take root on swampy and acidic soil.
The flowers of the male orchis are crimson in color, arranged in the form of a brush. The time of mass flowering falls on May-June. For treatment, the rhizomes of the plant are used.
Substances obtained from it are used for:
- gastrointestinal therapy;
- treatment of cystitis;
- pain relief;
- increasing immunity;
- healing wounds;
- infertility treatment in animals.
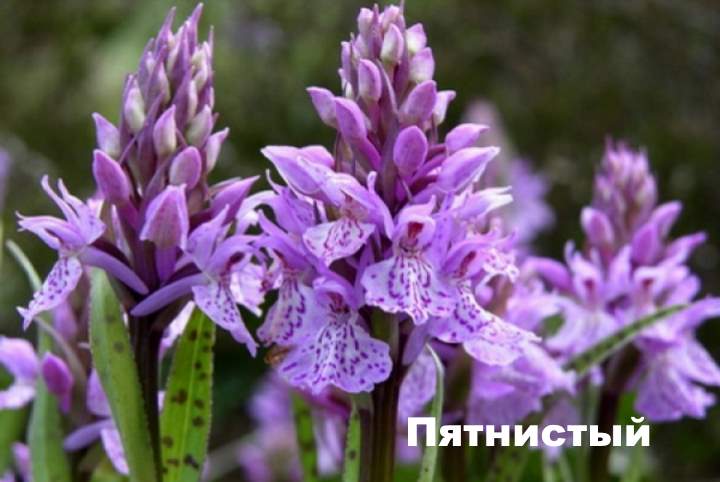
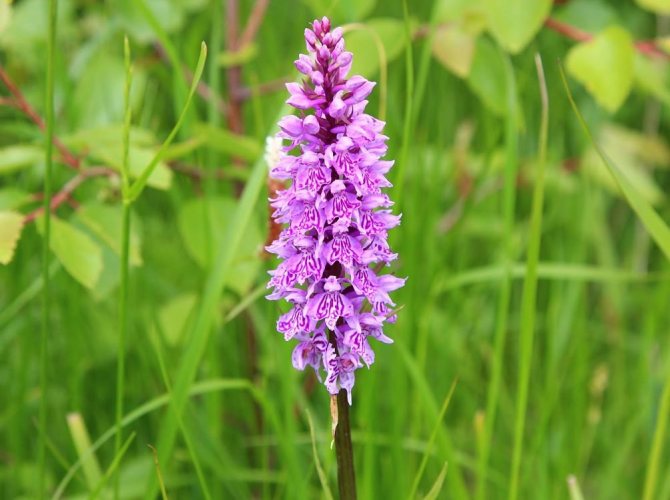
Orchis spotted
This species, due to the special elongated shape of the rhizome, has another name - finger root. Most often found in deciduous forests of Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. Another distinctive feature of the spotted orchis is its root, consisting of 2 tubers - a young one, which provides the main plant nutrition, and an old one.
On a rather high stem, there are up to 8 leaves, covered with small spots of lilac color. The flowers are light pink, in the shape of a helmet. Blooms in April-May until June. It is used for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Orchis
It is a classic 1-stem orchis variety with leaves at the very bottom. Its flowers are light pink, at the root there are 2 fully developed tubers. Orchis prefers dry, calcium-rich soil. Occurs in the fields and meadows of Russia and the Caucasus.
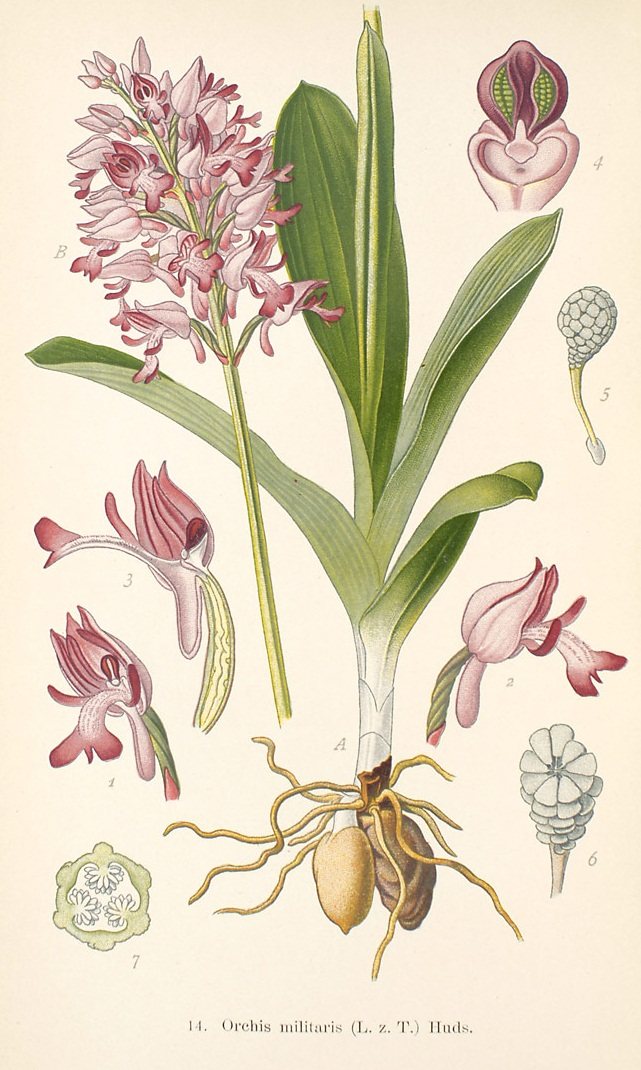


Medicinal substances obtained directly from the tubers of a plant are used for:
- normalization of potency;
- treatment of ailments of the respiratory system;
- normalization of the digestive tract.
Sometimes orchis rhizome powder is used to make soups and baked goods.
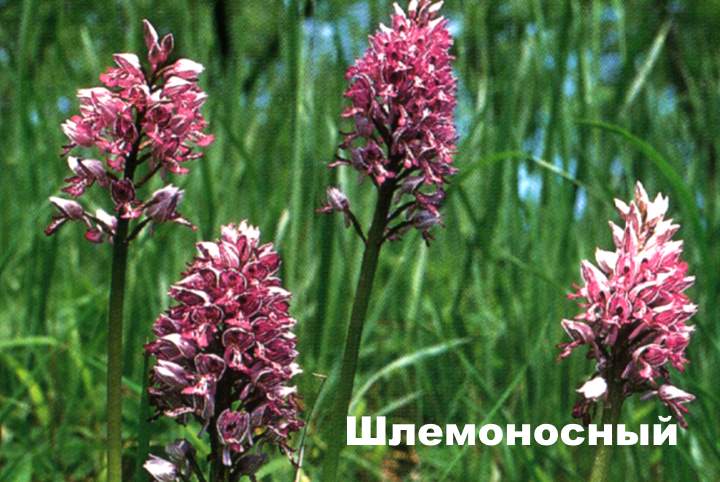
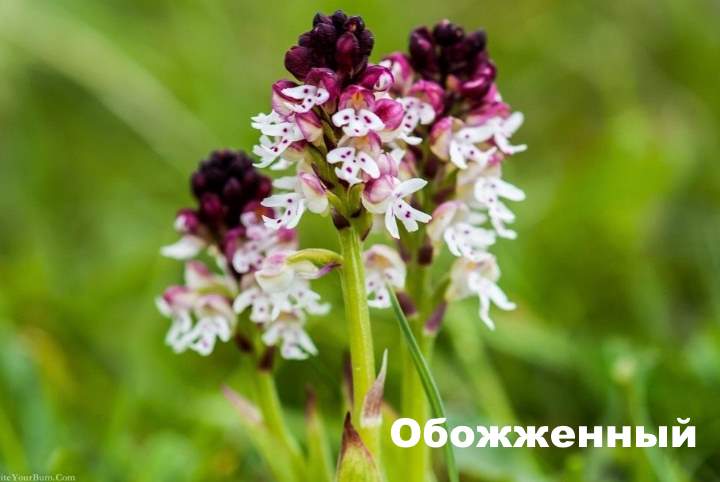
Burnt orchis
The rarest variety of the plant, which has one more name, is burnt neotinea. Prefers slightly alkaline soil of deciduous forests.
Habitat:
- European regions of Russia;
- Belarus;
- Anatolia;
- Ukraine;
- Scandinavia;
- Mediterranean.
The plant with a long stem has a helmet-shaped inflorescence with dark red flowers at the base and white at the edges. The rhizome is well developed with 2 oval tubers, on one of which is the bud of the next tuber.
Decoctions from tubers and seeds of neotinea are used for:
- acute inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- epilepsy;
- acute forms of poisoning.
Photo gallery
Growth features
Spotted orchis and other types of grass usually grow in moist soil, although they do not really tolerate excessive waterlogging.
In the driest and hottest period of summer, such plants go into a dormant state. They remain in the soil in the form of tubers and rhizomes until the next favorable season.
In autumn, orchis begin to grow actively, hurrying to go through their life cycle until July.
Most species of a plant such as orchis are calciphiles. In other words, they like to grow in lime-rich soil. There are also species that prefer alkaline or mineral-rich soil.
Almost all orchis for their growth choose areas with high illumination (for example, meadows, sparse forest zones, forest edges). Although some plants can still be found in the shade.
Finger-root as a garden culture
Spotted fingernail is a fairly hardy plant. It tolerates transplantation well.Therefore, such a flower can become a real decoration for your garden. He will not require any special care from you. The plant can easily endure even winter frosts. The only thing that the fingerling root does not like is dry sandy soils. But a shady flower bed or too wet area is quite suitable for the plant.


As for reproduction, everything is not so simple here, since the plant blooms only after six to eight years. Orchids generally grow extremely slowly. And yet, the palm root is a beautiful flower worthy of growing in the garden.
Here are some healing recipes:


- In case of gastric ulcer, salep is prepared as follows: one gram of powder should be poured with a tablespoon of water (only cold), and then cooked without ceasing stirring. It is constantly necessary to add water in small portions until a hundred milliliters of solution is obtained. Salep is taken one tablespoon up to five to six times a day (always before meals).
- As a stimulant, as well as in the treatment of the gastrointestinal tract or poisoning: five grams of powder is poured into a glass of cold water. The mixture is constantly stirred and liquid is added. Mucus should form in ten minutes. It is taken three to four times daily before meals.
- For dysentery and diarrhea: the powder is diluted 1:10 with water, gradually add boiling water and do not stop stirring. Then the mixture is shaken well until a homogeneous mucus is obtained. Flax seed decoction can be added to such an emulsion. The mixture is used for enemas.
- For potency, the tuber tincture is taken in a spoon (teaspoon) twice a day before meals.
Preparing the orchis for wintering
Despite its name, the wild orchid is not at all a thermophilic plant that is afraid of frost. Orchis winters well without winter shelter, even in the middle lane. But so that the excess moisture does not affect the quality of wintering, and the plant better tolerates temperature changes during periods of thaw, the bushes need to be prepared for the cold weather.
As soon as the orchis begins to dry out in anticipation of the first autumn cold weather, it is better to immediately cut off all the ground parts of the plant to the base. Do not wait for the shoots to die off themselves, but feel free to carry out a cardinal pruning. So the rhizome will better prepare even for the most unstable winters.
Harvesting of spotted fingernail
What is interesting for people spotted fingerling? Its use for medicinal purposes began a long time ago, ever since people discovered that it is a medicinal plant.
For medicinal purposes, tubers are usually used. They are harvested precisely after flowering, when a young tuber has already formed. The dug roots must be strung on a thread and dipped in boiling water for a couple of minutes. This is done so that the nodules cannot germinate in the future. Next, the threads are hung to dry under awnings so that direct sunlight does not fall on the roots.
Dry tubers are called salep. Most of them are mann polysaccharide, which forms useful mucus. In addition, the roots contain starch, dextrin and other substances.
General information
Orchis translated from ancient Greek means "testicle". He received this name due to the shape of his rhizome, which resembles 2 eggs. There are species of this plant, the roots of which are slightly elongated - finger-like. The orchis reproduces by dividing the roots and by self-seeding.
The people often call him:
- forest orchid;
- the tears of a cuckoo;
- dog tongues;
- core.
This plant does not tolerate an excessively hot and dry climate, therefore it is most common in the Northern Hemisphere, in areas with cold, subtropical and temperate climates and moist soil. In Russia, orchis grows almost throughout the territory, but most often it is found in the Crimea and the Caucasus mountains.
Economic value and use of the herb
Orchis in a pharmacy can be purchased only in dried form.Moreover, not only its flowers and leaves, but also tubers go on sale. The latter contain starch, mucous substances and sugars. Dried rhizomes, or saleps, are actively used as an enveloping and emollient for poisoning, gastritis and colitis. Sometimes they are recommended to be taken by weak patients to strengthen the body.
It should also be noted that the herb in question is used in veterinary medicine for intestinal catarrh in pets.