What is it and what is it used for?

Fungicides belong to the category of chemical (less often biological) drugs, the main purpose of which lies in the prevention and treatment of various fungal invasions in the overwhelming number of plants that exist on our planet.
In addition, the curative action of fungicides also has a beneficial effect on the treatment and prevention of several other diseases, which is a kind of pleasant side effect.
Safety engineering
When working with antifungal drugs, you need to work in protective equipment:
- protective suit;
- respirator;
- glasses;
- gloves;
- rubber boots.
- it is recommended to tie a headscarf or wear a hat on your head.


Important! Do not process ripe fruits and herbs before eating.
After work, clothes should be washed, containers and tools should be rinsed with running water.
How do they work?
Fungicides for plants are divided into two categories, each of which has its own principle of action.
So, contact fungicides are not absorbed and do not spread inside the plant, but only envelop it with a thin film, which protects and also adversely affects the already existing fungal invasions, quickly causing their death.
Systemic fungicides are absorbed and absorbed by plants, and also effectively deal with both external and internal fungal diseases, but they are not susceptible to weather conditions (fungicide cannot wash away the rain).
Regardless of which group the fungicides belong to, they all have a similar detrimental effect on the fungus, which is expressed in the following points:
- They disrupt the process of fungal respiration.
- They neutralize the ability of the nucleus of fungal cells to divide, which is more important for fungicides of systemic action.
- They stimulate the formation of substances in the plants themselves that have a detrimental effect on fungi. The resulting substances are harmless to humans and plants.
- When applied externally, they can destroy the outer parts of the plant affected by the fungus, simultaneously causing necrosis in them. This measure is necessary to prevent the possible spread of fungal spores into healthy plant tissues after the drug is discontinued.
- It removes and breaks down pathogenic toxins in the plant body, which can provoke the development of both fungal and other diseases, as well as weaken the immune system.
- They prevent the production of ergosterol in fungal cells, the suppression of which also leads to the death of fungal invasions.
- Suppresses the formation of nucleic acids in the cells of the fungus, which makes their development impossible.
- It inhibits the energy metabolism in fungal cells, which finally reduces their vital activity to nothing!
Also, there are biological fungicides, the effect on the fungus of which is contained in the following points:
- After entering the plant, they stimulate the production of substances, which in turn begin to fight the fungus.
- It actively competes with pathogenic strains for the inoculation process in the plant itself.
- Promotes the appearance of hyperparasitism, due to the decomposition of the fungicide in the body of the plant into individual toxins that hit the fungus from all sides.
Biological action of fungicides
When caring for the garden, summer residents often have to use highly effective drugs - fungicides for plants, which are potent chemicals that can effectively combat pathogenic microorganisms that cause the development of fungal diseases, such as:
- powdery mildew;
- gray rot;
- root rot and others.
Fungicidal agents are divided into two groups according to the method of exposure:
Every gardener should know what fungicides are, how to use drugs in home gardening.
The use of fungicides for plants excludes the possibility of penetration of active substances inside. They manage to cover only the outer part of the culture, where the generative and vegetative organs of the fungus are located, causing further progression of the infection.
All funds are capable of acting for a different period, which depends on the duration of the stay of chemical compounds on the surface of the culture. A special result is seen with regular treatment every 3-5 days with an interval of 10-12 days.
The key feature of contact fungicides is local action on green spaces. They are not used to treat signs of damage, but to destroy pathogenic fungal formations that are located on the surface or in plant tissues. It is important to understand that fungicides are not able to penetrate other parts of the plant, therefore, processing with their help is completely safe.
Act
systemic drugs is built on a different principle: during processing, they affect all internal systems, moving through tissues and introducing a number of changes in the physiological and biochemical processes that take place inside plants.
Subsequently, they decompose in the internal organs of flowers, garden or agricultural crops, which causes the rapid formation of metabolites. In this state, the plant develops strong immunity, which contributes to the rapid cleaning of harmful fungi.
Some gardeners are of the opinion that it is unsafe to use systemic fungicides, since decomposition products formed after processing can harm the plant. To prevent possible complications, it is necessary to use chemicals of the first type - contact... However, it is important to have time to carry out all processing procedures one month before harvest.
Views


As mentioned above, fungicides are of chemical and biological origin, and are divided into:
- Contact drugs.
- Systemic drugs.
In turn, in each group of fungicides there are drugs aimed at treatment, prevention, or treatment and prevention at the same time, which should be taken into account when choosing each individual agent.
In addition, in each of the categories there are drugs aimed at priority control of one of the two main families of parasitic fungi, such as downy mildew fungi and all their varieties, as well as powdery mildew fungi and all their varieties.
When buying a fungicide, remember that the preparations are excellent at fighting any fungal invasions, but to increase their effectiveness, purchase fungicides targeted specifically to one of the above fungi, depending on which of them appeared on your plants.
Depending on the purpose of use, fungicides can be divided into the following points:
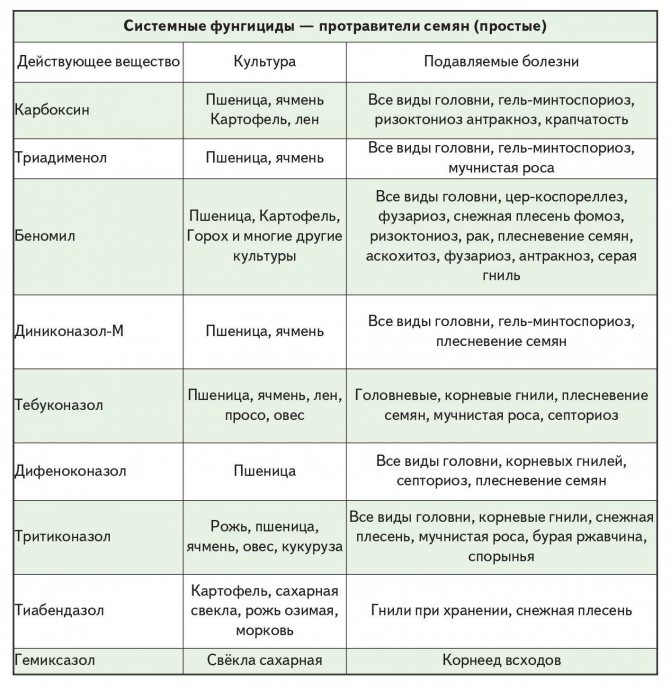
- Fungicides for seed treatment. Preparations intended for the pre-planting treatment of seeds, or for their treatment before a long storage period, in order to eliminate the risk of their damage by fungi and mold, which can lead to the death of the entire future crop, or significantly spoil the crop itself obtained from infected seeds. Seed dressing fungicides are essential for all crops.
- Fungicides for greenhouse and greenhouse soil treatment. These preparations are necessary for disinfecting the soil from the spores of parasitic fungi in cases when it is planned to grow annual plants from seedlings in the greenhouse. Preparations for this purpose are highly volatile, and are recommended for use only in closed greenhouses and hotbeds;
- Fungicides for the treatment of perennial plants during their hibernation, which is also true for indoor flowers. It often happens that fungal invasion affects the plant during hibernation, when the use of other drugs can simply kill the plant. Fungicides for processing plants in winter will help out in this situation, and will rid the plant of the fungus, without harm to health;
- Standard fungicides for processing plants during the period of active growth. Drugs in this category belong to the most numerous and popular variety among the average user.
In general, today there are more than 14 chemical classes of fungicides, the list of which is presented below:
- mushroom fungicides;
- children carbamates;
- imidazoles;
- karabamats;
- morpholines;
- pyrimidines;
- triazoles;
- organophosphorus pesticides, etc.
Features of preparations for indoor flowers
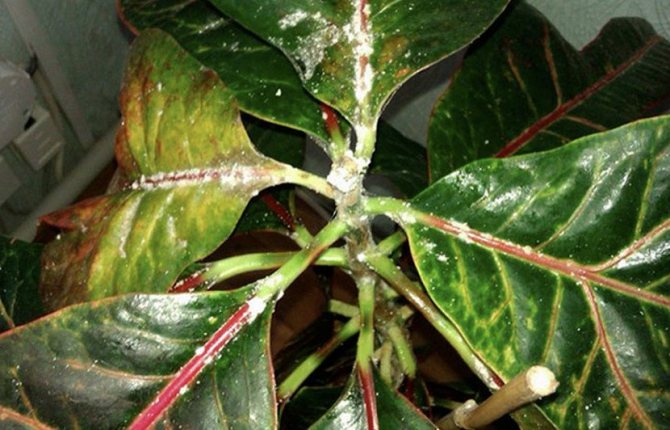
Fungicides are used to protect and treat indoor plants from various types of fungi, bacteria, viruses. The drugs have different compositions and affect pathogens in different ways. All fungicidal agents fight against microorganisms, the parasitic activity of which causes spotting on the leaves, the formation of holes, decay of some parts of the plant, the appearance of rust, mold, and plaque.
There are fungicides that affect only one pathogen, although most fight several fungi at the same time. True, a plant usually settles some one pathogen.
The sooner the disease is detected, the more chances are to save the indoor flower. Fungicidal agents are most effective at the initial stage of infection.
Instructions for use


Fungicides are often used in three main ways, such as:
- Etching.
- Spraying and dusting.
- Introduction to the soil.
Dressing consists in treating seeds or tubers with a fungicide for dressing before planting in order to protect the seeds from fungal infection and prevent their death.
Spraying and dusting consists in the treatment of plants mainly with contact fungicides, which are sprayed on healthy or damaged plants using a spray bottle. As a rule, several such pollinations are carried out per season, starting in spring and ending in autumn.
Adding it to the soil allows it to get rid of fungal spores and pathogenic microorganisms. Systemic fungicides are used for soil cultivation, so that, in addition to disinfecting the soil, they can be absorbed by the root system of the plant.
Fungicides for the treatment of indoor plants are also very popular among the masses, the most effective and safe of which we have presented below:
- Fundazol. The fungicide has a systemic effect, and is both a curative and a prophylactic antifungal agent that can be treated with most indoor plants. Foundation solution is prepared at the rate of 1 gram of the drug per 1 liter of water. Fundazole can be watered or sprayed on plants, but when sprayed, it can leave light spots on the leaves that are not dangerous, but spoil the appearance;
- Agate-25K. A prophylactic fungicide that can be used as a light fertilizer. Fungicide is a biological-type drug, and its solution is used at the rate of 1 scoop of the drug per 3 liters of water. The plant should be sprayed with the solution about 3-4 times, at intervals of 20 days. The preparation is also suitable for seed dressing;
- Vectra. The drug is effective against powdery mildew, septoria and gray mold. The drug is diluted at the rate of 0.3 ml of active ingredient per 1 liter of water. After the completion of treatment, the drug retains its effect for about 2 weeks;
- Oxyhom. Fungicide, which has both contact and systemic action, and is perfect for both the garden and indoor plants. The drug exhibits the most pronounced qualities in the fight against diseases such as late blight, macrosporiosis, black bacterial spot, septoria, powdery and downy mildew. Oxychoma solution is diluted at the rate of 4 grams of substance per 2 liters of water. The diseased plant is sprayed about 3 times, at intervals of 14 days.
Fungicides for plants growing in open ground, especially as crops, can be successfully treated with the above preparations, as well as some other fungicides presented below:
- Colloidal sulfur. The drug has proven itself well in the fight against powdery mildew, anthracnose, ascochitosis and even ticks. A solution of this sulfur is made at the rate of 10 liters of water per 100 grams of the drug. Plants are treated in 5 approaches, at intervals of 2 weeks;
- Speed One of the best drugs today, which has a long period of action. Skor is a systemic fungicide that protects plants from almost all fungal invasions. The solution is made at the rate of 30 milliliters of the drug per 1 liter of water;
- Strobe. An excellent remedy for powdery mildew, downy mildew, rust and all other fungi. Suitable for vegetables, cereals and fruit trees, as well as for wild plants in our latitudes. The strobe solution is made at the rate of 0.4 ml of the drug per 1 liter of water.
"Moon"
The fungicide "Luna" is characterized by a preventive, curative and eradicating action against fungal infection. The combined preparation is used for processing vegetable and fruit crops. Effective against:
- scab,
- oidium,
- gray rot,
- alternaria,
- powdery mildew.
Fungicide "Luna" is produced in the form of a concentrated suspension, the active ingredients of which are: pyrimethanil - 375 g / l and fluoripam - 125 g / l.


The drug is active at different periods of crop development, which allows it to be used both at an early stage of plant development and before laying the crop for storage (2-3 weeks). Recommended dosage:
- 0.6-0.8 l / ha - against powdery mildew and Alternaria;
- 1.0-1.2 l / ha - against gray rot;
- 0.8-1.0 l / ha - against moniliosis and scab.
"Luna" is effective even at low dosages, characterized by the absence of phytotoxicity in relation to crops. It helps to increase yields and improve keeping quality of products. Release form - 5-liter containers. Shelf life is 3 years. The price of a fungicide per 1 liter is 5000-6000 rubles.
List of drugs on our market and their names
A huge number of fungicides are presented on our market, which are constantly updated with new samples. The most popular and well-proven drugs are presented in the following list:
- Previkur Energy. An effective systemic fungicide that fights a number of diseases: late blight. oversporosis, root rot, black leg. The drug is used for a large number of vegetables: cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers, and also protects flowers, ornamental shrubs and seedlings of fruit and berry trees. The product stimulates plant growth and strengthens the root system.
Previkur is the only product in Russia that can be eaten after 24 hours. Easy to use: according to the instructions, the required amount of the drug is diluted with water and poured into the ground, under the root of the plant. - Consento, KS... Produced in the form of a suspension, it belongs to systemic fungicides.Prevents late blight on tomatoes and potatoes, downy mildew on cucumbers and onions, mildew on grapes, root and root rot when growing seedlings. The drug begins to act from the first day after treatment, has a prophylactic and therapeutic effect, has a high heat resistance.
Easy application: pour 5 l of water, measure out 20 ml of the preparation, pour into water and stir.
Pour the solution into a sprayer, pump up pressure and spray evenly over the plant until the leaves are completely wetted.
- Abiga Peak. It is produced in the form of an aqueous suspension, and is suitable for the treatment of fungi and bacterial infections of all vegetable, flower and fruit crops. The drug can be used at any time, and its dosage, as well as the scheme of use, should be studied in the attached instructions;
- Acrobat MC. It is produced in the form of water-dispersible granules and is suitable for antifungal treatment of potatoes, cucumbers, tomatoes and grapes. Spraying is carried out exclusively during the growing season, and the last treatment is done no earlier than 30 days before harvesting, so that the fruits have time to get rid of this toxic drug;
- Alirin B. It is a biological fungicide and is available in powder or tablet form. The drug is focused on the treatment of the root system of plants from rot, as well as the destruction of fungal spores in the soil itself. Moreover, the drug removes toxicity from the soil after its treatment with other pesticides, by restoring microflora in it, and breaking down toxic elements into safe chemical compounds. Suitable for all garden and home crops. Processing can be carried out in any season, when it becomes necessary to destroy fungi in the soil, or to save the root system from death;
- Bordeaux mixture. It is produced in the form of a powder, and is intended for fungal protection of all vegetable, citrus, fruit, fruit, grain, melons and ornamental crops. The mixture is toxic and must only be used with protective clothing. The treatment is carried out during the period of active growth of the plant, and the fruits are plucked a month after the last treatment. The drug is compatible with most other fungicides and pesticide preparations;
- Gamair. It is produced in the form of a powder or tablets, and belongs to the category of biological fungicides. Suitable for the treatment of fungal invasions, as well as the fight against necrosis of the heart of the stem, soft rot, bacterial cancer of tomato. Combines with most types of both garden and indoor plants. It is used during the growing season, and for its manufacture requires the addition of liquid soap to the gamair solution, at the rate of 1 milliliter per 10 liters of working fluid;
- Glyocradine. Supplied in the form of tablets or suspension concentrate. Biological fungicide for the suppression of fungi in the soil, and the destruction of their spores. Suitable for all types of fruit, vegetable and indoor crops. The drug should not be combined with other chemical fungicides. Carry out processing at any time of the year when it is necessary to suppress fungal spores in the soil;
- Quadris. It is a powder and a contact fungicide with a broad spectrum of action, which is suitable for fruit, vegetable, fruit and berry crops. Processing is carried out during the growing season. Processing is prohibited during flowering plants, as well as if the ambient temperature exceeds 30 degrees. The drug begins to act after 2 hours, and continues to act for 7-12 days, until the next treatment;
- Oxyhom. Supplied in the form of a soluble powder, it is a systemic contact fungicide, focused on the protection of tomatoes, cucumbers and potatoes. Use during the period of plant growth, however, it is prohibited to use during the flowering period;
- Thanos. Supplied in the form of granules. The product is focused on protecting potatoes. Thanos is used up to 4 times per season.The drug is applied to the soil at intervals of 10-15 days;
- Fundazol. Supplied in powder form, it is a common systemic fungicide that has earned respect among the masses. Fundazol is used throughout the growing season, carrying out 3-5 treatments per season. The last treatment should be carried out 7, 10 or 20 days before harvest, depending on the crop;
- Hom. Supplied in powder form, packaged in sachets. It is a systemic contact fungicide that has proven itself in the fight against apple and pear scab, late blight and curliness. The drug is used during the growing season, with the exception of the flowering period. Treatment with the drug is prohibited at ambient temperatures above 30 degrees.
- Horus. Supplied in the form of granules, and is aimed at protecting pome fruit crops. It manifests itself best in cool weather, not exceeding 15 degrees Celsius. Used throughout the season, starting in early spring. Discontinue use 15 days before seed harvest and 30 days before seed harvest.
Work rules
An important factor in carrying out protective measures in the garden is the observance of safety measures. Treatment of plants can turn into a disease of a person, if the latter, not fully realizing the full danger of interacting with poisons, negligently treats the event. Several important rules for working with fungicides, the adherence to which guarantees the safety of both the gardener himself and the people around him:
- It is necessary to store chemicals only in hermetically sealed containers.
- Before using the composition, you should carefully read the instructions, namely, information about the consumption rate, the degree of toxicity, properties, frequency of application, the permissible timing of the last treatment before harvesting.
- It is required to check the serviceability of the sprayer.
- The composition should be diluted in protective clothing, shoes and gloves. To protect your eyes from the ingress of poisonous substances, you need to wear glasses, to protect the respiratory organs, use a respirator, if not, use a cotton-gauze bandage.
- Do not subsequently use containers from under the chemical solution for other purposes.
- It is recommended to process plants in dry, calm weather in the early morning or evening. In the summer, it is required to choose cloudy days, since in hot conditions the water contained in the solution quickly evaporates, saturating the space with drugs in a strong concentration that are unsafe for others.
- At the end of the fungicide treatment, you should take off your clothes, clean your nose, rinse your mouth well, wash yourself thoroughly and, if possible, take a shower.


Important: in the process of working with the chemical composition, you must not eat, drink, or smoke. This is hazardous to health, as is the presence of children, pregnant women and sick people in the vicinity of the treated area.
To rid the body of toxins, it is recommended to drink a glass of milk.
Ant remedies


The drugs can be used to get rid of garden pests and ants that have bred in the house.
Muracid
It is an emulsion, which is watered in a diluted form on an anthill. For enclosed spaces, bait is made by mixing with sugar.


Thunder-2
Small granules of the substance are scattered over the soil surface; 2 - 3 cm of the top layer of the soil is removed beforehand. Dangerous for fish and birds.
Anteater Super
Highly effective bait for garden and red house ants. It is used dry and as a paste. To prepare a paste, a few drops of water are added to the granules.


The industry produces a wide variety of products for all types of pests. They should be used strictly in accordance with the instructions, not forgetting about personal protective equipment.
Bordeaux liquid
Bordeaux liquid heals the plant against fungal diseases (scab, melanosis, root rot), prevents the further development of chlorosis (discoloration of leaves and stems). The duration of the protective effect is 1 month. In order to prepare Bordeaux liquid you will need:
- calcium oxide - 100 g.;
- copper sulfate - 50 gr.;
- water - 2 l.
Stir the ingredients, bring the mass until smooth. Strain the solution through cheesecloth. You should have a deep blue mixture. Spray the affected parts of the plant. Use the product only on the day of preparation. Duration of storage in a closed container - no more than a day.
Acaricides
List of chemicals that have a detrimental effect on arachnids. These include various types of mites.


Apollo
Selectively affects ticks, including the red spider mite, a common visitor to garden plots. Apollo is non-toxic to humans and insects.
It destroys eggs, larvae, adults do not die, but are sterilized.
Plants are thoroughly sprayed, especially the bark of trees.
The protective action is enough for 2 - 3 months. Preventive treatment is carried out in the spring, before the beginning of the growing season.


Oberon
Acaricide - insecticide: in addition to ticks, it destroys thrips, whitefly. After processing, it is absorbed by plant tissues, but does not spread along the vascular bed. The drug is hormonal, acts on eggs and larvae. Adult mites are sterilized.
Anti-mite
Works in a contact-intestinal way. The effect occurs within a few hours. May be addictive, so it is alternated with other acaricides.


Neoron
A highly effective substance that has a detrimental effect at all stages of tick development. It is safe for insects - pollinators, therefore it is allowed for use during flowering.