Quince is one of the few fruit crops for which both vegetative propagation and seed are acceptable. It may seem to a novice gardener who first decided to plant this healthy tree with delicious fruits that the propagation of quince seeds by seeds is a troublesome and hopeless process. In fact, growing a quince from seeds is no more difficult than from a cuttings or root suckers. It is about these three simple ways of quince breeding that will be discussed in the article.
- 1 Propagation by seeds
- 2 Video "Reproduction"
- 3 Propagation by cuttings
- 4 Using root suckers
- 5 Video "Root propagation"
Botanical description of Japanese quince
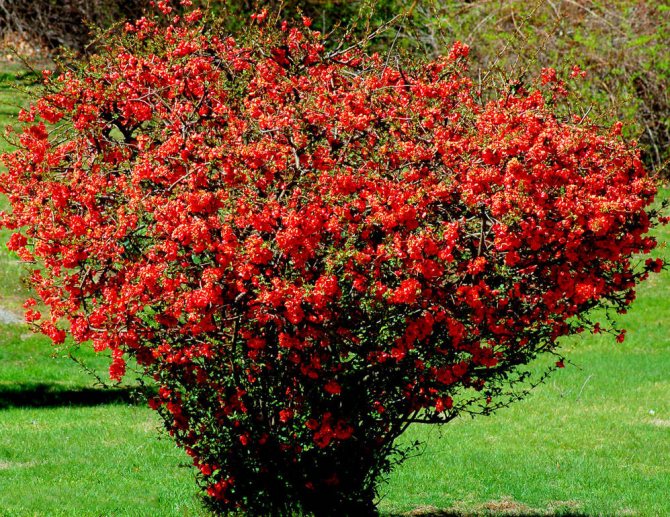
Deciduous shrubs can grow up to 3 m in height. Branches are dark brown, juicy green at a young age. The leaves are obovate with jagged edges.
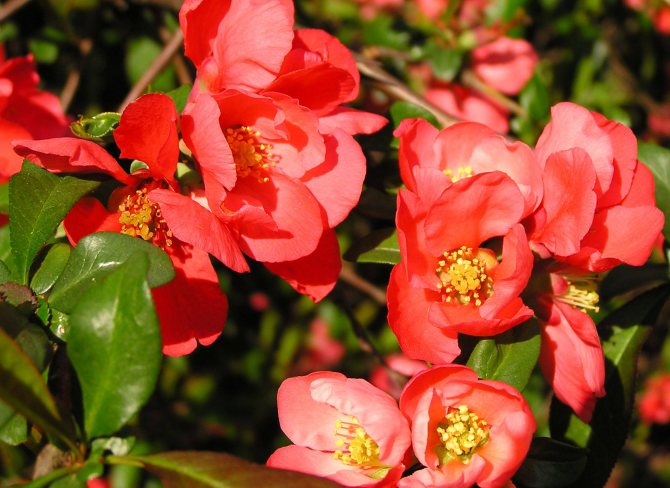

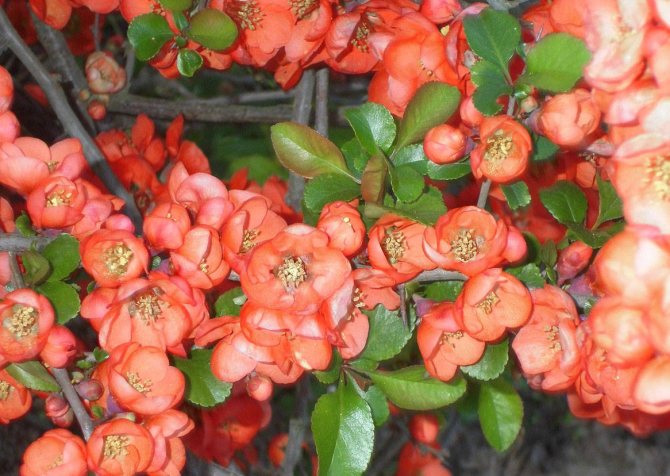
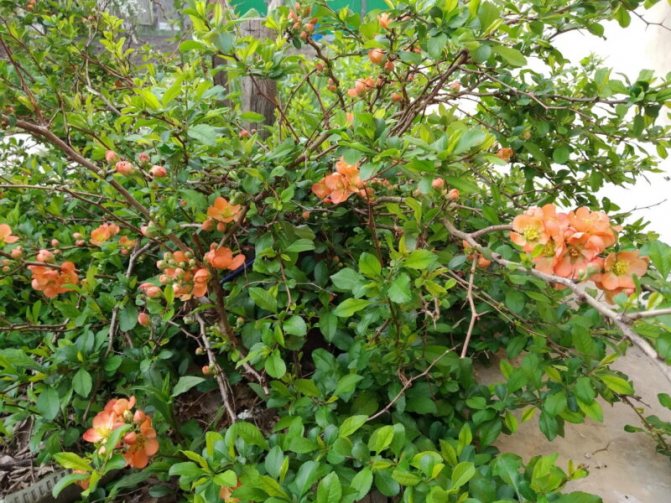
The flowers are bright, the palette of petals - from pale pink to deep crimson, glowing orange, scarlet and cherry red.
Sepals are oval, almost round, pubescent from the inside, fall off during fruit formation.
The petals are also almost round or obovate. Spectacular stamens peep out from the center of the rim.
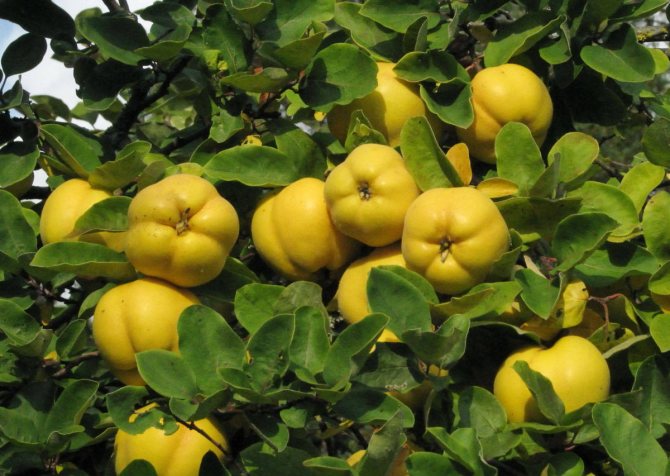
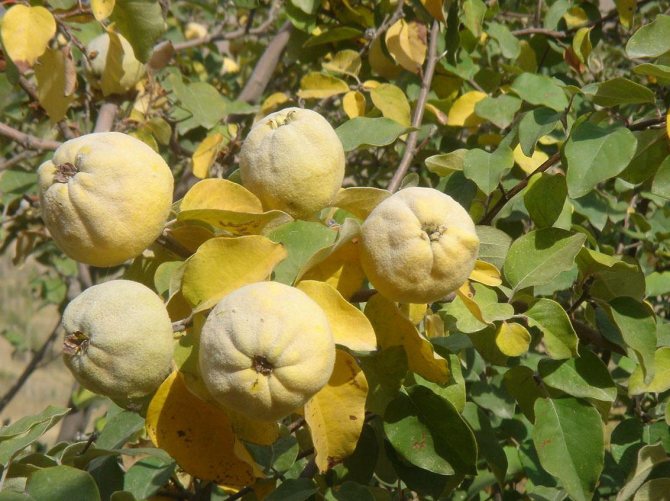
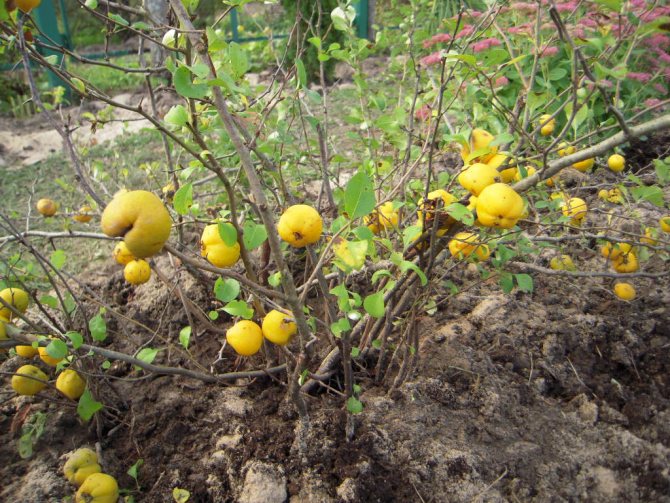
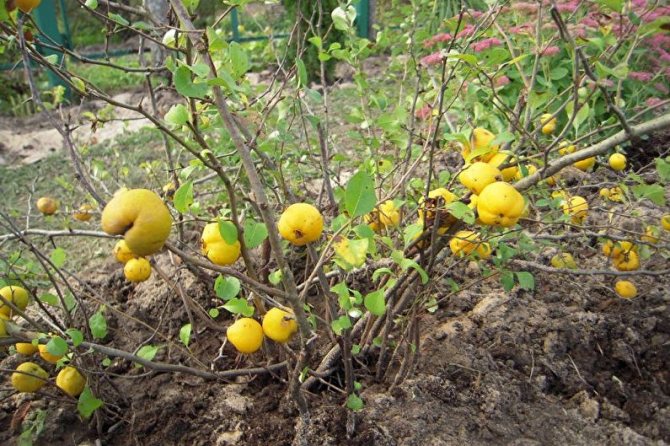
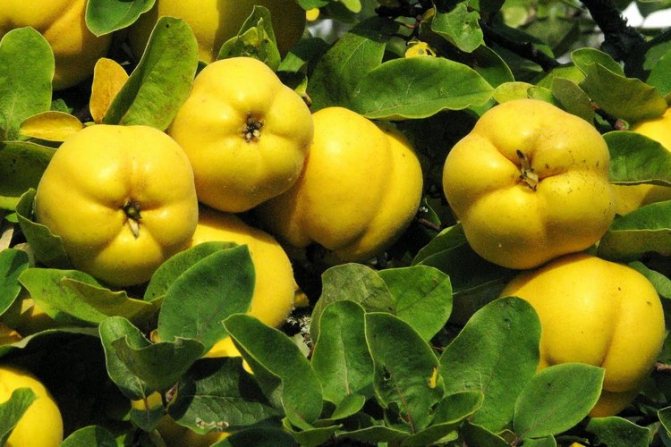
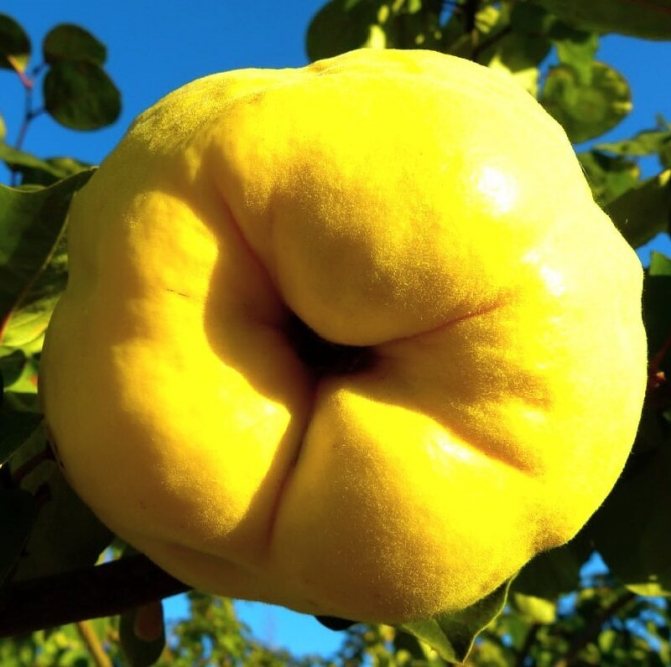
Fruits are small amber apples about 4 cm in circumference with a lot of brownish seeds. They are edible, but they are sour and less used for the preparation of compotes and preserves than the fruits of the common quince.
Varieties for cultivation in the Moscow region
In central Russia, low-growing varieties up to 1 m in height are grown, with arched branches and a spreading crown.
Of the domestic varieties, the most common are:
- Fragrant - bush up to 1.2 m high, winter-hardy, fruit weight 50-60 g, with a pleasant aroma;
- Nikitskaya - early ripening, medium vigor, winter hardy;
- Vitamin - winter-hardy, compact bush, with bright yellow fruits weighing up to 100 g;
- Muscat - a large-fruited variety (fruits up to 200 g), self-pollinated, winter-hardy;
- Teplovskaya - a variety of late ripening and long-term storage of fruits.
The most famous foreign varieties:
- Gaillardi - variety with large orange flowers;
- Malardi - gorgeous pink flowers with a white border;
- Papel - an interesting variety with yellow flowers and a pink border around the edge of the petal.
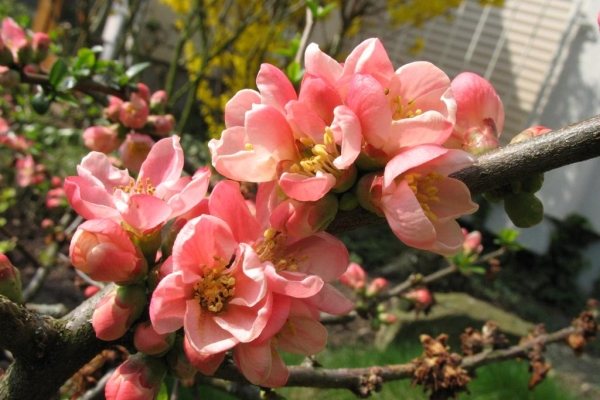


In central Russia, low-growing varieties are grown up to 1 m in height, with arched branches and a spreading crown
Growing conditions for Japanese chaenomeles
Thickets of Japanese quince can often be found along the highway, where it grows without any care and cultivation, once again reminding of its unpretentiousness and ease of maintenance.
Choosing a place at a summer cottage
The shrub thrives on open, sunny places. The more light, the more abundant the flowering.


Japanese quince is already distinguished by its slow development, adding 3-5 cm of pagon length per year, and in partial shade its growth is generally invisible.
In addition, it produces much fewer flowers from a lack of lighting, and its crown is lighter than that of plants planted in the corners of the garden with a sufficient amount of sunlight.
Chaenomeles' winter hardiness is average. During significant drops in temperature, the ends of the branches freeze over, especially those bushes that are exposed to strong gusts of wind suffer.
That is why it is advisable to plant shrubs in a secluded corner of the site, where a lot of snow accumulates, which protects against freezing, especially if winters are with severe frosts - up to 30 degrees below zero.
What should be the soil for quince


The plant prefers light, moderately moist loams with a slightly acidic reaction, rich in humus, or sandy loam.
It grows well on sod-podzolic soils with a high content of organic residues and a pH reaction from 5.5 to 6.0.
Intolerant of soil salinity and excess lime in its composition, which can cause a chlorotic state.
What you need to know when planting Japanese quince
Having chosen a place for planting a shrub, they prepare a site.
Soil preparation
To do this, determine the acidity of the soil, if the soil is strongly alkalized, measures will have to be taken to acidify it.
In the fall, high-moor peat, leaf compost or rotted conifer needles are introduced; fertilization with fresh manure due to excess nitrogen shortly before planting the plant will have the expected effect.
Mineral compounds are also used - colloidal sulfur, ferrous sulfate; for light acidification, ammonium nitrate is suitable in the spring or under the autumn digging of potassium sulfate or ammonium sulfate.
If you need a quick result, use acid solutions - citric or sulfuric.
Vinegar destroys the soil microflora and can provide an unwanted service.
Siderates, dug into the ground since autumn, do very well with the task - legumes, oats, mustard.
How to plant a quince correctly
It is best to plant only two-year-old seedlings in open ground. In early spring, before bud break, holes are dug in the prepared area, commensurate with the size of the root system, about 40 cm deep and 60-80 cm in diameter.


The distance between them is kept within 0.5-1 m. It is permissible to plant a quince in the fall, but it will have to be reliably spud.
A mixture of leaf earth, sand and peat compost, made in a ratio of 2: 1: 2, is poured into the dug hole at the bottom, mineral and organic fertilizers are added - 30 g of potassium nitrate and 200 g of superphosphate, a little manure.
It is important not to deepen the root collar; it should remain at ground level.
The hole is carefully covered with soil selected from it and lightly tamped.
Around the trunk circle is formed, watered and mulched with sawdust.
For better rooting, the branches of the seedling are cut off 1/3 of their length above the bud by 1-1.5 cm.
Since Japanese quince is a cross-pollinated plant, usually 2-3 bushes are purchased to ensure fruiting.


Indeed, even during the formation of apples, the plant is incredibly decorative - strewn with fruits, like solar beads.
Outdoor planting and care
Quince is not demanding on growing conditions, but there are several conditions that must be taken into account when planting a seedling:
- the planting site should be sunny, since the shrub grows and blooms poorly in shade;
- in order to avoid freezing of the bushes in severe winters, plant them in places protected from northern winds;
- the acidity of the soil should not exceed 6.5pH (slightly acidic);
- having a taproot deeply going into the soil, the plant does not tolerate transplanting from place to place, we plant immediately and forever;
- the distance between the bushes is 1-1.5 m, when forming a hedge 0.8-1 m.
Landing rules:
- pour about a bucket of humus with wood ash (0.5 kg) and superphosphate (0.3 kg) added into the dug planting hole (60 * 60 * 50cm), mix with a shovel with a small amount of earth;
- we place the seedling in the hole in such a way that the root collar was at the level of the soil;
- we cover the roots of the plant with earth and water it well;
- it is advisable to mulch the soil around the bushes (sawdust, crushed tree bark, peat).


It is preferable to plant quince in spring, during autumn planting, the plant may not have time to take root and freeze
Further care for a young seedling consists of watering, but waterlogging of the soil should not be allowed in order to avoid rotting of the roots, regular loosening of the soil around the bushes.
Since during planting all the necessary batteries were introduced, then no need to feed the plant for two years after planting.
Adult plants in the spring, after the snow melts, are fed with ammonium nitrate about 20 g per bush. In the summer, they give liquid fertilizing with organic matter (diluted mullein or bird droppings). Superphosphate is introduced in the fall.
To do this, you can use spruce branches or cover small plants with covering material (spandbond or lutrasil), put wooden or plastic boxes on top and sprinkle with fallen leaves.
Quince fruiting annually, starting from the third year after planting.
Chaenomeles cross-pollinated plant, therefore, for better pollination and increase yields, 2-3 bushes need to be planted nearby.
Features of planting chaenomeles:
Japanese quince care
The main measures for keeping a plant at a summer cottage are watering, fertilizing and loosening the soil in the near-trunk circle.
Help in the first year of life - how to tie up chaenomeles
It is not easy to get a beautiful ornamental bush, you need to make some effort to form the crown from the first days of planting.
Simultaneously with planting the plant in the hole, a support is also installed about a meter higher than the growth of the seedling. All pagons are tied to it so that they look up.
With the growth of the bush, the garter is moved higher along the pagons. The support is removed only after the plant gets stronger and begins to bear fruit.
Watering and feeding Japanese quince
Frequent watering for the shrub is optional. In moderately rainy summers, if there is no precipitation for a long time, the plant is moistened with 3-4 buckets of water once a month.
Be sure to water it on the eve of flowering, in the middle of summer - for better fruit formation, and towards the end of August - so that the apples grow liquid and not dry or wilted, which often happens when the end of summer is issued without rain.
During the growing season, chaenomeles is fed, as a rule, three times - in the spring, nitrogen fertilizers are applied, scattering them around the bush, after flowering and harvesting the fruits, the bushes are watered with a solution of potash and phosphorus liquid fertilizers in a dose of 200-300 g per bucket of water.
How to properly prune a chaenomeles
Given the slow growth of the shrub, annual pruning is not performed.
In the 5th or 6th season in early spring, before bud break, old (more than 5 years old) and broken or frozen branches are removed.
They make sure that the middle of the crown does not thicken too much, because it draws excess juices from the plant, and does not give either decorativeness or fruit.
However, intensive pruning can produce an abundance of apples, which, with a large number of them, will be very small.
Preparing a shrub for winter
Young seedlings are covered with spruce branches for the winter. Plants, grafted on a trunk, are tilted to the ground and covered with a dense breathable cloth, snow is sprinkled on top of them, reliably protecting them from freezing.
Adult shrubs of quince in the Moscow region are spudded for the winter, and in areas with severe frosts they wrap the branches with burlap and loosely wrap them with wire at least at a height of up to 1.5 m.
How to cut quince correctly: crown formation
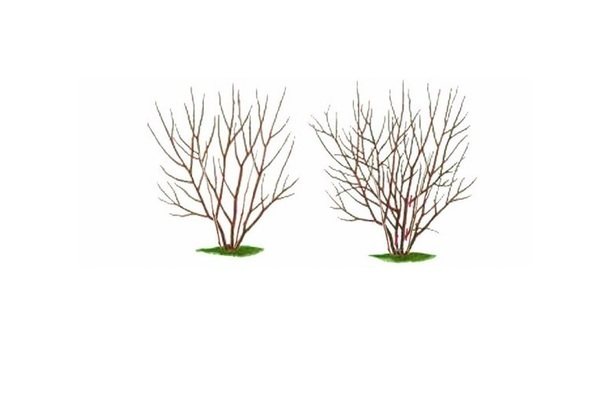


How to cut quince correctly: crown formation
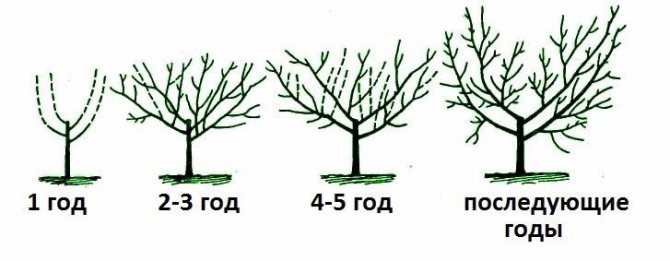
For good light transmission and illumination of the crown, it is necessary to carry out a depression of the longline formation for it. It is applicable to annual seedlings: they measure 60 centimeters from the grafting point and, after counting about 8 buds, they begin to form the 1st tier. The 2nd tier is formed with single branches spaced every 20-35 centimeters or two double branches every 50-60 centimeters.With the help of such a formation of central branches and taking into account the angle of inclination of the branches from the trunk (at an angle of 45 degrees), the crown of the plant will form and bear fruit correctly. A biennial plant is formed by shortening the lower main branch by 50-60 centimeters from the base point. Other branches are shortened, focusing on this level. Everything, except for the conductor, which is cut 20-25 centimeters higher. The goal of the first years of growing this crop is to form a strong base through the correct choice of branches of the 2nd and 3rd order. The 1st branch of the 2nd order is formed from the trunk by 30-40 cm, and the second one symmetrically on the opposite side. When the tree bears its first fruits, it is thinned a little. When the fruiting period is over, partial rejuvenation of the crown is required.
Reproduction of Japanese chaenomeles in different ways
In the presence of mature, well-developed plants, the shrub is propagated by root suckers or layering.
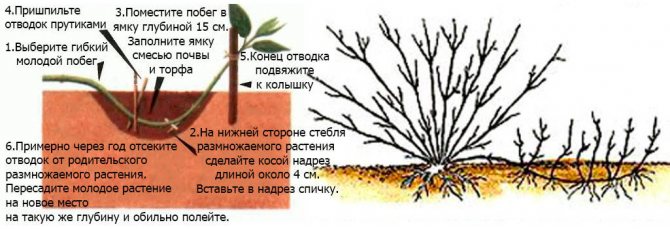

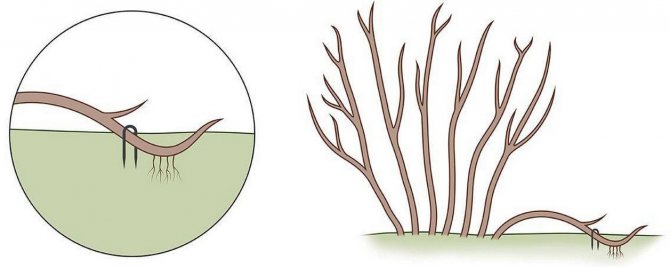
These methods are considered to be the simplest. Root shoots are dug up in the spring and transplanted to a new growing site.
The cut is formed in autumn by bending a low-lying branch to the ground and sprinkling it with earth.
By spring, it grows roots, and it is cut off from the mother bush in order to be transplanted separately.
Propagation by cuttings
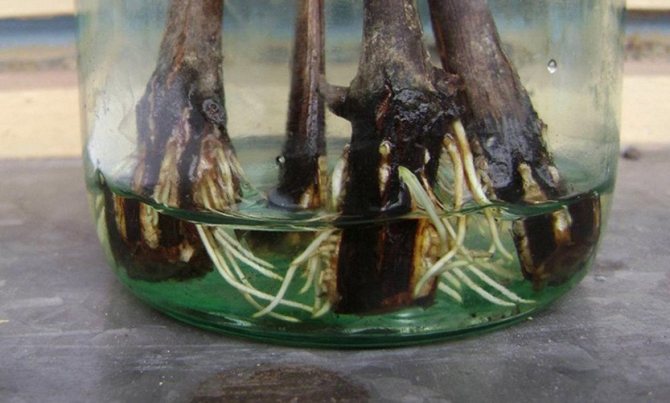
The method of propagation of chaenomeles by cuttings is also simple. In June, the top of a young pagon is cut off and rooted in a cold greenhouse.
The percentage of obtaining new plants using this method is quite high - 70-90%.
Growing quince from seeds


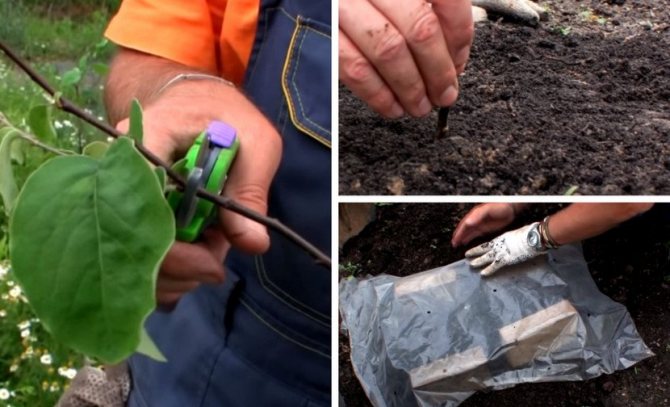
Non-varietal plants are propagated by seeds. To do this, remove seeds from overripe fruits, wash and dry.
It is better to use planting material freshly harvested and sow before winter, although Japanese quince seeds do not lose germination for 2 years.
If it is decided to sow in spring, it is necessary to stratify the seeds of quince within 2-3 months at temperatures from zero to 3 degrees Celsius.
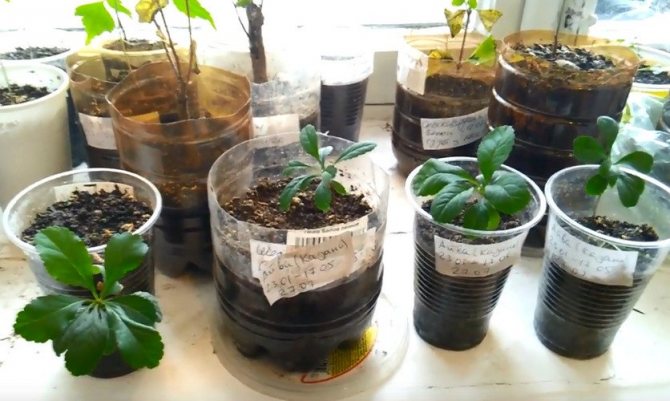
In early April, they can be sown in open ground or at the end of February in special containers, sprinkled with peat-sand soil mixture with a layer of 1 cm.
Seedlings appear in 3 weeks.
They are dived at least 2 times: the first - at a distance of 5 cm from each other, the second - at 17-20 cm.
Quince seedlings are planted in a permanent place only in the second year or they are used as a rootstock.
Plants obtained from seeds bear fruit much later than those grown vegetatively.
Reproduction by grafting
The most difficult breeding method for Japanese quince is spring grafting or summer budding, which are sometimes done on high boles from 1 m to 1.5 m.
Such plants are very decorative, but under the long branches that form on the trunk, it is necessary to substitute supports.
Irga, mountain ash, hawthorn, pear, and in the south - common quince are used as rootstocks.
Quince: seed propagation
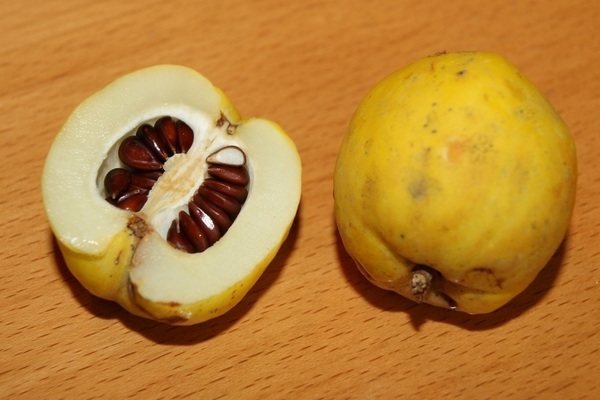


Quince: seed propagation
For propagation by seeds, take large, mature seeds and in February they are placed in a moistened sand mixture in cellophane with holes. All this, in turn, is placed in the refrigerator for 2.5 months. Seeds are sown in early spring (favorite medium is loose, not sour, fertile soil). In the fall, you can see sprouts up to half a meter in height. At the same time, small trees are relocated to a permanent place protected from the wind. They are planted not deeply, maintaining a distance of up to 1 meter between seedlings and 2-3 meters between rows. By winter, with the help of spruce branches, they arrange the process of snow retention: they make small shields, lay out spruce branches, and thus, when snow attacks, the plant will survive (during not very frosty winters). If the temperature in winter is very low, then such a protective system will not help.
Varieties and varieties of Japanese quince
The decorative forms of Japanese chaenomeles are incredibly beautiful. Flowering varieties are especially popular in the garden cultivation of European countries:
- Malardi - with rich crimson petals, outlined along the contour with a thin white border;
- Gaillardi - with sunny yellow flowers, elegantly bordered with a white stripe;
- Papel - with glowing orange flowers.
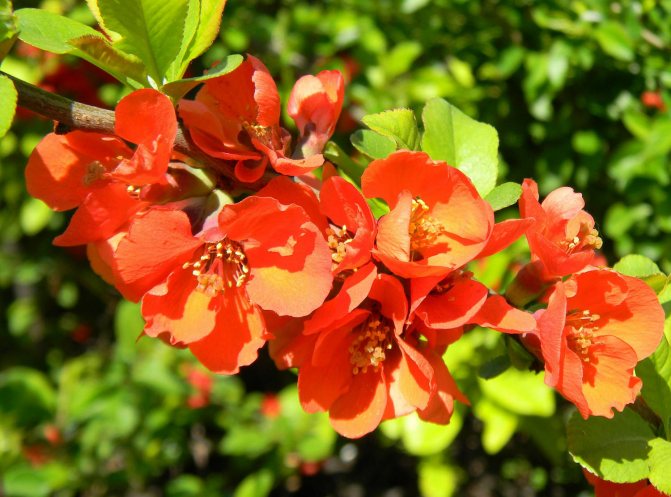


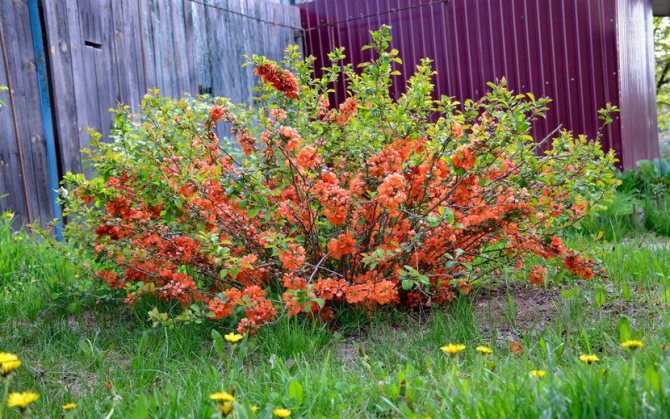
Chaenomeles Maulea, or Japanese quince, is shorter than the typical plant of the genus, reaching a height of only 80-100 cm.
Its branches are arcuate, with sharp thorns up to 1 cm long. It blooms with dark orange, almost terracotta flowers for 2-3 weeks. The bright yellow fruits ripen by the first frost and smell like pineapples.
Bright forms are known - alpine up to half a meter high and tricolor with leaves decorated with crimson patterns.
Hybrids of chaenomeles Maulei and Japanese quince are especially decorative, but in open ground they are grown only in the southern regions.
Among them there are many spectacular varieties with beautiful flowers, including terry ones:
- Nivalis is a white-flowered variety that forms buds twice a season - in May and early August;
- Nikolina - glows with cherry blossom in the month of May, it is distinguished by a light green hue of ripe fruits;


Quince variety Nikolina

Blooming Nikolina - Diamond - with hot red petals;
- Holland - flowers are salmon-scarlet, densely covering branchy shoots;
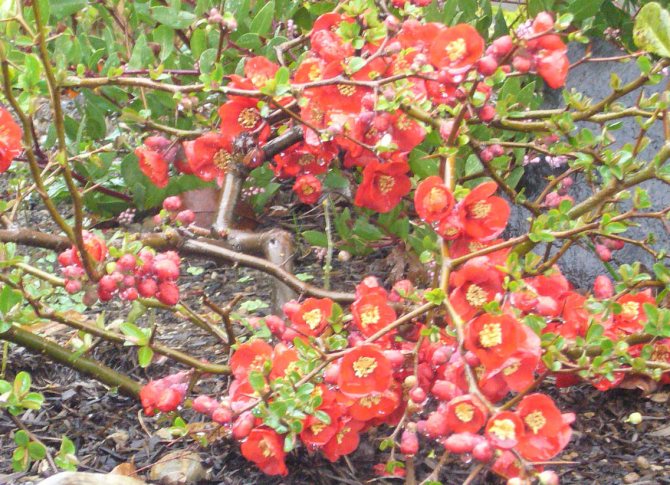


Quince variety Holland - Vesuvius - with maroon petals and lemon yellow apples;
- Pink Lady - with pale pink or deep crimson flowers and rounded fruits that ripen very late in the fall.
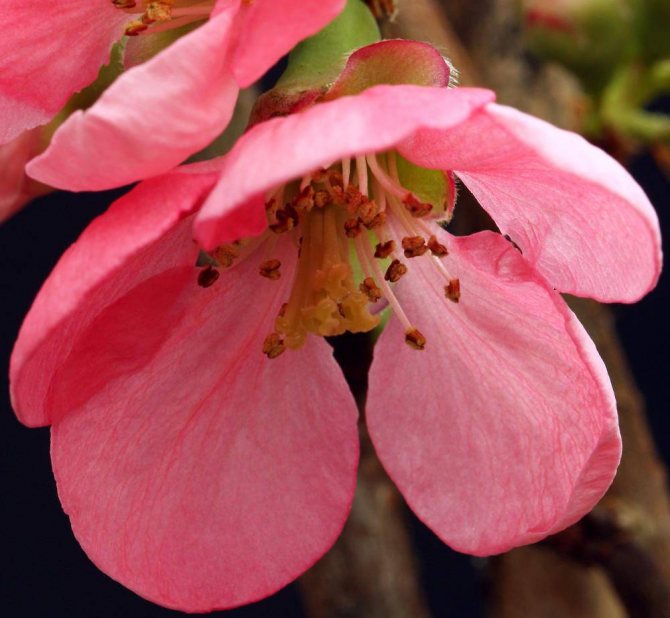


Pink Lady variety
Chaenomeles pruning rules
The shrub tolerates pruning very well, but most gardeners, due to the thorniness of the plant, do not do it in vain. Quince pruning is necessary to improve growth and crown formation for decorative purposes.
There are three types of trimming:
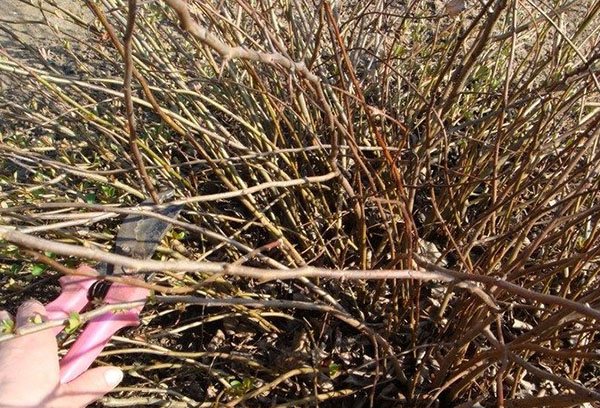
- Sanitary - dry, frozen and broken branches are removed in early spring.
- Formative - they begin to do it from the age of 4, when the branches begin to branch. Shoots growing inside the bush and thickening it are cut out, excess root growth is removed, leaving no more than 2-3 young shoots annually to avoid strong expansion of the bush in breadth. Shoots creeping on the ground are also removed, they take food on themselves and thicken the bush.
- Rejuvenating - it is produced from the age of 8 in the bush, when the annual growth becomes less than 10 cm. Thin and elongated shoots are removed, leaving the strongest 10-12 in the bush. When thinning, you need to remember that the most productive are shoots at the age of 3-4 years, older branches must be removed.
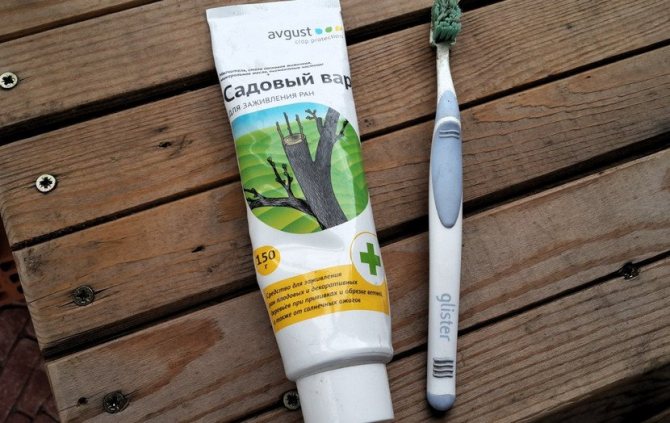
In order to avoid the penetration of diseases into the plant, all sections must be treated with garden varnish.


Quince pruning is necessary to improve growth and crown formation for decorative purposes.
Diseases and pests of chaenomeles
Japanese quince is resistant to damage by pests, it also gets sick relatively rarely, in contrast to the common fruit quince.
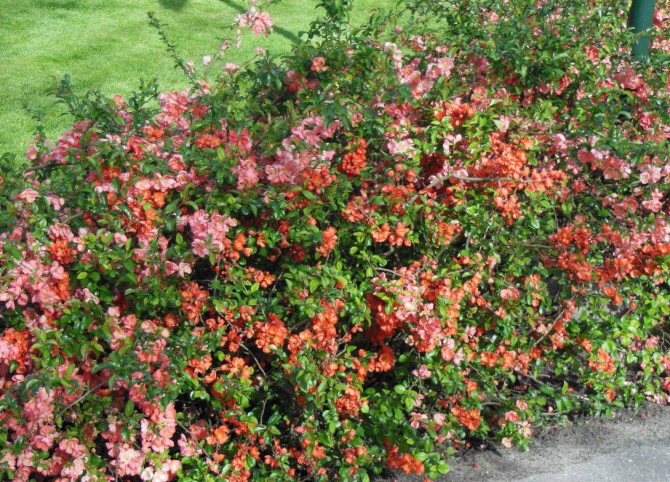


In a very rainy summer, necrotic spots appear on the leaves of the bush.
Sometimes brown spots are observed on the leaf blades - symptoms of ramulariasis.
Elliptical light brown spots signal the presence of cercosporosis pathogens.
Features of the development of quince
Quince is a deciduous tree with a height of 1.5 to 4-5 m. Its branches do not rise in a straight line. The height and structure of the branches affects the nature of the crown formation procedure.
Pruning is a structured and orderly procedure for removing branches from a tree or shrub to improve its growth and development potential.
The age of the branches is easy to determine by their location and size - the thinner and closer to the edge of the crown, the younger. You can also determine the age by the color of the bark. In old shoots, it is dark gray, reddish brown or blackish brown; in young ones it is brownish-gray. Color helps identify “suitable” areas for removal. This is especially true of the rejuvenation process.
The timing of fruiting depends on the specific plant variety. Blossoming in May-June. Fruits ripen in September-October.The timing of the growing season helps control the optimal timing of pruning.


The stem is the distance from the root collar of the trunk (ground level) to the lower tier of the skeletal branches. Skeletal branches - those that extend directly from the trunk, are the basis of the crown of the tree.
The use of Japanese quince in landscape design
Chaenomeles is grown to create hedges in the garden or curbs, looks spectacular on a rocky hill or in a small group in the center of the lawn.
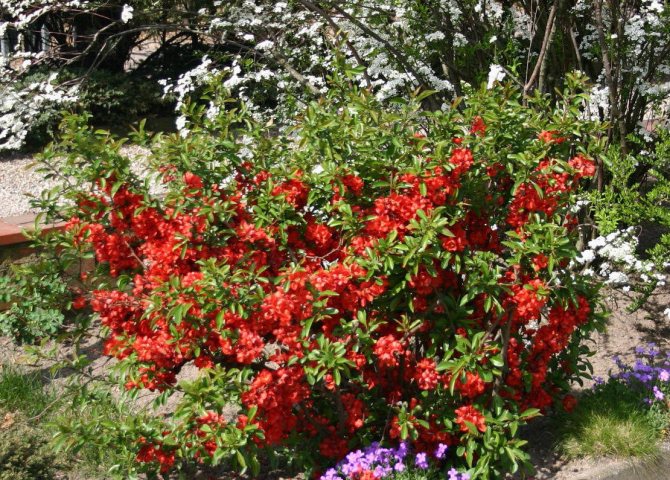


The best partners in the garden for chaenomeles are various varieties of forsythia, undersized almonds, heathers, spirea, and mahonia.
A shrub flaring with orange-scarlet flowers against the background of an emerald carpet of lawn grass is an extraordinary accent of any garden composition.
CherryLink plugin not found
Features of the growth of quince
In the first years from the beginning of growth, quince gives a large number of shoots more than a meter long. But when the tree enters the fruiting period, its growth slows down. Depending on the variety, the main place for laying the ovaries changes.
- Young trees and low-growing varieties bear elongated annual growths.
- Other quince trees produce fruits on perennial generative branches - shoots that overgrow large branches. They bear fruit within 5-10 years.
Skeletal branches should be evenly spaced along the trunk, and sunlight should freely penetrate the entire crown.
It is necessary to cut off the branches until the bud, which is facing outward from the crown.
In the south, quince seedlings are often formed as a bush - in four or six to seven trunks that come from the root. On each of them, the direction of the side branches is controlled so that they do not interfere with each other.


Seed method
This is the easiest and most efficient way to grow a plant. For planting, you need seeds from the fruits of the new crop.
In autumn (September or October), seeds are removed from the pulp and planted in open ground. The survival rate of seeds during autumn planting is 50-60%. The risk of their freezing is too great. Therefore, many gardeners plant seeds in the spring after the threat of the last frost has passed.
Before the onset of spring, the seeds are stratified. First, soak in warm water with the addition of any growth stimulant. After 2 hours of soaking, the seed is mixed with wet coarse sand in a ratio of 1:10. The mixture is poured into cellophane, tied tightly and placed in the lower section of the refrigerating chamber.
To provide the seeds with access to oxygen at the bottom of the bag, make several holes with a needle or awl.
In such conditions, the seeds will be stored for about 3-4 months. During this time, they should be periodically inspected for mold and rot. Rotten specimens are removed. To prevent drying out, the seeds are periodically moistened with a spray bottle and ventilated no more than once a week.
If everything is done correctly, by the spring the quince seeds will hatch. They are planted in shallow grooves (2-3 cm) with a nutritious and light substrate (humus, sand, garden soil and wood ash, mixed in equal amounts).
Ways to rejuvenate a tree
Periodic intensive pruning continues fruiting for up to 50 years. Fruit buds are evenly distributed throughout the tree.
- Cut off all branches where there are gains over the previous 3 years.
- Shoots that were formed in the period from 4 to 7 years are removed.
- With strong pruning, 10-12-year-old branches are shortened.
- The quince tree is completely rejuvenated when more than half are removed - up to two-thirds of all branches.
Thanks to the many dormant buds, the quince tolerates pruning normally and, over time, completely restores the volume of the crop.
If the tree is heavily pruned, it needs feeding.


Landing rules
To plant a tree in the fall, you will need a ready-made annual seedling with a closed root system. You can buy it in any gardening nursery.If you are using two or three year old seedlings, it is desirable that they have an open root system. So you can assess its condition and check for diseases, pests and mechanical damage.
It is important that the roots are intact, without rot and cuts, otherwise you will not be able to get a healthy fruiting tree.
Quince has a massive root system, so it should be planted at a distance of five meters from other plantings and outbuildings.
Site preparation
This plant should be planted on fertile, loose and light soil with a neutral acidity level. Quince loves to grow under the sun, therefore, if you want to get a good harvest, it is advisable to plant it in a sunny place where there are no winds and drafts.
Preparation of a place for planting a seedling is carried out in the spring. Nutrients are added to the plot: per 1 sq. M. superphosphate (50 g) and potassium salt (20 g). Next, they dig up the soil and moisten it well.
Landing
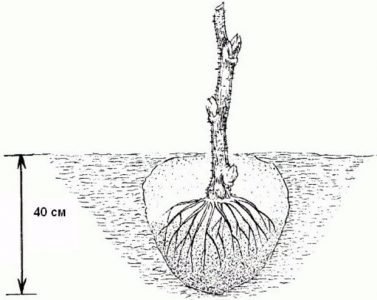

Two weeks before the planned planting, it is necessary to dig a hole about 50 cm deep, 50 to 90 cm in diameter. The width of the hole will depend on the size of the root system of the seedling.
Before planting the plant in the pit, a layer of clay is poured, then a nutrient mixture from garden soil, superphosphate (150 g) and wood ash (50 g). A peg is driven in for the stability of the plant. The roots of the seedling are laid on top of the soil and straightened. Sprinkle with soil, slightly trample and watered abundantly: two buckets of water per tree. The trunk is tied to a peg with twine.
To retain moisture in the soil, the place around the trunk circle is mulched with a thick layer of peat or humus soil.
When to trim?
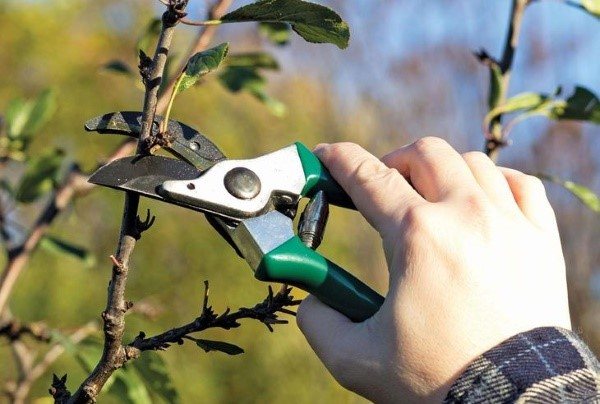


To speed up the formation of the crown, formative pruning can be carried out in the summer. In this case, at the beginning of summer, annual shoots are shortened, and until the end of July, only wen are cut out. In addition, the removal of the central shoot will help to restrain the growth of the crown. This should be done in the summer, leaving side branches, then the tree will grow not in height, but in width.
In the spring, the young branches formed in the summer must also be shortened. At the same time, the work to curb the growth of the crown does not stop, and only horizontal lateral shoots are left from young shoots, and the central ones growing vertically are removed completely, unless the goal is to get a large tree.
To speed up the onset of fruiting, you can make a notch of the fruit buds.
How to trim?
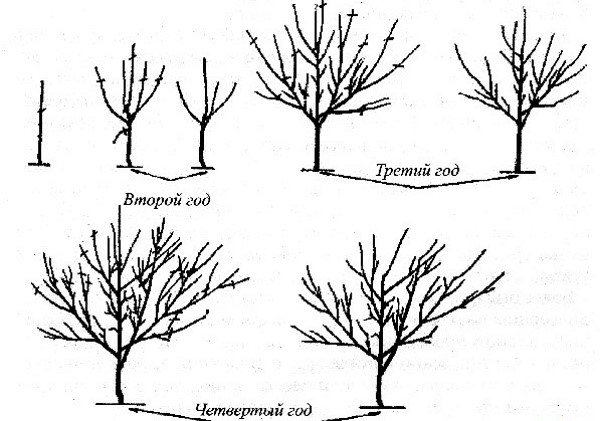

If you decide to grow a quince with a tree, the first step is to expel the stem, that is, the central, main, trunk. To do this, leave one, the most important, shoot, and cut out all the rest of the shoots from the root.
Now you can proceed directly to the formation of the crown itself:
- At a height of 50-70 cm from the soil level, shorten the top of the central (and so far the only) trunk.
- When the seedling releases lateral branches the next year, they must also be shortened, leaving no more than 40 cm.
- Do the same with each subsequent group of lateral neoplasms, cutting them at a height (length) of 40 cm and branching the crown.
All root shoots that develop during the growing season must be completely cut out.
It should be borne in mind that too strong pruning will only harm: it will push back fruiting and cause active growth of shoots, which will lead to thickening of the crown.