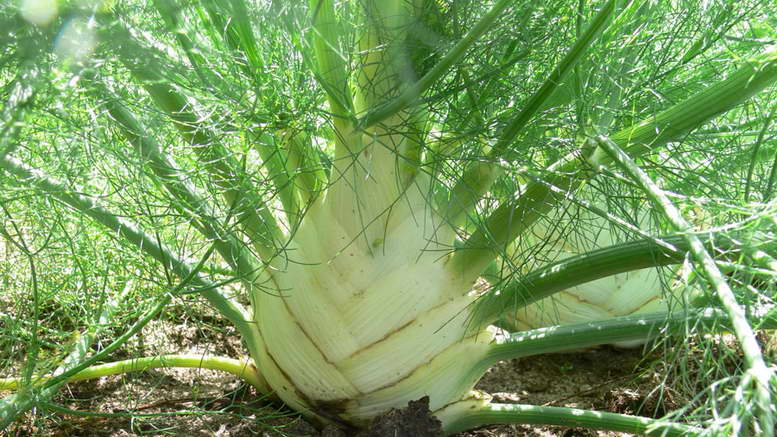
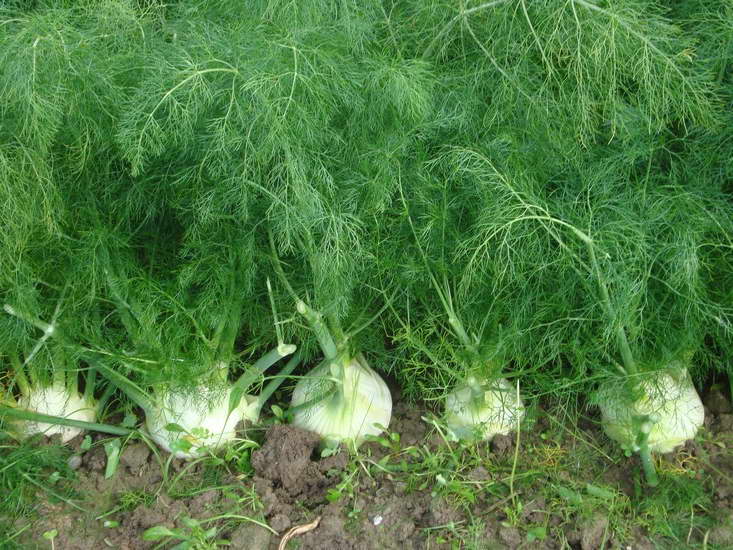
The word fennel, which is unusual for Russian gardeners, puzzles and raises concerns: is it possible to grow a spice in the country in the climatic conditions of our country. In fact, fennel - drugstore dill - is a relative of the usual fragrant dill.
The ancient Chinese, Egyptians, Greeks and Romans attributed miraculous beneficial properties to the plant. Leaves, stems, roots are used in cooking. Growing fennel and caring for spicy grass outdoors is similar to growing dill, but it also has its own peculiarities. In agriculture, two types have found application: ordinary or pharmaceutical and vegetable (Italian). In the latter, in addition to the green parts, a thickening in the lower part, reaching 10 cm in diameter, is used in cooking. How to grow fennel from seeds at home is described in the article.
Fennel plant - description
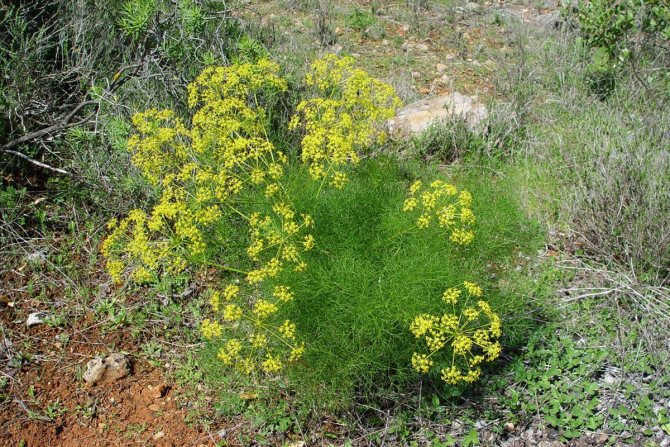
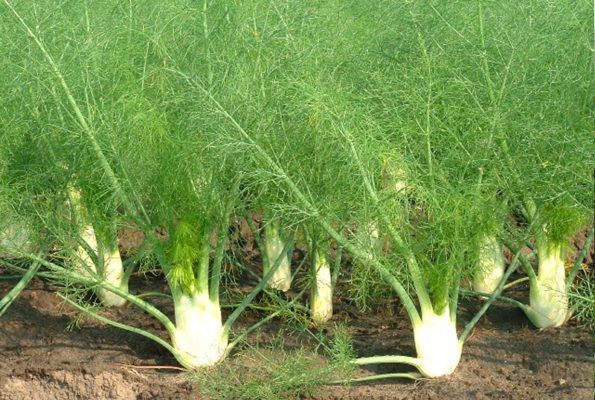
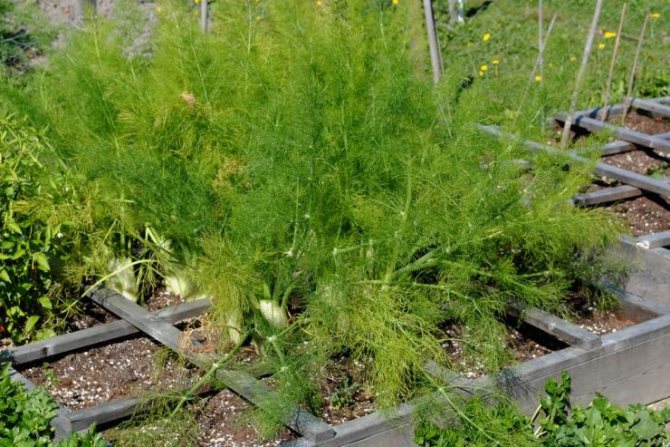
Fennel is a perennial thermophilic and photophilous culture, does not tolerate cold weather, and freezes in areas with severe winters. Therefore, in the non-chernozem zone, the plant is grown as an annual. Fennel has been known since ancient times as a spice and medicine on the table. In everyday life, he is familiar to many as pharmaceutical dill. The plant really has some similarities with dill, its only difference is its specific aniseed aroma. In addition, fennel is very useful and has a large complex of vitamins.
Fennel does not have such popularity among modern gardeners, because there is a lot of trouble with the cultivation of this crop, and the harvest is small. In addition, fennel is bad for carrots and tomatoes. Therefore, it is better not to plant fennel next to them. For the sake of sweetish and very fragrant seeds, it is practically not planted in gardens, since it is easier to buy a plant in a supermarket or pharmacy. However, thanks to glossy horticultural magazines, fennel has earned the title of a trendy vegetable crop for the ornamental garden.
Seed selection
Before you buy seeds, decide what you want to end up growing: greens, heads of cabbage or seeds. Depending on this, choose the right variety of this crop.
Fennel is:
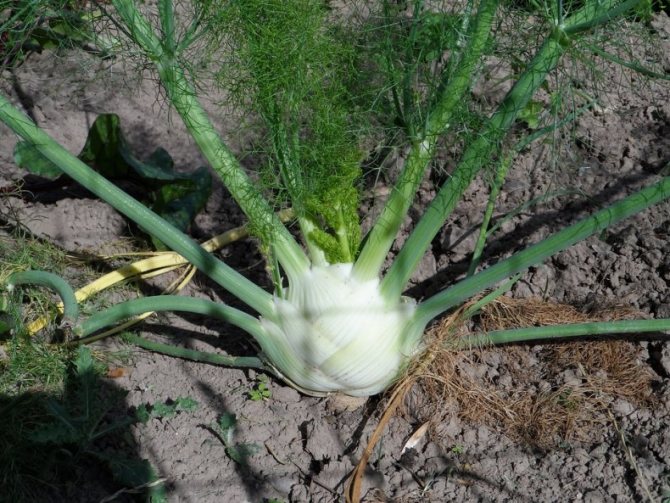
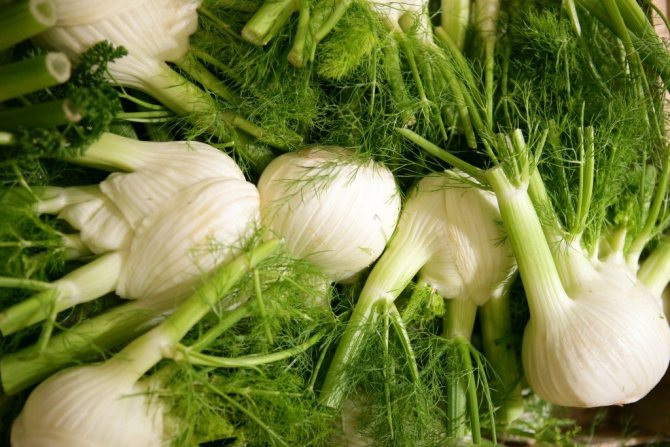
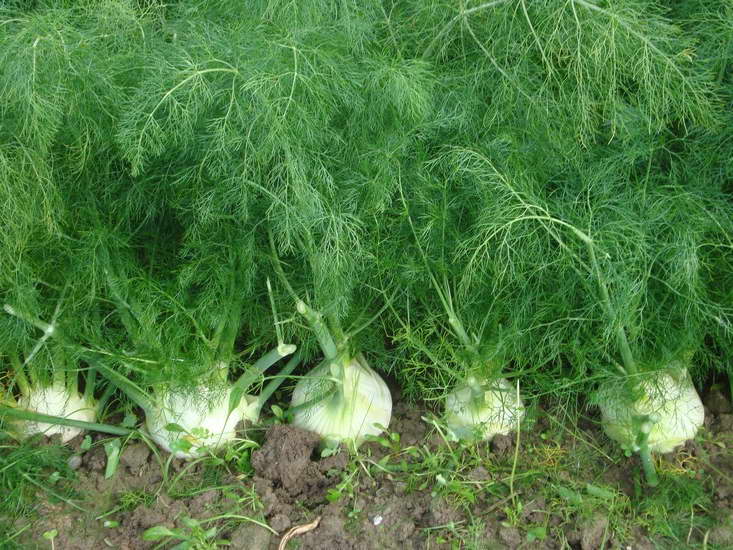
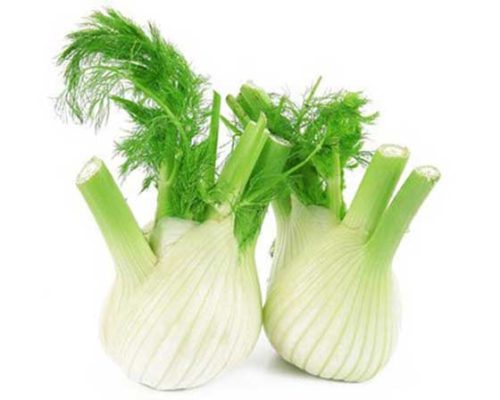
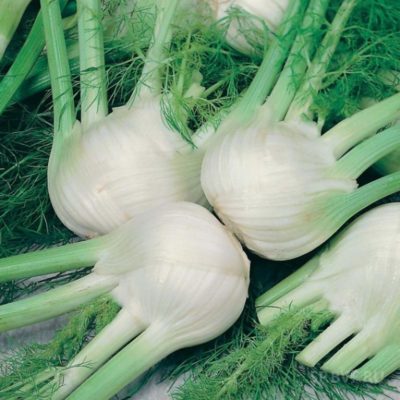
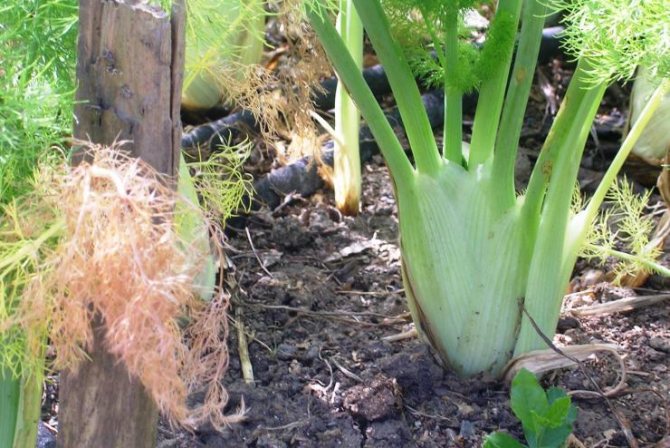
- vegetable (Italian, cabbage). He uses heads of cabbage for food. In appearance, such fennel resembles kohlrabi cabbage or an unusual radish that seems to grow above the ground. There are many varieties of vegetable fennel (Udalets, Luzhnikovsky Semko, Corvette, Soprano), and breeders are constantly working on new species. Such fennel is also called root, but this is wrong - the heads of cabbage are formed above the ground, and the root of such a plant is long and deep;
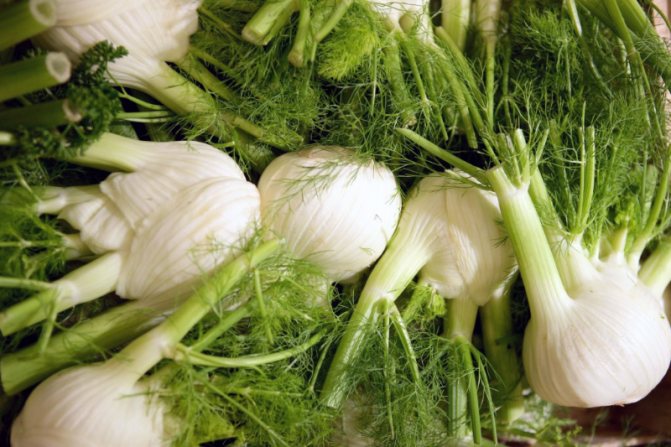

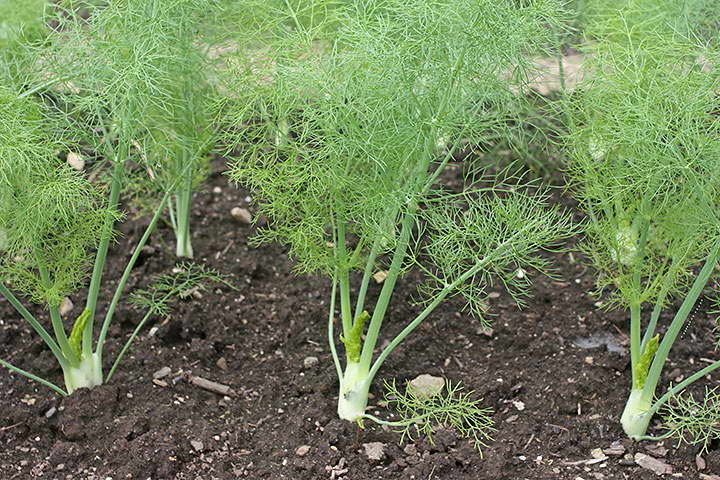
- ordinary (sheet). In appearance, it looks like the dill we are used to. It is what the people call it - pharmaceutical dill. It can grow up to 1.5 m! He, in turn, is divided into 2 large groups: varieties that are more suitable for growing greenery (such a plant has a lot of leafy green mass and a pronounced aroma, for example, the variety "Pepper", "Ogorodny") and varieties that are suitable for growing seeds (they have a higher content of essential oils, for example, "Crimean").


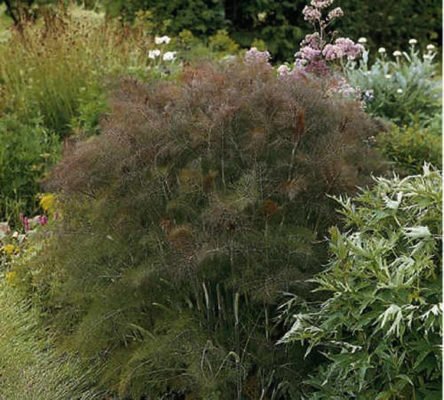
Advice! There are decorative fennel varieties. For example, "Giant Bronze". This plant has young twigs of a bright bronze color with an amazing purple hue.And the variety "Purpureum" will simply amaze you with its copper leaves, which will turn brown-bronze closer to autumn. The cultivation of such varieties is an interesting and exciting activity.
The culinary properties of fennel
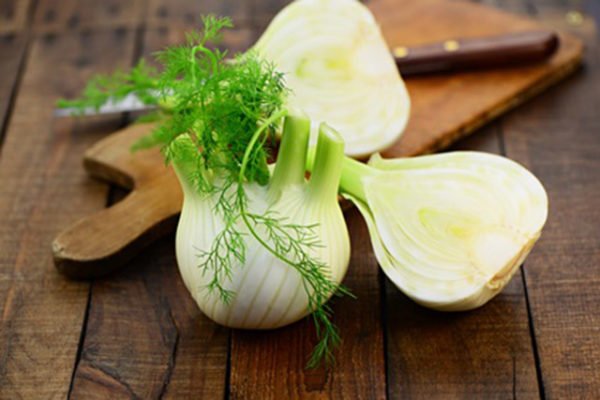
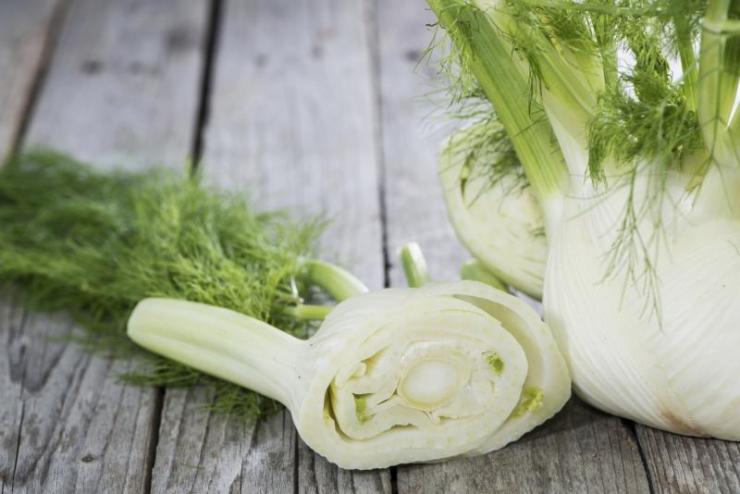
Because of its beneficial and aromatic properties, fennel is also quite well known to European culinary experts. Leaves, young shoots, large white heads of cabbage and fennel stalks are used in the kitchen. The leaves are used as dill, adding a little fresh herbs to food. Fennel heads are baked in the oven, stewed or fried. Sometimes they are eaten raw and added to salads. Petioles are perfect for pickling in jars for the winter. Fennel seeds can also be added to dishes to add flavor to soups, wine, puddings, and breads.
Why the plant is useful and how to use it
In terms of the content of vitamins and microelements, fennel is far ahead of the usual dill. Particularly noteworthy are vitamins of group B, A, C, calcium, magnesium, potassium, selenium, copper, chromium, iron.
All parts of fennel are widely used in traditional medicine. It is on its basis that the well-known dill water is prepared, which is used as a diuretic, antispasmodic and disinfectant. Its action is very mild, it is recommended even for infants with colic, bloating and intestinal cramps.
Fennel essential oil normalizes the condition of the gastrointestinal tract, helps to remove toxins and toxins from the body. It is also indicated in order to eliminate the effects of overeating and to improve appetite. In aromatherapy, it is used to relieve chronic stress, to get rid of unreasonable anxiety. This remedy also helps to normalize the state of the nervous system with frequent bouts of aggression and simply improves mood.
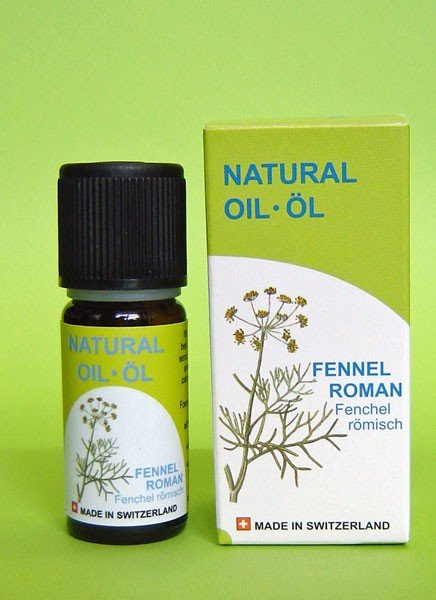


Fennel essential oil has a pronounced calming effect, has a beneficial effect on the nervous system
Fennel leaf tincture has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. It is used externally for the treatment of fungal diseases, wound healing, ulcers, dermatitis and other skin problems.
In dry form, fennel is part of many expectorant fees. They are prescribed for bronchitis, pneumonia, laryngitis, and other respiratory diseases.
A decoction of herbs is recommended for women who are breastfeeding. It has been scientifically proven to have a positive effect on lactation. And for pregnant women, this remedy helps to get rid of bouts of morning sickness and regain appetite. It is also useful for gum problems and bad breath.
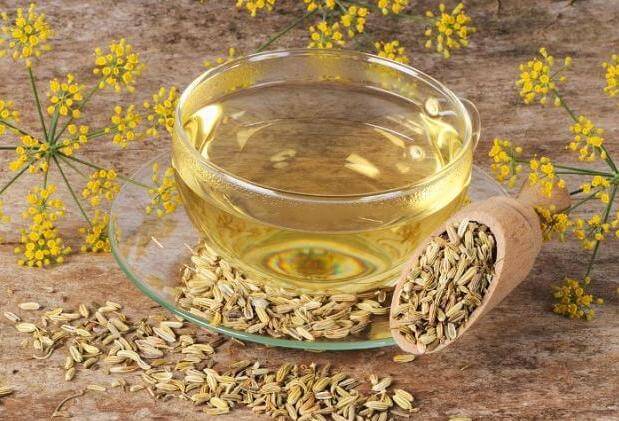


Decoction of fennel leaves is extremely beneficial for women during pregnancy and lactation.
Fennel leaves and seeds are widely used in cooking. It is practically an integral part of the Mediterranean cuisine. They are added to salads (even fruit), soups, meat and fish dishes. Fennel is also suitable for home canning. It can be included in recipes for pickled tomatoes, cucumbers, and sauerkraut. "Kochanchiki" are also eaten. They are boiled or baked whole, used as a side dish. The seeds are added to the filling of all kinds of confectionery and bread dough, they are used to flavor alcoholic beverages.
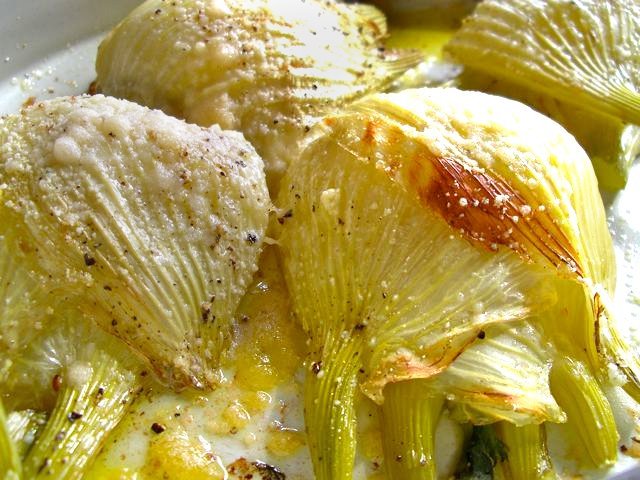


Fennel "heads" are widely used in Mediterranean cuisine
There are also contraindications. It is strictly forbidden to use fennel for epilepsy. And if you eat it immoderately, it is quite possible to earn an upset stomach and intestines. There is also an allergic reaction. Fennel should be used with caution for those who suffer from frequent bouts of diarrhea.
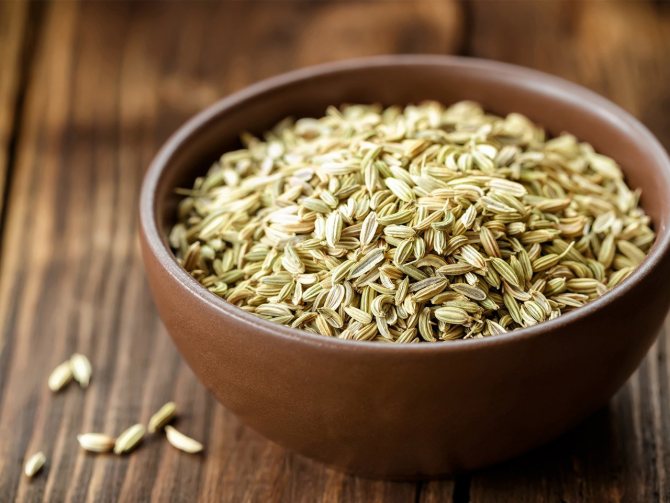


Fennel seeds are widely used in both traditional medicine and cooking.
Video: health benefits of fennel
Growing fennel from seeds
Preparing fennel for planting
One of the main features of growing a vegetable crop is the correct selection of the necessary seeds for planting.On the shelves of horticultural shops, you can find seeds of two varieties: ordinary fennel (also called pharmaceutical dill), and vegetable fennel (sometimes called Italian fennel). The first type of this culture is bred to obtain greens and seeds, and the second variety allows you to grow dense white heads of cabbage for use in food.
Fennel on the plot
Sowing fennel outdoors in spring
It is customary to plant fennel seeds of a vegetable variety in the ground in early spring to a depth of 2 cm. In southern regions with not harsh winters, summer residents can sow seeds before winter. Like all crops in the celery family, fennel seeds sprout slowly due to their high content of essential oils that block germination. Gardeners should soak fennel seeds in warm water 2-3 days before planting in the beds. Then cover the soaked seeds with burlap. After that, the fennel seeds must be dried and sown in the ground. The sowing bed must be prepared in advance. Fertilize the soil with humus (put one bucket of humus per 1 m² of the plot), then fill the ground with a two-liter jar of sawdust and add two tablespoons of superphosphate. If necessary, the soil is limed. During sowing in the spring (in the middle lane from April to May), the site is insulated with foam to preserve moisture. After 5-10 days after the shoots appear on the surface, it is necessary to thin out the beds. The distance between plants should be about 20 cm, as a head of fennel can grow up to 10 cm in diameter. After this procedure, the vegetable crop must be strengthened with dressings, since the ground part of the plant develops rather slowly. Mullein infusion can be a good fertilizer.
Growing fennel seedlings and planting seeds in the ground
Summer in most of Russia is rather short and unpredictable in terms of weather. And the growing season for some varieties of fennel (especially vegetable) is 4 months or even more. Therefore, in order for the crop to ripen, it is advisable to grow it with seedlings.
Seeds remain viable for three years. They are sown in such a way that the seedlings of root varieties are transferred to a permanent place in the first half of May, and vegetables - in the last decade of June. At an earlier planting, due to a lack of heat, the plants can stretch out, the "heads" will not form. Due to the high concentration of essential oils, fennel seeds take a long time to germinate. It will take about 20 days to wait for seedlings, this is normal for culture. In general, growing seedlings takes about 9-10 weeks.
Recent Entries
Rose Petal Jam and Its 7 Health Benefits You Likely Didn't Know About What Fruit Are You According to the Zodiac Sign 11 Best Grape Varieties That Will Help You Create Unique Homemade Wine


Fennel seeds germinate for a long time, the gardener will have to be patient
Seedlings are grown according to the following algorithm:
- The seeds are soaked for 4-6 hours in water at room temperature, a solution of any biostimulant or potassium permanganate (pale pink), wrapped in a damp cloth. To prevent the development of fungal diseases, you can then additionally etch them for 15–20 minutes in a solution of a fungicide of biological origin (Alirin-B, Ridomil-Gold, Baikal-EM). Then they are dried to a free-flowing state.
- Fennel does not tolerate transplanting very well, so it is advisable to immediately sow 3-4 seeds in peat pots, deepening them by 1.5-2 cm. They are filled with universal soil for seedlings or a mixture of humus with peat chips and sand (2: 2: 1 ). The substrate must be disinfected and watered abundantly. After planting, the seeds are watered again, cover the containers with film or glass. Until emergence, they are kept in a dark place at a temperature of 20-23 ° C.The "greenhouse" is ventilated daily for 5-10 minutes to prevent condensation from accumulating.
- Once the seeds have germinated, the fennel is transferred to the sill of a southeast or southwest facing window. Seedlings are protected from direct sunlight. She does not need additional lighting. Seedling care consists in regular watering, as soon as the topsoil dries out, gently loosening the soil. After two weeks, they can be fed with a solution of any complex fertilizer for seedlings.
- 7-10 days before planting, the seedlings are sprayed with a 1% solution of carbamide or other nitrogen-containing fertilizer (this has a positive effect on plant immunity) and begin to harden, taking them out into the open air and gradually extending the time spent outdoors.
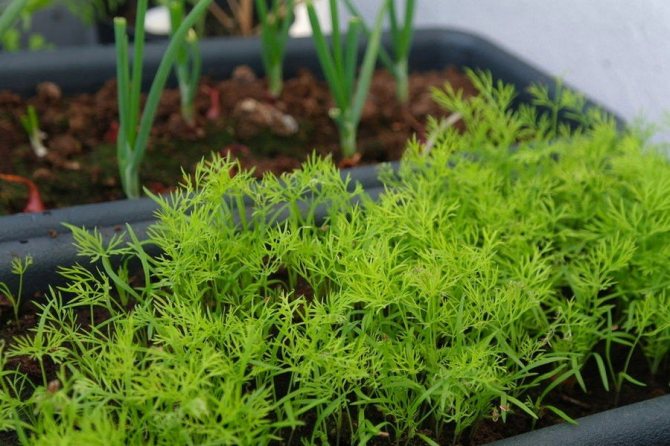


Fennel seedlings are planted in the ground only when it becomes warm enough outside.
Video: how to grow fennel seedlings
About a week before planting the seedlings, the soil in the garden should be well loosened and leveled. Simultaneously, simple superphosphate is introduced in the same dosage as in the fall. Phosphorus is especially necessary for vegetable varieties.
Fennel seedlings are ready for planting in the ground in 45-50 days. The interval between plants is about 40 cm, between rows - 50-60 cm. If the pots are peat, you do not need to remove them from the containers. Fennel is buried in the ground to the first cotyledon leaves. Then the planting needs to be watered abundantly. Until the seedlings take root and start growing, they are especially carefully protected from direct sunlight.
When planting seeds directly into the ground, they are sown as evenly as possible in the grooves with an interval of 50–60 cm between them. From above they are covered with peat chips or humus (layer 1.5–2 cm thick) and watered. Until the seeds germinate, the bed is covered with plastic wrap or black covering material. The best time for the procedure is the first half of May.
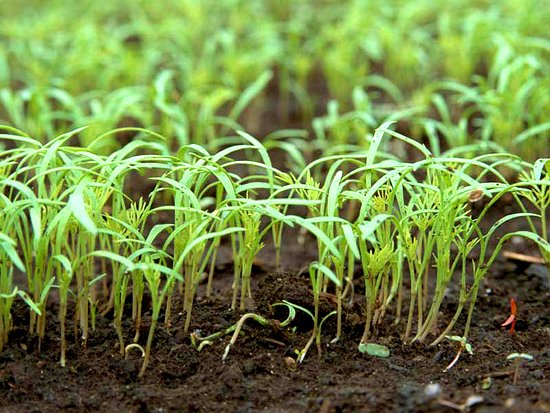


When thinning plantings, "extra" fennel seedlings are not pulled out, but cut at the root
7–10 days after the emergence of seedlings, they are thinned out, leaving 20–25 cm between neighboring plants if it is vegetable fennel and 10–15 cm if it is root. "Extra" seedlings are not pulled out, but cut with scissors.
In regions with a warm climate, where it is possible to grow fennel as a perennial, it is practiced to sow seeds in the fall, at the end of July or in August. In October, the planting will definitely need to be "insulated" by covering it with a layer of humus, peat, pine needles, sawdust at least 10 cm thick.
Fennel care in the garden
Hilling fennel
At the end of May, fennel crops must be slightly huddled. Some gardeners suggest spilling the plant several times. This will whiten the developing head of cabbage. However, as experience shows, frequent hilling leads to contamination of the white bases of the petioles. That is why, in order to avoid pollution, around the beginning of June, the lower part of the culture should be fenced. You need to take a two-liter plastic bottle and cut out two 20 cm wide rings. The ring is put on the plant, slightly pressing it into the soil. Spud the fennel, taking into account the height of the plastic ring. Another option for protection against contamination is a plastic strip. It is freely threaded around the plant and neatly attached.
Fertilizing fennel (fertilizing) and watering
During the ripening of the plant, fennel is strengthened several times with dressings. Fertilize with infusion of mullein or fermented grass, and in dry weather, regular watering is carried out. Throughout the summer, right up to flowering, greens can be harvested from fennel, and by autumn the heads of cabbage ripen from the plant. After the diameter of the petioles at the base of the root rosette reaches 8-10 cm, the heads are removed. With the onset of autumn, fennel can be completely dug up, lowered into the basement and buried in the sand. Thanks to this, the plant will remain fresh for a long time.
Vegetative propagation of fennel
Reproduction of fennel by dividing the root is rarely carried out, since the survival rate is low.You can divide adult bushes, and in the conditions of central Russia, fennel is cultivated as a one- or biennial plant.
It is very important that no root injury occurs during division. Dig out the bush carefully, divide it into several parts, each of which should have 2-3 growth buds.
Description of fennel
Fennel is a perennial crop and belongs to the umbrella family. It is often grown as an annual plant by gardeners. Most popular vegetable fennel, which is loved for tasty and healthy fruits - heads of cabbage.
Fennel has an erect stem about two meters high. It has a blue bloom and dense branching. The root system is quite massive and has a rod-like shape. Each plant has several root branches with a diameter of 1 to 1.5 cm.
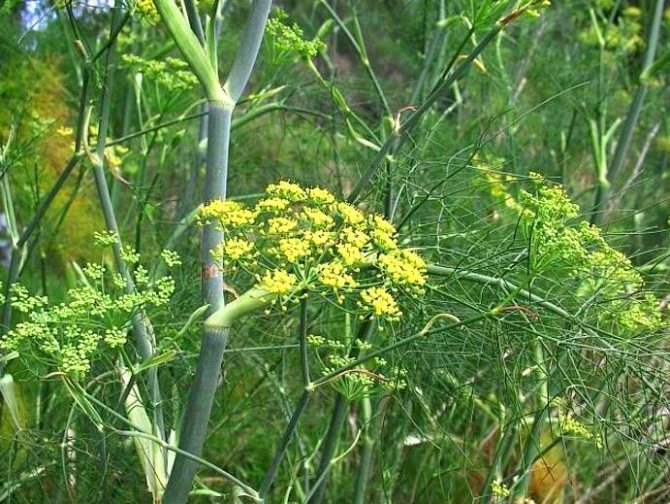
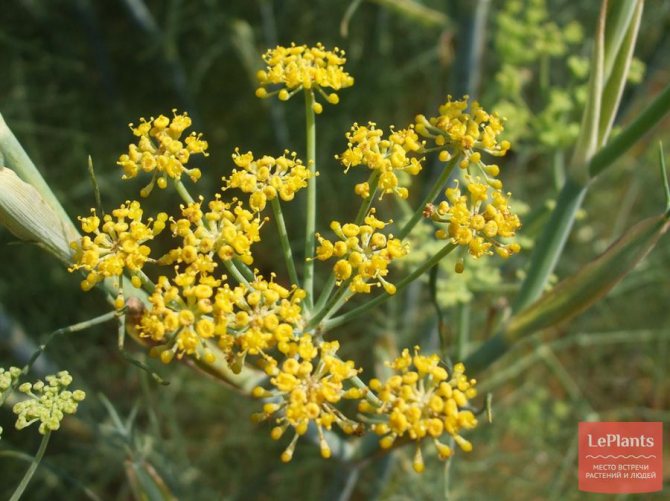
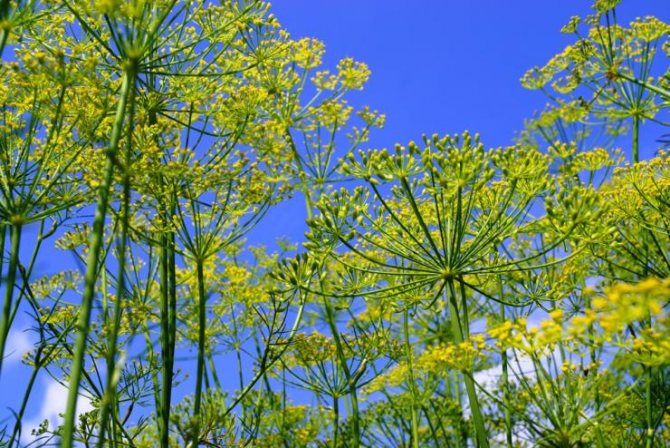
The shape of the leaves is the same as that of dill. Their color is saturated green. At home, growing fennel blooms throughout the season. It begins to bloom in a year, the field of planting seeds.
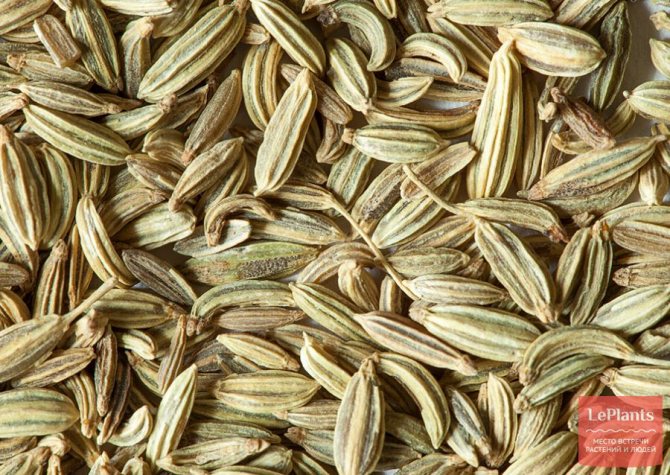
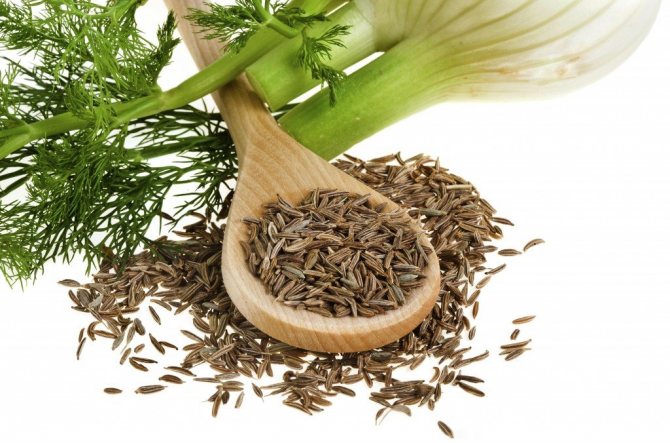
Fennel seeds are small, oblong, about 10 mm long and 3-4 mm wide. They taste sweetish. The mass of 1 thousand grains is about 6-7 g. Seeds ripen in autumn.
Description of common varieties
There are not so many varieties and hybrids of fennel. Most of them are vegetable varieties. But there are also decorative varieties that are widely used in landscape design. They are distinguished by an unusual shade of leaves.
Fennel varieties grown by gardeners:
- Aroma. The variety is of medium ripening, the greens can be cut 75–85 days after planting. Productivity - 2-3 kg of green mass from a bush.
- Luzhnikovsky Semko. A fairly compact plant, not exceeding 0.5–0.6 m in height. "Heads of cabbage" are snow-white, rather dense, with small voids. Average weight - up to 200-220 g.
- Utter. A medium-ripening variety, one of the smallest (up to 0.5 m high). “Heads of cabbage” weighing 100–120 g. They are formed even in conditions of long daylight hours.
- Corvette. One of the novelties of breeding. The variety is late, it takes 120-125 days for the “heads” to ripen. They are painted in white-green color, reaching a weight of 250-380 g. The height of the plant is about 60 cm, but from it you can get 1-1.2 kg of green mass. Productivity of "heads" - up to 2.7 kg / m².
- Soprano. Medium late variety (vegetation period - 110–115 days), "heads" are white or greenish, very aromatic, dense. The height of the bush is about 1.5-1.8 m, the plant is powerful, intensively branching. The average weight of an elongated "head" is 100 g. The yield from 1 m² is about 3-4 kg of greens and up to 2.4 kg of "heads".
- Leader. Ultra-early variety, technical ripening occurs 1.5 months after planting. The bush is powerful, about 170-180 cm high, densely leafy. The leaves are large. Leaves are removed for greenery before flowering begins.
- Autumn handsome. Another early ripening variety, ready for cutting in 38–40 days. The bush is fast-growing, about 150-180 cm high. The greenery is very delicate, with a light aroma.
- Rudy F1. The plant is hybrid, it will not work to collect viable seeds, even if it is cultivated as a perennial. "Heads of cabbage" are large (up to 300 g), pale salad color, almost regular spherical shape.
- Giant Bronze. Freshly blossomed leaves are cast in copper. Gradually change color to greenish brown.
- Purpureum. Young leaves are bright purple with a bronze tint. Over time, it changes to gray-silver.
Photo gallery: popular fennel varieties among gardeners


Fennel Aroma - a common variety of medium ripening The compactness of the Luzhnikovsky Semko fennel bush does not affect the yield in any way


Fennel Udalets forms "heads of cabbage" even under conditions of longer daylight hours than is usual for the culture


Fennel Corvette - one of the latest achievements of breeders


Fennel Soprano stands out for its unusual shape of "heads"


Harvest Green Fennel Leader must be cut before flowering


Fennel Autumn handsome - one of the earliest varieties Fennel Rudy F1 is distinguished by a very presentable type of "heads"


Fennel Giant Bronze not only brings crops, but also beautifies the site


Purpureum fennel looks very impressive and is widely used in landscaping
Choosing a site for growing fennel
Fennel in cultivation and care requires a special approach. When choosing a planting site for fennel, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of neighboring crops, since it has an adverse effect on some of them.
Fennel precursors
Fennel is best grown on soils where the predecessors were crops that required organic fertilization. And these are potatoes, cabbage, cucumbers and peas.
Lighting requirements
Fennel is quite demanding in terms of lighting, so for planting it it is necessary to choose open areas
which are exposed to sunlight throughout the day. Also note that the plant should not have tall neighbors (corn) that can create shade for it during development.
Soil for planting
It is best to plant fennel in fertile, moderately moist soil. It's good if the soil is limestone, sandy loam or loamy
... It is necessary to cultivate the soil thoroughly, by arable method and at the same time adding organic fertilizers.
In order for fennel to winter calmly, it must be insulated with peat, manure, sawdust and humus.
Before warming, all the greens from the bushes must be cut off.
Conditions for growing a crop
Fennel is deservedly considered a fairly demanding crop for growing conditions. In Russia, where the climate is radically different from the Mediterranean climate he is accustomed to, his “wishes” should definitely be heeded if there is a desire to harvest.
The fennel bed must be located in a place well warmed by the sun. In the shade and partial shade, "heads" are practically not formed, the greens coarse, the aroma becomes weak. Fennel loves heat, but does not tolerate extreme heat and drought very well. Therefore, it is advisable to build a canopy over the garden bed from any white covering material that protects the planting from direct sunlight. Paradoxically, the plant does not need a long day of light.
At the edges, it is advisable to limit the bed with slate sheets dug to a depth of 20-25 cm - with a moisture deficit, fennel forms long roots, which can easily reach neighboring beds and deprive the crops grown there of water.
Good neighbors for fennel are cucumbers and cabbage. All these plants need abundant watering. In addition, with its aroma, fennel repels many pests, which cucumbers and cabbage do not lack, and attracts pollinating insects. But the spinach, caraway seeds, beans, bell peppers located nearby affect the culture negatively, inhibiting its growth and development. Any tall plants (such as corn) create unwanted shade.
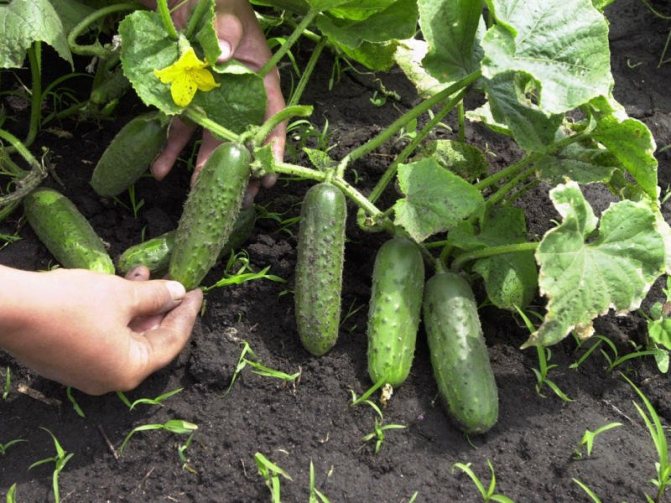


Cucumbers get along well with fennel - both crops need abundant watering
It is best to plant fennel where vegetables were previously grown that require large doses of organic fertilizers (potatoes, cabbage, cucumbers). If a new bed is being prepared, in the fall it is thoroughly dug up, cleared of plant debris, humus or rotted compost (8–10 kg per linear meter) is introduced. Fresh manure is categorically excluded. Of the mineral fertilizers, only phosphorus and potash fertilizers are needed (10–15 g per running meter). Then the bed is covered with a film and left until spring.


Humus introduced into the garden has a positive effect on the fertility of the substrate
Light sandy soil, as well as heavy clay soil, is not suitable for a plant. The best option is black soil, gray soil or loam with a slightly alkaline reaction.To neutralize acidic soil, slaked lime, dolomite flour, crushed chalk, sifted wood ash are introduced.
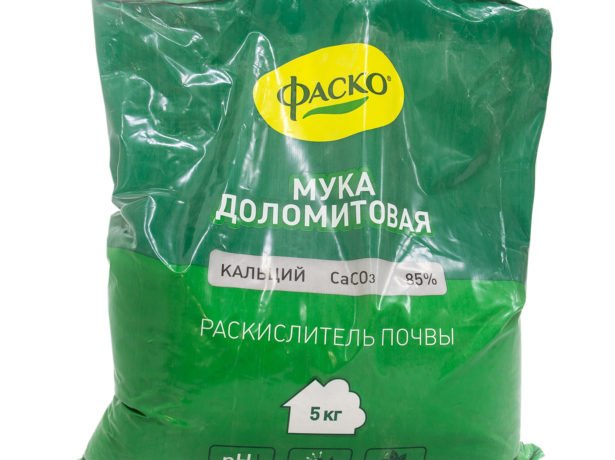


Dolomite flour is a natural soil deoxidizer, if you follow the dosage, there will be no side effects
The substrate in which the fennel is planted must be well moisturized. In this regard, lowlands are suitable, where melt water stays for a long time. But there is often not enough sun. Therefore, about a week before the procedure, you need to carry out moisture-charging watering.
The optimum temperature for germination of fennel seeds is at least 20 ° C. They will not die even at 10 ° C, but in this case, you will have to wait for seedlings at least a month. It is important to follow the planting pattern and provide the plants with sufficient watering. Otherwise, vegetable fennel is likely to go to the "arrow".
Fennel can be planted in the same place for 3-4 years. Then the soil becomes impoverished, this negatively affects the yield.
How to plant fennel: plant propagation
Before planting fennel, preparatory work is carried out, in particular, it is necessary to fertilize the area on which the plant will be planted. One square meter will need a bucket of compost, manure or peat, as well as several cans of sawdust.
Growing fennel from seeds
Fennel seeds can be stored for three years without losing their properties. To achieve their maximum germination, it is necessary to sprinkle the grains on the fabric, then wrap it up and lower it into any container filled with a growth stimulator (it is possible in a weak manganese solution).
Make sure that the cloth with the grains is completely submerged in the solution. This water treatment should last 4 hours. Fennel seeds can be sown either directly in open ground or for seedlings:
- Sowing fennel outdoors. In the question of how to plant fennel seeds in open ground, it is very important to guess the date. The plant should be planted in the garden in the month of April. However, some gardeners plant seeds in the fall, in the first decade of September.


Fennel, sown at the beginning of spring, does not require additional maintenance, while during autumn sowing, additional insulation is required. Regardless of the season, planting fennel seeds is carried out by burying them 2-3 cm into the soil.
The site must be prepared in advance. It is worth calcifying the soil and adding humus to it (one bucket per square meter), sawdust (2 liters per square meter). You can also add a small amount of mineral supplements.
Sowing seeds in spring, cover the beds with foil before sowing. This is done in order not to lose moisture. The distance between the rows should be 50-60 cm. The seeds germinate on the sixth day (they need a minimum temperature of +6. +8 ° С for this). Thinning must be carried out seven days after sowing.
Remember that the distance between shoots should be 20-25 cm.
Growing fennel seedlings. In areas where summers are short, seedlings are considered the best way to grow fennel. When to plant fennel seedlings?
Seeds must be sown in boxes in February or March. After the first shoots have appeared, the plant must be dived into separate pots. Or thin out in such a way that there is a distance of 20 cm between the shoots.
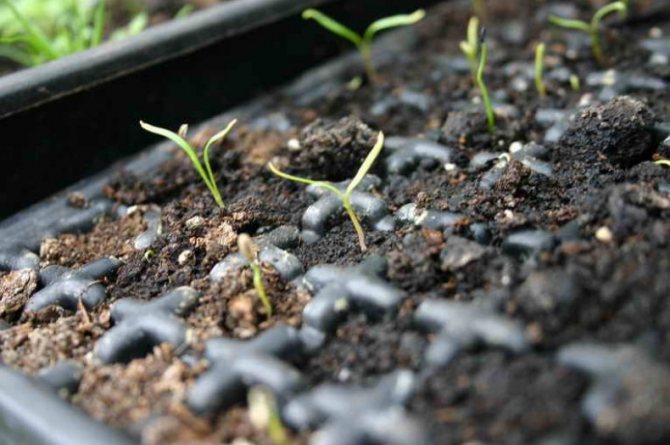


One month after the emergence of seedlings, the seedlings can be transplanted to a permanent place. Sowing fennel for seedlings should be done in such a way that the distance between the bushes is 40 cm.
Planting fennel seedlings is most suitable for growing its vegetable varieties. It often happens that plants cannot fully form heads of cabbage when sowing with seeds (they are hampered by long daylight hours).
Division of roots
Reproduction of fennel by dividing the roots is not very common among gardeners. This method is used extremely rarely due to its great complexity and worse survival rate. It is very important that the roots are not damaged when cutting the bush, as the plant will not be accepted and will disappear.
Where to plant and next to what
Since fennel is our Mediterranean guest, he loves the right climate.
Warmth and light
This culture is thermophilic. She is very fond of regions with long warm summers. However, he also does not tolerate heat and dryness, especially vegetable varieties. Therefore, for planting such varieties, choose partial shade, a sunny place is more suitable for an ordinary one.
The soil
The plant likes fertile light loams. It does not tolerate too light and acidic soils. If the soil is poor, be sure to add humus (10 kg per 1 m²), sawdust (2 liters per 1 m²) and phosphorus fertilizer (2 tablespoons per 1 m²).
Neighbors
Fennel is just a king, he does not tolerate any neighborhood. And what is even worse - it oppresses almost any vegetable, releasing its long roots and taking moisture from its neighbors. Fennel has a bad effect on tomatoes and carrots. Plant it away from cilantro, cumin, pepper, dill - these plants tend to be cross-pollinated, which reduces seed production and affects flavor.
Perhaps this is the only such capricious garden culture. Therefore, give him a completely separate area and plant it separately. However, fennel has two friends Are white cabbage and cucumbers. These vegetables can be sown together. Partly also because of such a quarrelsome nature, gardeners are afraid to grow this plant.
I have an idea! If you don't have a lot of space in your garden, plant the fennel in your flower garden. There he surely won’t offend anyone! The delicate leaves of this plant will look very impressive. And bright yellow inflorescences will adorn any flower bed!
Outdoor Fennel Care Basics
Fennel is not demanding when it comes to planting and nursing outdoors. It is necessary to maintain cleanliness in the garden, weeding weeds. Only you should not pull them out, but it is better to cut them off, since many representatives of weeds improve the structure of the soil and protect it from drying out.
How to properly water the plant
Fennel is very picky about water. It needs to be watered every five days. (per square meter - 10-15 liters of water
). If this is not done, then its long roots begin to take moisture from neighboring crops. This can destroy your entire crop. Watering fennel is also necessary in dry autumn.
How to fertilize fennel
You need to feed your pet immediately after the first thinning. As a top dressing, an infusion of mullein is ideal. It can be used in two ways:
- for application to the soil: it is necessary to dilute a bucket of manure with a third of the bucket of water;
- and for watering: you will need a mullein solution used for application to the soil (in a ratio of 1 x 10).
You need to feed the plant twice a season. You can also substitute chicken droppings for mullein, which can be fertilized more than twice. To do this, you need to dilute the litter in a ratio of 1 x 50.
Hilling a fennel bush
Hilling is carried out 2-3 times per season. You need to spud the plants 3-7 cm in height. This procedure is done to produce fleshy and bleached fennel heads.


Pest control. Traditional methods
Who is eating? I must say, this fragrant plant is loved by harmful insects. They are not averse to feasting on May beetles, scoops, various butterfly caterpillars. This is the favorite dish of aphids and umbrella bugs. Do not mind snacking on juicy twigs of carrot and caraway flies, as well as firewood.
Since greens are constantly eaten, it is best to fight this scourge with folk methods. There are a lot of them. They are safe to grow and care for outdoors. These products need to be sprayed with fennel several times per season.
- Potatoes... Tops are used for pest control. Take preferably green. 1 kg of harvested greens, you need to pour 10 liters of hot water and leave for about 4 hours.
- Nettle... You will need a bucket of fresh nettles.It needs to be crushed and filled with 1 bucket of hot water. Let stand for a day.
- Onion. Both feathers and husks can be used. Take 200 g of raw materials, fill it with a bucket of water. Pour in grated laundry soap (2 tablespoons) and leave for at least 5 days.
- Dandelion. Leaves, stems, roots, and flowers can be used. Take 400 g of chopped plant matter and fill it with a bucket of warm water. Let it brew for 2-3 hours.
- Chamomile... This plant also helps fight pests. Take a plant (with flowers and roots). You will need at least 1 kg. Pour raw materials with a bucket of hot water and let stand for 12 hours. When using, the infusion must be diluted 1: 3.
- Garlic. Twist 200 g of garlic (together with herbs). Pour 10 liters of warm water. Insist during the day.
- Wood ash. You will need 3 kg of ash and 1 bucket of water. Ashes need to be poured with water, let it brew for about 2 days.
- Dry mustard... Take 100 g of mustard and pour 10 liters of hot water over it. Wait 1-2 days and use.
Advice! All infusions are best prepared on the day of use, in which case they will be more effective.
Fennel is a very interesting and unusual plant, which is not yet very common in our country. However, its culinary qualities are amazing: tender heads of cabbage with a sweetish taste of anise are eaten like a vegetable - they prepare salads, put in the first and second courses. It can be fried separately or baked under cheese, combined with any meat, added to soup. The stalks and umbrellas are placed in the blanks for an absolutely gorgeous aroma!
Try fennel with trout or mussels. Mmm ... lick your fingers. Fennel with nuts and fruits is incomparable, and if you put it in a dessert or jam, an unusual spicy note is simply provided for you. Try and grow this amazing plant.
IMPORTANT! * when copying article materials, be sure to indicate an active link to the source:
If you liked the article - like it and leave your comment below. Your opinion is important to us!
Fennel: when and how to harvest?
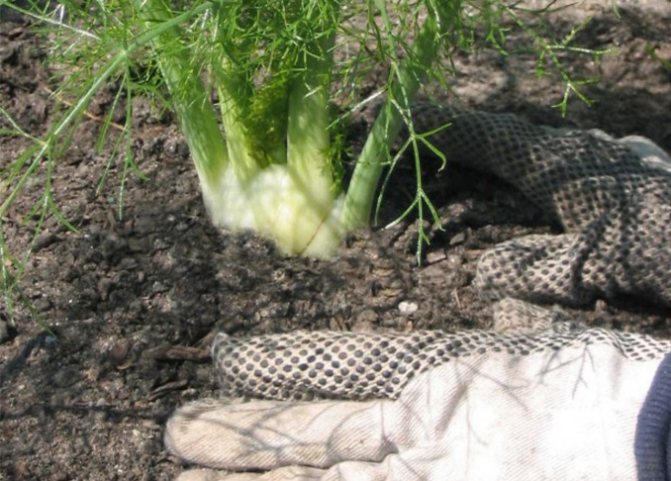
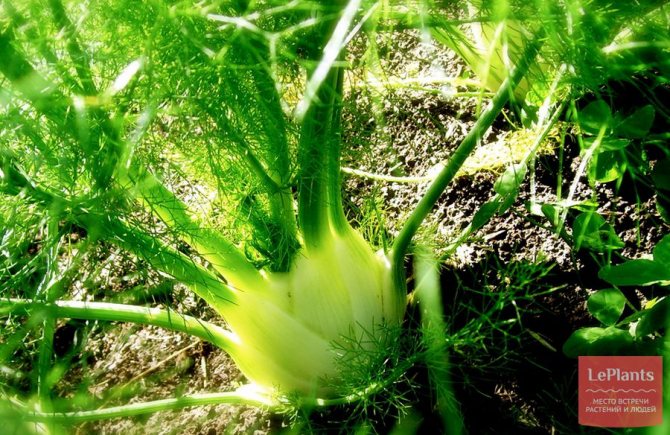
Heads of vegetable fennel are cut almost near the surface of the ground (they begin to be harvested at a diameter of 8-10 cm). If you cut the head of cabbage 3 cm above its base, fresh young leaves will begin to grow in that place.
You need to store the heads of cabbage in a cool place buried in the sand. Just before digging in, you need to remove all the leaves, and leave only one petiole of 10 cm. You can store the heads of cabbage in the refrigerator, but they will not lie there for more than a week.
When growing ordinary fennel, its green part can be cut off when the plant reaches a height of 25-30 cm. With this growth, fennel greens have the brightest aroma. The best time for harvesting greenery is late evening or early morning, during dew.


Fennel varieties with photos and names
Vegetable fennel varieties are distinguished by their productivity, ripening speed, and a high degree of leafiness. The varieties bred to produce greens have a rich leaf mass and a rich aroma. The development of seed varieties was aimed at a high concentration of essential oils in the seeds - which the breeders have successfully achieved.
Fennel Luzhnikovsky Semko
Luzhnikovsky Semko - vegetable fennel with large-fruited heads of cabbage. Ripening periods are average, 55-60 days. From 1 m² of plantings, you can collect from 1 kg of fruits.
Pepper is a variety grown to produce spicy herbs that are used fresh or dried. The roots are not edible. Umbrella inflorescences can be used for salting.


Fennel Udalets photo and description
Udalts is a vegetable variety preferred by most gardeners. The technical maturity of the heads of cabbage occurs after 47-50 days. Fruits are formed steadily, the yield is 1.5 kg per 1 m².
Crimean - grown on an industrial scale. Bred specifically for obtaining seeds for oil. The greens are tough and have a faint aroma.Growing on a personal plot is not advisable.
Fennel Rudy F1 Photos
Rudi F1 - gives a rich harvest of heads of cabbage (about 3 kg per 1 m²). The ripening period is 60 days.
Garden - a variety for greens. It is juicy, has a mild aroma, and is excellent both for fresh consumption and for preservation.
How do I get fennel seeds for planting?
To get fennel seeds, you need to wait two years for it to bloom. The culture will tell you when the seeds will ripen - at this time the inflorescence will change in color. It turns from greenish to yellow-brown. Then you need to carefully cut the umbrellas and hang them to dry, after which you need to shake off the seeds and place them in separate paper bags.
To grow fennel, seeds can also be purchased at the store. However, they should be chosen correctly. Most often, stores offer two varieties of seeds. The first is regular fennel, which is used to grow herbs and seeds. The second is vegetable fennel, with the help of which delicious heads of cabbage are grown.
Growing fennel outdoors is straightforward. It is only important to follow all the basic rules, fertilize and moisturize the soil, and then your efforts will not be long in coming, and the pleasant aroma of fennel will spread throughout your garden.
What do they eat: tops or roots?
Fennel is edible almost entirely: roots (heads) are consumed fresh or after heat treatment, shoots are added to various dishes, herbs and seeds are a spice, essential oils are used in baking, as well as in the medical and alcoholic industries.
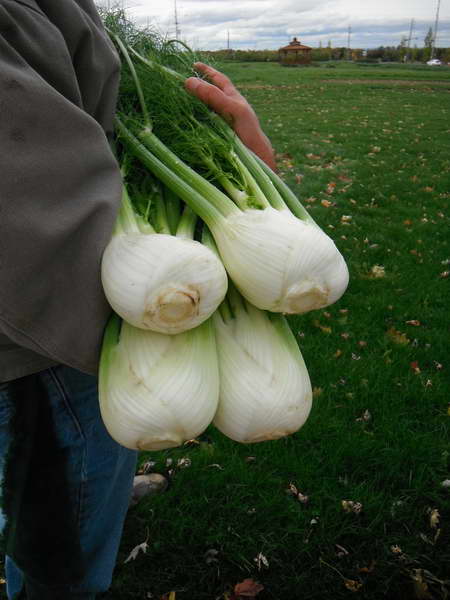


Fennel root growing from seed crop photo
Indeed, the appearance of fennel (its leaves) is similar to dill, but has a completely different aroma. Fennel root is fusiform, wrinkled, fleshy, consists of several branches with a diameter of 1-1.5 cm, branchy at the top. The top of the rhizome protrudes above the soil surface. The erect stem is between 90 cm and 2 meters in height. The leaf plates are three times, four times pinnately dissected, the upper ones are sessile, the lower ones are attached on long petioles. The color of the ground part is rich green with a bluish tint, the rhizome is snow-white.
Flowering occurs in the second year of growth. Fennel seeds are oblong, small (about 1 cm long, 3-4 mm wide), sweetish in taste. Very light: 1000 grains weigh only 6-7 g.
This vegetable crop is not very popular, but gardeners are increasingly interested in how to plant and grow fennel on the site. The process has its own characteristics and nuances, which you will learn in detail in this article.
Description of the appearance of the culture
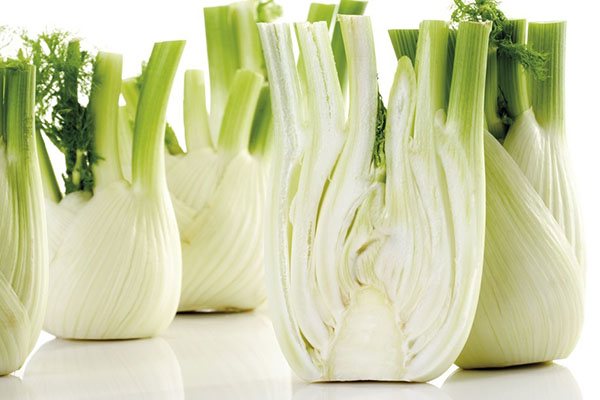


Fennel belongs to the umbrella plants, being a perennial, but more often it is cultivated as an annual. Its most popular variety is vegetable fennel; it is highly valued by culinary experts for its healthy fruits with a bright taste.
The plant reaches 2 m, has a strong erect stem, which is covered with a light bluish bloom, dense branches. The root is pivotal, strong, massive. One plant has several branches from the root. They reach 1.5 cm in diameter.
The main varieties and types of fennel:
Fennel leaves one to one resemble dill. Their color is rich green. After sowing the seeds, fennel blooms only the next year, flowering continues throughout the season. The seeds have a sweetish taste, they ripen in the fall. In length, the grains reach 1 cm, in width no more than 4 mm. Moreover, they are very light: a thousand pieces weigh only 6 grams.
Choosing a landing site
The homeland of the spice is the Mediterranean, similar conditions are created during cultivation, that is, fennel should be planted in a sunny place, protected from strong winds, because shading conditions reduce the amount of accumulated essential oils, and strong winds can break hollow stems.Fennel grows poorly in wetlands and areas with a close occurrence of groundwater - high beds are made here.
Fennel can be planted near cucumbers and cabbages. Plants have a similar watering regime, and the smell of spice scares away vegetable pests.
How to grow fennel in the country: selection of beds
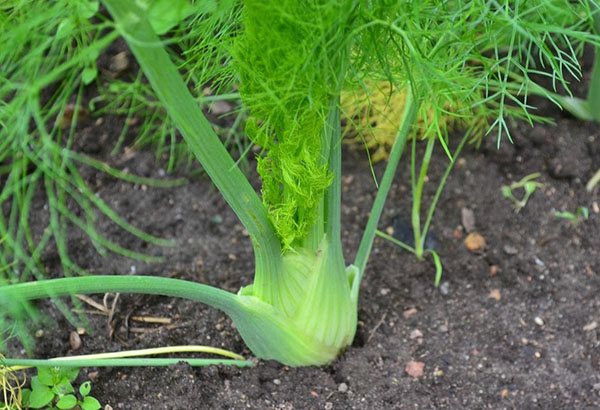


The choice of a place for planting this culture should be taken responsibly, be sure to take into account the neighborhood with other garden plants.
Fennel does not always have a positive effect on plants that grow nearby.
Fennel precursors
The optimal place for planting fennel is in the beds where crops that are demanding on the introduction of organic matter were grown.
The best precursors for the herb:
Lighting requirements
Fennel needs a lot of light, so you will have to choose an area for it that is warmed by the sun throughout the day. Shade from trees or buildings can negatively affect its development.
Land for planting
The soil for planting this culture should be selected sufficiently nutritious, fertile. Loamy, sandy loam or calcareous varieties of soil are preferable. The site is plowed, adding organic components. In order for the plant to calmly endure wintering, it is required to cut off the entire above-ground green stem, and then insulate it, sprinkling it with peat mixed with manure or humus with sawdust.
Fennel wintering
Fennel is capable of wintering successfully in open ground only in the southern regions. In the conditions of central Russia, fennel is cultivated as an annual, you can try to preserve the planting by building a good shelter. As a reward, you will receive excellent fruits, you can collect fennel seeds yourself (flowering occurs in the second year of growth). Before insulation, cut off the above-ground part, mulch the plantings with manure, peat, humus or sawdust, cover with spruce branches on top. When it snows, add additional snow to the landings.
Vegetable fennel: growing it from seed
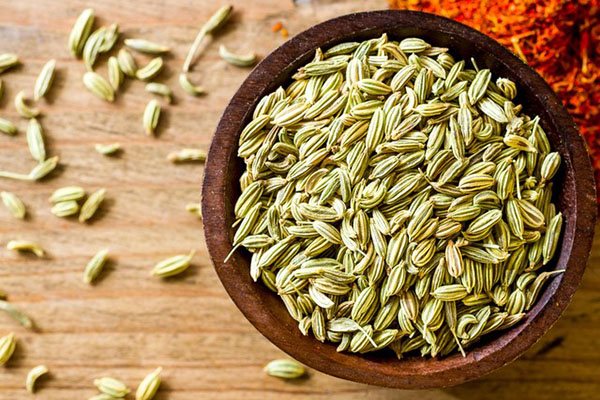


Fennel seeds do not deteriorate and do not lose their germination when stored for 3 years. In order for them to germinate faster, it is necessary to properly prepare them. Seeds should be placed on a small piece of fabric, wrapped and dipped in a growth stimulant solution so that the fabric is well wet. In this state, fennel seeds are kept for about 4 hours.
Sowing in open ground


Gardeners sow seeds in different ways. Some plant fennel seeds in the spring. The main advantage of this period of planting in the beds (in April) is that the plant does not require any additional care. Some summer residents prefer to plant crops in the fall - at the very beginning of September. With this approach, the bush needs to be insulated for the winter.
When sowing at any time of the year, fennel seeds are immersed in the soil only 2 or 3 cm. The bed is prepared in advance. Lime is added to the soil, as well as a bucket of humus. This amount will be required for each square meter of the site. Also add 2 buckets of sawdust and mineral compounds to the soil.
Gaps of 0.6 m are left between the rows. At a temperature of about +7 0 C, after a week, fennel seeds sprout. At this time, they are thinned out. There must be a distance of at least 20 cm between the specimens.
Sowing seeds for seedlings
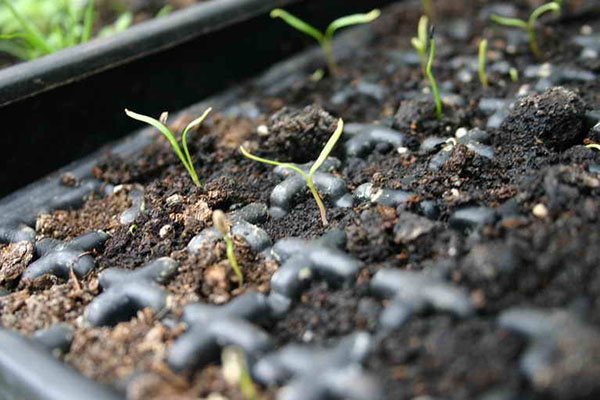


To obtain seedlings, sowing seeds is carried out in boxes filled with nutritious soil. The procedure is carried out from February to March. When the first shoots break out of the ground, the seedlings are transplanted and dived into individual containers. You can continue growing in boxes, but keeping a distance of 20 cm between specimens. After 4 weeks, the plants can be planted in open beds.
With the help of seedlings, it is preferable to grow vegetable varieties of a spicy crop.
Growing seedlings
Fennel can be grown via seedlings. It is advisable to do this in March-April. First, prepare the boxes.Fertile soil must be poured into them. Now sow the seeds, water and cover with plastic wrap. Keep the ground always moist.


As soon as shoots appear, remove the film. After about a week, you can carefully thin out the sprouts. And 7-8 days after thinning, the seedlings can already be transplanted into separate pots. It is better to choose peat-humus - in this case, when planting in the ground, the sprouts will take root faster and will not hurt. If you have a deep box, you can simply thin out the seedlings, leaving at least 20 cm between the plants, and fill up the earth.
As soon as the plants are a month or a half and the threat of frost has passed, the seedlings are planted in open ground. Transplant early in the morning or late in the evening so that there is no heat. The distance between seedlings should be at least 40 cm - only in this case you will get large heads of cabbage.
I have an idea! You can sow 1-2 seeds in peat tablets. And then just gently place the tablet with the plant in a large pot and sprinkle with earth. The seedlings will not hurt at all and will grow very strong!
How to properly care for fennel in open beds
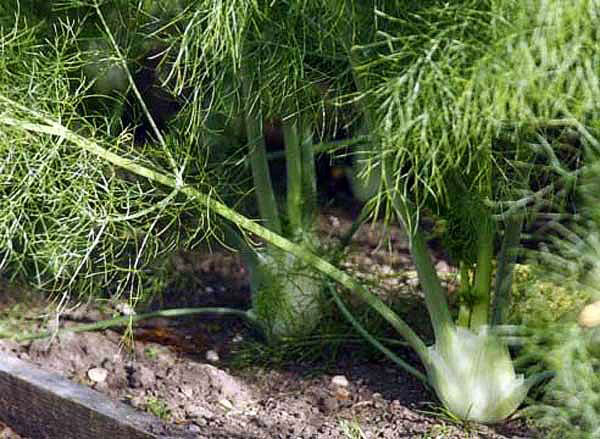


Cultivating a spicy plant in your garden is not particularly difficult. The main thing is to remove weeds in time by weeding the beds. Pulling up weeds is not the best option; it is more productive to cut them. This will leave more moisture in the soil.
When sown directly into the soil, the culture does not always have time to form large heads of cabbage due to the long daylight hours.
Plant watering rules
It is a moisture-loving crop, very sensitive to watering. Plants are irrigated every 4-5 days. In this case, the water consumption is from 1 bucket to 1.5 buckets for each square meter of the beds. If you water the culture less, then with its long powerful roots it will take moisture from closely growing plants. Because of which, over time, not only the fennel will dry out, but the rest of the crop will also die. The fennel beds are also moistened in the fall, if the weather is dry.
How to fertilize fennel


It is necessary to start feeding immediately after the fennel shoots have been thinned. One of the best fertilizers for a spice plant is a common infusion mullein.
Fennel can be grown on the balcony.
There are two ways to fertilize the beds with a mullein:
- To add it directly to the soil, add 3-4 liters of water for every 10 liters of manure and stir.
- To water the plants, you need to prepare a less concentrated solution: the mixture that is intended for introduction into the soil is taken 1 volume and 10 more volumes of water are added.
Nutrients are introduced under the fennel bushes twice during its growing season. Instead of a mullein, it is permissible to use chicken droppings, and you can feed them the culture even more often than 2 times. To do this, you will need to take 50 volumes of water for 1 volume of litter.
Hilling a fennel bush
During the season, the crop is spud twice or thrice. Sprinkle with earth to a height of 4 to 7 cm. If this procedure is carried out, then the heads of cabbage at the soil surface will be snow-white and fleshy.
Diseases and pests typical of the plant
Fennel by nature has good immunity, so it rarely suffers from diseases. And the spicy smell inherent in greens quite effectively scares away many pests from it. But sometimes infection still cannot be avoided.
The best prevention is proper plant care. Timely watering and feeding are especially important. It is also imperative to follow the landing pattern. If the plants in the garden are closely spaced, diseases spread much faster.
Of the diseases for fennel, the most dangerous are:
- Cercosporosis. The leaves are covered with small yellowish, as if "broken" spots. Gradually they darken, grow, merge with each other, the affected tissues turn brown and die off. For prevention, the garden bed is powdered with wood ash or crushed chalk, water for irrigation is periodically replaced with a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate.To cope with the disease, any fungicide is used. Of the old time-tested remedies, a 2% solution of Bordeaux liquid or copper sulfate is the most effective. But you can also use modern copper-containing drugs - Kuprozan, Captan, Skor.
- Rust of leaves. Reddish-brown bumps or spots appear on the front side of the leaf, the wrong side is covered with a continuous layer of "fleecy" saffron bloom. Preventive measures are the same as for cercospora. If the disease is noticed at an early stage, it is quite possible to cope with it with folk remedies - a solution of soda ash, colloidal sulfur, an infusion of onion or garlic arrows, diluted with water 1:10 kefir or milk whey with the addition of iodine (a drop per liter). In severe cases, fungicides are used - Horus, Topaz, Oleocobrite, Raek.
- Stem rot. On the stems, starting from the base, a white "fluffy" plaque appears, resembling cotton wool, then brownish-green spots oozing with muddy mucus blur at this place. For the prevention of the plant, it is necessary to periodically dust it with wood ash or colloidal sulfur. Having found a disease, the plaque is washed with a soft cloth soaked in vodka, the affected areas are disinfected by washing with a bright pink solution of potassium permanganate or 2% copper sulfate. Then they are sprinkled with crushed chalk or activated carbon.
- Root rot. The disease is very difficult to detect in time. The plant seems to lose its tone and wither for no reason. Only when it has already gone far, the base of the stem turns black, becomes slimy to the touch, spreads an unpleasant putrid smell. Mold may develop on the soil. It is best to immediately dig up and destroy the plant, thus eliminating the source of the infection. The soil in this place is disinfected by spilling with a 5% solution of copper sulfate. If the disease was noticed on time, watering is sharply reduced to the required minimum, replacing the water with a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate, granules of Trichodermin, Glyokladin are introduced into the soil.
Photo Gallery: Symptoms of Typical Fennel Diseases
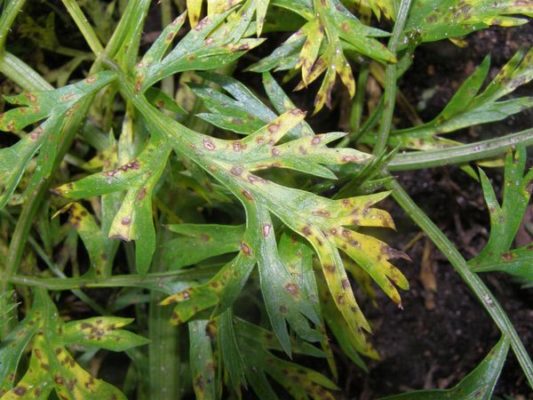


To combat cercosporosis, any copper-containing preparations are used.


Leaf rust is a common fungal disease in horticultural crops
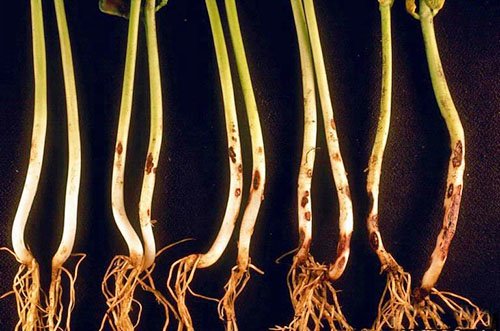

Stem rot spreads from bottom to top


Root rot is extremely difficult to notice in time, and it can only be dealt with at an early stage of development.
The culture is affected by the following pests:
- Aphid. Small black-brown or yellow-green insects stick around young leaves and inflorescences. They feed on plant sap, so the affected tissues turn yellow, discolor and dry out. For prevention, fennel is sprayed with infusions of onion or garlic arrows, dry tobacco leaves, hot red pepper, orange peel. The same folk remedies will help to cope with the pest if its appearance is noticed on time. Only the frequency of treatments should be increased from once every 7-10 days to 3-4 times a day. In the absence of an effect, general-purpose insecticides are used - Mospilan, Tanrek, INTA-Vir, Iskra-Bio.
- Thrips. Vague yellowish spots appear on the front side, thin silvery strokes appear on the wrong side. If you look closely, you can also see small black "sticks" - these are the pests themselves. For prophylaxis, plants are sprayed with foam of household or green potassium soap, a solution of colloidal sulfur. To combat the pest, Confidor-Maxi, Admiral, Fury, Aktara are used.
- Wireworm (larva of the click beetle). It gnaws at the roots of plants, as a result, the fennel dies without receiving sufficient nutrition. For prophylaxis, any siderates are planted in the aisles, except for beans. Especially the wireworm does not like mustard leaves. Traps also give a good effect - containers dug into the ground, filled with pieces of raw potatoes, carrots, beets. In the event of a mass invasion, the drugs Bazudin, Provotox, Pochin are used.
- Caterpillars of a butterfly butterfly.Caterpillars feed on greenery and are able to eat plants in a matter of days, leaving only bare stems. To protect against adults, Bitoxibacillin, Lepidocide, special pheromone or homemade traps are used. Butterflies are lured with the help of containers, which are filled with sugar syrup, diluted with water, honey, jam. Decis, Actellik, Fufanon are used to combat caterpillars.
Photo gallery: what pests dangerous for fennel look like


Aphids are one of the most active garden pests; they will not refuse fennel either.
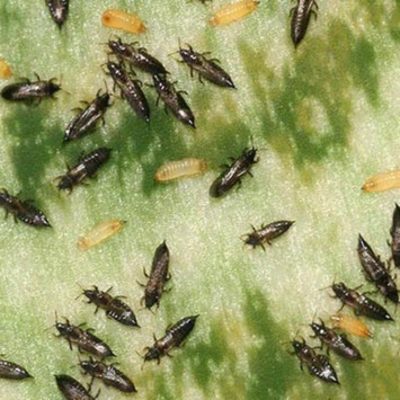


Thrips feed on plant juices, as a result, it loses color
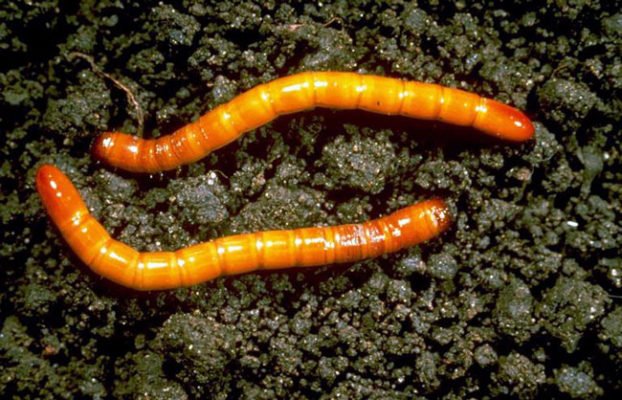


There is hardly a gardener who has never seen a wireworm.
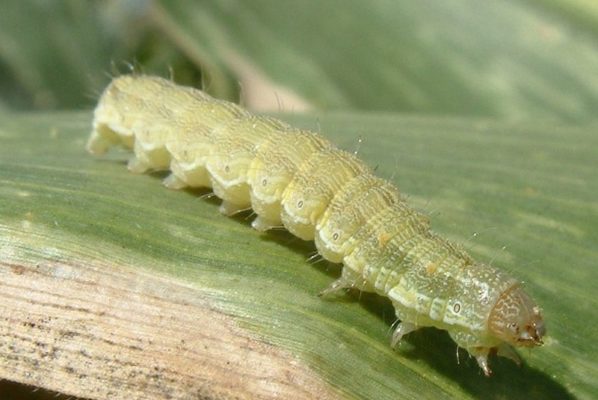


The caterpillars of the scoop butterfly are able to eat all the greens from the fennel bush in just a few days
When and How to Harvest Fennel


With proper care, heads of cabbage grow up to 10-12 cm in diameter. They are cut off at the very surface of the soil. If you detach them a little higher, about 3 cm from the base, then the plant in this place will begin to release new foliage.
The best option for saving white heads of cabbage is a cool place and a box of sand. Before you bury them, you should get rid of all the leaves, leaving only one short petiole up to 10-12 cm. When storing fennel in the refrigerator, it will not lose its original properties within 7 days, it should not be saved longer.
When cultivating regular fennel, solely for the sake of greenery, the top of the plant is cut off when it reaches 0.3 m in height. With this growth, the leaves of the spicy culture have the most pronounced, rich taste and aroma. It is recommended to cut it in the morning or late at night.
Growing a spicy crop in the garden is not at all difficult. If properly watered and fertilized, and if you follow the basic rules for caring for fennel, the plant will give fragrant foliage and heads of cabbage for culinary creations.
Fennel at home
Some varieties of fennel may well be grown at home as potted crops. In "captivity" the plant rarely exceeds 0.5 m in height, but "heads" are formed despite this, if the roots are not disturbed. It is advisable to choose a volumetric container for it, with a diameter of 25-30 cm. A large drainage hole is mandatory.


Fennel can be grown in a pot on a windowsill, the dimensions of the plant allow it
For growing fennel, a universal soil for indoor plants with the addition of fertile turf (3: 1) is quite suitable. To prevent the development of fungal diseases, a little crushed chalk or activated carbon is added to the finished mixture.
Seeds are sown in pots of 3-4 pieces. At the bottom of the container, a drainage layer 2-3 cm thick is required. Then they act in the same way as when growing seedlings. The greens can be cut when the height of the bush reaches 30–35 cm; it takes an average of 2.5–3 months for the “heads” to ripen.
Fennel does not like direct sunlight, as well as extreme heat, so a pot with a plant is placed on the windowsill of a window facing east or west. For the summer, you can take it out into the fresh air.
Plant care consists in regular watering and feeding. Fertilizers are applied every 2–2.5 weeks, using any store-bought means based on vermicompost. Water the fennel as soon as the topsoil dries 1.5–2 cm deep. In extreme heat, you can additionally spray the plant or increase the humidity in other ways.
Growing fennel: varieties, planting and care
Is it possible to grow a useful, medicinal, spicy-aromatic plant in your garden without unnecessary hassle? Easily! Pay attention to fennel - a close relative of celery with a spicy taste and many valuable properties. All parts of this amazing plant are edible: leaves, seeds, stems and roots.To obtain bleached heads of cabbage, fennel is grown through seedlings, and fresh fragrant greens are obtained by sowing seeds in the ground. Caring for fennel is easy: just feed it, water it regularly and weed it. Then in the fall you can taste the delicious harvest and collect the seeds.
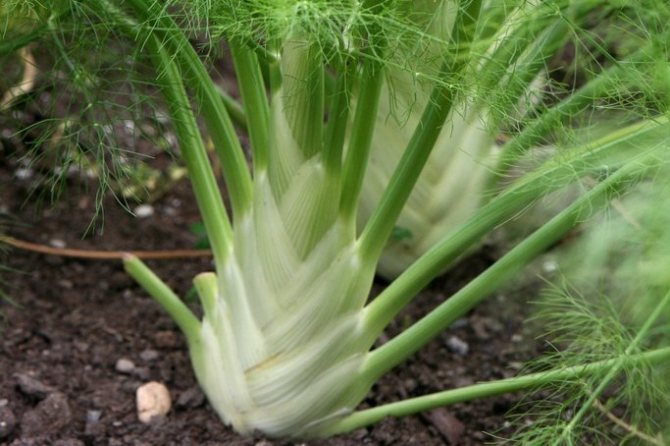


Fennel: description and beneficial properties
Of the two forms - common fennel (pharmacy) and vegetable (sweet) - common fennel is more common.
- Vegetable fennel has a fleshy thick trunk, ordinary fennel has fragrant fluffy stems.
- Fennel is popularly known as sweet anise or anise dill, because outwardly with its umbrellas it resembles dill, and in taste and aroma - anise, but sweeter and more pleasant.
- Fennel is a perennial plant, but depending on natural and climatic conditions, it can be cultivated in an annual or biennial culture.
| Fennel has long been cultivated as a medicinal plant. Prized for its medicinal properties and strong, pleasant scent of leaves and seeds |
- Fennel is rich in vitamins A, C, B2, PP, E, K.
- Fennel tea is successfully used for infants, infusions to improve the functioning of the digestive system.
- Fennel is part of the medical collection for gastritis.
- Fennel can be grown as fresh kitchen herbs.
The collection of fennel for medicinal raw materials is carried out in October.
Fennel is consumed fresh, dried, canned. Young green leaves and heads of cabbage are used for food.
- The most useful are leaves that have grown 20 cm - they are the most delicate and fragrant.
- The taste of the heads of cabbage resembles parsnips, they can be stewed, fried, baked.
Fennel is good in salads, as a seasoning for soups, meat dishes, various vegetable preparations. You can even eat the roots stewed or boiled, and the seeds are added to conservation.
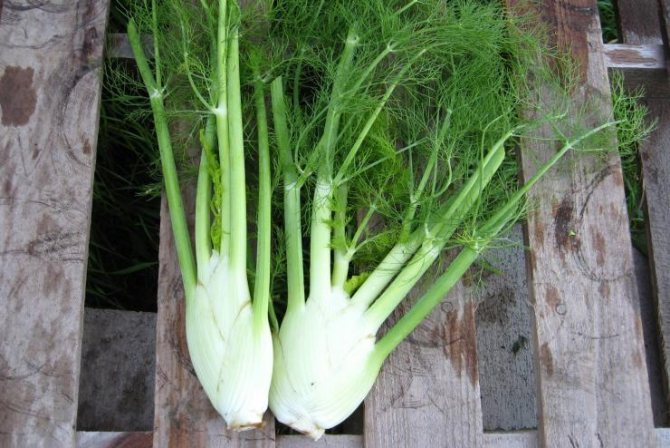


Growing conditions for fennel
It is capricious enough to watering and strongly depends on the length of daylight hours during the formation of dense heads of cabbage.
- The culture is thermophilic, it winters badly.
- Prefers open, well-lit places.
- It reacts to the introduction of organic fertilizers with a powerful development of the vegetative mass, so you need to be more careful with organic matter.
Soil for fennel
To grow fennel, you need fertile cultivated soils, sandy loam or loam, with a deep arable layer. It will be even better if the soil is limed and made easily permeable so that the soil is loose and moist.
- Fennel prefers loose, light, fertile soil.
- According to the acidity of the soil, neutral ones are suitable.
Temperature for fennel
Fennel is a thermophilic culture, but at the same time it is cold-resistant.
- The optimum temperature for germinating fennel seeds is between 20 and 30 ° C.
- The sprouts will begin to hatch as early as 6-8 ° C.
- At a temperature of 15-16 ° C and sufficient humidity, the seeds will hatch 4-5 days after sowing.
Fennel wintering
Fennel winters poorly without shelter in the Russian climate, and it does not tolerate frosty, and even more severe, winters.
- Therefore, the plants are either covered or dug up for the winter.
- If you leave the roots for the winter, the plants need to be cut in the fall, leaving a stump of 5-7 cm, loosen up the aisles, tuck the plants and cover them with straw, peat, manure, humus or special covering material.
- At the same time, some stems are left without cutting to ensure the accumulation of snow on the site.
- In the spring, after the snow melts, the shelter is removed and the soil around the bushes is loosened.
| Thus, fennel can overwinter in the conditions of the Middle Belt. |
In colder regions, fennel is also dug up in the fall and stored until spring in a dark place at a temperature of 1-2 ° C.
- If the fennel is dug up by the roots and buried in a warm place (for example, in a winter greenhouse), you can enjoy the fresh greenery until late autumn.
- In the spring, the plants are relocated to open ground.
Fertilizers for fennel
With an excess of organic fertilizers, fennel begins to fatten and ripens more slowly.
- It is undesirable to introduce fresh manure when planting fennel, it negatively affects the maturation of seeds.
- Organic matter in the amount of 6-7 kg per 1 m² is recommended to be introduced in advance - under the previous culture.
- It is better to prepare fennel beds in the fall by digging the soil onto a shovel bayonet.
When preparing a plot for fennel, the soil is filled with mineral fertilizers immediately before sowing: nitrogen, phosphorus and potash in the ratio: 30:20:10 g / m².
For example:
- 25-30 g of ammonium nitrate,
- 15-20 g superphosphate,
- 10 g of potassium salt per 1 m².
When sowing, it is recommended to add mineral fertilizer superphosphate at a rate of 5 g per 1 m².
| Being not only a useful vegetable crop, but also a valuable medicinal plant, fennel makes special demands on the application of mineral fertilizers. |
Reproduction of fennel
When growing fennel in a perennial crop (in the south), it can be propagated vegetatively:
- the bush is divided so that 2-13 buds remain on each part.
But propagation by seeds is more often used. In addition, fennel is often self-seeding.
- Seeds can be sown directly into the ground or grown fennel through seedlings - depending on the region of cultivation and the desired yield.
- Most often, you can get a head of cabbage (the so-called "root", "tuberous" fennel) only by seedling.
- For cutting for greens, the crop grows well in the open field and produces crops many times per season.


Planting fennel
Planting fennel is possible by seed in open ground or through seedlings. For growing early products, film shelters, greenhouses, greenhouses are used. When planting, the recommended planting scheme should be followed.
The landing dates are quite extended:
- usually seeds are sown in the ground in the second half of May to get greenery,
- for the ripening of a head of cabbage - at the end of June,
- sown for seedlings in March-April.
Fennel planting site
Fennel is a culture of long daylight hours.
- Therefore, it is better for him to choose a well-lit place with a low groundwater table.
- In lowlands and marshy areas, fennel will not be pleasant.
- In one place without transplanting fennel can be cultivated for 2-3 years.
| When choosing a place for planting fennel, crop rotation should be observed and the proximity to other crops should be taken into account. |
Good precursors for spice will be e crops under which organic fertilizers are applied:
- cucumber,
- potatoes,
- cabbage.
Can be planted after green manure and where annual grasses grew.
- In joint plantings, fennel feels good together with peas, kohlrabi cabbage.
- But fennel should be kept away from tomatoes and beans - they are incompatible.
Planting fennel outdoors
Growing for greens
- Growing fennel seeds is convenient for producing young greens, but not heads of cabbage.
- For this, fennel can be sown every 2 weeks, from April to the end of July, depending on the climatic conditions of the region.
Growing heads of cabbage
| To obtain a fennel tuber, it is sown in open ground at the end of June, when daylight hours are waning. |
The fact is that with a long daylight hours, fennel may not grow heads of cabbage, but stretch out in long shoots and bloom in July-August.
- In the south, summer sowing of fennel with dry seeds is also possible in July-August.
- Sowing of fennel seeds in winter is also possible.
Seed preparation
Before sowing, fennel seeds need to be prepared -
- moisturize and germinate at a temperature of 13-22 ° C,
- dry sprouted seeds,
- you can treat seeds with growth stimulants.
Landing scheme
When sowing fennel seeds in open ground, the distance between the plants is observed:
- a distance of at least 40 cm is left between the rows,
- seeds are sown in grooves every 15-20 cm,
- buried to a depth of 1-2 cm on heavy soils, 2-3 cm on light soils.
| When seedlings appear in 10-15 days, the fennel is thinned out so that a distance of at least 10-15 cm remains between the seedlings |
Planting fennel seedlings
Growing through seedlings makes it possible to get the so-called. onion, head of fennel, and not just green shoots.The seedling method is suitable for growing in regions with short, cold summers. It is best to grow seedlings in greenhouses or greenhouses.
Sowing dates for fennel seedlings
The timing of sowing fennel seeds for seedlings will depend on the climatic conditions of the region and the timing of planting seedlings in the ground.
- Therefore, the sowing time can be extended from April to mid-May.
- Fennel seedlings are usually planted in the ground at 45-60 days of age.
Sowing seeds
To grow fennel through seedlings, seeds are sown in seedling boxes or pots. Peat-humus pots, plastic cassettes or seedling plastic individual containers are preferable, because fennel does not tolerate transplanting well.
- The seeds are not buried deeply.
- At a temperature of 20-25 ° C, seedlings usually appear a week after sowing.
- At the age of 3 weeks, the seedlings dive (preferably in peat-purulent pots) and grow at a temperature of 8-10 ° C.
Fennel seedlings are planted in the ground when the threat of return frosts has passed:
- from the second half of May into warm soil,
- the distance between plants is 15-20 cm, and between rows 40-60 cm.


Fennel care
Caring for the planting of fennel consists in loosening row spacings, weeding, carrying out light hilling, watering.
- It is necessary to loosen it 2-3 times per season, starting immediately after germination.
- Top dressing is made of mineral 1 time per season.
- Watering is carried out regularly and abundantly.
- As soon as a thickening begins to form at the base of the stem, the plants are spud so that the heads are tender and ripen well.
- Once the tuber has grown to 10 cm in diameter (in thickness), you can harvest.
Fennel feeding
1. The first complex fertilizing with mineral fertilizers is carried out in the phase of 3-4 true leaves:
- 10-12 g of ammonium nitrate,
- 20-25 g superphosphate,
- 10-12 g of potassium salt per 1 m².
2. If you need to get seeds, you need a second feeding. It is carried out when peduncles appear:
- 10 g of ammonium nitrate,
- 5-8 g of superphosphate per 1 m².
3. The third feeding is also aimed at fruit ripening:
- 2 g of phosphate fertilizer per 1 m² of moistened soil.
Watering fennel
As a guest from the Mediterranean, fennel is drought tolerant, but requires adequate moisture, and does not tolerate swampiness. He needs infrequent and abundant watering, especially during the period from sowing to the formation of a rosette.
- In dry hot weather, watering is mandatory.
- If the soils are light, watering can be done more often.
| On average, the watering rate for fennel will be 2-4 times per season, 15-20 liters per 1 m² |
Insufficient moisture can cause early flowering (due to which the tuber will not form), therefore, in the absence of precipitation, fennel must be watered.
Diseases and pests of fennel
Fennel is not resistant to diseases and pests.
- Young plantings of fennel can be annoyed by cravchik beetle and May beetle, aphids, thrips.
- Plants are gnawed by scoops, swallowtail caterpillars, umbrella moth.
- The greatest danger to him is represented by umbrella and striped bugs, coriander seed-eater, umbrella moth, phomosis.
Phomosis of fennel
Phomosis is especially dangerous when growing fennel for seeds.
- Phomosis becomes noticeable in the middle of summer.
- Signs of damage appear in the form of small specks of plaque on the leaves and stems.
- As a result, in September-October, the plant dries up, and the fruits crumble.
The fight consists in observing correct agricultural practices, because during the ripening of greens, chemical treatments with insecticidal preparations are unacceptable:
- remove plant residues in a timely manner,
- adhere to the landing pattern,
- not to violate the cultivation technology.
Collection and storage of fennel
Fennel begins to bloom in July, yields in September-October. Fennel seeds can only be obtained for 2-3 years.
- Young greens of fennel are cut for harvest before flowering at a plant height of 25-30 cm.
- The fennel crop must be harvested before the first frost, the leaves are the first to suffer from them.
- The heads of cabbage are cut at the root and all the leaves are removed - so the heads of cabbage will not wither.
Well-developed heads of cabbage grow to the size of a medium apple, 8-10 cm in diameter.
- Fennel tubers will be kept safe in wet sand.
- Fennel greens for storage for the winter must be thoroughly dried and stored in tightly closed containers. They will retain their aroma and spicy taste for a long time.


Fennel varieties
For 2019, 12 varieties of vegetable fennel, suitable and recommended for cultivation in the country, are entered in the State Register. All of them are suitable for growing in all regions:
- Amicante (2018, early ripe hybrid of Italian origin, weight of cabbages approx. 500 g, yield a little over 1 kg / 1 m²)
- Scent (2002, ripens in 75-85 days, recommended for growing greens, yield 2-3 kg / 1 m²).
- Casanova (2011, mid-season variety for greens, yield - almost 4 kg / 1 m²).
- Corvette (2005, forms a head of cabbage in 115-127 days, weight about 300 g and more, yield of greens a little more than 1 kg / 1 m², heads of cabbage - about 2 kg)
- Leader (2003, gives greens in 40-50 days, yield more than 2 kg / 1 m²).
- Luzhniki Semko (2000, mid-season variety, forms a head of cabbage in 55-65 days, weighing more than 200 g, yield slightly more than 1 kg / 1 m²).
- Autumn handsome (2003, gives greens in 40 days, yield a little over 1 kg / 1 m²).
- Prelude (2015, Dutch hybrid of mid-early ripening, forms dense heads of 300 g, yield 3 kg / 1 m²).
- Rondo (2009, mid-early hybrid of Dutch selection, forms a head of cabbage weighing 250-350 g, the yield of greens is up to 5 kg / 1 m², heads of cabbage - up to 3 kg / 1 m²).
- Soprano (2003, forms a head of cabbage in 115 days, weighing about 100 g, yield of greenery 4 kg / 1 m², heads of cabbage more than 2 kg / 1 m²).
- Dandy (1996)
- Phenomenon (2015, mid-season variety, gives a little more than 1 kg of heads of cabbage with 1 m² weighing 210-220 g).
Description of varieties of vegetable fennel (sweet)
- Autumn handsome
The variety ripens quickly enough - in a month and a half from the emergence of shoots. It reaches a height of one and a half meters. Greens cut before flowering have a delicate, less pungent odor. Productivity - more than 1 kg per 1 m².
- Leader
A fast-ripening vegetable fennel variety that yields up to 2 kg of greens per 1 m² in 40-50 days from germination. The greens removed before flowering will perfectly complement the taste of soups, meat and vegetables.
- Luzhnikovsky Semko
A mid-season variety will ripen in 2 months from the emergence of seedlings to the formation of a "head of cabbage". The plant reaches a height of just over half a meter, a head of cabbage is formed weighing 200-220 g. The yield gives 1 kg per 1 m². Good for use on fresh and dried greens; heads of cabbage, and leaves, and shoots, and seeds are also eaten.
- Dandy
Mid-season variety, forms a head of cabbage in 1.5-2 months. It gives a good stable birth, is appreciated for its resistance to stalking (forms a head of cabbage even in conditions of long daylight hours).
- Scent
The variety will need 2.5-3 months to ripen from full shoots. The plant turns out to be powerful and tall up to 2 m in height. The yield of greenery can be up to 2-3 kg per 1 m². It is perfect fresh and dried as an addition to soups, meat and vegetable dishes.
- Soprano
The variety is late, will yield a harvest not earlier than in 3.5-4 months. At the same time, the result will be impressive: the plant will stretch up to 1.5-2 m, and you will collect up to 4 kg of greenery from 1 m². The variety gives good dense white one-hundred-gram heads of cabbage, the total weight of which per 1 m² will be at least 2-2.5 kg
- Corvette
Another late-ripening variety, will delight with the harvest in 115-125 days from full shoots. The plant is not tall - a little more than half a meter, but the "head of cabbage" is dense and weighty in 250-350 g. The yield of greenery will be almost 1.5 kg per 1 m², heads of cabbage - approx. 2.5 kg.
Description of varieties of fennel ordinary (pharmacy)
Fennel is grown as a medicinal, aromatic and essential oil plant. Differs in a high content of essential oil, fat in seeds.
- Bachata
A relatively new variety included in the State Register in 2019. It is distinguished by high winter hardiness and resistance to pests and diseases (to cercosporosis, brown spot, rust).
- Mercisor
This early ripening variety is suitable for growing in warm climates - Krasnodar Territory, Rostov Region, Stavropol Territory, Crimea, Adygea, Dagestan, Ingushetia, Kabardino-Balkaria, Alania, Chechnya. It is used to obtain a large early harvest on farms.
- Santorino Sixty
This early maturing hybrid is more suitable for growing for sale as a business. It requires mild climatic conditions of the south and central part of Russia, thin-film shelters. Good for cultivation in Bryansk, Vladimir, Ivanovo, Kaluga, Ryazan, Smolensk, Tula regions, Krasnodar Territory and Rostov region, in the Crimea, etc. Kochanchik grows dense weighing 1-2 kg with excellent taste.


The experience of growing fennel through seedlings in the open field
Anna Chumak, a regular author and reader of the Summer Club magazine, from the Altai Territory, shares her experience in growing fennel.
I am always glad to add something new to my garden with spicy crops. So I decided to grow vegetable (Italian) fennel. The Greeks believed that the plant is capable of endowing a warrior with incredible physical strength, energy and fearlessness.
How I Sow Fennel Seedlings
I was interested in getting bleached heads. In the first year of sowing, she did not achieve success, but she was not disappointed. I bought new seeds, and in the second year everything worked out.
I always grow my fennel through seedlings. I take the soil for seedlings.
- Seeds are sown dry at the end of March in small cups, usually 2-3 seeds per cup. Fennel seeds are quite large.
- I water the crops, cover with foil. I take it off after germination (after about 1.5-2 weeks).
- When the seedlings grow up, I leave one in each glass. I usually grow 8-10 plants.
- I water the seedlings very carefully, because they are very delicate, thin in fennel.
You can sow fennel directly into the ground:
|
How I plant fennel seedlings outdoors
The planting time for fennel seedlings in the Altai Territory falls on the first decade of June:
- carefully transfer the seedlings from the cups into the holes,
- watering well
- I mulch with humus,
- I will definitely shade for a few days.
The distance between plants is 50 cm.
How I care for fennel
Fennel loves sunny places, fertile soil and timely watering.
- During the summer, 1 time (in June) I feed fennel with a complex fertilizer for vegetables.
- I regularly water, weed and loosen the soil near the bushes.
With good care, vegetable fennel can grow up to 2m in height!
| Fennel grows Against the backdrop of a blooming June garden, young fennel plants look scummy. But two weeks will pass - and fennel will begin to grow, it will begin to grow overgrown with lush hair of carved emerald leaves, similar to dill, but only with an aniseed scent. Fennel bushes are especially beautiful after the rain, when all the leaves are covered with droplets of moisture shining in the sun. |
How I Harvest and Seed Fennel
In the phase of the beginning of the formation of fleshy thickenings at the bottom of the stem of the plant, I spud it, but not with earth, but with clean sand (or tie it with thick paper).
- When the nubs are about 10–12 cm in diameter, the crop can be harvested.
- I dig out some of the plants, separate the heads of cabbage from the stems and leaves.
I add the leaves and stems to soups or put them in jars when pickling cucumbers and tomatoes. I wash the heads of cabbage, cut them into plastics and freeze them in containers or use them in the preparation of fish dishes.
| I leave a few plants for seeds - they begin to bloom in the year of planting. Umbrellas bloom on the stems like dill |
- Flowering is long, the fruits ripen only in late August - early September.
- After that, they easily crumble.
- Therefore, if the autumn is dry, sometimes I use gauze bags to collect seeds.
I advise everyone to grow fennel!
Growing
Fennel can be grown independently; cultivation is done by seed. Seasoning is planted in early spring, the soil must be abundantly fertilized, it should be of the best quality possible. When sowing, the distance between the rows should be up to two meters; the plant should be thinned out after the appearance of two full-fledged leaves on the shoots.
It is not difficult to take care of the growing pharmaceutical dill, you just need to constantly feed it, loosen the soil and remove the weeds in a timely manner. Leaves and stems can be harvested within a month and a half after sowing.
The use of seeds in cosmetology
In the fruits of this plant contains essential oil, which has an amazing taste, bitter and at the same time sweet. In addition, this oil has a large number of substances that are beneficial to the skin. It is used during massage and is added to many cosmetics: shampoos, tonics, lotions, creams and masks.


Useful
Fennel seed oil smoothes wrinkles, has anti-aging effects, improves skin elasticity and treats teenage problems like acne. Moreover, it slows down the aging process of body cells, and according to the assurances of some long-livers, it can prolong life.
Composition and calorie content
Fennel seeds represent a very healthy and demanded product from the face.
Despite the fact that the greens of this plant have a low calorie content (only 31 kcal), its seeds are a very nutritious product - their energy weight is 345 kcal per 100 g.
100 g of fennel seeds contain the following components:
- fats - 14.87 g;
- carbohydrates - 52.29 g;
- proteins - 15.8 g;
- saline - 8.22;
- water - 8.81 g.
The seeds also contain a number of vitamins: A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E. Seltzer composition is represented by the following set of trace elements:
- pyrolusite;
- iron;
- calcium;
- copper;
- magnesium;
- phosphorus;
- potassium;
- zinc;
- sodium
- selenium.
The seed package also includes essential oils, dietary fiber, essential fatty acids, glycosides and flavonoids. Essential oils cover up to 60% of anethole - an aromatic essential substance that has anti-inflammatory, antiviral and antimicrobial properties.
Varieties and varieties
Breeders do not pamper gardeners with a variety of varieties and varieties of fennel. To date, there are only two main types: vegetable and ordinary. The first is cultivated for the purpose of obtaining stems and fleshy petioles, and the second - seeds and leaves. Root fennel is sometimes simply called sweet by summer residents. Its height reaches 2 m. The plant is often used by beekeepers for feeding bees. Among vegetable varieties, the most widespread is Udalets, characterized by medium ripening times.
Also popular are:
- Luzhnikovsky Semko;
- Soprano;
- Corvette;
- Leader;
- Rudy;
- Crimean;
- Sicilian.
Harm and contraindications
There are almost no contraindications to the use of dill.


- You can not use it, in the first shot, for people with individual intolerance, so as not to cause allergic reactions.
- Except, as already mentioned, fennel is also contraindicated in case of a threat of miscarriage in pregnancy navigation. However, if there is no such threat, then it will even be of great benefit to expectant mothers: it helps to get rid of unpleasant symptoms in case of early toxicosis.
- It is also not recommended to entrust fennel to babies in the first 4 months of life. But after this age, this plant will also only benefit the kids.
- It is inappropriate to include in the diet of fennel in any form for digestive disorders, because this product has a laxative effect.
Here, perhaps, are all the contraindications regarding the use of this useful product.
Description of culture
Fennel is a perennial (more often grown as an annual or biennial) plant of the Umbrella family, which resembles dill in appearance and has a strong spicy aroma.Fennel is rich in nutrients (proteins, vitamin C, essential oils) and is widely used in cooking, perfumery and medicine.
In horticultural areas, common fennel (herbal) and vegetable fennel are most often found.
Fennel ordinary
This fennel is grown for its greens and seeds. As a rule, it is this plant that is left for the second year to wait for the seeds to ripen. Varieties: Pepper, Garden.
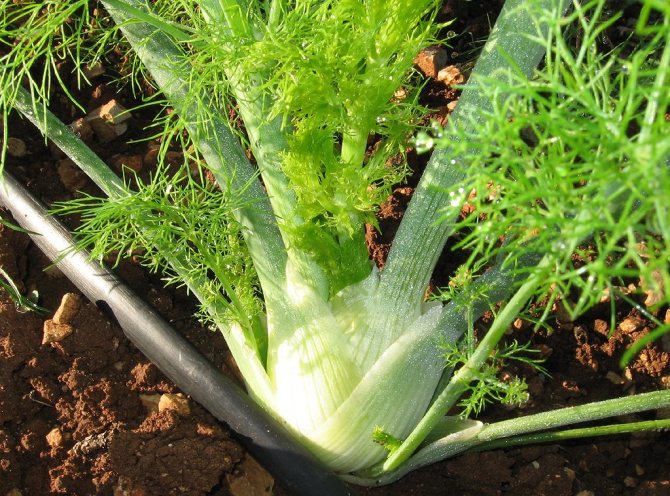


Fennel is grown for aromatic greens
Vegetable fennel
The main feature of this species is the formation of bulbous stems (heads of cabbage), which are then eaten. Because of this, vegetable fennel does not "live" longer than one season. Varieties: Udalets, Luzhnikovsky Semko, Soprano, Casanova, Rondo, hybrid Rudy F1.
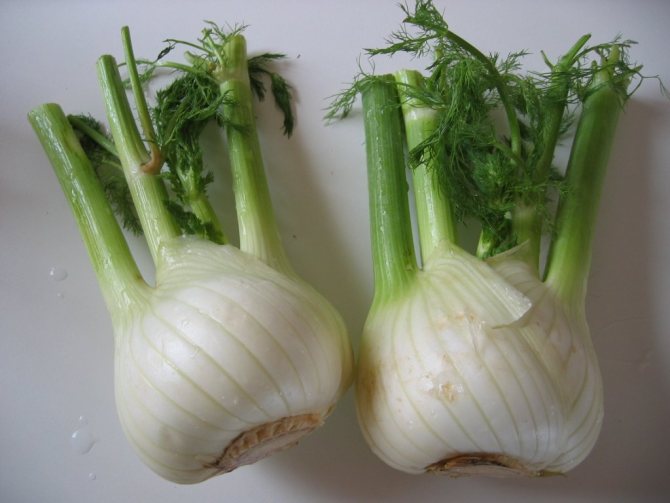


Vegetable fennel forms white heads of cabbage, which are eaten
Seed preparation for sowing
There are several rules for preparing seeds for sowing, the observance of which will positively affect the yield of your plant. Before sowing seeds for seedlings or in open ground, the following procedures must be carried out:
- soaking in warm water for two days. Please note that during the soaking period, the water will have to be changed at least four times. After soaking, dry the seeds on a napkin or paper towel until they are loose;
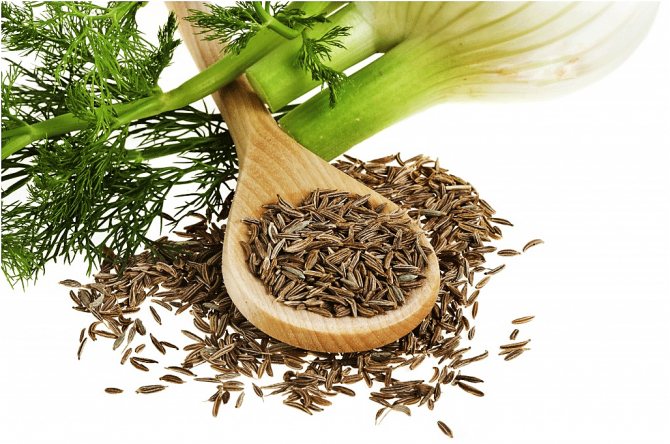


To ensure the best germination of fennel seeds, they must be soaked in warm water for two days.
- disinfection is advisable if you take seeds from a bush. To do this, prepare a hot pink solution of potassium permanganate (1 g of powder per 100 ml of water) and soak the seeds in it for 30 minutes, and then rinse.


Disinfecting seeds will help protect future crops from disease
The plant has a wide therapeutic spectrum of action.
It is prescribed as a diuretic, laxative, antiemetic, antispasmodic, choleretic agent. Used for flatulence, for sputum separation, blood purification, soothing.
Fennel relieves indigestion, relieves throat and lung diseases. Helps with menstrual irregularities, anemia. Copes well with constipation, gas formation, diarrhea, colic, eye diseases.
- The juice from the leaves of pharmaceutical dill is instilled into the eyes, relieving irritation and eye fatigue.
- To increase lactation, nursing mothers prepare the following collection: take an equal amount of dried and crushed seeds of fennel, oats, barley, hop cones, galega, dill, fenugreek, caraway. Brew 2 tablespoons of the mixture in half a liter of boiling water, leave for 2 hours, drink the strained solution half a glass after a meal.
- For flatulence, dill water is used. She also helps babies well. To do this, a handful of seeds are poured with 400 mm of boiling water, insisted for 40 minutes, cooled, filtered. You should drink 2 teaspoons three times a day.
- For colds, neuralgia, colitis 30 gr. dried raw materials insist on a water bath. Drink the infusion 60 mm after meals.
- For cough, a decoction of fennel seeds, mullein, mallow is used. Seeds are taken in equal parts and brewed with 200 ml of water, simmer for 15 minutes. Drink 3 times a day, 70 ml.
- Fennel helps women relieve unpleasant symptoms during menopause. Collecting herbs oregano, calendula, chamomile, string, woodruff, string, flaxseed, fennel fruits are poured with boiling water (0.5 l), insisted for half an hour, used in a glass three times a day.
Healers use ground fennel root to improve liver function, increase intestinal motility, gallbladder.
Many vegetable oils have health benefits. Fennel oil is no exception. It helps to remove toxins, toxins; normalizes the digestive tract, helps to cope with constipation and diarrhea. It is invaluable for women because it stimulates the production of their own estrogen, improves the functioning of the endocrine glands; relieves PMS and menopause symptoms.The oil purifies the air in the room and is used to treat fungal diseases of the feet and nails.
The aroma of the oil has a calming effect on the nervous system, relieves fears, obsessive thoughts.
Fennel oil is used as a skin rejuvenation agent.
It improves skin elasticity, smoothes wrinkles, and delays dermis fading. The oil nourishes, gives tone and elasticity to the skin.
Favorably affects the skin in the thighs, décolleté, abdomen, tightens it, removes cellulite.
The oil fights well against the appearance of acne, youthful acne.
- The mask is well recommended for tightening problem skin of the face and chest. With its help, fine wrinkles will disappear, the dermis will begin to produce collagen. The mask will remove age-related pigmentation, dry skin. For her, take 15 grams of white clay, 1 egg yolk, 15 ml of jojoba oil, drop by drop of fennel, pink, neroli oil. Everything mixes up. Lying down, apply on cleansed skin, after application lie down for half an hour. Rinse off with cool water. Apply this mask 2-3 times a week for a month.
- An anti-cellulite agent relieves the excess of the subcutaneous fat layer, orange peels on the thighs, shoulders: take 50 ml of olive oil, 5 drops of grapefruit oil, patchouli, lime, fennel, then mix. Apply to problem areas several times a day for two weeks.
- A nourishing mask for face and hands will help women of Balzac age. For her, you need a little cottage cheese, quince pulp, 3 drops of fennel oil, egg yolk. Everything is crushed, mixed until smooth. The gruel is applied to the hands and face for 15 minutes, then washed off.
Fennel seeds will strengthen and give your hair a beautiful, healthy shine. They are added to mouth rinses and elixirs and toothpastes.
Fennel pests and diseases
Fennel diseases
Fennel is very rare, but sometimes it can be affected by cercospora, root and stem rot, or rust.
When fennel is affected by cercospora, small angular yellow spots appear on all its green organs. With the development of the disease, the spots darken, merge with each other, the affected plant tissues turn yellow and die off. For preventive purposes, too dense plantings should be avoided, and to destroy the infection, fennel is treated with one percent Bordeaux liquid, Cuprozan or Kaptan.
Root rot causes the death of the plant. First, fennel leaves wilt, then wither, turn brown and die off. If you dig up the soil to a depth of 15 cm, you will find that the roots have turned black. The dead plant will have to be removed along with the soil adjacent to the roots. If you managed to diagnose the disease at the very beginning, immediately stop watering the fennel and treat it with a fungicide solution.
Stem rot affects the stems and shoots of plants. First, part of the shoot or stem rots, then dies off. Sometimes the infection also spreads to the leaves of the plant. Usually rotting occurs at the level of the soil surface and above, and the first sign of the disease is a white bloom, followed by small brown spots on the stem. As soon as you find the symptoms of stem rot, stop watering the fennel, wipe off the plaque and lubricate the damaged areas with a strong solution of potassium permanganate, and then dust them with wood ash.


Rust is a fungal disease, which is expressed in the formation of orange-brown tubercles and pustules on the ground parts of the plant, which cause increased evaporation of moisture, and with severe damage, leaf fall. At the first signs of the disease, it is necessary to remove diseased leaves and shoots, after which the plants are treated with a fungicide solution.
Fennel pests
The quarrelsome nature of fennel scares away not only plants, but also insects from it. Fleas, aphids, woodlice and snails don't like it, so fennel can be grown near vegetables that suffer from these pests.Of course, if the plants themselves get along with their savior. Enemies of fennel include wireworms, beetle larvae, scoop caterpillars and meadow moths.
The meadow moth is a polyphagous pest that can cause serious damage to your garden. This butterfly is about 1 cm long with a wingspan of up to 20 cm in males and up to 26 cm in females. The forewings of moths are gray-brown with dark spots and a yellow stripe at the outer edge, the hindwings are gray with two stripes. The caterpillar of the moth is black-headed, greenish-gray with a dark stripe along the back. The insect is very prolific, therefore dangerous. Caterpillars eat everything in their path, leaving only veins and petioles from the leaves. Butterflies feed on nectar, and during the years of mass summer of meadow moths, the amount of honey produced in a given area can significantly decrease. This happens once every 8 or 10 years, and then the gardeners have a hard time.
They destroy moths in different ways. If there are few of them, then they are collected by hand, and it is noticed that the fewer weeds on the site, the fewer moths and caterpillars. But with a massive accumulation of pests, you will have to resort to chemicals, the most effective of which are Fufanon, Metaphos, Phosphamide, Decis and Karbofos.
Winter moths are also ubiquitous polyphagous pests. The forewings of the winter moth are dark gray, almost black, with three even darker stripes and a thin black border. The hind wings of the male are white, the female is brownish. The moth caterpillars are earthy-gray; at a late stage of development, a dark stripe appears on their back. Both butterflies and extremely voracious caterpillars of the scoop are dangerous for fennel. To protect crops from these pests, it is necessary to comply with the conditions of agricultural cultivation and regularly destroy weeds. With a massive defeat of fennel with scoops, you need to treat the area with one of the insecticides that were listed above.
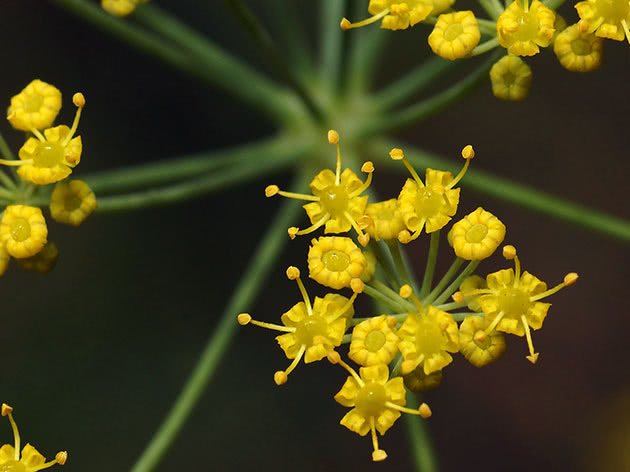


We have detailed how to deal with wireworms and beetles in the articles already posted on our website.
Interesting Fennel Facts
The first mentions of fennel are found in ancient Indian books, where this spice is described as giving a pleasant taste and protecting against many diseases. In addition, in India, it is still customary to chew its seeds after eating to freshen the mouth and cover the teeth.
However, on the Mediterranean shores, in Ancient Greece and Rome, fennel was familiar from before this time more ancient times. It is believed that it was the Roman legions who spread fennel seeds to the east, which later took root in India.
The word "fennel" (distorted feniculum) is translated from Latin as "hay". There is speculation that the original name for fennel was "marathon" - after a city near the famous battlefield, where the Greeks defeated the Persians. In this place, the very fragrant herb grew, which the Greek soldiers began to associate with forced, military success, victory - we all know fennel.
In the Middle Ages, dill was so popular in European cuisine that it was sown and grown in whole fields. Allegedly, that the name of the city is even associated with the name of fennel: the capital of the island of Madeira is called Funchal.
Among the ancient Anglo-Saxons, dill was one of the nine plants considered sacred. There was a belief that dill, in combination with St. John's wort, has the ability to drive away witches and evil spirits. Another legend claims that snakes rub their skin against fennel before changing it so that it slides off more easily.
Here is such an amazing transplant exists next to us. Take a closer look at it, and it will give you wonderful bloody taste and health!
How to choose and where to buy
Fresh fennel is often sold in the vegetable section of supermarkets in major cities. Choose bright white, flawless, heavy and dense bulbs.The stems must be firm. Avoid bulbs with overly loose outer layers that are cracked.
It is best to buy fennel with stalks attached, or at least those with leftover stalks. These bulbs last longer than those from which they are completely removed.
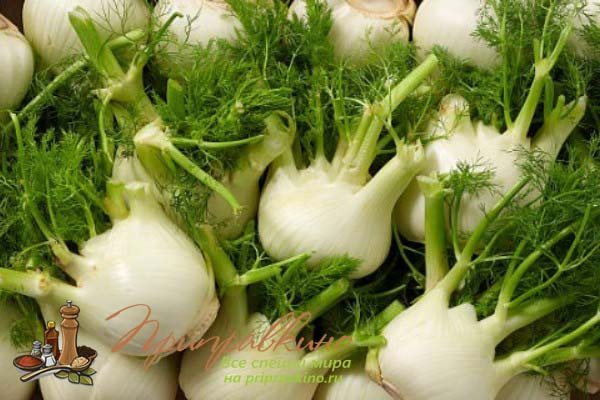


When buying seeds, look for them in colors ranging from bright green to light green. The freshest and best quality is usually bright green, plump, with a strong fennel aroma. Old seeds lose this vibrant color over time.
How and how much to store
Store whole seeds in a cool, dry place, in an airtight container, away from sunlight. The spice will not lose its aroma for 6 months.
Keep ground fennel in the refrigerator in airtight containers and use as soon as possible: it has a short shelf life, as it quickly loses its flavor due to the evaporation of essential oils.
Fresh leaves are best consumed immediately. In the refrigerator, they retain their beneficial properties for 3-4 days, but the aroma gradually disappears.
Wrap the bulbs tightly with plastic wrap or a damp cloth and refrigerate. They will be usable within 10 days.
Growing features
To get a good harvest at a summer cottage, you need to know some of the features of this capricious culture:
- fennel needs regular watering, since, due to a lack of moisture, it will take it from nearby plants using its root system;
- the culture can multiply by self-seeding;
- winter crops are good predecessors;
- cabbage and cucumbers will be good neighbors in the beds, but only with abundant watering of all plants;
- fennel has a depressing effect on growing nearby tomatoes, peppers, peas, beans, spinach;
- the aniseed aroma of the herb attracts beneficial pollinating insects to the garden;
- does not develop well in the shade, so the landing site should be sunny and open;
- the most suitable soil is loamy or black soil with a rich nutrient composition and a small lime content;
- loose soil is required, mulch will help to maintain it in this state;
- As a preventive measure against the appearance of pests, it is recommended to carry out regular weeding and collect ripe seeds in a timely manner.
Description and photo
Consists of a powerful root system with a main taproot or several about 2 cm thick, a tall, straight stem with strong branching (up to 2 m in height), juicy green leaves, very small yellow flowers in umbrella-shaped inflorescences and many small oblong seeds with sweetish taste. The flowering period lasts the entire summer season. Flowers and leaves are very similar to dill.


All parts of the plant have useful properties and are used in cooking, folk and official medicine, in confectionery and perfumery, in the garden and in the garden to repel pests and attract beneficial insects. All this is due to the valuable composition of fennel, which contains vitamins, trace elements, essential oils and many other useful components. The culture is propagated by seeds and dividing the bush. Seed propagation is more popular and acceptable in the Moscow region.
Read also: Growing radishes in a greenhouse: instructions for beginners from sowing to harvesting
Most often in the garden you can find two types of fennel - "Ordinary" and "Vegetable". Popular varieties include:
Care rules
Thinning
Thinning the planting in time, you can get lush, juicy and beautiful greens. This procedure allows the plants to be saturated with air and grow freely.
You can water the culture with ordinary water in moderate volumes, the frequency of watering is 1-2 times a week. For 1 sq. meter planting requires about 10-15 liters of water. Excessive moisture can lead to the beginning of rotting of the root part, and a lack of moisture can lead to its drying out.
Regular removal of weeds from the beds leaves more moisture in the soil for fennel. Weeding and loosening makes the soil light and promotes full growth.
Hilling
This procedure is essential for the development of high-quality and nutritious vegetable fruits. While in the ground, heads of cabbage develop more actively.
The only drawback is their contamination during hilling. To preserve the whiteness and purity of the fruit, individual protective devices for each plant can be used from cut plastic bottles, cardboard, remains of large diameter plastic pipes and other aids. Before hilling, they are put on a bush and buried a little in the soil.
It is better to use organic matter as a top dressing - herbal infusions, liquid mullein. The interval between fertilization is 15-20 days.
Possible diseases and pests
- Stem rot,
- root rot,
- white mold
- rust,
- wireworm,
- meadow moths,
- aphid,
- grub larvae.
Preparing for winter
All greens of fennel should be cut off in early autumn, and the plantings should be covered with a thick layer of humus, sawdust or peat. Such a cover can help one-year crops overwinter, and the next season they will form fruits.


Harvesting
For consumption, fennel leaves are used, which can be harvested for future use, as well as heads of cabbage (if it is a vegetable variety). In addition, you can collect plant seeds, which are later used for sowing.
Harvest time:
- you can collect leaves all summer. It is advisable to cut them off when they reach a height of 30 cm;
- heads of cabbage are cut when they reach 8–10 cm in diameter. This usually occurs in late August - early September;
- you can collect seeds in the second year, when they are fully ripe and turn brown. Keep in mind that the seeds do not ripen at the same time. To prevent self-seeding, wrap the inflorescences with thin gauze.
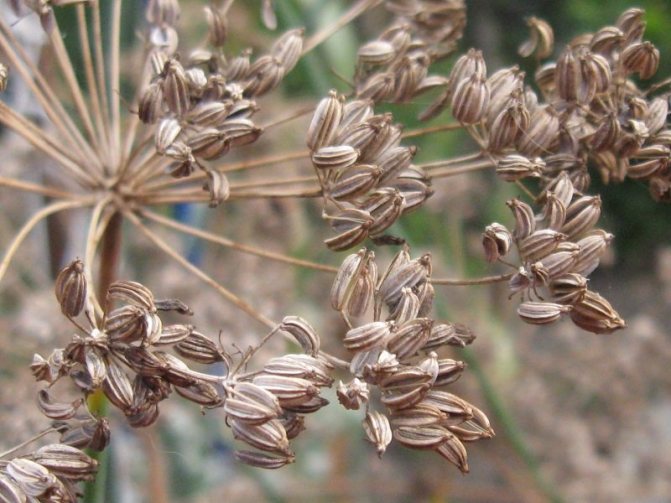


Fennel seeds can be harvested in the second year when they turn brown
Protection against diseases and pests
The fennel harvest serves as a treat for garden pests (caterpillars, aphids, bugs). To keep the plants safe and sound, it is recommended to spray them with green soap, Bordeaux mixture. Around the bushes, trapping grooves are dug for the handsome and the May beetle.
To prevent possible diseases, the seeds are soaked in a weak solution of potassium permanganate before planting. It is also recommended to water the garden bed with a similar preparation before sowing seeds there.
What to replace
Anise seeds can be used as an alternative to fennel as they taste similar. Anise has a stronger aroma, so less is required when using this substitute. Cumin and dill can also be used as substitutes for fennel.
If you are using it as a vegetable, it can be replaced with bok choy (pak choy) or celery stalks. To duplicate only the flavor of the fennel and not the volume, you can add a teaspoon of anise seeds for every 0.5 kg of onion.












































