Do you know why forest trees and shrubs feel good even in dry summers with a lack of moisture?, and at the same time delicate plants in the garden and in the garden are often doomed to perish without human intervention?
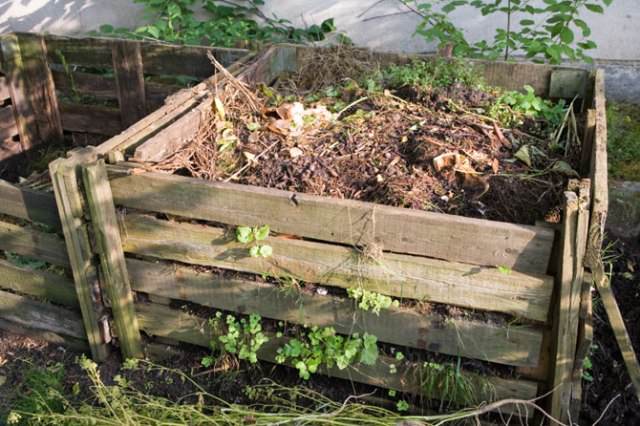
The soil in the forest is covered with a natural layer of fallen leaves and needles, dead branches and other natural materials, therefore it is protected from drought, erosion, leaching, and in addition to everything, it is also enriched with useful substances. Many farmers followed this idea and covered the unoccupied soil surface between the planted plants with organic matter or polyethylene. This process is called mulching.
Let's consider what methods of mulching exist, how to use them and what material is most suitable for this undertaking.
Mulching effect
Mulch prevents moisture evaporation, keeps the soil loose, replaces several weeds, prevents weeds from reaching the soil surface, improves metabolic processes. Microorganisms, bacteria, earthworms transform the mulch, using it as an additional source of nutrition. It is these organisms that improve the characteristics of the soil.
Types of mulching
For mulching, you can use several methods and types of materials:
- put polyethylene or other similar material;
- cover soil areas with organic waste.
Mulching can be done with black film used for most vegetables, strawberries in greenhouses, white for cabbage, red for tomatoes. Transparencies are not suitable for this because they do not inhibit the growth of weeds.
Plants mulched with foil require less nutrients and bear a third more fruit. If you mulch strawberries or strawberries, then the berries are much easier to pick. Black film for mulching in greenhouses creates an unfavorable environment for mice.
Fertilize the soil before mulching. Using organic debris instead of film will add additional benefits to the soil. The following organic materials are suitable: straw, hay, sawdust, grass removed from the crop bed, manure, pieces of tree bark.
A layer of such materials will be useful for every vegetable and ornamental crop, most of all - white cabbage, tomatoes, radish, garlic, celery. If you mulch a cabbage bed with tomato stalks, this will scare off the cabbage pest - the whitewash.
It is advisable to keep berry crops mulched all year round, using dry and green materials in the summer and manure in the fall.
Fruit trees can be mulched with fresh grass, bark, small plant residues, fresh compost, prolonging the mulch effect for a longer period. The normal layer of mulch is about 5 cm. Such a coating gives a positive effect for more than one year. Needles can be placed under plants growing in acidic soil.
When to mulch
Mulching is carried out in late autumn and summer. In the fall, after harvesting, its residues are introduced into the soil (stems, roots, damaged fruits, unripe manure). It is desirable to add mineral flour to organic residues, so that the unpleasant odor disappears as soon as possible and the metabolic processes accelerate.
For better soil warming in spring, you need to clear the beds from winter mulch.
Straw and fertilizer - where is the connection?
Grain agronomists know that straw as fertilizer is an excellent residual material to replenish the soil. In the fall, it is plowed when digging up personal plots, and is used as one of the components for preparing mulch and compost.
Inexperienced farmers practice straw burning in the fields. This action causes irreparable damage to the fertile surface. Soil temperature reaches extremely high levels, destroying worms, wood lice, loosening the ground cover.
The smoke after combustion is equivalent in terms of its impact on the environment to the emissions of harmful substances at industrial enterprises.
It is more efficient to use straw as an organic fertilizer: in comparison with manure, it is 4 times more economical.

The action is cumulative: it will take about 8 months to get the result. Straw will contain phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, calcium, nitrogen. The last component accelerates the process of decay and the formation of humus, which increases the yield. Its ratio to carbon should be 20: 1.
Introducing straw into the soil performs the following functions:
- increases soil fertility and structure;
- provides food for earth insects;
- activates nitrogen fixers;
- reduces soil erosion;
- improves soil water and air absorption.
Straw protects the ground from pests, from glaciation in winter, prevents it from overheating, and also adds looseness and lightness to the soil due to the presence of carbon dioxide.
Dry organic matter helps to get rid of weeds, can be used in garden beds by gardeners in the summer.
Different straws - different nutritional elements
If we compare cereals and legumes in terms of the amount of nitrogen, then in legume residues it will be three times more. There are many nitrogen components in buckwheat and corn residues.
Most of the phosphorus is in sunflower stems. Less in cereal straw. Therefore, to balance nutrients, you can combine raw materials, crushing them into the same particles.
The potassium content also varies by cultivar. In winter cereals of this substance about 1mg / kg of raw materials. In sunflower up to 5 mg / kg. 2.5 mg potassium in buckwheat stubble.
Video: Turn Straw into a Rich Harvest
Calcium is higher in pea tops and sunflower stalks. If you mix wood ash with straw and embed it in the ground, then the acid-base balance can be significantly balanced.
Magnesium, which is involved in the formation of chlorophyll, is found most in corn, peas and sunflowers.
Description and properties
Straw is the dried stem of various crops. It looks like a tube with an empty middle, is distinguished by its golden color and the absence of remnants of rot, mold and mildew. Common crops for straw production are legumes and cereals.
Wheat
Wheat contains iodine, manganese, magnesium and iron, sodium and cobalt, carotene, vitamins D, group B. These elements are useful for the root system, trunk, grain.

Barley
Barley is rich in fiber, calcium, lysine, protein, mass of extracts, vitamins A, PP.
Oatmeal
Contains a lot of cobalt, iron, carotene, protein. Useful substances are absorbed into plants when fertilized with oat organic matter.
Pea
Dry vine contains a large amount of lysine, protein, trace elements and vitamins, antioxidants. It decays quickly compared to other species.
Using bark to your advantage
Once we described in detail a garden shredder (mentioned literally in the last section of the article), which can become not only an excellent assistant in the country, but also the equipment that will help to recycle unnecessary into useful.
We are talking not only about the branches, which the shredder transforms into chips, but also about the bark of trees, which, after the shredder, becomes an excellent material for mulching and even decorating the soil.
Wood chips from the bark are most suitable for protecting the soil in an orchard, where it can be covered with a 5-7 cm layer of tree trunks. So the root system will not dry out, and the soil will maintain its integrity.
Woodbark is also a good fuel, but it is worth remembering that very often, due to its structure, it smokes. Therefore, if you decide to make a fire from the bark, it is better to use it on the grill, and not in the home oven.
In addition, there are many more ways to use tree bark with benefit in the country, but all of them require additional costs or special equipment.
So, for example, valuable fuel pellets can be pressed from the bark, which perfectly keep heat, produce organo-mineral fertilizers, use them as an additive in special substrates, etc.


The effect of straw
The effect of straw on soil and plants varies.
On the ground
Favorably affects the land: it becomes fertile, gives a rich harvest of pumpkin, potatoes, melons, corn, beets, carrots. A high result is observed when used in combination with green manure grown for further digging and planting of winter crops. For this purpose, mustard and radish are used.
Decomposing, dry stems form protein compounds and simple carbohydrates, cellulose, lysine. Nitrogen acts as an accelerator of decay, therefore it is effective to add fertilizer based on this element to a dry stem. The dosage is 10 kg per ton of material.
On plants
The decomposition products of straw have a negative effect on plantations. The root system is affected by the ingestion of the following acids:
- acetic;
- formic;
- dairy;
- sorrel;
- benzoic, etc.
When nitrogen is introduced, they are neutralized. An effective replacement is urea or saltpeter. The input is carried out in a proportion of 150 g per 1 m2.


Rules for fertilizing soil with straw waste
Professional agronomists, who are forced to save resources and use everything that is to restore the land, advise using green manure together with straw. It happens as follows:
- After harvesting, nitrogen substances are introduced into the soil - urea or saltpeter, straw residues are added dropwise.
- From above, siderates are immediately sown, for example, cruciferous - mustard.
- They wait until the mustard grows up, cut it off and dig it up all together.
This method accelerates mineralization and enriches the soil with nitrogenous substances.


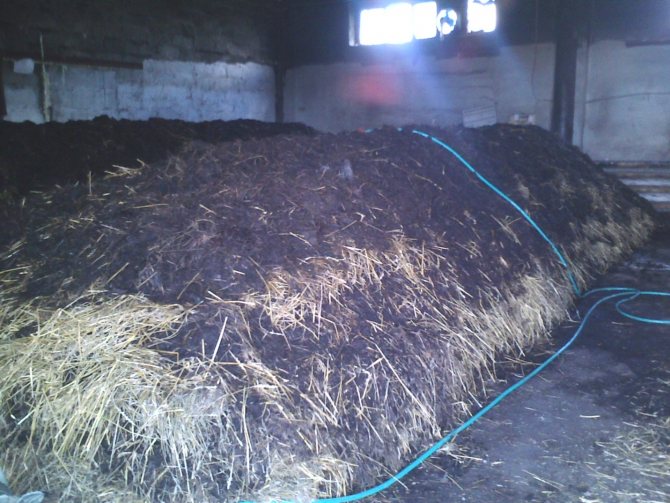
If the soil still allows you to harvest, but the number of fruits is gradually decreasing, you can lay a compost heap in advance and wait for the components to overheat. It takes on average 9 - 12 months. If you do it according to the rules and apply bacterial biological products, then the compost is prepared for 3 - 4 months, but these months should be summer or autumn.
Straw compost
When composting, the amount of straw about 100 kg spread to the bottom. It will act as a cushion that inhibits the leakage of nitrogenous substances during combustion. Further, according to the rules for composting, the remaining components are added. In this case, the proportions of nitrogen and carbon substances must be observed, otherwise the combustion process will not start.
When using biological accelerators, each layer is spilled with a preparation. A few days after this, bacteria multiply and begin to process organic matter. In a week you can begin to transfer the components to an adjacent box to enrich with oxygen, without which microorganisms die.


With the right technology, compost will be ready in 3 - 4 months. It is introduced into the soil just before planting in the spring, since the nutrients are already ready to enter the plant roots.
Application methods
The use of straw as fertilizer must be strictly controlled. A positive result is achieved only with correct dosing.
Straw beds
Agronomists practice growing vegetables in straw, using it as soil. The method is characterized by the absence of the need for weeding, watering, hilling, fertilizing, pest control (Colorado beetles, etc.), making the cultivation of vegetable crops economically less costly. Straw retains moisture, fertilizes plantings, and prevents weeds.
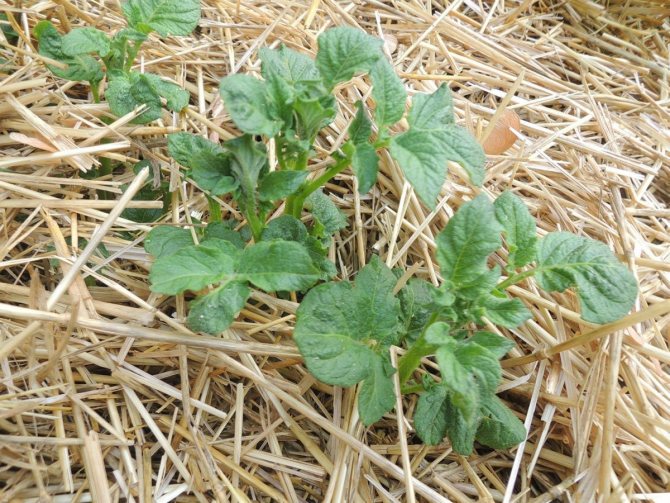
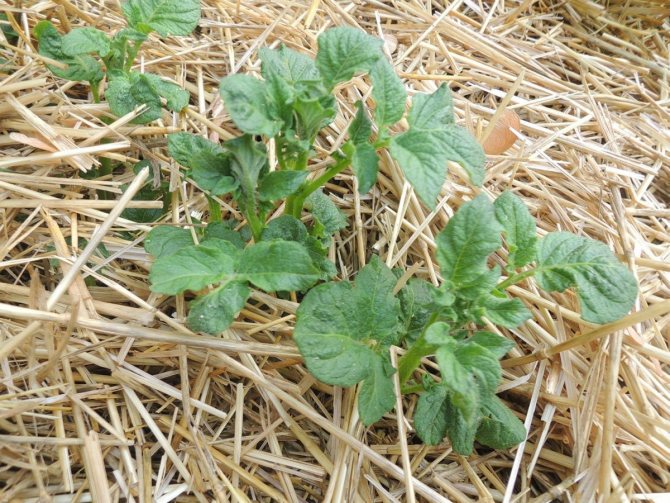
This method is most popular when growing potatoes. Planting begins with peat filling in a trench 0.25 m deep, chaotic scattering of tubers and subsequent covering the cultivated area with straw with a layer of 35 cm. If there is a lack of rain, it is necessary to irrigate 1-2 times. With this approach, a rich harvest in the fall will delight gardeners: the tubers will turn out to be smooth, not spoiled, and tasty.
The formation of a bed and scaring away rodents from it is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Spread out cardboard, paper, newspapers.
- Pour wood ash (the other is not suitable) at the rate of 1 bucket per 5 m2.
- Lay out the straw bales tightly without gaps.
- Water for 3 days, soaking the structure well with water.
- In the next 4 days, water with herbal infusion.
- Then moisten the soil with compost tea for three days.
- After the expiration of the specified period, cover the bed loosely with a film for air circulation, leave the "windows". Plant the plants after 10 days.
An alternative method of using dry grass as a garden bed:
- dig a trench up to half a meter deep;
- lay out a layer of straw;
- sprinkle with earth.
The considered method is suitable for growing strawberries, cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers.


Straw mulch
- protection against freezing of the earth in winter, drought - in summer;
- preventing the emergence of large weeds;
- bait of beneficial insects.
The soil becomes light, airy, optimally moist.
The disadvantage of using mulch is that the nitrogen content of the soil is reduced, which leads to nitrogen starvation. You can get out of the situation by using fertilizer based on this element.
STRAW IN NATURAL AGRICULTURE!
Straw, along with other plant residues, is one of the main sources of soil organic matter replenishment. In terms of organic matter, one ton of straw is equivalent to 3.5 - 4 tons of manure!
What is the value of straw? What are its properties? How can you quickly increase soil fertility with straw? How can straw be used correctly in Natural Agriculture? Its role and application in Natural Agriculture!
Today we will analyze all these and other questions related to straw! Don't miss - all the fun, things you need to learn about straw! ...
For many regions of Russia, this phenomenon is considered normal. You can often see such a picture when straw swaths or ricks in the fields are burned! And this is a disaster!
This causes catastrophic damage to both the soil and its inhabitants! Burning up instantly, the straw creates a temperature on the soil surface up to 3600C, and at a depth of 5-8 cm this temperature reaches 50-700C!
Humus, which has been accumulating for decades, disappears in an instant in such wildfires in the fields! Studies have shown that on leached chernozem, humus burns out to a depth of 5 cm and burns out 1.2 tons per hectare!
And the loss of water in the soil when burning straw occurs to a depth of 10 cm, and naturally, its water-chemical composition deteriorates and its biological activity decreases!
So why are hundreds of tons of straw burned annually in the fields? ... What do farmers think? ...
Why did I start this conversation? Getting straw is a huge problem for me! Well, all our state farms closed and all collective farms fell apart ... Well, we don't grow wheat or rye ... The fields have not been sown for 10 years, or even more ... And there is nowhere to take straw ... And you have to order from afar, for a lot of money!
But once, driving through our regional environs, I saw a field with bales of straw on it! This, in principle, is not very far from us, and I happily went to look for who owns this field! I didn’t have to search so long ... since I know how to talk to people ... but the day was a day off ... The manual was not on the spot ...
My husband had to take a day off in the middle of the week to go back to the straw-rich places! And what do you think I see literally after 4 days? All the straw was burnt !!!…. I was just shocked ... There was no limit to my indignation! And I still got to the people I needed! And I managed to negotiate the supply of straw in the future!
In general, the situation is that the excess unused straw is forced to burn ... Isn't it easier to distribute it to the people! I think that it is unlikely that it would seem superfluous to someone who works on the earth ?! BUT? Would you refuse?
Therefore, if you know where it is burned in your neighborhood - go and get it! They do not need - WE NEED TO !!!
Straw occupies all significant positions in our gardens every day. It is widely used by gardeners and this is far from coincidental.
Almost every tenth gardener has already tried growing potatoes under straw - and not one spoke badly about this method! Why is straw so popular for environmental reasons? What are its advantages and what properties of straw make it particularly suitable for use? The main role of straw in agriculture is mainly soil fertilization! Because straw plays a big ecological role!
Chopped straw is used more efficiently. The annual use of straw as mulch and its subsequent entry into the soil and decomposition there:
- Increases soil fertility and reduces soil compaction!
- The soil becomes looser,
- Its moisture capacity increases,
- The content of nutrients in it increases,
- The soil is protected from wind and water erosion,
- And in the spring it dries out faster, which makes it possible to start garden work earlier!
- Promotes the development of soil fauna - increases the activity of bacteria, earthworms and other organisms!
- The agrochemical and physical properties of the soil are improved!
But straw is not only effective as a mulch! It is no less effective to build straw ridges out of it! And how to do this correctly will be discussed further!
First, let's figure out whether it is worth making straw beds and what can be grown on them?
Since I have been engaged in natural farming for a long time, more than 13 years for sure, then during all this time I have carried out a lot of experiments. And before I tell you something here, I first experience it myself, in my garden, and then I write the results of my experiments. (Therefore, you can feel free to seek advice if you need help urgently. I have something to share with you, I willingly help everyone who applies!)
And straw is no exception, I gradually began to introduce it into my plantings, conducted a lot of different experiments with it, planted under it, and on it, and with it, and it too! Well, when I realized that straw is this cool thing, and it's difficult to get it from us, we started to grow it ourselves, since we have two abandoned ones around the site, from one we mow grass, and on the second we began to sow wheat, barley and rye !
for five years, I have tried straw in different ways and now I can confidently say that you can grow anything on it! Not only great potatoes grow UNDER the straw, but everything grows ON the straw!
What do I like about straw beds and who do I recommend to try them for sure?
I really like straw ridges because they can be easily built on any soil, even on scorched earth! You don't need to dig anything, weed anything, loosen it up, you don't need to huddle anything! But for a year of its existence, such a bed is capable of making any soil under it fertile !!!
Yes, yes, you heard right! Therefore, I recommend that anyone who has soil problems start with straw beds. Even if straw costs money, it fully justifies itself and you will definitely not be left without a crop!
It will take no more than 10 days to create a straw bed! But first you need to purchase straw bales. When buying, inspect them so that they are free of mold and they should not be caked, i.e. we need fresh bales - not last year's!
Decide on a place, such a ridge can be located anywhere in the garden, even on an uncultivated area, on the most problematic! To begin with, start with less, that is, build a small bed in several bales, try it out and then you can already plan more.
Here you can give a flight of imagination, creating any geometric shape of the ridge, even in height, even in shape! In any case, the bed will turn out to be high, which can be useful for people with back problems! You don't have to bend down, all the fit is almost at waist level - very convenient!
Many gardeners are afraid to use straw for one simple reason that rodents can settle in it! I'll tell you frankly - rodents can be present in the presence of straw and in its absence. These are animals that don't care about everything, but you can insure yourself.
Mice do not like wood ash; when licking paws, the ash gets into the stomach of rodents and irritates it. Therefore, they avoid ash places. Therefore, you can take care of this before laying the ridge. We spread newspapers or cardboard in the place chosen and marked for a straw bed, and on top of it we sprinkle ash from the amount of a bucket of 5 square meters, clean wood ash!
You can put together a wooden box for such a bed, or you can without it. We put the bales tightly to each other and wrap them tightly with twine. This is to prevent gaps between the bales.
Now you need to thoroughly water the garden bed for three days, so that the straw is saturated with moisture. And within 4-5-6-7 days we pour water with microorganisms! Baikal or any other em-preparation will do, or you can pour it with a good herbal infusion prepared in advance! Now active microbiological processes begin to take place inside the bales and the straw begins to warm up from the inside! For the next three days, we continue to water it a little, you can just water, or you can use weak compost tea.
All 10 days we cover the bed with a film, but not tightly, but so that the air can circulate freely, it must be ventilated. During these 10 days, the process of straw decomposition starts, which will last until the end of the season, but for the first 10 days it is very active, so we start planting something after these 10 days.
A straw bale perfectly accumulates moisture in itself, therefore microorganisms begin to actively work, because the straw breathes freely, providing oxygen necessary for the activity of microorganisms. Bacteria begin to multiply actively and carbon dioxide is released during their vital activity - the main factor for the development of any plant! This is the uniqueness and effectiveness of the straw bed!
While the garden is being prepared, think about whether you need some kind of support for the plants that you are going to plant here? For starters, I recommend trying on low and medium-sized plants, for example, peppers, tomatoes, not only tall ones, cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkins. If you plan to plant varieties more than a meter in height, then immediately install a trellis or other support. Because the straw, when decomposed by the end of summer, becomes loose and it will not be able to hold the huge plants, they will tumble down. So, are you already starting to understand what is the trick here? The fact is that while you are preparing the main vegetable garden in the plantings - prepare the beds, sow green manures ... This bed is only 10 days and is ready to place any plants on itself! Accordingly, the harvest will be earlier! And if you consider that straw beds can be installed with the same success in a greenhouse ....? !! Imagine how much easier your work is, in comparison, for example, with warm beds!
And if you put a warm bed on the sides with straw bales ?! No ... no ... You first try a tiny straw bed, and then you will not be stopped, you yourself will start combining the beds! And this is great! The less work in the garden, the more loved it becomes !!!
Let's go back to our straw bed, it is already ready, the supports are installed and now you have two options: you can sow something with seeds on it, or you can plant ready-made seedlings!
If you plan to plant seeds, then the surface of the straw ridge must be covered with a thin layer of soil (vermicompost or compost).
If there are seedlings, then make holes in the straw with a scoop and plant the seedlings strictly with a lump of earth.
They were planted, if there is a threat of return frosts, then they are terrible only for the ground part, because the temperature inside the straw is good, and the top of the plants can be protected in the usual way - we install arcs and stretch the covering material, also applies to greenhouses. We are doing a kind of greenhouse in a greenhouse!
Further, all that is required of you is watering! And this can be dealt with once and for all - by installing drip irrigation, you can rest! If this is not possible, then pour it with a watering can! But we water over straw, not over foliage! It is very important that the plants do not get sick!
By the way! I forgot to notice that it is necessary to water the straw bed with HB 101 before planting, although it is possible to scatter the granules over the surface of the bed. As for the sores, it's also not scary, if the seedlings are grown correctly, then the plant is strong and healthy, do not water the foliage, form it on time, use mixed plantings on a straw bed too! And no diseases will arise!
The most interesting thing is what to do with this garden bed in the fall? Yes, nothing, leave it to stand like this until spring - in the spring this waste, rotted straw will go for mulch, you can, in principle, disassemble it and cover the garden with it in the fall. But the main thing here is that waste-free production! Straw will serve your garden for a long time, which will transform year after year! In just a few years of using straw in this way, you will not recognize your soil - it will become truly healthy and alive! Check it out!
And if you decide to put the spent straw in a warm bed or compost heap in the fall, then removing it from this place you will be pleasantly surprised! Beneath this bed of straw, you will see the healthiest and most lively soil, teeming with earthworms, which all these months, while the garden toiled for your harvest, they worked to create fertile soil! Now you can grow even the most demanding vegetables in this place! By the way, on straw beds you can successfully grow a variety of, including whimsical, flowers!
And in conclusion, I want to add ... Don't be afraid of mice! Plant a few blackroot bushes around the perimeter of the site and you will not see a trace of rodents. They will bypass your site (only negotiate solidarity with your neighbors), but the black root gives seeds only in the second year. Namely, its seeds are so hateful to rodents, although the smell scares them off, since we do not feel it!
Live in harmony with Nature and with yourself! Decorate the earth with paradise corners of your gardens and orchards, Love mother earth, work on it rationally and consciously! Enjoy every minute you spend on your land!
superogorodnik.
Fertilizer production
There are many dry stem feeding options.
Straw compost
To prepare this type of organic matter, you first need to determine its potential location. Further, the material should be laid in layers in the following sequence:
chopped straw - 150 kg;
weeds or grass - 20 kg;
mineral solution: water - 40 l, superphosphate and potassium chloride - 6 kg each, saltpeter - 4 kg.
The compost heap is reheated for a year, then mixed and put into the ground.


Humus
Straw is introduced dry according to the rules:
- Maximum chopping: the cut should be 20 cm, the length of the straw should be no more than 10 cm, the particle size should be up to 5% of the volume.
- Introduction of mineral nitrogen.
- Spread the hay in a thin layer of even appearance without rollers.
- Plowing the soil with a harvester designed for this purpose. Straw filling is carried out immediately, the drying of chernozem is not allowed.
The optimal period for the introduction of straw as fertilizer for the garden is autumn or spring. Application after harvest makes it possible to store up to two weeks in the beds without digging. Nitrogen is added before digging. Re-plowing is carried out after several weeks.
Incineration to produce ash
Straw ash is valuable for potassium, the dose of input is 70 g per 1 m2. You need to burn on a separate territory (not on a personal plot). Mixing with calcium-containing wood ash is recommended.
Mulch: benefits and harms in the garden
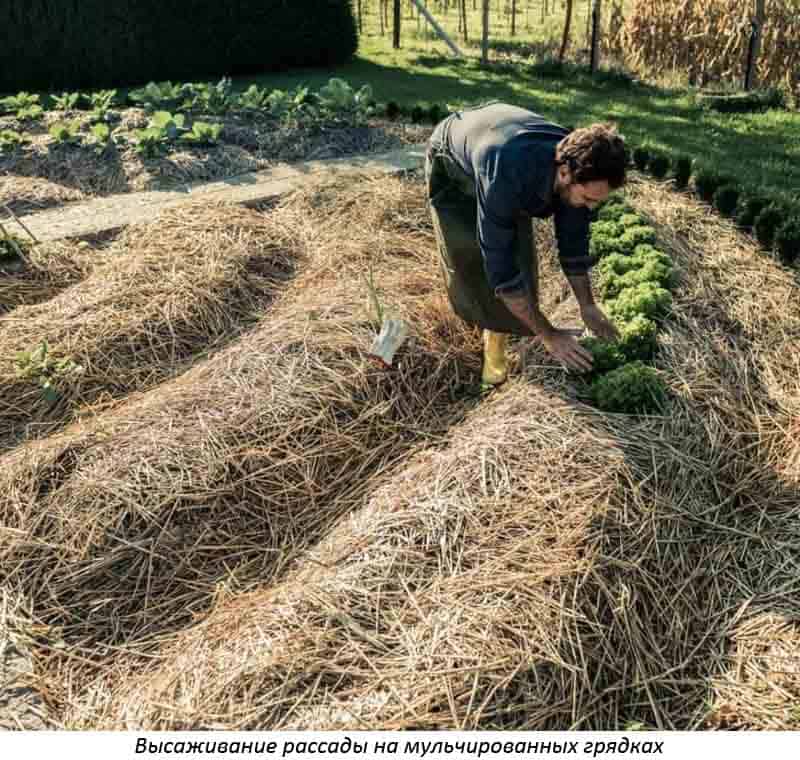
It is important not only to find the right material, but also to find the perfect solution for each culture. Mulching with straw in the greenhouse and outdoors is a great option for multiple crops.
Hay or straw for mulching
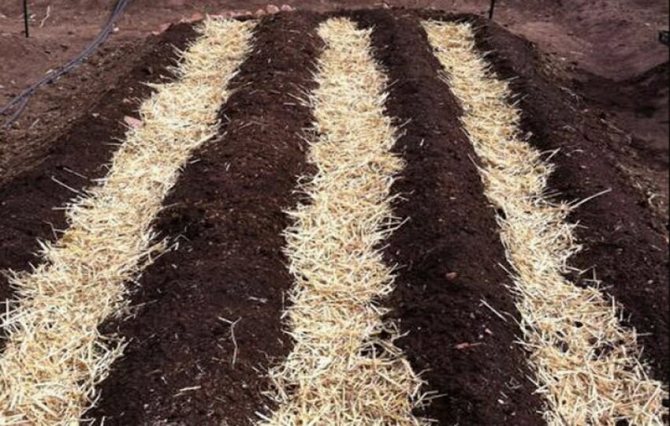
Straw mulching is suitable for several crops at once:
- The most common mulching of strawberries with straw. This material does not acidify the soil, and after rotting it also serves as additional fertilizing. It is important to mulch strawberries with straw after they are well dried. Do not lay wet mulch, as this will lead to debate and rotting. The straw is laid in a layer of about five centimeters. Cover the soil at the flowering stage of the bush. In the future, even after sediment, the berry will not lose its presentation, will not be affected by a fungus and will not start to rot.
- Mulching the beds with straw and potatoes is also a common option. In this case, we also use cardboard. It is laid directly on the beds immediately after the snow melts. After such a shelter, weeds will die without light. Next, we make holes for planting potatoes. The hole size is slightly larger than the tuber itself. Next, we lay a layer of mulch about 20 cm just on top of the cardboard.
- Mulching with straw in the greenhouse and in the open field is also suitable for garlic, basil or blackberry planting. If you lay a layer up to 20 cm, it will gradually settle and you will get a shelter of about 5-6 cm.
Mulching with straw gives you the opportunity to lay a kind of blanket in your garden beds. This blanket reflects the sun's rays and retains moisture in the soil, and also prevents the fruits from contacting the soil after precipitation and rotting, and it will help save the crop from some pests.
Pros and cons of using
Benefits of using straw include:
Prior to the introduction of the three-field farming system, the value of straw was practically zero.
- Odorless (unlike manure), relative safety.
- Natural composition, unpretentiousness in terms of storage and use.
- A rich complex of nutrients, micro- and macroelements, vitamins, minerals.
- The ability to improve the condition of the soil, saturate it with carbon (a component of photosynthesis).
- Airiness, lightness.
- Moisture storage.
- Strengthening soil activity - enzymatic and biological.
- Elimination of weeds and pests.


- contains the larvae of harmful insects;
- in the absence of precipitation, additional watering is required;
- it takes 2-3 years to get the result;
- uncontrolled decay leads to damage to the roots of plants and their death.
The considered drawbacks of straw can be easily avoided:
- Do not sow cereals for a long time.
- Scatter straw strictly every year.
- Apply to the following garden plants: potatoes, legumes, row crops.
- Do not exceed the introduction rate, otherwise the straw will begin to destroy the root system of green spaces.
- Grinding raw materials up to 4 cm to accelerate decay.
- Use in conjunction with nitrogen.
The use of straw is an effective and economical method of soil enrichment with useful substances. The benefits of fertilization are undeniable, but to achieve maximum results, you must strictly follow the rules for working with dry stems.
Monday, August 25, 2014 11:23 pm + in the quote pad


The family of the Mishurny settlers share the secrets of growing food under straw.
Fertility in the ecovillage and Zvon-Gora near Vitebsk, where Vlad and Alla Mishurny live, do not quite mean what we used to mean.
Fertility, explains Vlad, is not what a person takes from the soil, but its ability to extinguish and smooth out climatic influences, suck water, transport minerals inside, decompose organic matter, retain water vapor and gases, bind nitrogen from the air, balance and to restrain the size of its population and many more properties. By the way, ideally, the soil regulates its population - these very kilograms of bacteria, insects, worms and fungi - so that the ratio is in favor of plants.
Extensive farming, which the Tishurnye people have been doing for eight years, is precisely aimed at preserving all these properties, that is, soil fertility. And not just keep it, but build it up from year to year. A straw garden is the ideal solution for this.
What to do with old tree stumps
Grubbing an old orchard or just trees outside the territory of the dacha is already a difficult job to still think about what to do with old stumps. But in this situation, it is possible not to look for a solution to the issue, because it has long been there. Any old tree stump can be used as decoration on the playground, which is called rutaria. If you apply a little imagination, not only single figures, but also whole compositions are obtained from the stumps.
In addition, stumps can be used in the place where the tree itself previously grew. There is no need to waste energy on digging and uprooting, undermining a large stump with a tractor or other power equipment, because you can always make a pretty landscape object out of a stump, inside which to organize a flower bed.


Flowers, herbs, spices, berry bushes, and even bonsai can be planted in the hollow of an old tree stump.
From straw to first harvest - 2 years
We warn you right away: if you decide to cover your garden with straw right now in the hope of getting a record harvest, nothing will come of it. No, good mulching has not damaged a single vegetable garden. But, like the Mishurnykh, it will not work. Because they are in no hurry. - The earth checks a person, the seriousness of his intentions, his strength, - Vlad is sure. - Checks for a long time. But then, if he entered into resonance with her, he rewards. It can work by inertia for several years, even if you do nothing.
Don't touch the moles!
I would especially like to say about the moles. Many in their garden plots struggle with them. They put bait, poison, rags with gasoline. I have a lot of moles on my site, but I do not fight with them, since they are very useful. Our gardens are amazed by the beetle larvae, which are very difficult to control, because you have to dig everything up on a shovel bayonet in order to pick out these pests. And in my garden I only work with a flat cutter and a hoe, I don't dig anything. May beetle larvae are eaten by moles. Since they bury themselves deeply, the moles follow them deeply.
Well, yes, when watering, bushes of cucumbers, tomatoes, and onions often fall through my mole passages. So what? It’s not scary, I don’t suffer from greed. Spill, pour in, and the bushes are restored. And to poison your land with chemistry for the sake of dubious extermination of moles - no, in nature everything must be balanced. Each pest has its own predator.
Straw like onions and strawberries
Tinsel straws are underlain by everything - from bulbs to flowers in flower beds. And they all grow.
- Here are the thickets of strawberries, - Vlad continues the excursion. - For three years it grows, bears fruit, does not rot. Even last year, when it rained, it did not rot. This is because of the straw. Potatoes in a straw garden grow in three tiers. When it begins to break through from under the straw, it is again covered "headlong". And so two or three times. On the lower tier, the bulbs are the largest, on the upper tier they are smaller. Carrots, garlic, onions - everything grows in the straw. In a greenhouse, tomatoes are also planted in straw, only already pretty rotted - it's more convenient this way. And cabbage loves straw. Cabbage is moisture-loving, and the straw keeps the soil moist. Peas, beans, cucumbers - you can list it for a long time.
How much does it grow? The Tishurnye now get the same potatoes from their straw garden in a ratio of 1x25. That is, they planted one bag, and dig it up 25 in the fall. And when the children grow up, Vlad dreams, all soil indicators will improve so much that he will be able to give them all fifty bags for one planted. The family provides itself with all vegetables and fruits for a year with interest.
Extensive farming, in general, is not a novelty, but rather a well-forgotten old knowledge. Now it is gaining more and more popularity among summer residents. And what about the scale, for example, of a medium-sized agricultural enterprise?
- It is quite appropriate, because extensive agriculture was used on an industrial scale in the nineteenth century, - Vlad Mishurny is sure. - I was very impressed by Ivan Ovsinsky's brochure. This is the first Russian agronomist to prove the uselessness of a plow! At one time, Ovsinsky made a splash in tsarist Russia: he increased the grain yield tenfold, fourfold reducing the cost of labor and funds.
| Categories: | Flowers, dacha, vegetable garden .. |
Cited 2 Times Liked: 1 user
The straw that remains after grain crops is an excellent fertilizer for the personal plot. It is buried in the fall, used for composting and mulching. Straw heals the soil, fills it with useful microelements, protects garden crops from freezing in winter and pests in summer.
Composting and mulching - which is better
Mulching the soil under the plants with straw protects them from freezing in winter, prevents weeds from growing, but does not affect the nutrition in any way, or rather, it happens very slowly: while the straw is crumbling and equal to the soil, only then the microorganisms will gradually begin to process it. It may take 2 to 3 years for crops to receive nutrients from the mulch.
Compost is prepared two or more times faster, so it is more profitable to compost plant residues. To do this, it is advisable to acquire some amount of manure, so that its amount was ¼ of the weight of the straw. For example: a ton of straw - 250 kg of manure. In this case, the proportions will be correct and the compost will mature quickly.
Did you like the article? Share with your friends:


Hello dear readers! I hope the information from the article was helpful. Always open for communication - comments, suggestions. Peace and happiness to everyone!
Can I use it?
Straw has always been used since ancient times, when no other fertilizers were heard. However, this natural raw material has both advantages and disadvantages.
Benefits
- Does not require additional investment.
- More pleasant to use than manure.
- Contains many organic substances, vitamins, amino acids.
- Improves the structure of the soil, loosening it and making it water and breathable.
- Does not require special storage conditions.
- Saturates the soil with carbon, creating favorable conditions for plant photosynthesis.
- Promotes moisture retention in the ground.
- The use of several types of straw can completely restore depleted soil.
- As a mulch, it protects plants from burning out, inhibits the growth of weeds.
disadvantages
- Often contains larvae of pests, which will then impair the growth and development of cultivated plants.
- Insufficiently decomposed raw materials damage the root system of plants, as it releases harmful acids.
- Overheating of raw materials requires additional moisture.
- Useful substances do not enter the soil immediately, but after 2-4 years.
In terms of organic matter content, straw is several times ahead of ordinary manure.
To weaken the negative aspects of this organic matter, it must be applied annually, and immediately after harvesting, not forgetting about the dosage. If you add nitrogen, peat or chernozem to the dry material, the overheating rate will increase by 35%.
Plant nutritional composition
Using straw in the garden adds to the soil 25 kg of nitrogen substances, 4 kg of magnesium, 75 kg of potassium salts, 5 kg of phosphates and 15 kg of carbonates. This amount contains in 5 tons of cereal waste. A novice gardener might think that as soon as plant residues enter the soil, it immediately becomes richer. This is not true. It takes time for decomposition - about 8 - 9 months, and then, if you create favorable conditions.
When applied to the soil immediately before planting, no beneficial effect will be observed - plants may experience a deficiency of all of the above micro and macro elements.Often, gardeners do not understand why this is happening - they seem to have applied fertilizers, but they do not work.


For organic matter, there is one general law: it must be processed in the soil by bacteria, only after that the beneficial substances enter the soil. These mineral mixtures are added and after 3 days they are already effective. If your goal is to use safe fertilizers, you have to wait.
How to cook?
Straw is harvested both by hand and by means of special equipment. The last method applies to large volumes. Gardeners, on the other hand, prefer not to plant cereals on their plots, but to collect residues in the fields.
Application methods
The easiest way to use is by burying in the ground in early autumn. But it has one drawback - dependence on the amount of precipitation. If there is little rain, the straw will not start to overheat. Accordingly, in the next season, this site will not yet be suitable for planting.
Use as an integral component of the compost heap. Straw mixed with plant residues, manure, ash, minerals will decompose perfectly and will have a stimulating effect on the course of microbiological processes.
For a standard compost heap, first prepare a place, and then begin to lay the biomaterial in layers:
- The straw is placed at the very bottom, the approximate volume is 150 kg. It is advisable to pre-grind it.
- The second layer is weeds or just grass (20 kg).
- From above, the biomaterial is poured with a mineral solution: 6000 g of superphosphate, 4000 g of nitrate, 6000 g of potassium chloride are taken for 40 liters of water.
The compost heap needs at least a year to ripen. Then the contents are mixed and you can start using the most valuable organic fertilizer.
Straw ash is the most valuable in terms of potassium content (30%), so many gardeners are in a hurry to burn it. It is sprinkled with almost all cultures. The dosage is up to 70 g per meter.
Buckwheat and sunflower trunk are famous for a similar composition. However, straw ash is poor in calcium, and therefore it is better to mix it with wood ash.
How to get a big harvest on a straw bed
The use of straw in gardening is not new. Straw is an excellent mulching material and a good addition to soil and compost. And the insulation for greenhouses from it turns out to be a noble one.
And recently, straw in the garden has found a new use: chopped straw (chaff) is used as soil for growing vegetables. And, I must say, vegetables grow on such soil just for the sake of sight - tomatoes, for example, from "straw" 1 m2 are harvested at 40 kg, while on ordinary soil - 22-25 kg.
STRAW: BIOFUEL AND ECOLOGICAL PRIMER
Straw is often used as a biofuel. But even when used as a primer, the results are impressive. The yield on such soil is usually higher, and vegetables do not get sick. Ripening occurs one to two weeks earlier than in a traditional vegetable garden.
And, in addition, fruits grown on straw contain more dry matter, sugars and vitamin C than ordinary vegetables.
Straw has one very useful quality: undergoing partial decomposition and mineralization, it is able to supply vegetables with a large amount of carbon dioxide during the growing season. In addition, all the properties of an ecological soil are inherent in it.
WHICH STRAW IS BETTER?
It is best to use wheat or rye straw for gardening purposes. It is also allowed to use a mixture of them. The main condition is that the straw should not be affected by diseases and contain residues of herbicides.
Straw bales are used as biofuel in greenhouses. As a rule, this method allows you to completely get rid of root rot, streak, brown leaf spot.
Typically, the yield from straw beds reaches 18 kg per 1 m2, and it is harvested a week earlier than in greenhouses with ordinary beds.
HOW IT WORKS
First of all, old soil is removed from the greenhouse, the soil is disinfected with a 1% solution of potassium permanganate. Disinfection can be omitted, but then plastic wrap will need to be placed under the straw. And already on top of it - straw or straw bales.
The densely packed straw is heavily watered with hot water from a watering can, then sprinkled with dry fertilizers and watered again - until the straw is completely saturated with fertilizers. After that, the straw is sprinkled with lime and watered again.
For 1 m2 of area, 10-12 kg of straw are taken, therefore, a greenhouse with an area of 10 m2 will require 100-120 kg.
Before the second watering with hot water, fertilizers are applied so that the plants do not experience nitrogen hunger. For 10 m2 it is necessary to add 1.3 kg of urea, 1 kg of superphosphate, 1 kg of potassium nitrate, 0.5 kg of potassium sulfate, 1 kg of lime.
Hot water and the active vital activity of microorganisms heat up the straw to + 40 ... + 50 ° C. It is impossible to plant seedlings right away - you need to wait 7-10 days until the temperature drops to + 35 ... + 40 ° C. Now a ten-centimeter layer of earth is poured over the straw, wait another 7-10 days, and only after that the seedlings are planted. It is best to plant it by burying the roots in the straw. By this time, optimal conditions for the development of the root system will appear in the straw, and the plants will quickly grow.
FEEDING AND IRRIGATION
Problems with feeding with the "straw" growing method are solved even when the straw is impregnated with fertilizers. The only thing that needs to be done is to water the straw with a weak solution of urea (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water) every one and a half to two weeks. Feeding the plants once a month with complex fertilizer (1 matchbox per 10 liters of water) will help to increase the yield.
During the "greenhouse" season, the surface of the bales must be mulched twice with a straw chopper, previously impregnated with concentrated ammonium nitrate.
Straw beds can be used not only in greenhouses, but also outdoors. Their use is especially effective in areas where strawberries are infected with a nematode. Those bushes that grow in straw beds turn out to be much healthier. You just need to remember that you need to water them more often.
But cucumbers and pumpkins are rightfully considered the most grateful "residents" of straw beds.
garden.
Fertilizer for the garden
In soil, it first breaks down into proteins and carbohydrate compounds, and only then into cellulose, lysine. This process goes faster if a powerful catalyst, nitrogen, is added to the ground. Therefore, it is always best to combine the introduction of straw with the use of this mineral. The optimal dosage is 15 kg of nitrogen per 1000 kg of straw.
Some gardeners also add a third component - manure, so that the fertilizer becomes even more nutritious and rich in minerals. In addition, manure enhances the decomposition of bio-raw materials by increasing the activity of microorganisms.
Thanks to the introduction of nitrogen, the straw reheats faster and gives the soil nutrients.
Before proceeding with the laying of dry matter in the soil, it should be thoroughly crushed. The maximum size of straws is 16 cm, the minimum is 9 cm. In addition, it is recommended first to add nitrogen (urea or saltpeter). The dosage is 100 kg per hectare. Dry stalks are laid to a depth of 13 cm. The straw is reheated slowly, and therefore you need to wait a little with deep digging.
It is customary to use straw as an organic top dressing for potatoes and corn, beets and turnips, zucchini and carrots, watermelon and pumpkin.
Excellent results can be achieved by combined application with siderates. First, dry biomaterial is buried, and, for example, mustard is sown on top. All this gives the soil several sources of natural organic matter at once. Siderata provide additional mineralization, which will have a positive effect on future harvests.
Note. The combination of two types of organic matter significantly increases the yield of winter crops.
Gardeners' mistakes when planting residues in the ground
According to the rules of how to use straw in the garden and vegetable garden, it is crushed to particles up to 5 cm in size. This makes it possible to achieve the fastest decomposition, therefore, the release of nutrients into the root growth zone. When embedding large or solid particles, the process slows down several times.
If the cereals were not grown on their site, but were collected in the fields, then you need to pay attention to whether the straw is not infected with a fungus. It will look like a gray or black coating.
In this case, you cannot use raw materials - fungal spores will infect the site and cultivated plants will hurt. In this regard, it is preferable to add the remains of leguminous plants to the soil - they are more resistant to the effects of the fungus.


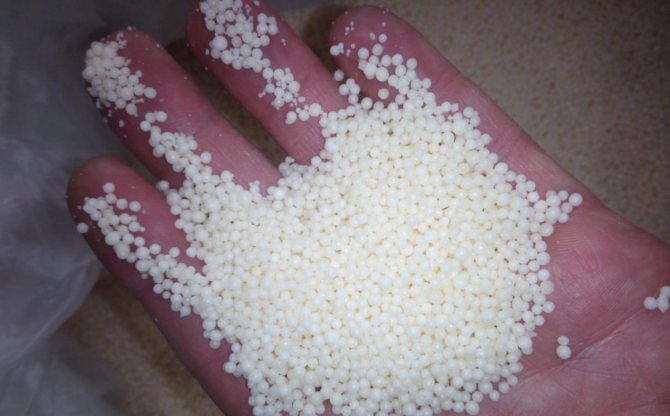
Cooking straw ash can also be considered a mistake if dry raw materials are not contaminated with diseases. The fact is that when straw is burned in your garden, the top layer of the earth is exposed to high temperatures and all microorganisms in it die. Question: who will be engaged in organic processing? Combustion volatilizes valuable nitrogen and carbon, which depletes the soil.
How and when to apply to the soil
If you have to burn straw, then you need to do it in an iron barrel, and then take it out into the garden and be sure to dig it up. In this case, the ground must be moist.
To speed up the decomposition process, it is recommended to mix saltpeter with the straw - 15 kg of nitrogen fertilizers per ton of stubble. If possible, manure is also added in the fall, in which there are already active microorganisms, ammonia, so such a fertilizer for plants will definitely benefit.


It is best to drop organic matter in the fall, but you need to monitor the amount of precipitation. If there are few of them, it will be necessary to water the site before frost to start the decomposition process. By the way, it is similar to the one that occurs when burning in a compost heap.
Straw instead of soil
Innovative gardeners use straw both as fertilizer and soil. So, there is a positive experience of growing potatoes in a layer of straw. This method does not require hilling, weeding, watering, fertilizing, and removing pests. Everything is done by dry organic matter: it retains moisture, nourishes plants with all the substances necessary for growth, blocks the growth of weeds, and scares off Colorado beetles.
The planting technology is as follows: peat is poured onto the garden bed (layer height is within 25 cm), potatoes are laid in any sequence, covered with straw. They take it up to 35 cm. That's all. At the end of summer, all that remains is to harvest the crop. If it is very dry, it is better to water the potatoes a couple of times.
Note. Potatoes grown in this way are usually large, even, clean and very productive.
Theoretical block.
Organic compounds are chemically stable and cannot be used by plants. They turn into forms accessible to plants only after the vital activity of microorganisms.
Microorganisms use the carbon compounds of straw as a source of food and energy. Bacterial transformations of substances affect, first of all, simple carbohydrates, and therefore a relative increase in the content of cellulose and lignin occurs in the composition of straw.
With the increased reproduction of cellulose-decomposing bacteria, cellulose is also destroyed. After the destruction of fiber, lignin becomes available to microscopic fungi, which they also decompose.
The decomposition of organic matter of plant residues occurs the faster, the richer it is in nitrogen. It was found that in 2.5-4 months up to 46% of the straw decomposes, in a year and a half - up to 80%, the rest later.
Straw mulching
Straw has become widely used as an excellent mulching material.She covers the beds for the winter in order to protect against frost, in the spring - to avoid burns, in the summer - to protect against overheating and to maintain optimal soil moisture.
In addition, mulch suspends or blocks the normal growth of weeds. Mulching helps to increase the amount of organic matter in the soil. The soil becomes looser, more airy. Under the influence of sunlight, the earth is deprived of many useful elements, and straw mulch prevents this.
The main tasks of mulch on a personal plot
More recently, it was not customary to mulch a personal plot. The garden was exemplary, in which, in addition to the crops grown, there was not a blade of grass... Digging, weeding, loosening, frequent watering took a lot of time for the gardener and required good physical fitness from him. Together with the gardener, the soil he cultivated also suffered.
Use of mulching materials on a personal plot helps the gardener to solve the following tasks:
- improve fertility and structure the soil;
- prevent soil overheating and protect plant roots from the scorching sun;
- ensure constant soil moisture and reduce the number of irrigations during the hot period;
- protect the soil from washing out nutrients;
- protect the soil cover from the formation of an airtight crust;
- destroy weeds without mechanical and chemical influences;
- protect garden and horticultural crops from hypothermia in cold weather.
What kind of material is suitable


There is no fundamental difference which straw to use:
- winter or spring;
- cereal or legumes.
You can use both fresh and last year's straw. If you mulch tomatoes with fresh straw, remember that plants in this case require more nitrogen, which is consumed in large quantities to decompose the mulch. Therefore, it is better to still use last year's or the year before last straw.
The material requires shelter during long-term storage, otherwise it quickly melts or damp, turning into compost. Overripe straw contains substances that inhibit plant growth. Damp straw cannot be used either, it rots very quickly.
Agrochemical aspect
A big mistake is the neglect of such agricultural practices as the introduction of nitrogen into the soil. The fact is that for the decomposition of straw, microorganisms of a protein nature are needed. and their reproduction to build the cells of these microorganisms, nitrogen is removed from the soil, which is replaced by protein. In this case, the ratio of carbon and nitrogen is of great importance, which is different in different organic residues. Mineralization will be complete if this ratio is 20: 1. In strawy plant residues, it is 50-100: 1. Under these conditions, straw mineralization (decomposition) can last for about two years. To reduce the C: N ratio, improve the conditions of mineralization and promote the active formation of the biomass of microorganisms, it is necessary to apply nitrogen fertilizers.
So, plowing straw without applying nitrogen fertilizers leads to a sharp decrease in the content of mineral nitrogen in the soil and a decrease in the yield of the following crops. And the introduction of straw in the amount of 35-40 c / ha with nitrogen compensation (at the rate of N10 / t of straw) in its effect on increasing soil fertility and crop yields is equivalent to the introduction of 18-20 t / ha of manure.
For the vital activity of microorganisms, a sufficient amount of phosphorus is also necessary: it is introduced at the rate of P8 for each ton of straw, this is especially important on soils with an insufficient content of available phosphorus. Phosphate and potash fertilizers should be applied here. At high temperatures, phosphorus and potassium will quickly become part of the soil complex and will be more efficiently used by the next crop of crop rotation (diagram).
Due to the mineralization of plant residues, a significant amount of nutrients are released from them, which are returned to the soil. For example, for every ton of grain with plowed wheat straw, N7P3K16Mg2 returns to the soil, and for every ton of rapeseed with a plowed mass, N14P6K40Mg3 remains. Then only the main part of the product - grain - takes out the elements of nutrition. The approximate content of macro- and microelements in plant residues of the most common crops is presented in Table 2.
The ratio of grain and straw, depending on the characteristics of the variety and cultivation technology, in winter wheat can be 1: 1.0-1.5. With a yield of 40 centners per hectare of grain, 40-60 centners of straw remain per hectare. Provided that the straw contains 0.5% nitrogen, 0.2% phosphorus, 1% potassium, 0.3% calcium, 0.15% each magnesium and sulfur, approximately the same amount of macronutrients N20 will return to the soil with this amount of straw. -30P8-12K40-60Ca12-18Mg6-9S6-9
The calculation was made only for straw, and part of the organic matter remains in the form of stubble and the root system of plants.
The best results are obtained by combining the two alternative organic fertilization methods. After chopping and embedding the straw into the soil, green manure must be sown. The most commonly used cabbage species. Then the soil is filled with organic matter from two sources: straw and green mass. In addition, green manures, their root system and green mass contribute to the mineralization of the straw, accelerating it. Late in the fall, the whole mass is plowed.
Under the condition of early harvest and sufficient moisture reserves in the soil, oil radish or white mustard, in the case of sowing from July 20 to August 10, form a high yield of green mass until September 20-30. Therefore, such a system of fertilization with straw and green mass can also be used for winter crops.
Straw is the non-cereal part of the crop, the length of which ranges from 30 to 180 cm, depending on the crop, variety, weather conditions during the growing season and the use of fertilizers. See below for the chemical composition of various types of straw (for comparison, the content of nutrients in manure: nitrogen - 0.5%, phosphorus - 0.25%, potassium - 0.6%):
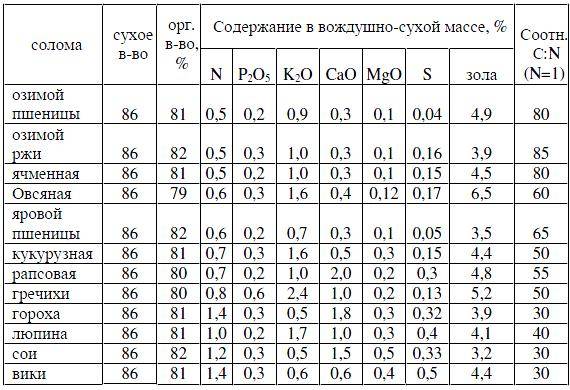

During the decomposition of the straw introduced into the soil, two main processes of transformation of organic matter prevail: to the final products - carbon dioxide, water and mineral elements - mineralization; before the formation of stable humic substances - humification. Humification of fresh organic matter in straw forms agronomically valuable physical properties of soils: structure, permeability, density, moisture capacity. Mineralization contributes to the transition to an accessible state of nutrients fixed in organic matter.
The content of nutrients, primarily carbon (C) and nitrogen (N), determines the rate of decomposition of straw, the narrower the ratio of C: N, the faster the straw mineralization processes. The optimal ratio for decomposition is considered to be a ratio of 20-30, when decomposition does not require nitrogen, except for that contained in the straw itself.
Pros of using straw as fertilizer:
1. Much greater availability of straw, compared to other types of fertilizers. In fact, before the widespread transition to a three-field system, it was a waste of little value, and even after this transition it was valued relatively low.
2. The process of obtaining straw takes much less time and effort than fiddling with the most common fertilizer - manure.
3. Working with straw is safer and more pleasant than with manure.
4. Due to the very low decomposition rate of straw, the loss of nutrients from it is minimal (about 50% of nitrogen and organic matter is lost from manure). It also makes it easier to store and apply on the field.
5. In terms of organic matter content, straw is 3-4 times higher than manure (the introduction of 1 ton of straw leads to the formation of 100-200 kg of humus), which, in turn,leads to the following: - the moisture permeability of the soil increases (precipitation is absorbed into the ground, and does not flow down the surface, causing erosion); - the water-holding capacity of the soil increases (the earth retains water (together with nutrients dissolved in it), and does not drain precipitation into the groundwater); - the physical characteristics of the earth improve, it becomes looser, which leads to an improvement in the living conditions of both plants and soil microorganisms, and the leveling of the influence of weather extremes on the harvest.
6. When straw is introduced, the general biological and enzymatic activity of soils increases, they are enriched with amino acids, vitamins and other physiologically active substances that have a beneficial effect on the development of plants.
7. The introduction of straw (due to its saturation with carbon) stimulates the development of nitrogen-fixing bacteria (one gram of carbon helps fix 15 to 20 mg of nitrogen, including atmospheric).
8. When straw decomposes, the near-surface layers of soil and air are enriched with carbon, stimulating the growth of green mass of plants.
9. When straw is introduced, it can perform a soil protection role (the field, after harvesting the previous crop, is mulched with straw, before its incorporation in late autumn). It minimizes erosion, suppresses the development of weeds, and provides additional moisture accumulation.
10. If, in addition to own straw, straw from other fields is used, micronutrient deficiencies in the soil will be eliminated. straw contains more of them than grain.
Cons of using straw as fertilizer:
1. The introduction of straw into the soil worsens the phytosanitary situation. Pathogens and pests remaining on the straw can reduce the yield of the next cereal crop by tens of percent. (If legume / buckwheat straw is added under the cereals, this minus will not play a noticeable role).
2. Since there is a lot of carbon in straw (in comparison with the nitrogen present in it), the microflora multiplying after its introduction binds not only the nitrogen of the straw and the atmosphere, but also a part of the mobile (easily accessible for plants) soil nitrogen. (Legume straw is free from this disadvantage)
3. When straw decomposes into the soil, fatty acids are released (especially a lot - under anaerobic conditions, when plowing to a depth of more than 15-20 cm) that restrain the development of all plants (the peak of these secretions is on days 2-6 of decay), and autotoxins that adversely affect cereals ...
4. For decomposition of straw, like any organic matter, water is required, which can become a problem in areas of insufficient moisture (since manure is 1/2 water, it does not have such a problem).
5. Due to the low decomposition rate of straw, the nutrients contained in it will become available to plants gradually, over 3-5 years (if the deficit of nitrogen nutrition is not artificially compensated).
Measures to combat the above disadvantages:
1. Do not sow cereals after straw application (the longer, the better, since the effectiveness of straw fertilization increases if it is carried out every year).
2. Introduce straw in the year preceding the sowing of the next crop, immediately after harvesting the previous crop (6-8 months before sowing, the concentration of growth inhibitors will drop to minimum values; phytotoxins will inhibit the development of weeds, not crops; stocks of mobile nutrients will not be washed out into the lower horizons of the soil, but immobilized in organic matter; the residual moisture of the straw itself and water in the soil will go to decompose the straw, and will not be lost).
3. The next crop after the introduction of straw in the optimal variant should be legumes (they receive nitrogen from nodule bacteria, and organic carbon is the best substrate for them); if for some reason this is impossible - row crops, best of all - potatoes.
4. Do not overdo it with the amount of straw introduced: the optimal value is 0.4-0.8 kg / m2.Large quantities can only be applied with additional nitrogen feed, otherwise the harm from the straw may outweigh the benefit.
5. Before adding straw, it is better to grind it to pieces of 5-10 cm, which will increase the rate of decomposition and uniformity of distribution over the field.
6. If possible, it is better to combine the introduction of straw with the introduction of nitrogen in an easily accessible form (in our case, human urine, about which there will be a separate post). For soils with relatively low fertility at the rate of 1 kg of nitrogen per 100 kg of straw, for chernozems - 0.7 kg of nitrogen per 100 kg. This will increase the rate of straw decomposition by 1/3; most of the nutrients contained in the straw will go into a form that is easily accessible to plants.
And in conclusion - in the Tomsk region, field experiments were carried out with the introduction of straw, mineral nitrogen and green manure into the fields. For their results, see Table.
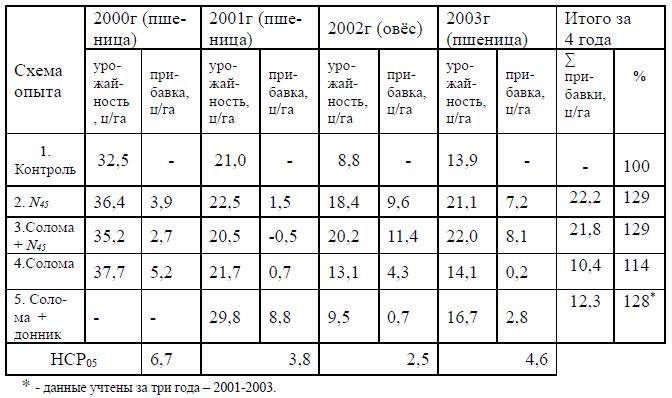

Conclusion: the use of cereal straw as fertilizer is possible in any historical era, and its introduction into widespread practice will have far-reaching and comprehensive consequences.
Common mistakes when applying mulch
- Laying material on unheated beds;
- Poor grinding of residues;
- Excessive watering of mulched crops, as a result - decay, fungal infections;
- Do not remove mulch in spring to warm the surface;
- Do not leave a free area around the root collar or trunk. Due to the compacted fit, decay occurs;
- Wrong order - first mulch seedlings, then watering. It is necessary the other way around;
- They do not take into account the characteristics of the soil - composition and PH, determining the thickness of the mulch.
Soil mulching is widely carried out in households and farms to preserve the living structure of the soil and increase fertility. From the materials used organic raw materials - straw, leaves, peat, needles, bark, branches. Geotextiles, black and colored films are popular. Materials are selected taking into account the composition and texture of the soil, the features of landscape design.
Now read:
- Planting, care and benefits of savoy cabbage
- The main technologies for growing peas and caring for them
- Choosing cucumbers for open ground according to your preferences
- The best varieties, growing rules, care for broccoli cabbage
Popular: Spring and autumn transplant of perennial peony in the garden
About
Agronomist of the state agricultural enterprise "Garovskoye" of the Khabarovsk region of the Khabarovsk region.
Do I need to mulch the grapes?
Loading mulch for vineyards is definitely worth it. Although this is a laborious process, it greatly facilitates the cultivation of the crop.
According to the rules, the procedure is carried out a year before planting. In the allotted time, the coating will be processed by microorganisms. Thanks to the shelter, the soil will become fertile, channels and tunnels will appear in it, along which air and water move. The grapes are more likely to take root in a new place and begin to grow actively. Its resistance to disease and freezing will increase significantly.
An exception is heavy clay soil. Coverage is not always useful here. The ground does not dry out after rains, so mulching material can impair the nutrition of the bushes. It is permissible to lay quite a bit, literally 2-3 cm.
How to apply corn stalk
Not everyone is interested in growing corn in the country, and even those who plant this plant in the territory of the country garden do it for different purposes.
Many people like boiled young cobs of corn, which can be simply nibbled with salt or added to salads. But many people grow corn to feed birds and other dacha living creatures. Therefore, it is worth noting that the harvest is harvested at different times, which means that the plant residues of corn will be in a different state.
Green corn stalks are great for livestock feed, so don't throw them away right away.From the stems, you can even prepare an excellent winter dressing called silage. But let's say right away that few of the summer residents are engaged in such matters, and a lot of green mass is needed for this.
But it also happens that corn stalks stand until autumn, and even completely dry out in the garden. This is not a problem, and you should not cut them down and burn them, because the dense structure of the dry stem makes it strong enough. Thanks to this, the corn stalk becomes a material for building temporary fences in the yard, or even material for garden paths in cold autumn weather, when it is damp and dirty underfoot.
The stems also serve as a covering material for berry bushes, as a bedding in a compost heap, as well as for wrapping young trees in the garden. Old-time summer residents also argue that if corn stalks are folded tightly and in several rows in a garden bed, then the earth in this place practically does not freeze, and this is the place that is most suitable for early planting.
Rules for using sawdust as mulch
Quite often, they are also used to protect crops from weeds, wind and other factors. If there are a lot of pests on the garden plot, then it is recommended to use this particular type of sawdust. They help prevent the development of fungal diseases. At the same time, they allow air to pass through well and can serve as an organic fertilizer.
It should be noted that sawdust should not be deposited. Therefore, there should not be too many of them. Accumulated sawdust contributes to the greenhouse effect and can harm plants.


Cones are also used for mulching.
Sunflower and Jerusalem artichoke stems
Many are trying to get rid of Jerusalem artichoke, since this plant grows too quickly in the summer cottage. But there are many advantages from him, as, in principle, from sunflowers. We will not talk about the beneficial properties or taste, but only confirm that you can use dry stems of these plants in the same way as dry corn stems.
In the country, you can usefully use a lot, and even plant residues. The roots, bark and leaves of trees are used, as well as plant stems, straw, and even dried flower petals, from which you can make jam, tea and some medicines. Therefore, do not rush to throw away what has already yielded a crop, because any plant can still serve you, even if it has died and dried up.
The use of plant debris and residues in the country is a good topic for practical summer residents, and we very much hope that this article will be useful to you. If you know other ways to use plant residues, or we forgot to mention something important, be sure to write about it in the comments to the article.
Mechanical aspect
Straw fertilization is not a simple agricultural practice. In order for it to become a truly valuable organic fertilizer, rather than a filler that interferes with tillage, the straw must decompose as soon as possible. Unfortunately, in most cases, fertilization with it is carried out with gross technological violations. In particular, the straw is crushed and left on the soil surface for a long time. During this time, moisture reserves in the soil are quickly lost, the straw dries up, and its decomposition begins only after heavy rains.
The effectiveness of straw fertilization depends on how it was crushed by a combine harvester, scattered over the field and embedded in the soil. Therefore, it is necessary to harvest the crop only with combines with shredders, observing the following requirements:
- cutting height during harvesting - no higher than 20 cm;
- the length of 75% of straw particles should not exceed 10 cm, and particles over 15 cm - no more than 5%;
- spread straw over the field evenly, without creating swaths;
- to close up the straw using a disc harrow (BDT-7) to a depth of 12 cm immediately after harvesting the crop, preventing the soil from drying out.Sufficient moisture ensures efficient operation of microorganisms and rapid decomposition of straw;
- apply ammonium nitrate before incorporating straw at the rate of N10 / ton of straw (roughly: 1 centner of nitrate per 1 ha);
- be sure to carry out autumn plowing.
If it is not possible to chop the straw due to the lack of combines with choppers, then the problem can be solved by adjusting the cutting height during harvesting. With direct combining, the stubble height can be 30 or even 40 cm, i.e. almost half of the straw remains in the field and is evenly distributed. After harvesting, such stubble is cultivated with heavy disc harrows.
We get negative results when burning straw and stubble. This is an unacceptable manifestation of mismanagement, since in this case many beneficial microorganisms are destroyed and the potential soil fertility is sharply reduced. Organic carbon and nitrogen are irretrievably lost. In addition, great damage to the environment is caused. Straw burning is perhaps the only agricultural damage factor that equates to industrial air emissions.
Making mulch from bark and chips
Bark and wood chips are in great demand, but before mulching, you need to know the nuances of these materials. The bark contains tannins that slow down the growth of crops. The bark makes the soil more acidic, conifers just take root in such a soil.
Spruce and cypress respond well to compost. The bark has many benefits. It is easy to use and allows oxygen to pass through. Natural material contains phytoncides. These components purify the air and drive away pests. Bark mulch looks beautiful. Chips are also not without benefits. It increases the fertility of the soil and makes it looser. Natural material retains moisture, prevents fungal diseases.
Features of mulching in the open field
In most cases, this work must be done at the beginning of summer, when the soil has time to warm up. Autumn mulching is possible only for some crops. It should be noted that the straw should not adhere tightly to the roots or stems of plants, so as not to create a greenhouse effect.
During the summer, the straw can be added as it subsides. It is also possible to spud the shoots for additional protection from external influences. Usually within 2 - 3 months, organic mulch will rot and become a good fertilizer for the soil.


Decorative mulching
Important. If you plan to grow carrots or parsley in the places where potatoes and cabbage grow, then it makes no sense to remove the mulch.