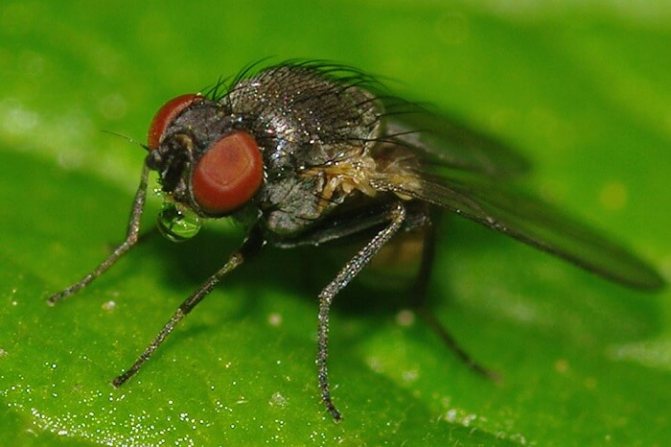
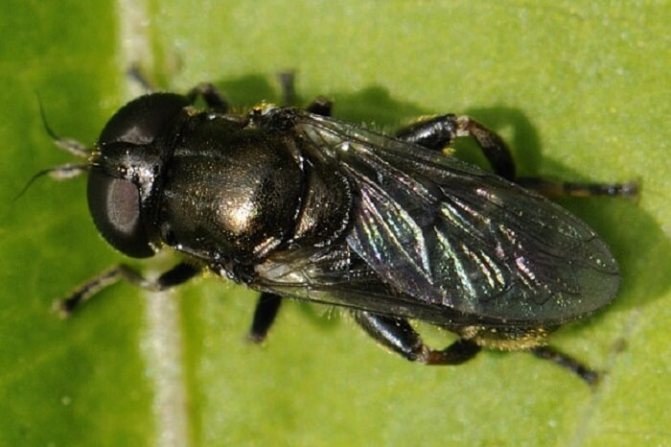
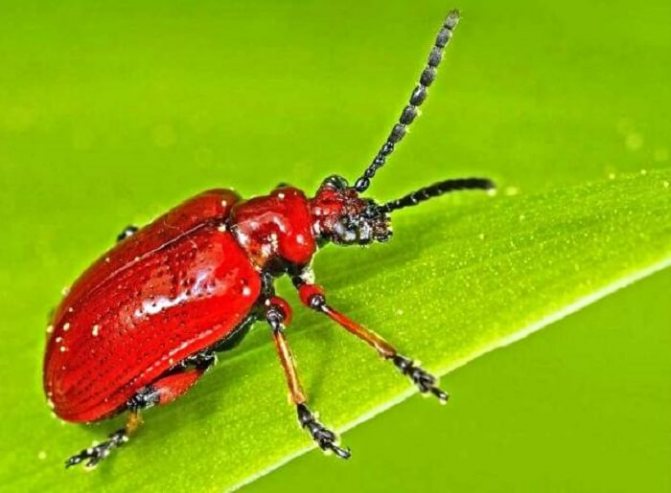
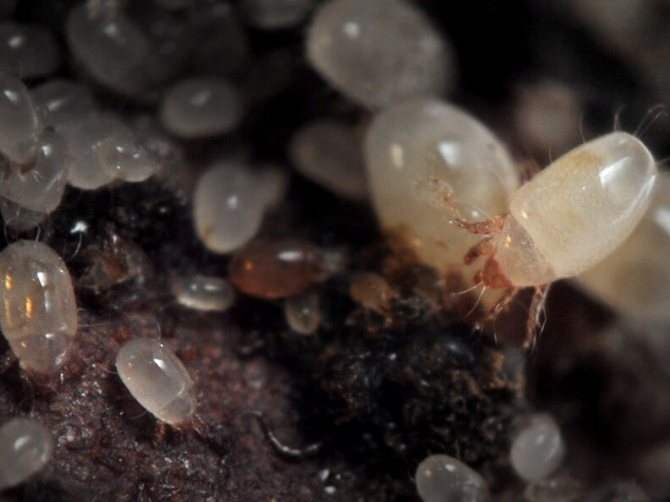
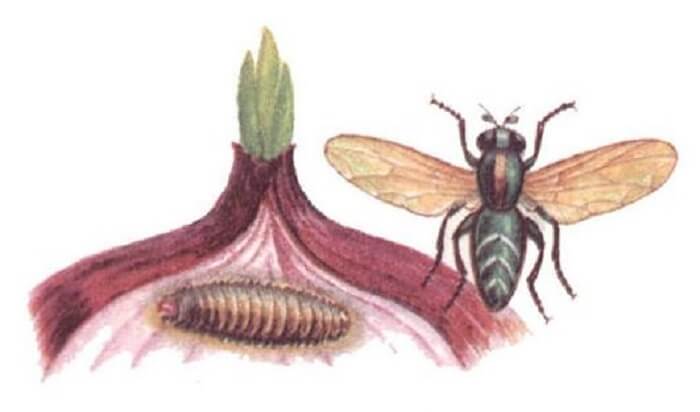
What is the danger
The pest is dangerous for almost all onions: turnip onions, chives, batun onions and many wild onions. Adult beetles can also harm garlic crops.
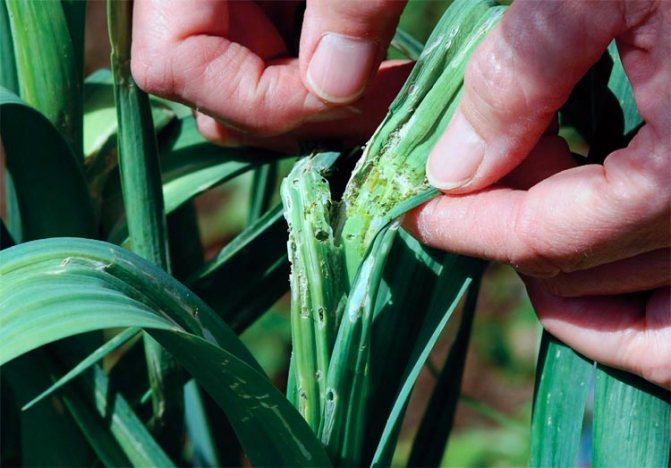
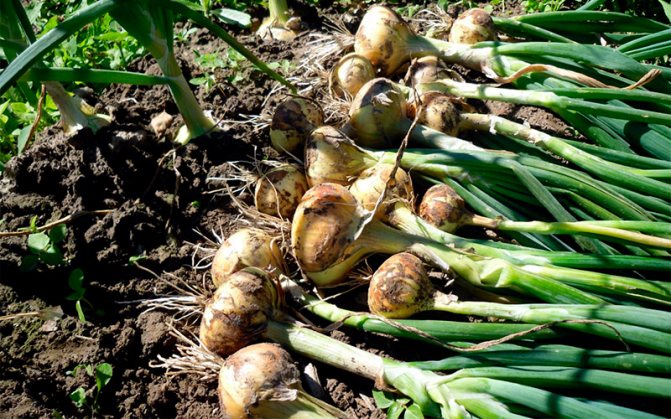
Crawling out of wintering places, the beetles first feed on sprouted old bulbs. Then they move to young onion crops and inflict great damage, feeding on onion greens. Damaged leaves are deformed and dry out. If onions are grown for greens, then this leads to a large loss of yield. When growing onions for a turnip, the damage is not so significant. During the season, onion leaves have time to grow, however, with a large amount of damage, the quality of the crop drops dramatically.
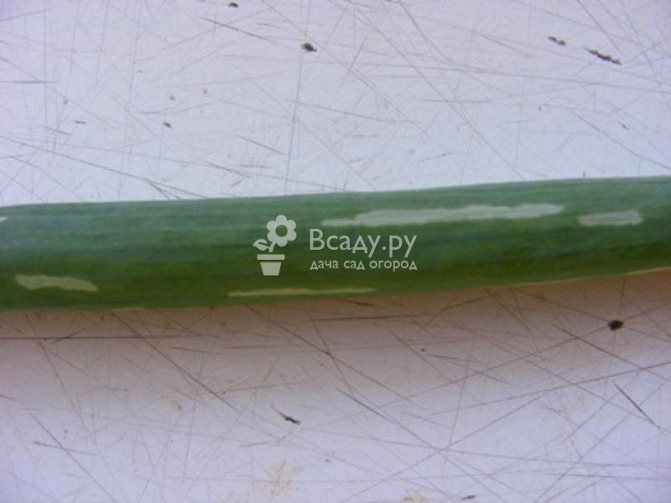
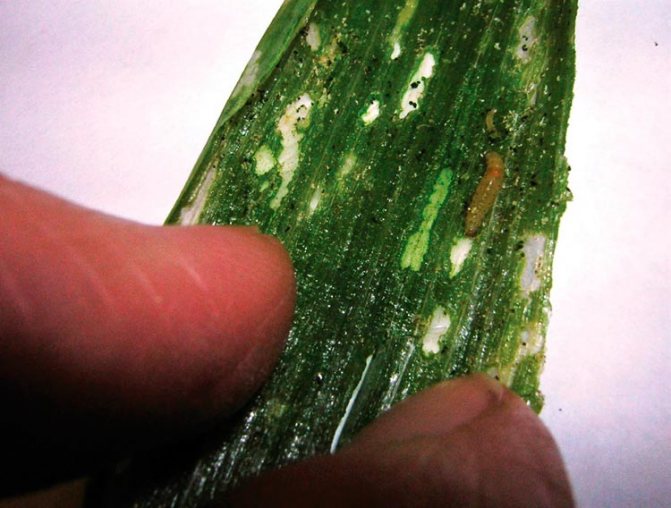
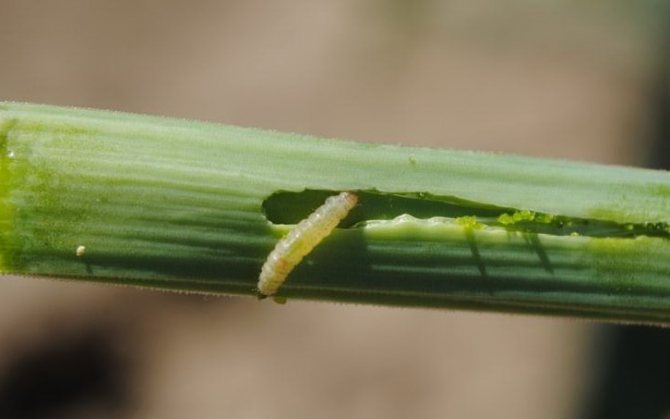
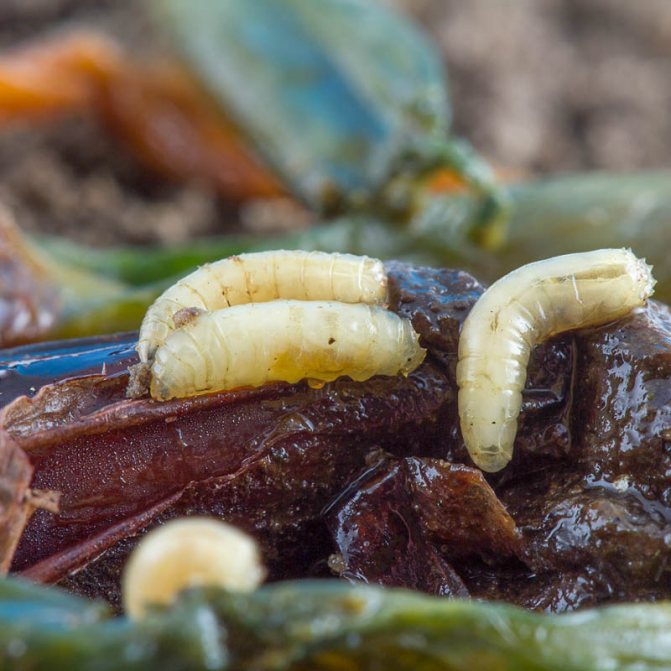
The larvae that emerge from the eggs feed on the pulp of onion leaves, gnawing the passages from the inside of the leaf. Externally, the damaged leaf becomes striped, dries up quickly and dies off. With a large number of larvae, onion greens are sometimes completely destroyed.
The exit from the pupae of young beetles coincides with the onion flowering period. They can destroy a large percentage of seeds and planting material. After harvesting the onion, the lurkers fly away to their wintering grounds.
Onion mite
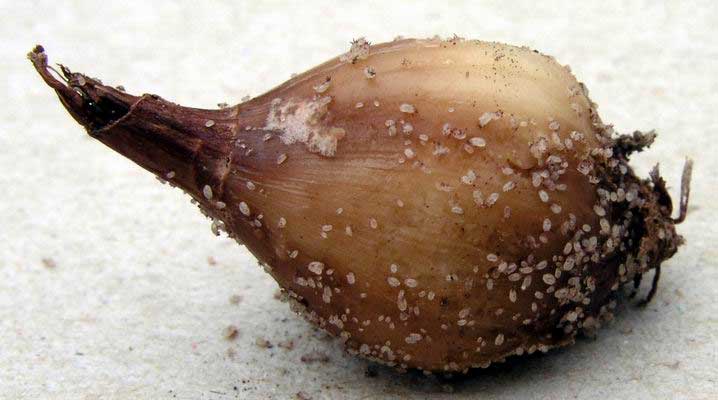
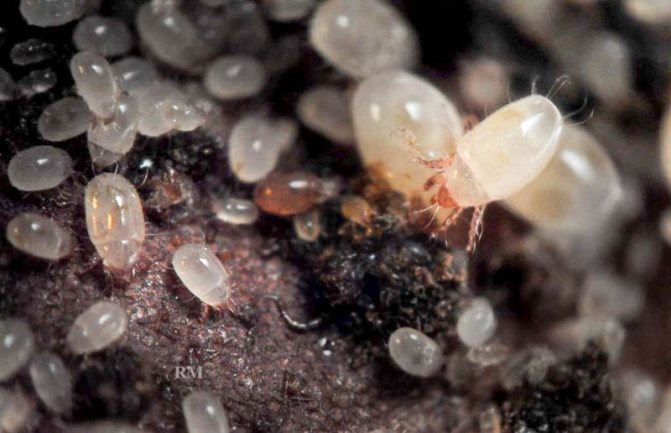
Onion root mite (Rhizoglyphus echinopus R. et F.) harms not only vegetable plants - onions, garlic, but also well-known ornamental crops - tulips, daffodils, hyacinths and other bulbs, both outdoors and during storage. The garlic mite (Aceria tulipae Keif.), Unlike the onion root mite, damages the leaves and scales of the bulb, causing great damage to onion sets.
The onion mite colonizes mechanically damaged (for example, cut) or weakened plants. With a strong lesion with an onion mite, the outer scales lag behind the bottom, it becomes rotten. On such bulbs damaged by an onion mite, roots do not form at all.
With a weak lesion, the mite can persist between the juicy scales, thus damaging the bulbs during storage.
The mite is quite moisture-loving and thermophilic; it multiplies quickly in humid and warm conditions. The onion mite spreads especially quickly during storage if the bulbs are stored in a humid and warm environment, and they are poured in a thick layer. Under these conditions, ticks quickly move into healthy bulbs through the bottom.
The female onion tick has the shape of a short oval, up to 1 mm in size. She lays up to 800 eggs. At the optimum temperature for the development of an onion mite from +15 to + 28 ° C, one generation develops within 10 - 30 days. If the developmental conditions change or nutrition ends, then the ticks move into a very stable form of existence - the hypopus. In this form, ticks can exist for a very long time without eating anything.
The onion mite spreads with plant debris, through inventory, soil.

Onion mite control measures
Use only healthy, undamaged bulbs for sowing. Before sowing, all planting material, as well as all plantings of onions, garlic, or flower crops 20 days before harvesting, should preferably be treated with a solution of colloidal sulfur (40 g of sulfur per 10 liters of water, consumption of 1 liter of working solution per 10 m2). After harvesting, you need to destroy all plant residues, dig up the soil.
The harvested harvest of onions, garlic, as well as tulip bulbs, hyacinths, daffodils after harvesting must be dried within a week at +35 +37 ° С.Onions and garlic are stored in ventilated and disinfected rooms. A small supply of garlic can be stored at home.
Insect description
The most common and known are the following species of this genus of weevils:
- seed rapeseed burrower, or Ceutorhynchus assimilis;
- leaf hidden proboscis, or Ceutorhynchus erysimi;
- rape lurking, or Ceutorhynchus napi;
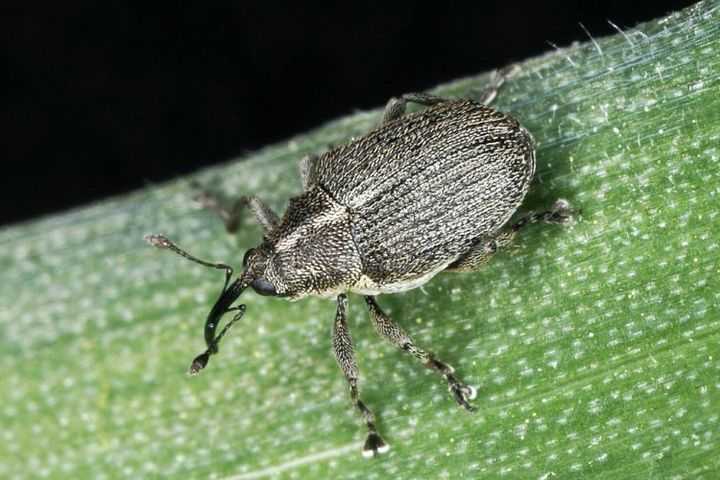
- onion lurker, or Ceutorrhynchus jakovlevi Schulze;
- cabbage stem hidden proboscis, or Ceuthorrhynchus quadridens.
Stem lurker is widespread everywhere, but especially harmfulness is observed in the south-west of Belarus.
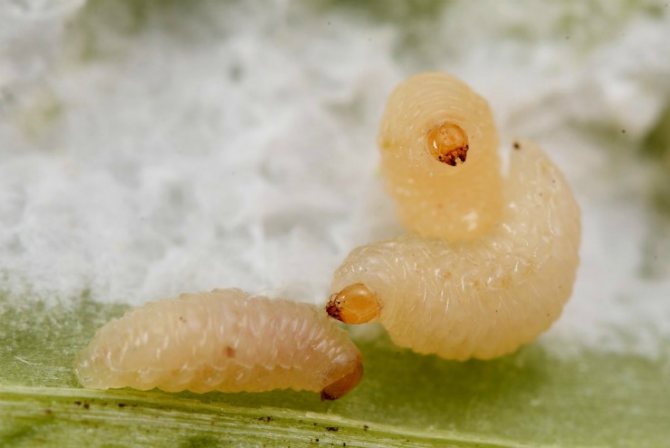
Larva


The egg of the stem lurker is oval and whitish in color. The development of the embryo takes five days at a temperature of 19 ° C.
The larva of all weevils has no legs or eyes. It has a slight ventral curvature and is characterized by the presence of a small chitinized head. The head capsule differs in size at the stages of different ages. At the third age, its width is about 0.5 mm.
The larvae gnaw long passages along the petiole of the leaf towards the stem. The pith is then eaten away and the larva continues down the stem to the beginning of the root collar. With large leaf sizes, the development of the larva does not end with the transition to the level of the stems.
Growing up of the larva takes place in three stages and takes about a month at a temperature of 20 ° C. The pupa resembles an adult's body shape and has weakly expressed rudiments of a head tube, wings and legs. Pupation occurs at the end of June in the soil in the presence of an earthen cradle. It takes about two weeks to develop.
We offer you to familiarize yourself with the Trap in the apartment for ants manufacturing and selection of effective
Adult
Development from egg to adult lasts about 12 weeks. The emergence of adult beetles of the new generation of stem lurking proboscis occurs in June-July. After emerging from the soil, these insects have a body length of no more than 3 mm and begin the process of feeding on leaves and stems of cruciferous plants. Their elongated body has black shiny integuments and is distinguished by the presence of gray scales and hairs. The underside of the body is covered with dense light scales.
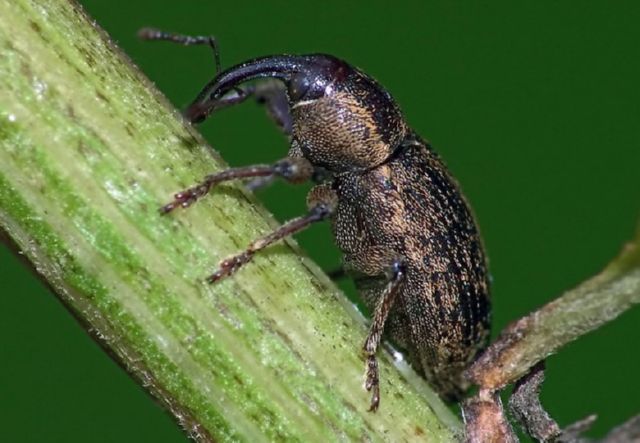


There is a small light spot behind the scutellum. The pronotum has a narrow longitudinal groove that contains narrow white scales. The lateral segments of the pronotum have large dentate tubercles. The thorax is less wide than the base of the elytra. The paws are colored red. Any plant debris serves as a wintering place for adults.
Waking up in early spring, pests colonize fodder plants that are in the immediate vicinity of the wintering site.
For feeding, these weevils use the tissue of the petioles and thick veins located on the underside of the leaf plate. The pest gnaws at first the thin skin of the plant, and then eats out shallow cavities. As a result of such injury, overgrown tissues form specific swellings. Damage to seedlings and testes by adults can often be observed.
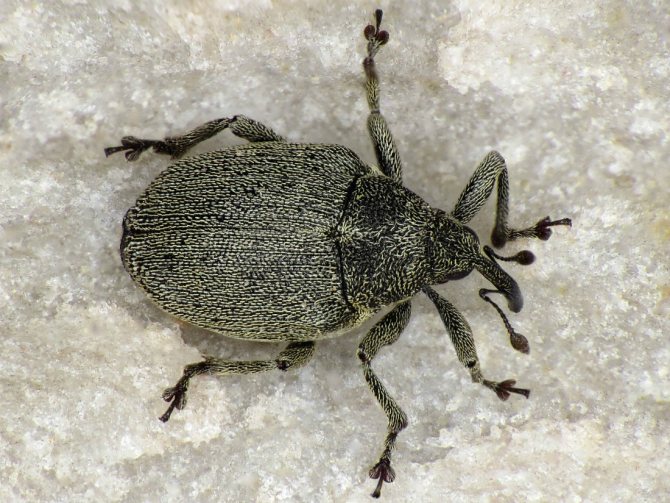
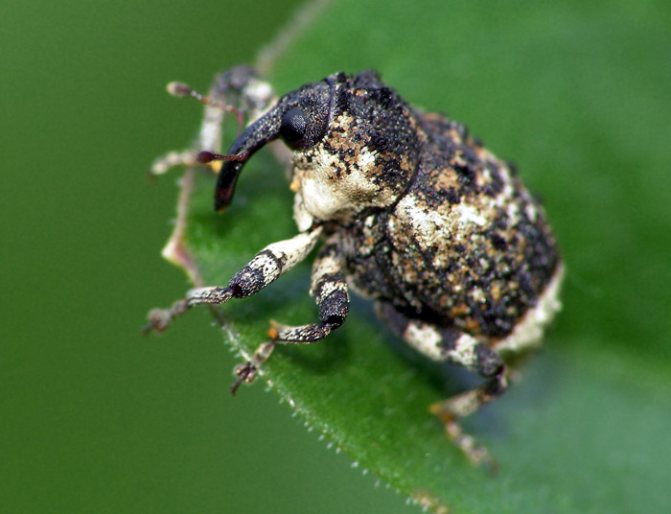
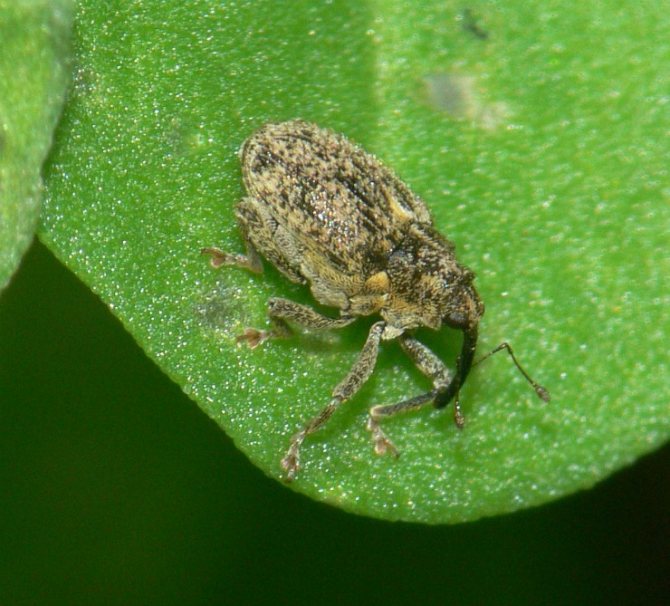
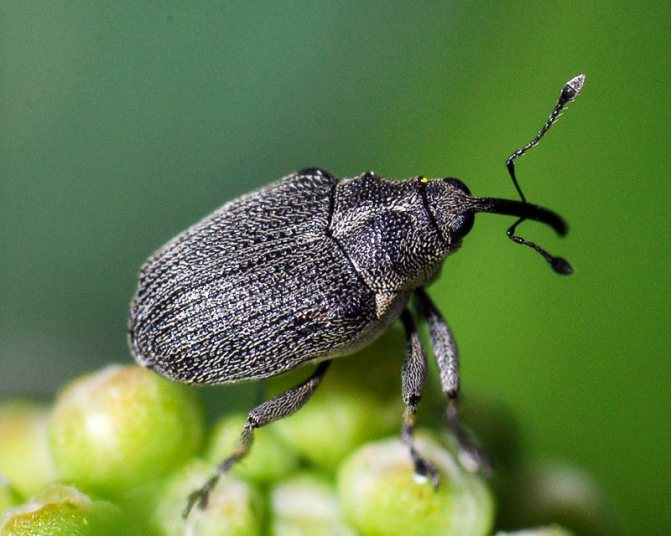
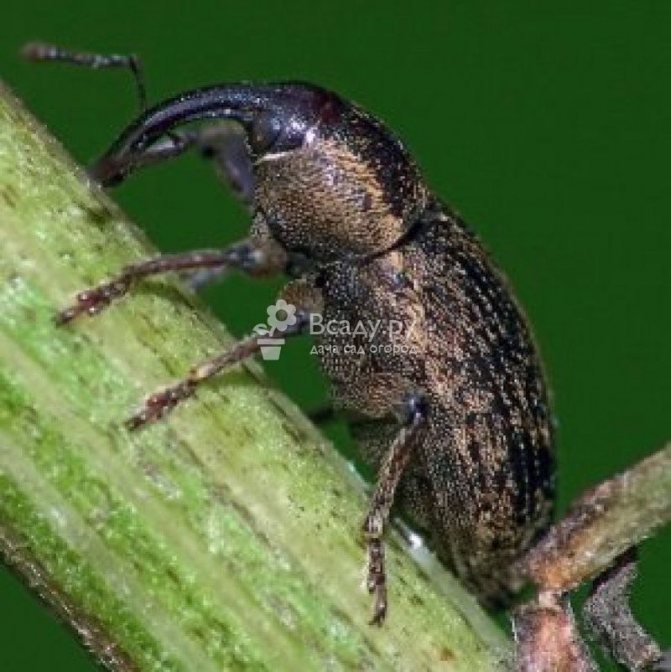
The hidden proboscis belongs to the order of weevils. Body length 2-2.7mm. It is oval in shape, has hard elytra covered with gray scales. A white stripe runs along the seam of the elytra. The elongated head ends with a proboscis turned downward, like an elephant. Antennae in the form of a club, i.e. with a thickening at the end.
The onion cobweb is widespread in the middle zone of the European part of Russia and in some years can cause significant damage to onion crops.
After wintering, the lurker goes out to feed on weeds, in early May, they start laying eggs.On the leaves, closer to the base, it gnaws a small hole, where it lays eggs in 5-7 pieces on the inner side of the feather of the onion. In two weeks, the larvae appear.
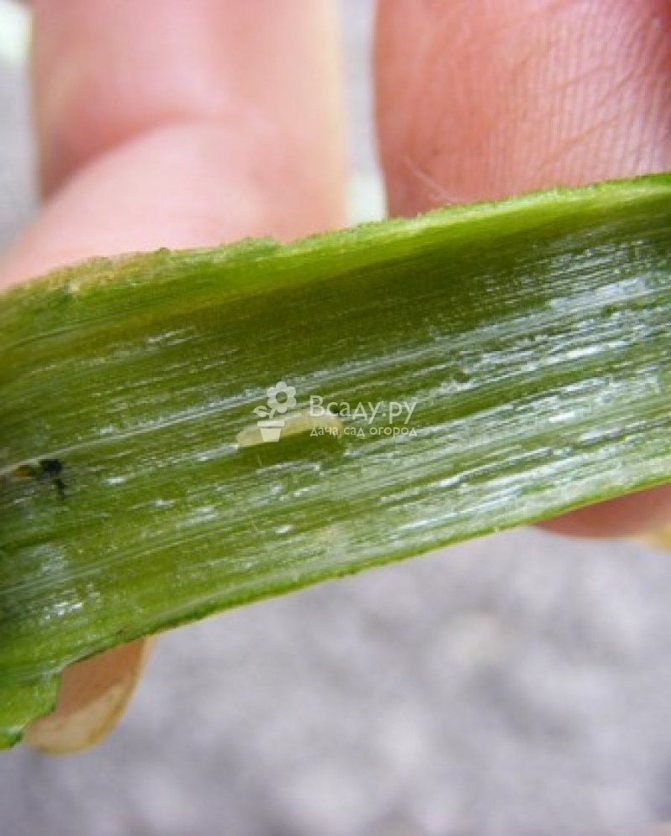
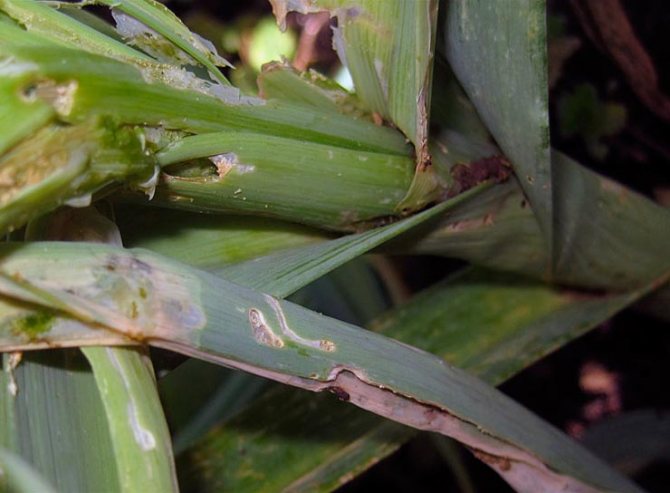
The nature of the damage in the form of stripes without damage to the integumentary tissues of the leaf. By eating soft tissues, the larva harms the plant. The tip of the leaf turns yellow and fades. With a high density of the pest on the plants, the infestation of the site can reach 100%, but at the same time, complete death of the plants is not observed. Affects mainly the size of the crop because the plant consumes elements of nutrition for the renewal of leaves.
After 20 days, the larvae crawl out and burrow into the soil at a depth of 3-5 cm., Pupate. At the beginning of June, beetles of a new generation appear, which also cause significant damage to the flowering testes of onions. In a year, the Lurker gives birth to only one offspring. For wintering, beetles fly away within a radius of 100-200 meters.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with What to do if cockroaches appear in the apartment
Miner tomato moth
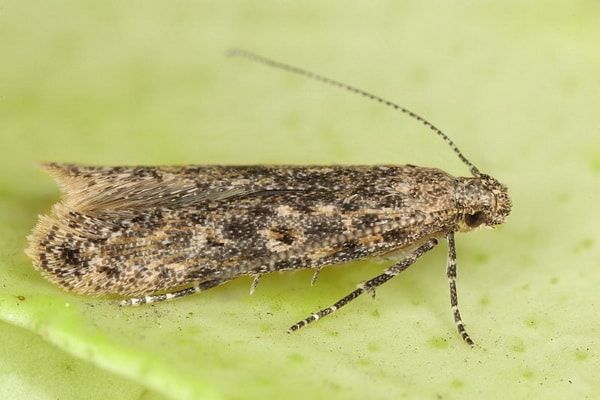


Miner tomato moth
The miner moth is a small insect with filamentous antennae and a tuft of scales. It can damage both leaves and fruits. To combat this parasite, the following folk remedies are used:
- Introduce predatory insects, such as horse riders, into the area;
- Pour water on tomato bushes regularly - it will wash away the pests and prevent them from laying eggs;
- Hang yellow sticky boards in the area. Many flying parasites like this color, so they readily land on the board and immediately stick to it;
- Treat tomato bushes with an aqueous solution of essential oils. To combat tomato moth essential oils of mustard, lavender, orange, rapeseed, mint and geranium are ideal;
- Plant the tomato area with one of these plants, if possible.
Time of appearance
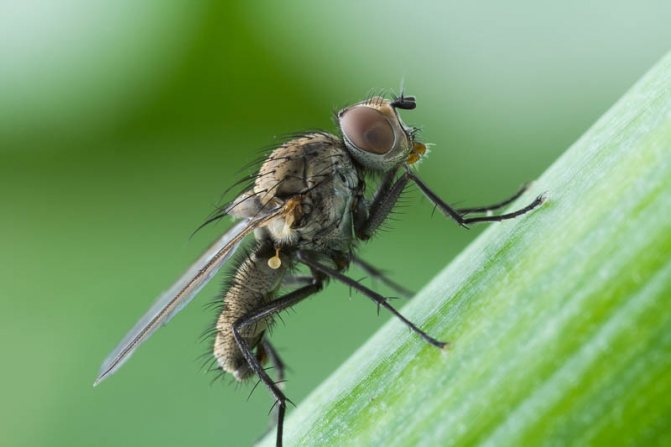
Beetles crawl out of their wintering grounds starting from April, depending on weather and temperature conditions, as well as the location (in Siberia, this happens in May).
After about a month, the females lay eggs, and within two weeks after that, the larvae that emerge from them begin to destroy the green onions.
After about 20 days, the larvae migrate into the soil, where they pupate and, starting in mid-June, new generation beetles emerge, which again begin to harm the onion crops.
Onion rattle
Onion leaf beetle, or onion rattle, (Lilioceris merdigera) is found almost everywhere where onions and garlic, asparagus, as well as plants of the lily family - lilies, daylilies, hazel grouses, are sown, but damages outbreaks. In case of danger, the beetle emits a very loud crack, emanating from the abdominal cavity of the beetle, hence the name - rattle. This beetle is also called a firefighter for its bright red color. The onion rattle has the whole body, the head and legs are red, and it is easy to confuse it with the lily rattle, in which the body is red, and the head and leg are black.
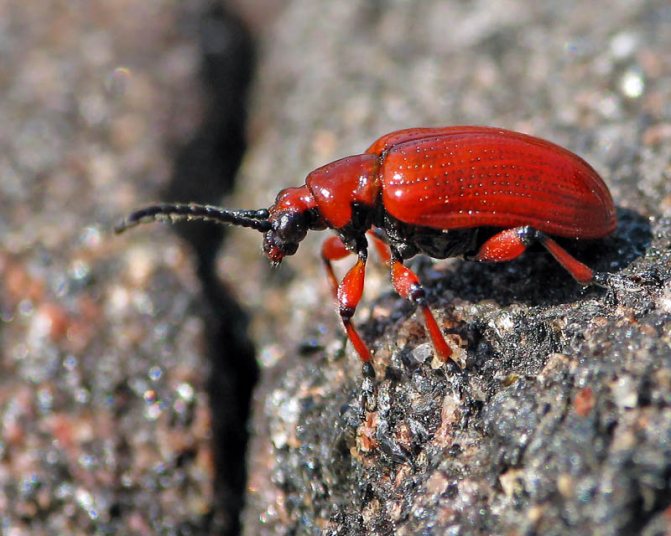


The cracker hibernates in plant debris. Before the appearance of the first shoots, the beetle feeds on unharvested bulbs, which were thrown aside during planting, and on last year's sprouted bulbs.
With the appearance of young shoots of onions, the beetle moves to young leaves, flower arrows - gnaws a feather and pedicels, lays eggs in flowers. The hatched larvae feed on leaves, flower arrows; after about a month they pupate in the soil. The onion cracker larvae are large and can be harvested by hand.
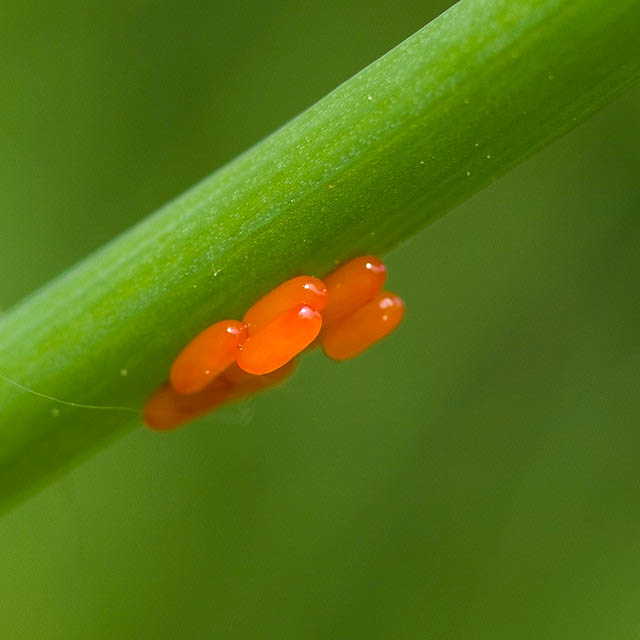


Reproduction
Weevils are characterized by the presence of sexual dimorphism. The heterosexual specimens of the stem lurking proboscis are distinguished by the different organization of the genitals. One generation develops during the full cycle of the growing season.
The mating period ends with egg-laying in April-May.Laying periods vary depending on the vegetation characteristics of the food base and the geographic range of the beetle.
Females lay eggs in a group way, directly into the middle vein of the leaf. Oviposition is sometimes performed in the lower part of the petiole or stem. The oviposition site rises slightly above the surface and vaguely resembles a wart. The maximum fertility of one female is 280 eggs.
How to recognize a pest on the site?
Gnawing small areas on the stem and thick veins of leaves, the pest contributes to the death of damaged plant tissues. There is a decrease in the general resistance of the plant to lodging, which is especially noticeable on sown areas with thickened plantings.
Plants affected by this pest are distinguished by early maturation and the presence of underdeveloped and small seeds. Drying of damaged stems leads to breaking off of the plant in the area of the root collar and premature shedding of seeds.
The lurker is a small beetle with a gray color. The length of its body rarely exceeds 3 mm, and the main instrument of the oral apparatus is the proboscis - a distinctive feature of all bugs of this type. Most of all, bugs are common in Kazakhstan, in Siberia and in the middle lane.
As soon as the cold weather recedes, the beetles fly out and begin to eat the organic remains that have been preserved from the previous season. As soon as the first shoots appear in the beds, the pest immediately moves to them, especially aster and cabbage crops. The female gnaws cavities in the leaves and lays one egg in each - visually, such a clutch can be determined in the form of discolored spots on the plants.
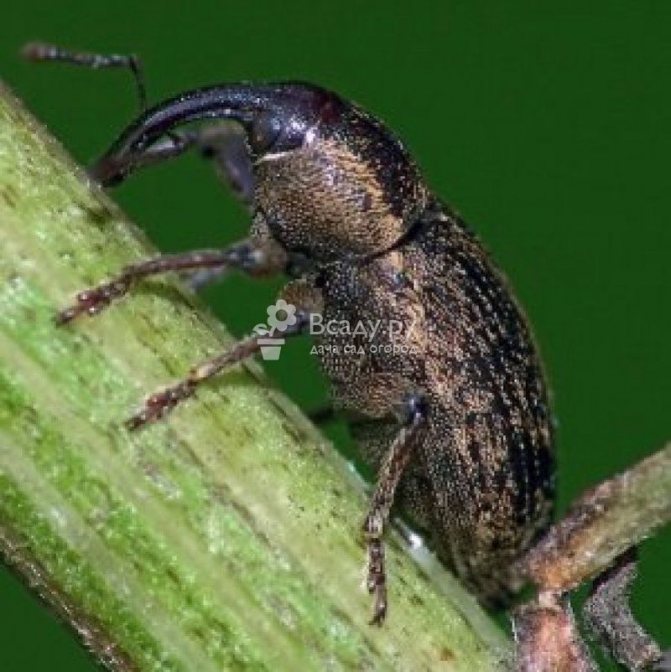


The larva emerges from the egg in a week or two (depending on what environmental conditions are created), and looks like a small white worm up to 5-6 mm long. Caterpillars immediately begin to feed on the flesh of young shoots without damaging the outer covers of the leaf. After 2-3 weeks, the caterpillars gnaw holes through which they go into the ground in order to move to the pupa stage.
We offer you to familiarize yourself with Parasites in the human body - who is the worst?
In late June and early July, a new generation of beetles emerges, which eat not only leaves, but also take for inflorescences, piercing tissues with their proboscis and eating out whole cavities in them. In this case, damage is caused not only to the crop, but also to future seed crops.
Poplar moth
If you look closely at the photo of this pest, you will notice that it is a moth with narrow velvety wings. The main danger of poplar moth lies in the enormous damage caused not only to poplars, but also to cucumbers, lettuce, apple trees, roses, pears, violets and chrysanthemums. You can fight poplar moths with the help of parasitic beetles or spring oil used to treat healthy leaves. Sick shoots are subject to complete destruction.
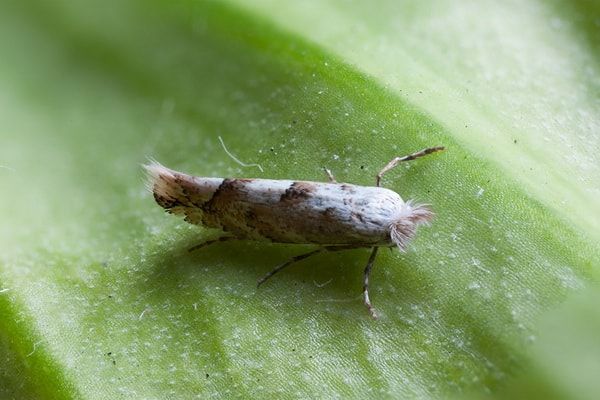


Poplar moth
We hope these tips will help you manage your garden pests. However, remember that folk remedies do not always cope with the task assigned to them. To save the harvest, act with confidence - seek help from qualified professionals!
Control measures and means
The use of agrotechnical methods shows high efficiency to combat the hidden proboscis. It is necessary to cull seedlings infected with larvae, destroy weeds. Compliance with vegetative irrigation and fertilizing significantly increases the resistance of plants to the pest. Deep loosening of the soil during pupation, the use of the method of deep autumn plowing and adherence to the timing of crop rotation works well.
In case of massive damage to plants by this pest, it is advisable to carry out treatment with modern insecticidal preparations.
- Removal of damaged leaves with larvae (for okroshka)
- Loosening of row spacings during the period of mass pupation of larvae
- Sprinkle the dew on the plants and the soil under them with a mixture of tobacco dust and wood ash (1: 2)
- Spatial isolation of new onion crops from last year. Sowing optimally early
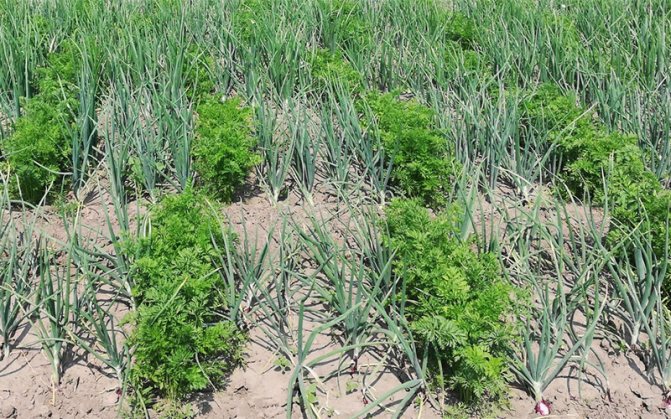
- Place the onion and carrot beds side by side. Plant phytoncides mutually repel pests. Some garden annual flowers can also repel insects (calendula, velvet)
It is not recommended to spray crops of onions with chemistry. But the harvest is said to be more expensive. The fact is that onions are used for feathers and there is a high probability of getting poisoned. I recommend that you allocate a separate garden bed for the consumption of onions for salads. In this case, the seeds of the third year of vegetation are best suited, which are usually planted on the arrow, the foliage is higher.
The beds, which are designed to obtain onions for turnips, can be treated with systemic insecticides during the period of pest activity.
Attention, the recommendation has not been tested in practice and cannot be a guide to action. in the list of approved drugs on the territory of the Russian Federation for 2014, there are no drugs recommended for use on onions against the latent proboscis.
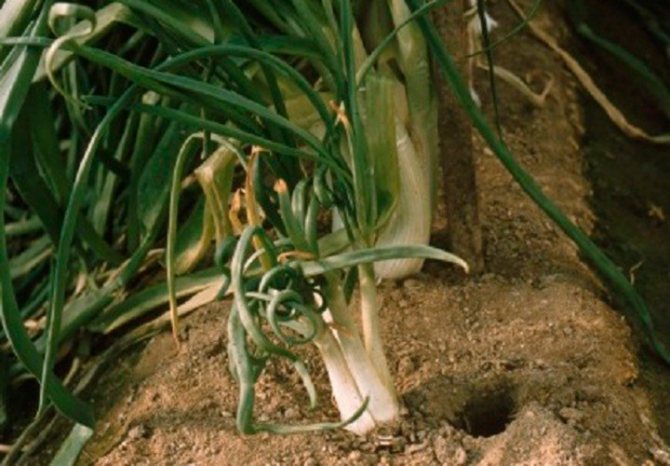
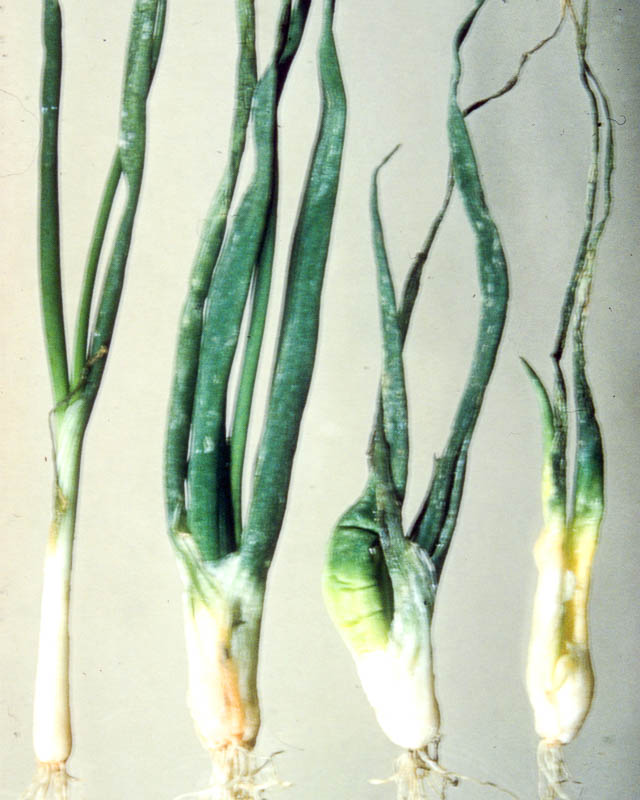
Stem nematode
Stem onion nematode (Ditylenchus allii Beij., Ditylenchus dipsacea) is found not only on onions and garlic, but also on other vegetable crops, for example, parsley, parsnips, tomatoes, radishes, cucumbers. The stem nematode is a very small, only 1–1.5 mm, filamentous white worm.


Nematode control measures
For recovery from nematodes before sowing the chives, the onion sets must be immersed in hot water: if the water temperature is + 45 + 48 ° C, then the immersion will be 10-15 minutes; if the water temperature is + 50 + 52 ° C - 5-10 minutes; if the water temperature is + 55 + 57 ° C, the treatment will take 3-5 minutes. Small onion sets are processed for 3-5 minutes.
With a weak nematode damage to chives or onion sets, they are soaked for 2 hours in water at a temperature of + 40 ° C, at a water temperature of + 16 + 18 ° C, the planting material is kept in water for about three days.
Before sowing, nigella (onion seeds) are pre-soaked for 4 hours in cold water, then immersed for 10 minutes in hot water heated to + 48 + 51 ° C, the hot water is drained, and the seeds are again poured with cold water.
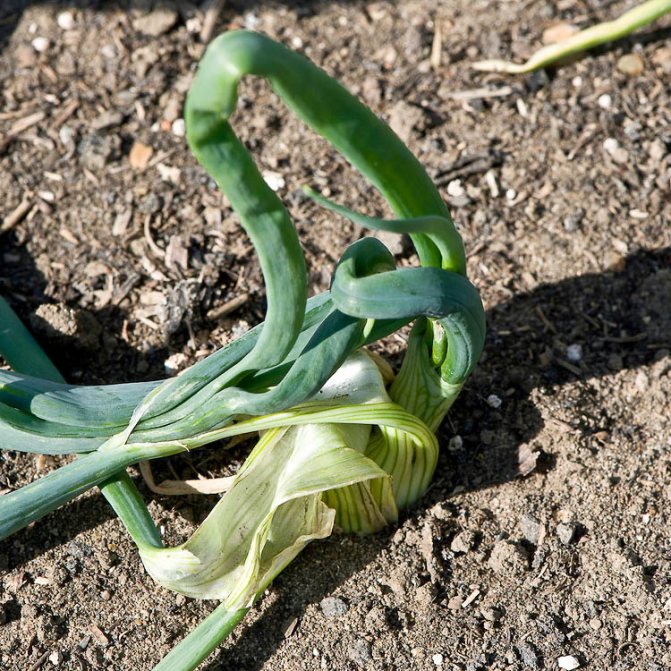


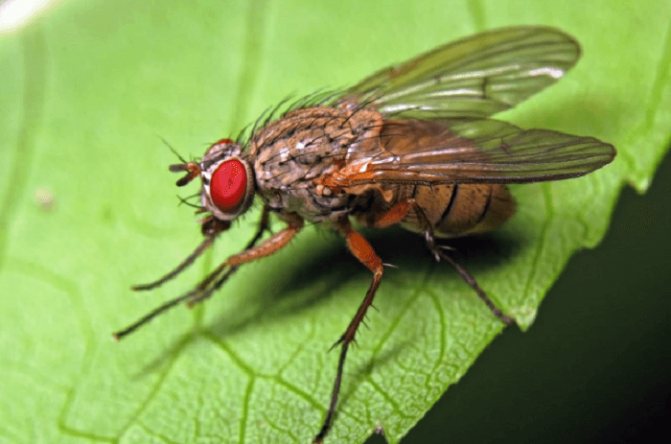
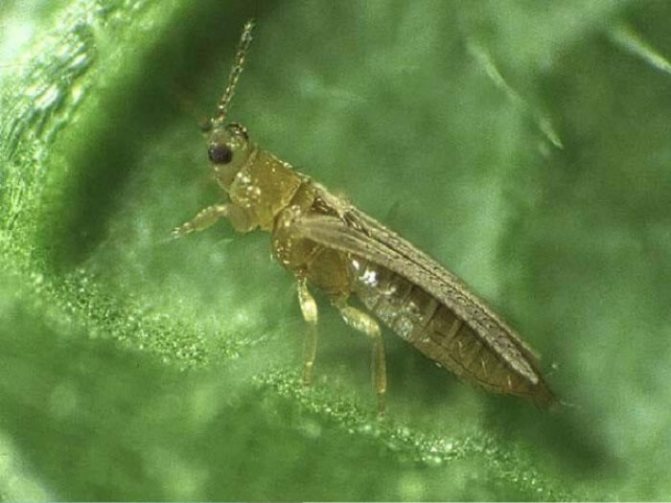
They also harm the plantings of onions and garlic bear, scoop, tobacco (onion) thrips.
How to fight
- During the probable period of pupation, frequent loosening of the soil to destroy the “houses” with pupae.
- Also during pupation, watering with fertilizers or deterrent solutions is desirable: garlic, red or black pepper, mustard.
- You can also treat with a mixture of ash and tobacco dust in a ratio of 2 to 1. To keep the mixture better, you can sprinkle the onion with water before processing.
- If damage to the leaves by larvae is found, maximum harvesting and destruction of them.
- Processing with Karbofos. A solution of 0.6% is consumed at the rate of 100 ml of solution per 1 square meter. If onions are grown for greens, then the use of insecticides is unacceptable.
Remember
- Start the fight with the stealthbug in time, otherwise, it will cause huge damage to the onion crop, it will become much more difficult to spread over the site and lime it.
- Take care of onions and observe prevention, so that it is not weakened, and pests do not visit your site: watch out for watering, fertilization and weeding, plant and harvest fruits correctly.
- Use folk remedies whenever possible. since they are not harmful to health, do not accumulate in the soil and are very cheap, and in terms of effectiveness they are not inferior to expensive purchased drugs.
- Observe safety measures when using chemicals, so as not to harm your health: use a respirator and gloves, do not eat or drink during work, and afterwards wash your hands and face thoroughly.