Unusual fruit trees do not always adapt to the domestic climate, although they are attracted by the color of the fruit. But apricot Black Velvet is an exception to the rule. The plant was bred by Crimean breeders who crossed the American variety and cherry plum. The result of the work was a medium-sized crop, on which fruits appear 3-4 years after planting. Domestic gardeners are just discovering the apricot alchew, but agronomists in Asia, the Caucasus, Western Europe and the United States have been growing the crop for a long time. The black variety is also called apricot plum, purple apricot, slibricot, Aprium, Plumkot, Pluot.
Botanical description
Apricot black velvet is a hybrid variety obtained by crossing a common apricot and cherry plum. The Crimean Experimental Breeding Station is determined as the originator of the culture. It was bred by domestic breeders G.V. Eremin, A.V. Isachkin. In 2005 it was added to the State Register for the North Caucasus region.
The tree is medium-sized, the height of an adult plant is within 4 meters. The crown is flat-round, medium density.
Lat. Prúnus armeníaca
Medium-sized leaf plate, deep green color. The shape is elongated, with a pointed end. There is no pubescence and wax coating.
It blooms a little later than the usual apricot varieties. The flowers are large, the petals are white or light pink. The variety is self-fertile and does not require additional cross-pollination.
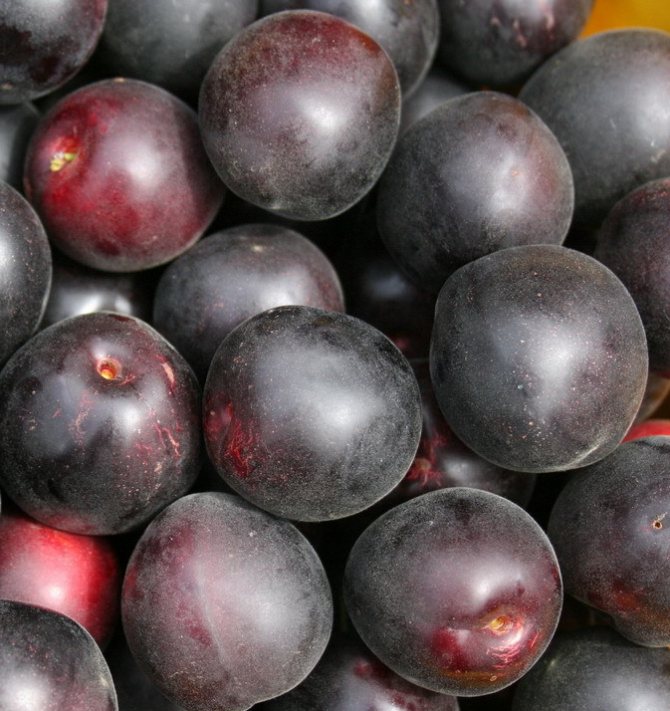
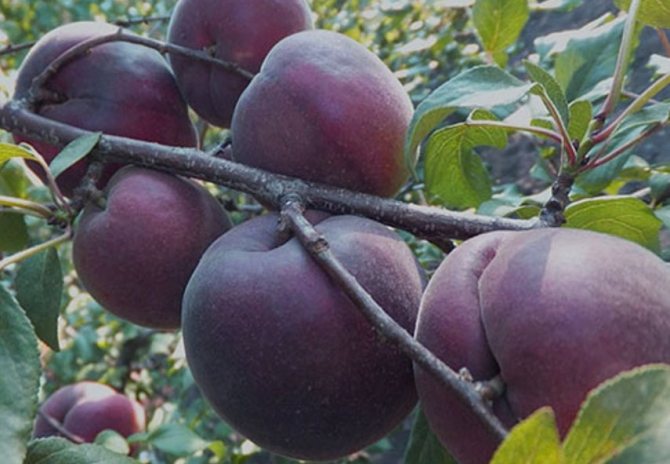
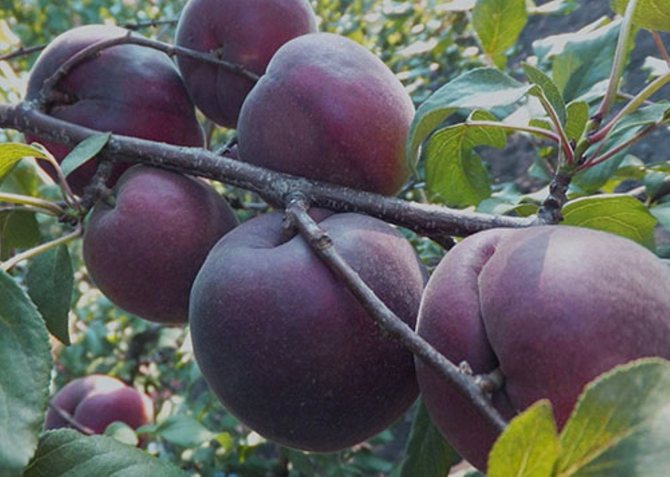
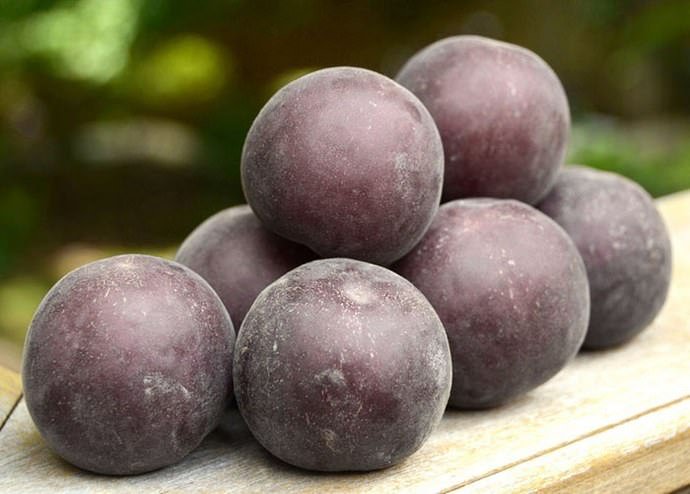
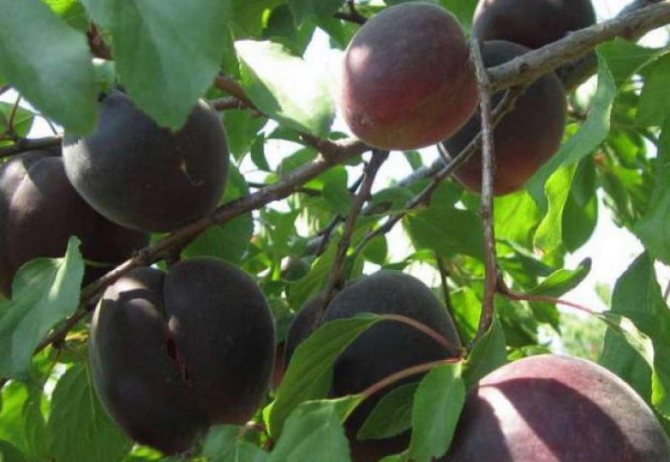
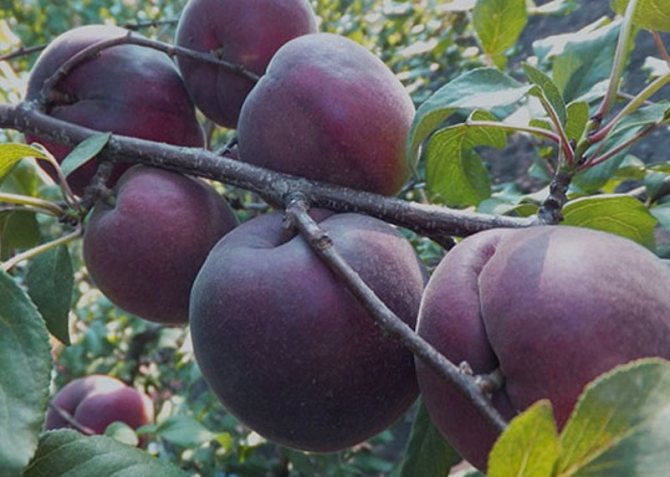
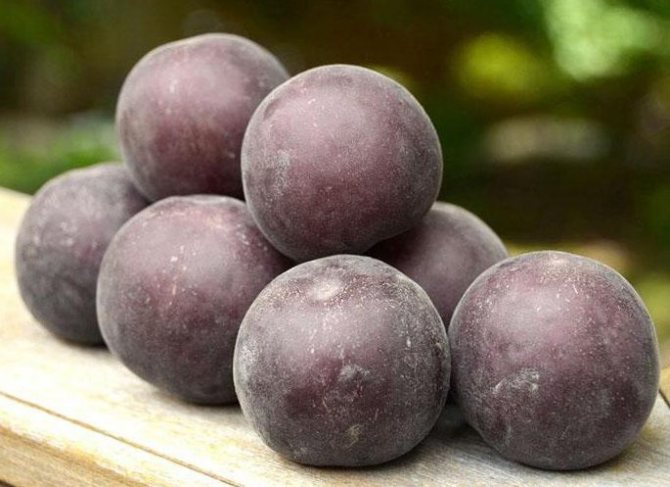
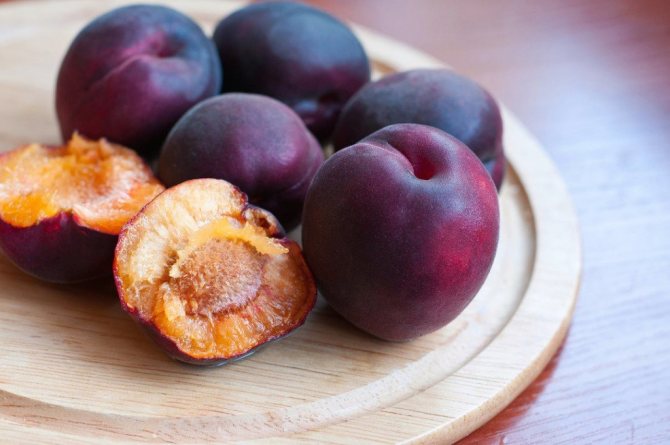
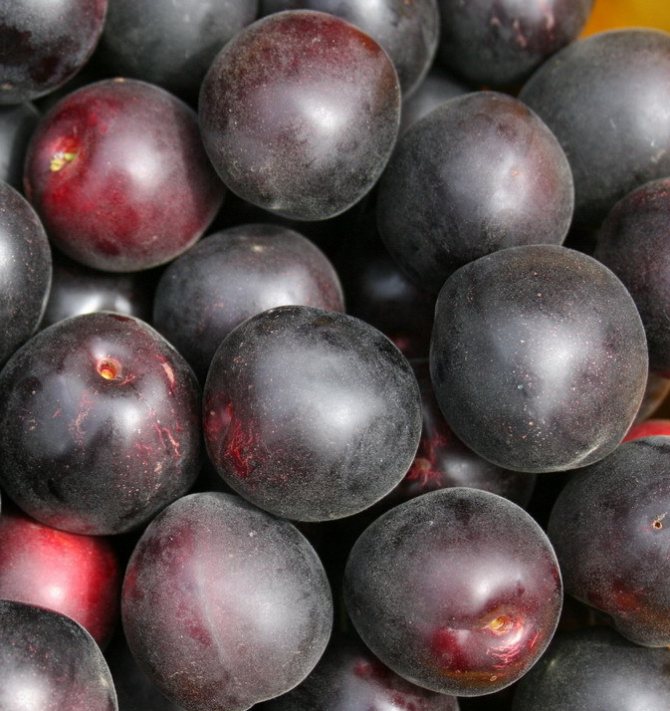
Fruits are numerous, but relatively small. The average weight of one apricot does not exceed 30 g. At the initial stage, they have a greenish color, but in the process of ripening they acquire a brown or blue tint. Covered with a velvety skin of medium density.
The pulp closer to the skin has a pink tint, near the stone it is yellow. The fruit is juicy, fragrant, of medium density. The taste is sweet and sour. The bone is easily separated from the pulp.
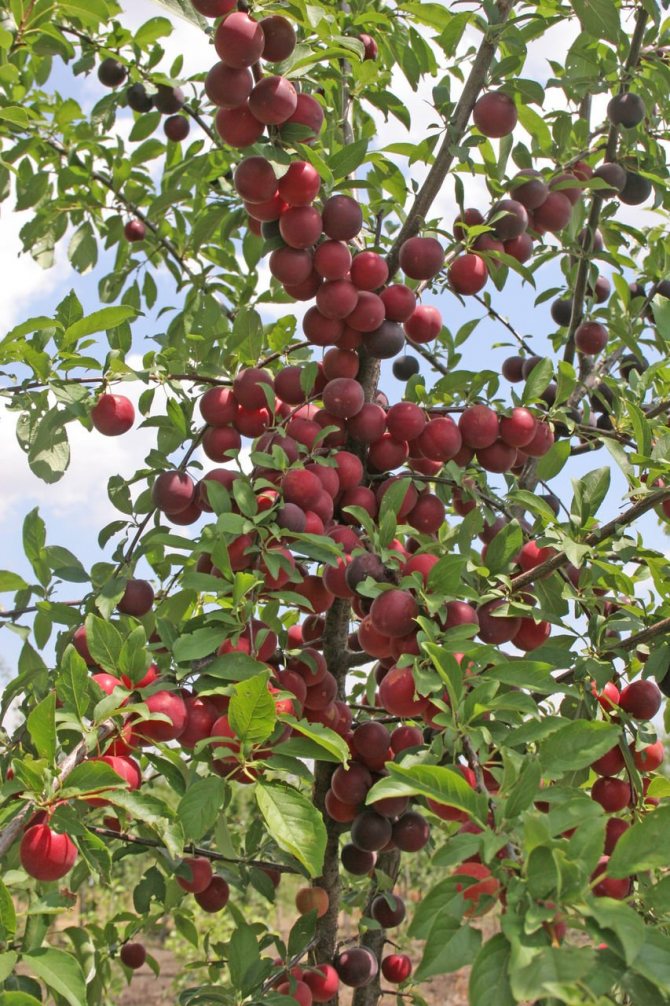
The first fruiting occurs at 4 years, after planting the grafted seedling in open ground. Highly productive variety. The yield of one tree is within 50-60 kg. Bears fruit regularly.
Apricot Black velvet is characterized by high frost resistance and winter hardiness. Also, the variety has a high immunity to fungal diseases and many harmful insects.
This apricot variety tolerates the effects of low temperatures much better than other varieties. Therefore, it can be grown not only in the southern regions, but also in regions with a temperate climate.
Apricot Black Velvet is a versatile variety. Therefore, it is suitable not only for consumption as a fresh dessert, but also for making preserves.
Characteristics of the variety
Apricot Velvet has the strong qualities of apricots and cherry plums. Before planting a crop, it is necessary to carefully study the characteristics and find out if the variety is suitable for growing in certain conditions.
Drought resistance, winter hardiness
The ideal condition for a bountiful and stable harvest is a sunny, calm, warm summer. The plant tolerates low temperatures well. In contrast to the usual varieties of apricots, during recurrent frosts, the flowers do not fall off, and as a result, the yield rises. But the summer drought Black Velvet does not tolerate well. Therefore, it requires regular watering.
Pollination, flowering period and ripening times
The variety is partially self-fertile, therefore it is required to plant pollinators nearby, which include:
- common apricot;
- Chinese plum;
- turn;
- Russian plum;
- cherry plum.
Flowering occurs later than the usual varieties of apricots. The fruits reach technical maturity:
- in warm areas in July;
- in the middle lane in August.
For better yields, it is recommended to plant several Black Velvet seedlings side by side.
Productivity and fruiting
The plant begins to bear fruit from the 4th year.
- small;
- with a velvety skin of medium density;
- multiple;
- weighing no more than 30 grams;
- brown or blue tint;
- fragrant, juicy;
- sweet and sour.
The tree at maturity gives about 60 kilograms of fruit. Bears fruit regularly. The variety is universal. Therefore, apricots are eaten fresh and used for conservation. Harvested on time, slightly unripe fruits without damage are stored for about 4 months in a well-ventilated basement. The harvest is pre-laid in three layers in boxes.
Disease and pest resistance
The plant is resistant to:
These are the most common diseases that commonly affect stone fruits. Due to its high resistance to fungal diseases and systematic preventive measures, the plant gives a bountiful annual harvest.
Pests dangerous for the variety:
Prevention is able to prevent the attack of pests by almost 100%.
How to choose a place and plant it correctly
For planting an apricot, it is necessary not only to find a suitable place and to prepare the planting pit in advance. The speed of development of the tree, as well as the time and financial expenses for care, depends on the correctness of the pre-planting preparation.
Apricot is a light-loving and heat-loving culture. Therefore, a plot is selected for it on the south side with free access to daylight and sunlight.
To prevent damage to the tree by low temperatures, it is better to plant the apricot near the walls of the house or outbuilding.
Young and adult apricot tree does not tolerate waterlogging. The groundwater level should be no closer than 2.3 m. Therefore, it is absolutely impossible to plant it in the lowlands. Also, when planting, be sure to provide good drainage.
Apricot grows well on light loam and loam. The soil should not be heavy, clayey or sandy. Soil acidity within pH 7.
When choosing a suitable place for the Black Velvet apricot, it should be borne in mind that the tree does not tolerate transplanting well. Therefore, the planting site must be a permanent habitat.
Planting an apricot seedling with an open root system in open ground is carried out only in early spring, container plants can be planted from early spring to the second decade of October.
If the planting of the apricot Black Velvet is planned in advance, a planting pit is prepared in the fall. To do this, a pit is dug with a diameter of 0.8 m and a depth of 1.0 m. A drainage layer of stone, broken brick and large branches is laid on the bottom. Then the soil is mixed with humus or humus in the amount of 20 kg. All the resulting mixture is poured back into the pit.
If preliminary preparation has not been carried out, before planting, the soil and the planting pit are enriched with potassium chloride - 25 g, superphosphate - 35 g.
After planting the seedling, the soil is slightly compacted in the hole. The tree is watered with a bucket of water, and the near-trunk area is mulched with sawdust or clean soil.
For fast rooting, it is recommended to treat the roots of the seedling with a special stimulant. This will allow the plant to better tolerate the change of place of growth and adapt to new climatic conditions.
Apricot care Black Velvet includes all procedures for the care of fruit and berry crops:
It is important to do everything on time, especially in the first years after planting.
A healthy apricot will delight every gardener
After the winter season, watering of the apricot begins with its flowering and bud formation. Active irrigation is necessary for the apricot during the active growth of shoots. For this, from the beginning of June to the second decade of July, the tree is watered every week. The depth of soil moisture is 30-40 cm. From the third decade of July, irrigation stops.
The apricot is very responsive to the nutrient composition of the soil, so it needs to be fed annually. In early spring, special complexes with nitrogen are introduced under the crown. You can also sprinkle urea under the crown at 35 g per square meter.
We recommend reading: Contents1 Tractor T-150: characteristics and technical features of management, modifications1.1 Characteristics of the tractor1.2 Engine T-1501.3 Gearbox1.4 Cab of transport1.5 Modifications of the tractor T-1501.6 Advertising: 1.7 → Reference → Articles → Forum2 Bodies ...
Nitrogen-containing fertilizers are added before flowering, after it and when the ovary falls. In early September, the apricot tree is fed with superphosphate - 130 g and potassium salt 90 g. In autumn, fertilizers with nitrogen cannot be used. In late autumn, a layer of organic fertilizers is poured onto the near-stem section.
In the first years after planting an apricot, it needs formative pruning. The best option for this crop is a sparse-tiered crown. Sanitary and rejuvenating pruning is carried out for mature trees. Regardless of its appearance, it is important to cut the branches onto the ring without leaving any stumps. At the same time, all sections are processed with garden pitch. This will prevent gum leakage. Apricot pruning is carried out annually at the very beginning of spring. If the shoots grow very quickly, at the end of summer they are shortened by 15 cm. This is necessary to increase their winter hardiness.
Read also: How to cook apricot jam for the winter: 5 main recipes for the hostess (reviews)
Apricot of this variety is prone to overgrowth. Therefore, it must be cut annually. You cannot dig it out, as you can damage the root system. It is also important to keep the near-stem area clean. Weeds are pulled out by hand.
Despite the high resistance of apricot Black Velvet to low temperatures, it is recommended to cover it for the winter. The trunks of young trees are wrapped with paper or spunbod. Also, the seedlings can be covered with a special spruce spruce dome. For adult apricots, it is enough to mulch the near-stem area with sawdust.
The apricot is propagated by grafting on cherry plum or another apricot. Reproduction by cuttings is also possible. This variety does not propagate by seeds.
Subject to all the conditions for the cultivation of apricot Black Velvet, the tree develops rapidly and brings a regular, abundant harvest of tasty fruits.
While watching the video, you will learn about the apricot black velvet.
Apricot Black velvet is a relatively new variety, but due to its unpretentiousness and taste of the fruit, it is quickly gaining popularity among gardeners.
Have you noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter to tell us.
Comments (5)
Ira
03.04.2018 at 00:15 |
Yes, it’s not an ordinary color and, apparently, taste too, if it’s a hybrid. I would very much like to grow one in my country house, but I don’t know where to get seedlings, I’ll look. The neighbors would be very surprised.Reply
Julia Expert Plodogorod
17.09.2019 at 00:28 |
Hello Ira! We recommend that you purchase apricot seedlings of the Black Velvet variety, like other planting material, in proven nurseries. It is important that the chosen company is located in one place for a long time. Still, it is better to read the reviews first.
When buying on the market, there are no guarantees that exactly what was announced during the purchase will grow. We especially do not recommend purchasing planting material from visiting sellers.Good trees are usually sold by entrepreneurs who value their reputation.
You can choose seedlings both in autumn and spring. But, when planted in spring, plants usually tolerate the first winter better. Although, much depends on the region of residence. If the climate is warm enough, you can try an autumn planting as well.
It is better to buy seedlings at the age of one, maximum two years. But, at the same time, the tree must be sufficiently developed. Before purchasing, it is important to carefully examine the selected copy.
Better to start with the rhizome. It should be healthy, free from rotted or softened areas, plaque, build-up or stains. Dried and brittle places should also not be.
The stem should be straight, strong, without cracks in the bark, mechanical damage, signs of disease. It is important that the side shoots are evenly distributed over the stem, and not only grow on one side.
Another nuance is that it is best to purchase seedlings in a nursery located in the same region where cultivation is planned. If you buy a tree in a place with a warmer climate, it will turn out to be unadapted and will not endure the winter well.
Reply
Maryana
23.07.2018 at 12:41 |
My sister grows such a variety of apricots. Personally, I like it even more than the common types. These apricots are insanely juicy. In cultivation, they turned out to be not picky at all.
Reply
Olga
16.09.2019 at 08:31 |
Hello dear gardeners and gardeners! I also have such a tree. Fruiting is not bad, but the problem is that yellow dots appear on apricots (on almost every fruit). It seems to be not rot, and you can eat apricots, but outwardly the appearance is very spoiled. What could it be? What is the problem?
Reply
Julia Expert Plodogorod
18.09.2019 at 00:37 |
Hello Olga! Perhaps the reason for the appearance of stains on the fruits of your tree is brown spot. This disease is also called gnomoniosis. Most often, this fungal infection affects foliage, less often fruits.
The symptoms that you describe are similar to the initial stage of the development of this disease. During this period, the spots are yellow, not too noticeable, but there are quite a few of them. In this case, the spots have a vague shape. In the process of development of the fungus, the affected fate begins to darken and turn brown, then dry out, and a bright yellow edging appears along the edges.
The next stage is necrosis and cracking of the areas where the spots were previously located. The pulp in this state is difficult to separate from the stone. Another symptom of serious damage is fetal deformation. Closer to autumn, black dots appear on infected apricots - these are the fruiting bodies of the fungus.
This disease not only spoils the appearance of the fruit or crown, but also provokes a general weakening of the plant, worsens its winter hardiness, and reduces the yield of future seasons.
Even if the described disease does not fully correspond to the symptoms that appear on your tree, it still does not hurt to apply general preventive measures and protect the garden from diseases.
So, at the very beginning of spring, it is necessary to carry out preventive treatment of the garden with Bordeaux mixture or HOM preparation. We recommend that you carry out the same measures when preparing plants for wintering.
In addition, it is important to carry out sanitation pruning, remove dried, broken shoots, thickening branches and growing inside the crown. It is important that there is good air circulation and access to sunlight inside the crown.
It is important to maintain cleanliness under the tree, to remove fallen leaves and fruits. Then the infection will not multiply. This is especially true when preparing for winter.
Sometimes such symptoms are triggered by viral diseases. It is difficult to cure a plant in such a case. It is important to maintain its immunity with timely and correct feeding, especially potassium.
It is also important that there are no pests on the plant, especially those sucking, for example, aphids. The fact is that it is they who usually carry various infections.
Reply
"Black velvet": variety description
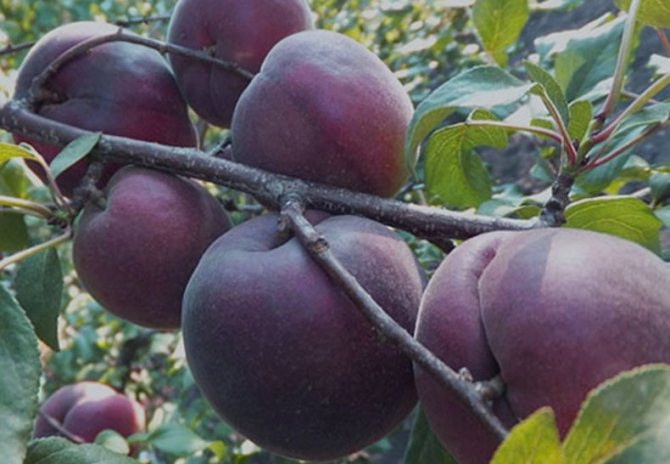
The unusual apricot of the Black Velvet variety was born thanks to the efforts of the Crimean breeders, who crossed the American Black variety with the usual cherry plum. As a result, it was possible to obtain a medium-sized tree, which begins to actively bear fruit in the third or fourth year after planting. The crown is flat, has a rounded shape and is medium thick.
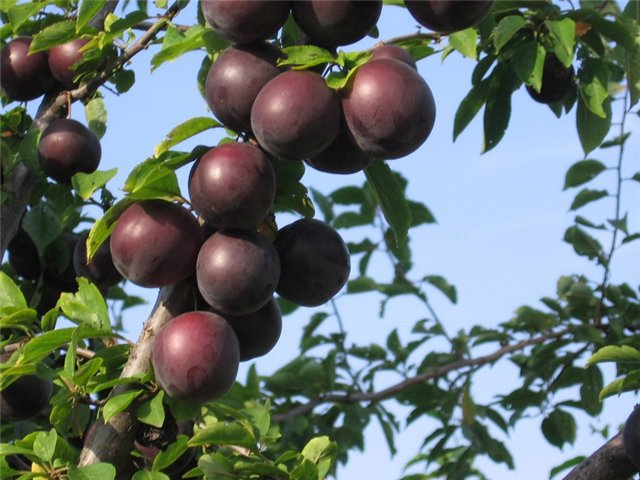
Outlandish dark purple fruits weigh 30 g. Apricot pulp "Black Velvet" is two-colored: yellow in the center and pinkish closer to the skin, which is also one of the main distinguishing characteristics when describing the variety. The fruit tastes sweet and sour, very juicy and aromatic. The stone is medium in size and separates well from the pulp.

Ripening of apricots occurs at the end of July, and after harvesting they can be consumed both fresh and canned. It should also be noted and good transportable qualities
varieties: you can safely transport fruits in boxes over long distances without fear of their appearance.
Choosing the Black Velvet variety for growing in your garden, you should also be aware of its partial self-fertility. This means that to get a good harvest, it is better to plant other varieties of apricots nearby. As for endurance under unfavorable conditions, the black apricot copes well enough (in comparison with other varieties) with winter frosts, has an average level of drought resistance and is able to withstand many diseases.
The history of the emergence of black apricot
The black apricot was born by chance. Somewhere, presumably in Asia, common cherry plum and apricot growing next to each other have become dusty. As a result, fruits of a dark purple color appeared, combining the properties of their parents.
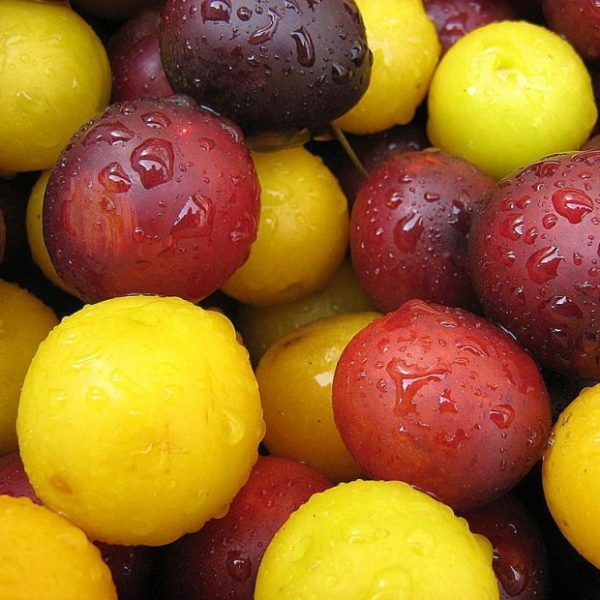


Depending on the variety, black apricot can smell like its relative - cherry plum
A seed of a dark fruit planted in the ground gave rise to a series of varieties of black apricot. At first, it was distributed in the countries of South and Central Asia, then in America and the North Caucasus. Currently, it is moving into central Russia. The first fruits did not taste good, but breeders showed interest in this original berry due to its unusual color. Now they were faced with specific tasks: to improve the taste of fruits, to increase productivity, to increase the frost resistance of the crop. It should be noted that these tasks were solved quite successfully. And a number of varieties have been identified that have good characteristics. Some were included in the State Register.
Sometimes black apricot is called plum apricot or apricot.
Conditions for growing black apricot
As with the cultivation of any other variety of apricot, in order to properly plant "Black Velvet", first you need to understand its preferences in terms of illumination and soil composition.
Where is the best place to plant Black Velvet, lighting
Representatives of the described variety, like the rest of the apricots, will be able to actively grow and bear fruit only in well-lit places. That is, before landing, you will have to determine the warmest and sunniest place on the site
... Failure to comply with this requirement will lead to a decrease in the sugar content of the fruits and a decrease in the total amount of the crop.
At the same time, apricot cannot be called a frost-resistant crop, so do not forget about protecting the place from the north and east winds. In order for the Black Velvet apricot to grow and develop well, it is better to plant it next to a house or other buildings on your site (for example, near a barn, a bathhouse, or between a house and a fence).
Also, when choosing a place, remember that apricot, in principle, does not like stagnant water in the soil, therefore, if there is a high probability of flooding in your area, then, if possible, it is necessary to drain or plant a tree on a hill. Otherwise, the plant will develop poorly or will soon die. The groundwater level should be at least 1.5-2 meters to the soil surface.
Soil for growing black apricot
The second, no less important issue when choosing a place for growing apricot varieties "Black Velvet" is the composition of the soil at the place of planting, which will also determine the characteristics of planting and further care of the tree. Apricot thrives best on light loamy or sandy loamy soils, while heavy clayey or sandy soils most likely will not be able to ensure proper development of the tree.
If you do not have much choice and the soil on the site cannot be called too suitable for the Black Velvet apricot, then make sure that the soil in the pits is not uniform in composition. To achieve the desired effect, clay is mixed with peat and sand in equal proportions, and the acidity of the finished substrate should be close to neutral: not higher than pH 7.0-7.5. Values above this norm will most likely lead to gum flow of the tree, and the fruit will begin to crack the stone. It is possible to achieve the normalization of the acidity level by introducing dolomite flour or other alkalizing substances into the soil.
Recommended reading: 2 EM 120/140/160/180/200 | Promintel-Agro
Black apricot: planting and caring for the "Kuban Black"
I propose to create a branch "Late flowering apricot varieties." For example, we have an epidemic of moniliosis - the time of fogs, April. Maybe there is something to hang on this branch - with flowering end of April-May?: Lamp:
I agree with you the topic is interesting, but we have another problem in Krasnodar, how apricot blooms necessarily a little frost and there is no harvest, from my own experience I will say I planted a late apricot variety, but it blooms like everyone else, but ripens 10 days later
I propose to create a branch "Late flowering apricot varieties." For example, we have an epidemic of moniliosis - the time of fogs, April. Maybe there is something to hang on this branch - with flowering end of April-May?: Lamp:
I propose to create a branch "Late flowering apricot varieties." For example, we have an epidemic of moniliosis - the time of fogs, April. Maybe there is something to hang on this branch - with flowering end of April-May?: Lamp:
Maybe someone will be interested in such information. I really don't know how relevant this is. Quote from the topic: ". The apricot bloom in 2007 was dying with spring frosts, which led to a partial (1-37%) or more (95-100%) folded well-grown buds and quotations. They didn’t know the little sorts of spring frosts (“Esperen Ranniy”, “Da-Huang-Hou”, “Dolgotsutka”, “Nukul Citronniy”, “Raudi Hatif”, “Harvest from Chatenay”). "
Read also: Raspberry "Maroseyka": characteristics, cultivation techniques
". Trivial period of great calm (up to 107-111 dib), increased winter hardness and frost hardness of mali: "Magrien", "Mari de Cenad", "Nagycorosi Bibor 463", 47-L / 11, "Callatis". "Laubert". "Mamaia", 425 / 77-16, "Sulina", 7 (3) -3-70 p, 47-L / 11 (European varieties); "Geogdzhanobad" (Iranian-Caucasian); "Yuan-Xin" (Chinese); Sundrop (American).
It is also a tsikavo, for which every hun-ben-sini, chi down huang-ho that іnshі does not get into the masi for reproduction. Can it be that the abstract on them is needed for show, for the purpose of the Chergov scientific step? And the axis is reality, as it is bachimo strongly seen in writing.
You need to look for Hungary nearby, Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia. You will find such a variety, test it, multiply and earn. A lot of people are walking across the border.
You need to look for Hungary nearby, Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia. You will find such a variety, test it, multiply and earn. A lot of people are walking across the border.
... I think if you search and select such a few trees in the south of Ukraine, there will be a list of their native hardy (late flowering) forms
Try by the way from the gentlemen and in the spring to create one or two heads for the new pagones.
I have not seen any positive experience in dealing with moniliosis due to late flowering. For myself, I decided to choose varieties for other reasons. And against moniliosis, use fungicides. Peaches and cherries bloom after the apricot. And this does not save them from moniliosis.
I believe, based on the example of my several apricot varieties, that resistance to moniliosis is very relative i.e. if the tree is not sprinkled, then any will hurt, and if sprinkled, then it is resistant to moniliosis, it will probably need to be sprinkled less. There is a nursery that has a website with a forum, where the question was asked "Are apricots resistant to moniliosis sick" and what do you think was the answer "Are sick".
Kuban black and Black velvet. Who do they grow up with and what do you say?
The so-called late-flowering apricots have a very weak relationship.
Link article for 2009. There is interesting information about the varieties of tasty, consistently productive, disease-resistant black apricot developed at the Crimean Experimental Breeding Station (in the Kuban?) - Kuban Black and Black Velvet. Who do they grow up with and what do you say?
I have a grafted black apricot, not yet bearing fruit. This culture is very worthy, but, strictly speaking, it is closer to cherry plum than to apricot. This is a hybrid of an apricot with a large-fruited cherry plum.
To search among late branching poles for specimens resistant to moniliosis - I probably would have agreed a couple of years ago :) But: sad: 2-3 years ago, a whole grove of poles that had been abundantly bearing fruit nearby for decades “burned out” for decades:
Strings of color do not flow into the stiffness until moniliose. (It was said about the same)
Now apricot is cultivated in the Samara, Tambov, Kursk, Voronezh regions. Moreover, the varieties are frost-resistant. For example, the Northern Triumph variety - perfectly tolerates severe winters and spring frosts. I wonder if these varieties are planted in the vicinity of Krasnodar, will they react to early spring thaws and bloom at the same time as the local varieties? Or will it bloom later? Or maybe their flowers will not be affected by recurrent frosts?
Of course, you can try, but it seems to me that the flowering will be at the same time as the local varieties.
I will repeat my post 2427 in the topic "Apricot, varieties, agricultural technology"
For any apricot variety, prune early in the summer. The regrown branches will form flower buds, which will bloom 7-10 days later than those that have not been cut off. You will get two flowering periods on the same tree. If the apricot variety is not self-fertile, it is advisable to plant a pollinator in the crown.
There is no need to look for "overseas" varieties of apricot, which bloom late and are not afraid of recurrent frosts. There is a Ukrainian variety called Frost-resistant. The author of the variety is L.I. Taranenko (Donetsk Experimental Breeding Station). The tree is medium-sized, self-fertile. The variety has high winter hardiness (up to -30 * C), drought-resistant, fast-growing, fruitful. Fruits are of medium ripening. The size of the fruit is medium (35-40 g), the skin is light yellow, usually without blush. The pulp is light yellow, juicy.
I will repeat my post 2427 in the topic "Apricot, varieties, agricultural technology"
For any apricot variety, prune early in the summer. The regrown branches will form flower buds, which will bloom 7-10 days later than those that have not been cut off. You will get two flowering periods on the same tree. If the apricot variety is not self-fertile, it is advisable to plant a pollinator in the crown.
I will repeat my post 2427 in the topic "Apricot, varieties, agricultural technology"
For any apricot variety, prune early in the summer. The regrown branches will form flower buds, which will bloom 7-10 days later than those that have not been cut off. You will get two flowering periods on the same tree.If the apricot variety is not self-fertile, it is advisable to plant a pollinator in the crown.
Read also: Top-10 varieties of remontant raspberries for the Moscow region
and one more thing - the same topic now, on a branch of apricot, varieties, agricultural technology. there are also interesting posts (partly in Ukrainian, if I understand correctly - the tsunami apricot blooms later - and this is not because it was transplanted in the fall, I recommend that those interested read it)
Basic rules for planting "Black Velvet"
The process of planting "Black Velvet" can be divided into two main stages: the preparation of the pit and the direct placement of the apricot seedling in it. In both cases, there are specific features that cannot be ignored to obtain a fruitful apricot.
Important nuances when preparing a landing pit
To plant medium-sized varieties, which include "Black Velvet", it is necessary to dig a hole 60 x 60 x 70 in advance, then place a drainage layer on the bottom (for example, from gravel) and lay out fertilizer (horse humus or humus in combination with potassium chloride - 20 g and superphosphate - 30-40 g).
Read also: Apricot pits - benefits and harms, useful properties and contraindications for cancer, how to take, video
How to properly plant a "Black Velvet" seedling
Planting of apricot seedlings of the Black Velvet variety should be carried out only with the arrival of spring (for a bare root seedling) and from spring to October (when planting container plants). Having placed the seedling in the hole and spreading its roots (you can immediately tie it to the peg with soft twines), start sprinkling them with soil mixture, but just keep in mind that the root collar should be 5-7 cm higher than the soil level.However, the whole procedure for planting this apricot varieties are no different from planting any other. After filling the hole with the seedling with the prepared substrate, it remains only to water the plant.
Landing features
Growing apricot Black Velvet on a personal plot basically follows the same rules that are developed for conventional apricots.
Recommended timing
The timing of planting Black Velvet in the ground depends on the type of seedling:
- bare-root are advised to plant with the onset of spring;
- container - from early spring to mid-autumn.
Choosing the right place
The area of the garden where the Black Velvet apricot will grow should have the following features:
- good illumination (ideally south side);
- next to it, a wall of an outbuilding is desirable, capable of serving as a shelter from the wind;
- groundwater should lie at a depth of at least 1.5–2 m from the surface;
- light sandy loam or loamy soil with an acidity close to neutral.


Poorly tolerates this variety:
- placement in the shade;
- stagnation of water at the roots;
- heavy soils with a predominance of clay and sand.
What crops can and cannot be planted next to an apricot
It should be remembered that the apricot is reputed to be an individualist and rather whimsical in the choice of neighboring plants.
He will react positively to those growing nearby:
- apricots of the same or different varieties;
- potential pollinators (cherry plum, thorns, some types of plums);
- dogwood.
Apricot will not like the close proximity:
- cherries;
- walnut;
- cherries;
- red rowan;
- apple trees;
- pears.
A warning! You should not plant raspberry or currant bushes next to Black Velvet - many pests that infect them pose a significant danger to the apricot.
Selection and preparation of planting material
The best option for growing Black Velvet apricots in your own garden is to purchase a seedling at the age of 1-2 years in a specialized nursery.
Signs of a quality seedling:
- the plant is healthy, has an attractive appearance;
- bark without visible damage, dried and flaking areas;
- the root system is lively, developed and elastic.


Just before planting, the branches of the seedling can be cut off.
Important! The roots should not be cut - it is advisable to just spread them out.
Landing algorithm
Correct planting of apricot Black Velvet takes place in several stages:
- if there are several seedlings, the distance between them should be observed (at least 4–5 m);
- the size of the pit for planting is 0.8 per 1 m, it is being prepared in the fall;
- drainage should be poured onto the bottom (gravel, broken brick, pieces of large branches), then - fill the hole with a mixture of soil with humus, peat and sand;
- lower the seedling into the hole, carefully spreading the roots and making sure that the root collar is 5–7 cm above the surface;
- fill the hole with prepared soil mixture, pour a bucket of water over the apricot, mulch the soil with earth or sawdust.
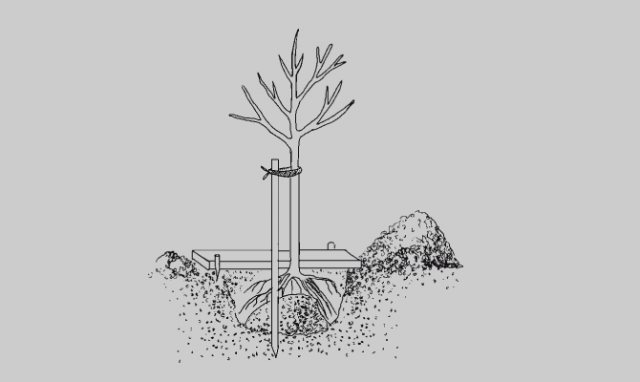

Attention! If the root system of the seedling is highly developed, the size of the planting pit should be increased.
What you need to know about caring for an outlandish apricot
Like the usual yellow apricot, its black variety needs proper and timely care. That is, you are required to regularly water using a sufficient amount of water, feed the plant and follow the rules for pruning. It is also important to know how the apricot tree is pollinated, as the partial self-fertility of the Black Velvet variety may require manual pollination.
Watering frequency
All fruit crops need a lot of moisture during the period of active growth of shoots, and, of course, apricot is no exception in this regard. Therefore, in the first half of summer, it is necessary to water the "Black Velvet" 4-5 times a month at the rate of 1-2 buckets of water per adult tree. Adequate watering is also very important in the period before and during the flowering of the plant, that is, from May to June and a few weeks before harvesting. In the second half of July, watering is completely stopped, otherwise the growth of shoots may be delayed, which will negatively affect the winter hardiness of the plant.
Plant feeding
With the arrival of spring, fertilizers are applied to the "Black Velvet" apricot tree trunk, which contain nitrogen
... A fairly popular top dressing is considered
urea
- 40 grams of it is introduced into the soil in several stages: before the flowering of the tree, after its flowering and with the massive fall of the ovaries. With the arrival of autumn, in September, 150 g of superphosphate and 100 g of 40% potassium salt should be poured into the trunk circle. In the future, in late autumn and early spring, the land is fertilized with organic fertilizers. Autumn feeding should be carried out with formulations without nitrogen content.
How to prune a black apricot correctly
Apricot varieties "Black Velvet" are prone to the formation of root growth, which requires regular pruning (excess shoots are cut out near the ground, since they consume a lot of nutrients, and the yield is almost always very low). As for the branches, when buying a young seedling, they are cut by almost a third, which contributes to the quick establishment of the crown.
It is worth remembering that apricot often grows faster than other trees in the garden, which means that with normal development it will have to be cut more than others, which is especially true for a later age.
With a reduced growth, the branch is cut to older wood (by 2-3 years).
It is important to perform the pruning procedure every year in early spring (before bud break). It is highly undesirable to prune branches in late autumn.
If a branch is completely cut, the cut must be carried out at the very base (the so-called "cut per ring"), without leaving any stumps.
In the case when the Black Velvet apricot grows too intensively, young strong shoots are pruned at the end of summer (cut about 10-15 cm). This helps the branches begin preparing for winter (they thicken).

The subtleties of growing and care
Like most varieties of apricot, Black Velvet is unpretentious, and care for it is standard, which comes down to watering, feeding and pruning. And yet it does not hurt to brush up on the basic techniques and rules.Moreover, it will be especially useful for novice gardeners.
When and how to water the apricot Black velvet
This variety, as noted above, is not drought-resistant enough, but it does not like dampness and high humidity. It follows that it needs to be watered often, but not too abundantly. It will be enough to water once every two weeks, 2-3 buckets for a young (up to 3-4 years old) tree. With the onset of fruiting, the dose is slightly increased. In hot weather, it is advisable to water the crown of the tree with sprinkling. The day after watering, the soil around the tree must be loosened to give oxygen access to the roots.
Top dressing
For the first four years, the apricot does not need fertilization, since enough was applied during planting. In the fifth year, when the tree has already grown enough, has begun to bear fruit and the supply of nutrients in the planting pit has depleted, you need to start feeding.
Table: types of fertilizers for apricot Black velvet, the amount and timing of application
| Fertilizer | Application rate | Timing and frequency |
| Humus, compost | 5 kg / m2 | Digging in the fall, once every three years |
| Ammonium nitrate | 20 g / m2 | Every spring |
| Infusion of mullein 3 liters per bucket of water Infusion of bird droppings 1.5 liters per bucket of water Infusion of freshly cut grass 5 kg per bucket of water After a week, one of these infusions is diluted with water 1 to 5 | 5 l / m2 | Immediately after flowering and two more times with an interval of 2 weeks |
| Superphosphate | 30 g / m2 | Every year in the fall for digging |
| Boric acid | 0.2% solution | During the flowering period, leaf treatment to increase the number of ovaries |
Pruning apricot
Pruning any tree, including apricot, is the most important agricultural technique. Typically, the following types of pruning are used for apricot:
- formative,
- sanitary,
- regulatory.
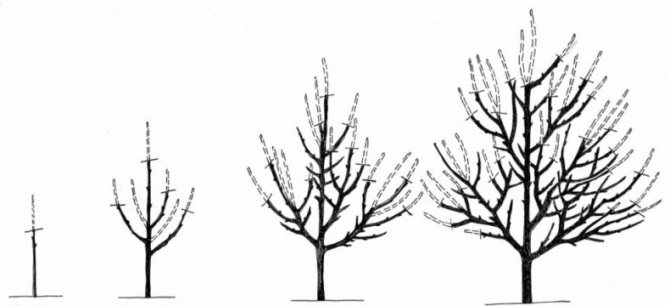
Formative crown pruning
Most important. It is she who lays for many years the correct structure of the crown, its height, the uniformity of filling the internal space. As a result, this increases productivity, facilitates care and harvesting.
Most often, when forming a crown, a sparse-tiered formation is traditionally used. Every experienced gardener is familiar with it, methods of its creation are described in many sources.
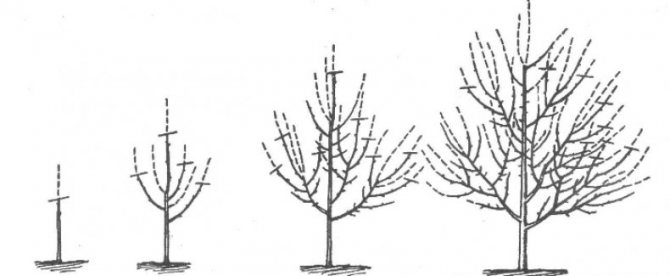
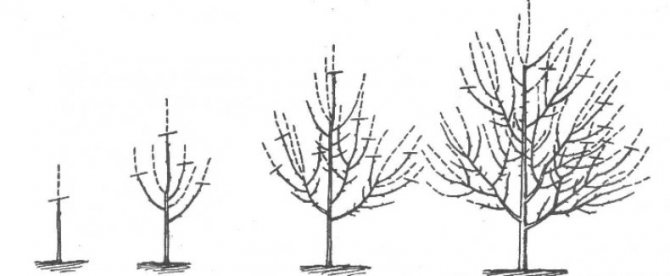
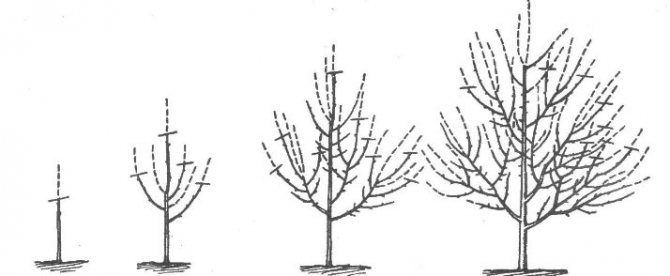
Recently, a new and promising crown shape has appeared, which is called a "bowl" or "vase". It has certain advantages - uniform illumination of the tree and growth control. This shape is ideal for black velvet apricots. The order of its creation is as follows.
- The first step was taken during planting - the seedling was cut to a height of 60–80 cm.
- Then you need to select 4 good, multidirectional buds, starting from the top of the seedling so that the distance between them is about 15 cm. All the buds below the selected ones are dazzling.
- If the shaping was started late, at the age of three, then the three best shoots are left, the rest are cut out “on the ring”. The central conductor is cut into the upper bud (shoot).
- In subsequent years, it is necessary to support the growth of skeletal branches so that they are equivalent and none of them has gone ahead, becoming the central conductor. For this purpose, the shoots are cut so that their tops are in the same plane.
- All shoots growing inside the crown are regularly cut out.
- On each skeletal branch, two branches of the second order are formed with a distance of 50-60 cm between them.
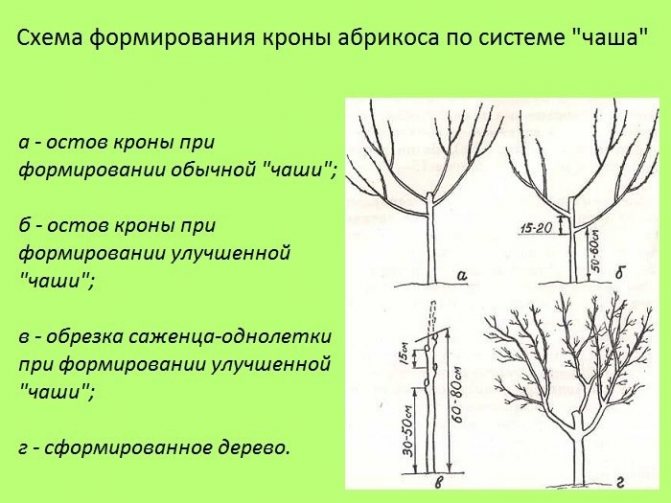

Crown shape "bowl" - the best option for Black Velvet
This completes the formation of the crown, from now on the hacksaw is no longer required, and all unnecessary shoots that arise that grow inside the crown are easily removed with a pruner.


Apricot crown shaped like a "bowl" is great for Black Velvet
Annual shoots, if tied to stakes and given a horizontal position, are densely overgrown with fruits and give a greater yield.
Sanitary & Regulatory Trim
Conducted regularly, as needed.Sanitary, as usual, consists in removing dry, damaged and diseased branches. Regulating - in the removal of shoots and tops growing inside the crown, transferring the growth of shoots outward. And also in the summer, one-third of annual shoots are pruned (chasing), which stimulates lateral branching, on which a large number of flower buds are formed next year.
Pruning rules
All types of pruning must be carried out in compliance with certain rules.
Recent Entries
5 of my favorite tomato varieties that are great for pickling 7 super early and delicious potatoes to plant in 2020 6 rare 2020 tomato varieties that will bring you a decent harvest
- Only sharpened tools are used - saws, knives, secateurs.
- Before trimming, the tool is disinfected with antiseptics - 1% solution of copper sulfate, alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, etc.
- When pruning branches, hemp should not be left. If the branch is removed completely, the cut is carried out “on the ring”. Cutting off annual shoots, leave wood 0.5–1 cm above the upper bud.
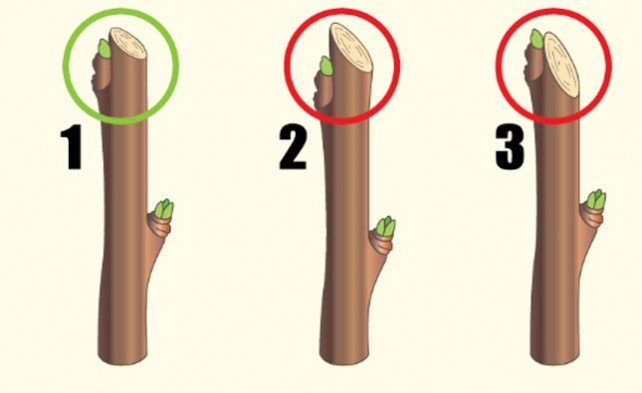

1 - correct pruning of the shoot; 2 - too much of the shoot is left above the bud; 3 - the slice is too close to the kidney
- Sections are covered with a thin layer of garden varnish or garden putty based on natural materials such as lanolin or beeswax.
When buying a garden varnish, one should give preference to one that does not contain petroleum products. The best bases for garden varnish are natural ones, for example, beeswax, lanolin.
Features of growing apricot Black velvet in the Moscow region
Although initially this exotic newcomer was zoned for the North Caucasian region, it quickly (albeit not widely) settled throughout the Middle Belt, including the Moscow region. This was due to its high frost resistance, and especially the resistance of flower buds to recurrent frosts due to late flowering.
In general, the cultivation of this apricot does not require any extraordinary methods and methods from Muscovites. These are the usual, familiar techniques for them, which are also used for other cultures, people from the south of the country.
- Pre-winter water-charging irrigation.
- Autumn sanitary pruning.
- Shelter of young trees with various materials from frost - spunbond, roofing felt, mini-greenhouses made of film, etc.
- Lime whitewashing of boles, followed by tying with roofing felt to protect against hares.
- Warming of the trunk circle by mulching with straw, sawdust, etc., followed by snow cover to a height of up to 60 cm.With the onset of spring thaws, the snow must be shaken off from the trunks in order to avoid damping, which often apricots are exposed to.
- In the spring, you need to carefully examine the bark of trees for the detection of frost holes, which quite often appear during temperature fluctuations. If cracks are found, they are cleaned with a sharp knife and a steel brush to a healthy bark, treated with a 1% solution of copper sulfate and covered with a thin layer of garden varnish.
"Black velvet": advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Apricot "Black Velvet", despite its exotic and unusual appearance, has not yet achieved universal love and recognition from gardeners. However, in fact, this variety has a number of advantages that distinguish it from other varietal varieties of apricot.
The main ones include:
- High quality fruit (well suited for long-term storage, can safely tolerate transportation) If they are collected until fully ripe and immediately removed to a cool place, then with good ventilation they can be safely stored for 3-4 months.
- Small tree size, compact and flat-round crown with an average growth of branches of about 15-20 cm per season.
- The variety has the highest winter hardiness among other black apricots.It can even be compared with cherry plum varieties, which were specially adapted to the conditions of Siberia in terms of the level of winter hardiness.
- Regular fruiting and high yield (compared to other apricot varieties).
It should also be noted that the black apricot is more resistant to disease and frost (especially to recurrent cold snaps at the end of winter) than its yellow brother. So, this variety is much less likely to affect moniliosis, clasterosporium and cytosporosis, which has a positive effect on the regularity of its fruiting. "Black Velvet" can be planted in regions with a more severe climate (for example, in the middle lane, up to Moscow or the Volga region).
We recommend to read: Grapes: growing from seeds at home, care features
The relative disadvantages of the Black Velvet variety are the small size of the fruits and poor pollination of the apricots (the variety is partially self-fertile). In the latter case, you will need information on how to manually pollinate an apricot.
Read also: Diseases of apricot trees and their treatment: the correct fight against diseases of apricot photo
As you can see, it cannot be argued that apricot "Black Velvet" is devoid of drawbacks in cultivation, however, a large number of its positive characteristics still dispose to its cultivation on its site.
Description and characteristics
The characteristics of a tree include a description of the tree's height, the appearance of the tree, fruits, the presence of resistance to diseases and adverse conditions.
Tree size
The apricot is medium in size, reaching a height of 2-2.5 m, the tree requires regular pruning to maintain a constant crown shape. Black velvet is characterized by a round crown with a spread type.
Fruiting
The terms of ripening, fruiting and flowering are average. Fruit ripening occurs from the 3-4th year of the growing season of the tree. Until this time, the plant is gaining growth, taking root, and increasing the number of fruiting shoots.
Pollination and flowering period
The variety is partially self-pollinated, the tree is capable of independently fertilizing about 20% of the buds. A pollinator is required to increase yields. Suitable for this are apricots, peaches or other stone fruits, with the same ripening period as Black Velvet. The flowering period depends on the growing region. In the south, the tree blooms in mid-July, in the north in early August.
Ripening time and yield
Ripening of berries varies from early August to mid September. It depends on the region of growth. High-yielding variety. At the peak of fruiting, from 50 to 60 kg of apricots are removed from the tree.
Taste and use of fruits
The palatability of the fruit is high. They have a sweet and sour pleasant taste. Outside, the skin is dark purple, almost black. Inside, a yellow pulp opens, which is difficult to separate from the stone. Drupes are processed into preserves, compotes, jams, food additives. They are sold because they are stored for a long time and can be easily transported.
Diseases of apricots
The tree is attacked by fungi with a decrease in immunity. This is due to a decrease in immunity, with improper agrotechnical manipulations.
Moniliosis
A fungal disease that can destroy most of the crop. Gray growths appear on the bark of the tree, foliage and shoots dry up and fall off. Fruits, being on a branch, burst, rot, flow and fall off. For control and prevention, antifungal fungicidal drugs are used.
Important! Moniliosis is capable of destroying more than 50% of the crop.
Coccomycosis
It appears as small spots on the leaves and shoots of a brown-brown color with a diameter of no more than 2 mm. They quickly spread throughout the plant. The fungus is transferred to the fruit. At the same time, they have time to mature, but they lose their taste. The micelles of coccomycosis spread very quickly throughout the plant.
Clasterosporium disease
The fungus infects all aerial parts of the apricot. Small specks 2 mm in diameter, red-brown or yellow-brown in color, are formed on the leaves. A red border forms around the spots, which is a hallmark of the disease. The center of the affected area dries up, then dies and falls out. Thus, holes with a red border appear on the foliage.
Pest exposure
In addition to diseases, the juicy fruits of the apricot infect harmful insects. They feed on foliage or drupe juice, get inside and completely eat out the inside.
Weevil beetle
A group of medium-sized insects, body length varies from 4 to 6.5 mm. On the front part there is a proboscis, with which the weevil makes its punctures in the leaves and fruits, sucking out the juice. The fruit variety is activated at the end of May. During the formation of the kidneys, it penetrates and causes them to cry.
After budding and the formation of ovaries, the beetle makes punctures in the fruits. Then the female lays eggs in them, in 1 month new individuals are formed, which actively feed on apricot juice. Weevils damage the drupes and make them unusable.
Khrushchi
May beetle larvae damage the root system of the tree. In the soil, the beetle goes through the entire life cycle, it lays the larvae, hibernates, pupates and feeds. The first 2 years, when the mouth apparatus is not yet fully developed in the beetles, they feed on humus and humus.
By the 3rd year of life, a gnawing mouth apparatus is formed, after which the beetles begin to feed on the roots of the tree, causing damage to it. The yield of apricots decreases, the roots do not absorb enough nutrients and minerals, which affects the immunity and health of the crop.
You can get rid of beetles with the help of insecticides, traps and manual extermination.
Drought resistance, winter hardiness
Winter hardiness of Black Velvet is high. The plant is able to withstand temperatures down to -38 ° C. The buds also tolerate frost easily, which keeps the tree productive and healthy.
The drought resistance of the tree is average. When grown in the south, the tree needs regular and abundant watering.
Short description
Velvet is a hybrid. Black apricots are best propagated by seeds. Experts say: in this way, you can get seedlings that can withstand frosts down to -45 ° C.
According to the description of the Black Velvet variety, it becomes clear that the slow development of the tree and its fruits is the main plus, since growth and flowering fall on the period when the frosts have already passed. Such vegetation has a beneficial effect on the yield percentage, making it high.
That is why many gardeners plant black apricots in central Russia, more often in the Moscow region.
Appearance
The tree is of medium height, sometimes it resembles a large bush. For a long time, the fruits of the black variety have a green color, but a few weeks before they are fully ripe, they darken, acquiring a rich light black shade.
Description of fruits
According to their characteristics, all fruits of apricot trees are small in size, round, oblong in shape. The harmonious combination of sweetness and sourness is another significant characteristic. Sometimes the fruit can be more acidic.
The pulp of the apricot is juicy, but does not flow. The bone is easily separated from the pulp. The aroma is bright and intense. The fruits can be eaten both fresh and ready-made: roll them up, making compotes or jam.
When cooking, you should periodically try the workpiece, since the variety can give sourness. The black color of the fruit is the main feature of this apricot.
Positive sides
Typically, apricot tree species need so-called cross-pollination: several trees on the site pollinate each other. Cherry plum, plum and other apricots are suitable for pollination of Velvet.
However, gardeners do not always have the opportunity to plant several trees in one area. But even in this case, an apricot of the Black Velvet type is perfect, because.he can pollinate himself.
This variety of apricots is considered rare. In addition, Velvet has excellent immunity to fungal diseases, moniliosis, clasternosporiasis and cytosporosis.
Diseases and pests
All varieties of black apricot are highly immune to fungal diseases and major pests. An almost complete guarantee of avoiding diseases is the regular implementation of a complex of sanitary and preventive measures. Therefore, one should not neglect them.
Table: how to prevent the appearance of diseases and pests
| Events | Duration of the | Scope of work |
| Collection and disposal of fallen leaves | Fall | Leaves and cut branches are burned. The resulting ash is collected for use as fertilizer. |
| Sanitary pruning | Late fall | |
| Digging the soil | Late fall | You need to dig up the ground with a flip of the layers. In this case, wintering pests will be raised to the surface and may die from frost. |
| Inspection and cleaning of the bark | Fall | The bark of the tree is examined, if cracks are found, it is cleaned to healthy tissues, disinfected with a 1% solution of copper sulfate and covered with garden varnish. |
| Whitewashing of trunks and branches | Fall | It is carried out with a solution of slaked lime with the addition of 1% copper sulfate. Prevents sunburn of the bark and inhibits the movement of insects. |
| Spraying with a 3% solution of copper sulfate | Autumn, spring | It can be replaced with a 3% solution of Bordeaux liquid or a 5% solution of ferrous sulfate. |
| Shelter of young trees from frost | Late fall | It is convenient to do this using a frame made of wooden bars, poles or plastic pipes. The frame is covered with polyethylene or spunbond. |
| Protecting tree trunks from hares | Fall | Roofing material, old linoleum or other improvised materials are used, wrapping tree trunks. |
| Installation of trapping belts | Early spring | For manufacturing, such improvised materials as film, roofing material, etc. can be used. |
| Treatment with complex preparations against fungi and insects | Early spring | Apply:
|
| Systemic fungicide treatments | After flowering and before fruit ripening at intervals of 2-3 weeks | You can use various drugs (preferably biological). Closer to harvest, drugs with a short waiting time are used. For example:
|
The main diseases of apricot
Apricot is most often infected with fungal diseases:
- clotterosporiosis. The spores of the fungus on the leaves germinate and form small brown or reddish-brown dots on the surface. As the dots grow larger, they turn into spots. If the air humidity is high, the process proceeds violently. In 10–15 days, the size of the spots reaches 5–10 mm, the inner part dries up and spills out, holes are formed;
- moniliosis. Spores of this fungus are carried on their paws by bees along with pollen when collecting nectar. Therefore, flowers are the first to suffer, followed by shoots and leaves. The affected parts wither, sag, as if scorched by a flame;
- cytosporosis. It occurs when there are unhealed wounds and cracks. Reproducing, the fungus causes the destruction of the bark, which, in turn, provokes gum leakage. Treatment is reduced to cleaning the damaged areas to healthy bark and wood, treating the wound with a 1% solution of copper sulfate and antifungal drugs.
Photo gallery: how apricot can get sick
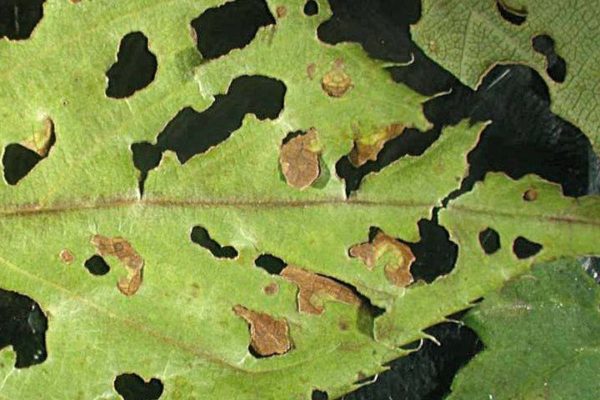


In 10-15 days, the size of the spots reaches 5-10 mm, the inner part dries up and spills out, holes are formed


Reproducing, the cytosporosis fungus causes the destruction of the bark


The affected parts wither, sag, as if scorched by a flame
Apricot pests
Apricots can also be attacked by insect pests.
Weevils
Weevils (small bugs with a long proboscis) hibernate in cracks in the bark, fallen leaves, and topsoil. When carrying out autumn preventive measures, the vast majority of these insects will be destroyed. The survivors, having awakened from hibernation, will climb the trunk (if not stopped by the hunting belt) to the crown. There they begin to satisfy their hunger, eating buds, buds, leaves, shoots, ovaries. At an early stage, when spring has not yet fully come into its own, and it is still cool in the mornings, and the air has not warmed up above 5 ° C, you need to go out into the garden, spread a cloth or film under the apricot tree and simply shake off the weevils sitting on them ...
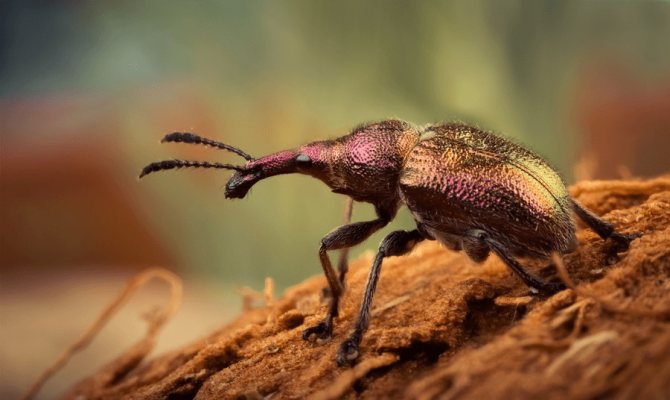


Weevils are small, beautiful bugs with a long proboscis
Treatment with DNOC or Nitrafen, planned for this time in preventive measures, should completely rid the gardener of annoying guests.
Khrushchi
In addition to weevils, many different beetles swarm around garden and vegetable gardens - April, May and others. All of them, having fed up with the first young greens, begin to lay eggs in the soil, from which larvae crawl out at the beginning of June - they are called beetles. In the weevil they are small - 4–6 mm, in the May beetle - 20–25 mm, the largest - in the April beetle - reach a length of 35 mm. These larvae feed on plant roots. Crunchy for young apricots is a great danger. You can fight them using the drug Diazinon (by treating the soil according to the instructions). For 20 days of action, it will cause irreparable damage to the pest colony. Does not accumulate in soil and fruits.


For the roots of a young apricot, crustaceans are a great danger.
Aphid
Aphids are a frequent visitor to gardens and vegetable gardens. Although there are many plants that are more tasty for her on the site, sometimes she does not disdain apricot either. You can find it by the folded leaves. If you expand them, you can see many small insects of black, green, white and other colors, depending on the type of aphid. It can eat not only leaves, but also young shoots. The fight consists in the mechanical collection of rolled leaves, followed by treatment with insecticides, for example, Decis, Fufanon.
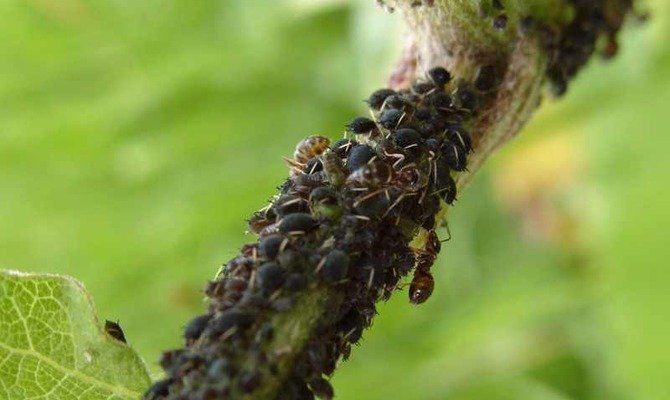


Aphids can eat not only leaves, but also young shoots
Features of growing velvet apricot
Apricot Black velvet is propagated by grafting using rootstocks of other apricots, plums, cherry plums. Can be propagated by Velvet and cuttings. Some experts advise trying bone propagation.
But this should be done with caution: you can create a new apricot variety, which will differ significantly in characteristics from the main type.
Seat selection
To choose the right landing site, follow a few simple rules.
- Give preference to the south side, or the area that is closed from strong northerly winds. The site must be well lit. The ideal location would be the south side near a fence or house.
- Pay attention to the ground. Black apricot is quite unpretentious, but it grows and develops poorly in soils in difficult clay areas, or where the percentage of acidity is high.
- Try to avoid areas with low planting, as well as areas where there is little groundwater. Such lowlands are dangerous for seedlings due to low moisture levels and cold wind currents. The result: significantly reduced yields.
If the soils are too close to the surface
If, for some reason, in your garden plot, groundwater is located too close to the ground, then there are several ways for you to plant apricot seedlings.
The first way is to plant a seedling in a "barrel":
- dig a hole;
- pour a few cm of drainage on the bottom of the pit;
- fill it with a few cm of sand, humus, peat or compost;
- on the previous layer, place the barrel without a bottom and a lid: the total height of the barrel should not exceed 1.5 m above the ground.
Such a planting principle will reliably protect the root system from strong groundwater, and, in addition, completely protect the tree trunk and lower branches during heavy snowfalls.
Where did these hybrids come from - black apricots
Black apricots (actually, not jet black, but red-purple or deep purple) are not the result of deliberate efforts of breeders. The new hybrid was the result of accidental cross-pollination of apricot and cherry plum. From the first, he inherited the characteristic aroma of the fruit, from the second - the bone, which is problematic to separate from the pulp.


The selection achievements of nature sometimes turn out to be more successful than the results of the purposeful work of specialists, black apricots are evidence of this
Specialists have improved the selection achievement of nature. Black apricots have many undeniable advantages:
- bloom at the latest among all stone fruits (as a result, the risk of falling under return frosts is minimized);
- good immunity against moniliosis, cytosporium, clasterosporium;
- frost resistance of both the tree itself and the buds (leaf and flower) due to the longer duration of winter "hibernation" on average up to -30 ° C;
- almost annual fruiting with rare interruptions (due to high frost resistance and unpretentiousness);
- good yield (30–40 kg in optimal conditions, up to 20 kg in more severe climates);
- self-pollination of most varieties (the tree does not need "companions" for the mass formation of ovaries);
- in most cases - slow growth, compact crown (black apricot is more a bush than a tree, reaches a height of 2.5–3 m, the crown is not prone to thickening);
- good adaptability (the ability to develop in different types of soil, to produce crops with a shortage of heat and light in summer, to endure waterlogging and drought).


Late flowering of black apricots in regions where return frosts in spring are by no means a surprise increases the likelihood that the flowers will not be affected by the cold.
They also have disadvantages:
- the taste of apricots (they are not honey-sweet, but noticeably tart, with a noticeable sourness, but they make wonderful homemade preparations);
- fruit size (less than a classic apricot, a little more cherry plum);
- watery and palpably fibrous pulp, difficulty in separating the bone.


Black apricot jam turns out to be unusually dark, but amazingly tasty and aromatic
Based on the description of the hybrid, we can conclude that black apricot is a suitable crop for central Russia, where classic orange apricots do not always survive. Its crops are obtained even in the Urals and Siberia.
Video: what are apricot-cherry plum hybrids
Correct care
Caring for this type of tree is not much different from the standard one. The trees themselves require special care. This is necessary to limit the early ripening of the fruit.


Black Velvet apricot requires special care
Watering the plant
Immediately after planting, the seedlings must be watered regularly for active growth. Experts advise doing this every 2 weeks in a volume of no more than one full bucket. By the end of July, watering should be stopped, since there is no need for it.
The plant has already stored water. The active growth of branches and the formation of young shoots begins.
If watering does not stop on time, the branches will not have time to ripen before the frost begins, which will affect the yield.
Positive qualities of the variety "Kuban Black"
Advantages of "Kuban Black" apricot, which distinguish this variety from some other fruit trees:
- This apricot / plum hybrid is distinguished by its late flowering. The trait is very positive, as it helps to protect flowers from freezing. Indeed, quite often the winter cold can manifest itself even when spring is already on the calendar, especially at night.
- The variety is quite resistant to various kinds of diseases.
- Black apricot "Kuban black" is not capricious, does not create difficulties in planting and care, almost every year it bears fruit.
- Apricot firmly tolerates winter and spring frosts due to a fairly long dormant period.
- If you water this black apricot correctly, the growth rate will be low, and the tree itself will be compact. This will facilitate maintenance, pruning and harvesting.
- Drought tolerant.
Read also: Gerdela and apricot - what's the difference? Let's figure it out together!
We recommend to read: How to install a heat metering unit in a high-rise apartment?
To settle such an original inhabitant as a black apricot in your garden is the dream of many gardeners. Indeed, it makes sense to try to grow this unusual fruit tree. Indeed, with proper care, a rich harvest of delicious juicy apricots of an interesting color will not keep you waiting.
Reviews of gardeners about the variety
Black apricot is not so exotic for Russian gardeners. Dozens of varieties have been bred and successfully grown. The fruits ripen in the conditions of the Moscow region, the Volga region and even Siberia. Simultaneously with the popularization of culture, its selection continues.
Svetik84
Alena, 45 years old, Perm: “Apricot Black velvet has been growing on my site for 7 years already. From the third year, 8-10 boxes of fruits were collected. They keep well in the cellar until mid-winter. The plant is frost-resistant, so the harvest has time to ripen to the end. "
Lydia 60 years old, Krasnodar: “Apricot Black velvet is pleasant for its keeping quality, unusual color, pleasant taste. 2 trees of this variety grow on the site. We collect a large harvest from them, sell part of them, process the other and use fresh. The plant requires regular and abundant watering, otherwise it is unpretentious. "
Vladimir, 39 years old, Novosibirsk: “Apricot Black velvet has been making us happy with its harvest for many years. The main thing is not to overexpose the fruits on the branch, otherwise they overripe, are stored less. The tree is unpretentious to care for, tolerates winter well.
This is not to say that you cannot do without black apricot. But if the gardener wants something exotic, then why not please yourself and your loved ones. There are a lot of varieties of this original fruit. And growing is not difficult if you adhere to all the rules for planting and care.
What kind of fruit is a black apricot?
Black apricot is considered a novelty that is just beginning to spread across Russian gardens. However, this fruit was described by Michurin. The miracle was created by nature itself, dusting the nearby growing cherry plum and apricot. Some of the gardeners tasted the fruit, appreciated the taste and sowed a seed. This is how the black apricot appeared.
Breeders all over the world, including Russian ones, cross varieties to nullify the disadvantages of the hybrid and multiply its advantages.
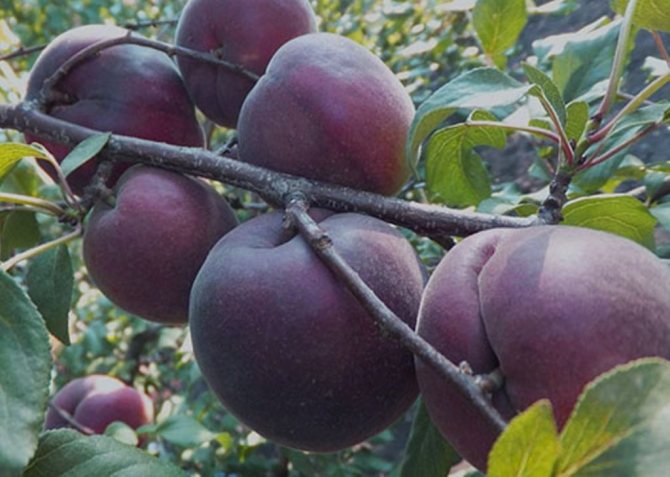


In a black apricot, the fruit is smaller than usual, pubescent, has an almost black color
Black apricots are common in Asia, the USA, and Western Europe. In Russia, this unusual garden culture is planted in the Transcaucasia, the Volga region and the Moscow region, and some varieties are grown in Siberia and the Far East.
Description of the species
The plant is not a very tall tree, like a bush. The crown of most varieties is not thickened, it is easy to prune. From cherry plum to apricot, the ability to bloom and set fruits in late spring was transferred. Therefore, return frosts do not affect the harvest. There is no periodicity in fruiting, like a regular apricot. Black varieties bear fruit every year.
The fruits are smaller, the pulp is more fibrous, the stone is difficult to separate. The surface is velvety, ranging in color from orange to dark purple and violet. The aroma is apricot, the taste is spicy with sourness. If fresh black apricot is inferior to the traditional taste, then for preservation, without any doubt, they give it preference. Black apricot blanks are both more appetizing and aromatic, and the taste is multifaceted.
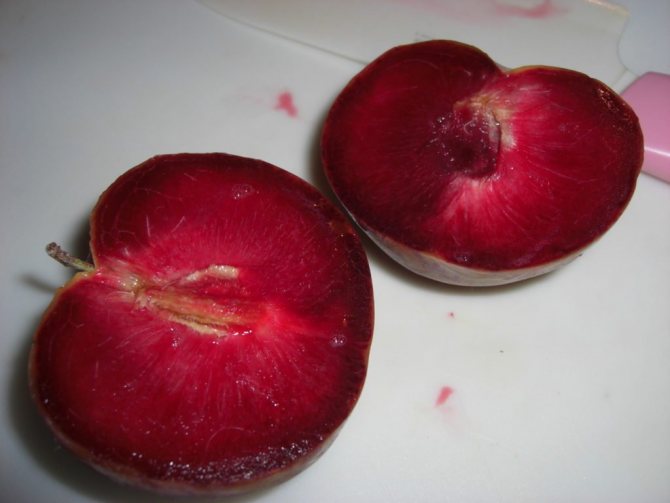


The pulp of the fruit is juicy, fibrous, does not separate from the stone
Biological features
Being an intergeneric hybrid, the apricot tree has combined the characteristics of both parental cultures and occupies, as it were, an intermediate position between them, although in the appearance of the tree, more from the common apricot is taken from it. It is no coincidence that this culture is known under the name "black apricot". True, in many varieties the trees are shorter than those of the common apricot, among them there are also real dwarfs.
At the same time, the fruits of apricot-cherry plum in many varieties taste more in common with cherry plum (although tastier than it), and in appearance they are something in between: they have a pubescent skin, most often of a dark purple color (in different varieties it can be different, up to to yellow), the pulp is almost cherry-plum in consistency, but it smells like apricot, the bone from the pulp does not separate well. The average fruit weight is 20-30 g.
Apricot has inherited many positive qualities from cherry plum. This culture is more winter-hardy than the common apricot (including much better tolerates the destructive spring frosts for it), bears fruit more regularly and much less often apricot is affected by moniliosis (one of the varieties of rot), clasterosporia and other diseases dangerous for common apricot, which in itself makes this culture very promising.
Pollination in black apricot is cross. All varieties pollinate each other well.
Another interesting feature of apricot-cherry is its ability to interbreed with common apricot and cherry plum, as well as with representatives of other species and genera - thorns, plums, cherry plums and other fruit crops, which can also act as pollinators.