Climbing multi-flowered roses are flowers with a single flowering on the side shoots of last year's long branches. Flowers are medium in size - up to 8-10 cm. They are powerful plants. During the season, these climbing roses form only a few basal shoots. The bulk of flowering stems are formed higher on older stems. Pruning climbing roses after flowering is reduced to removing old lashes as new ones appear. These roses are formed horizontally. These roses include, for example, the varieties Albertine, Chaplin′sPink.
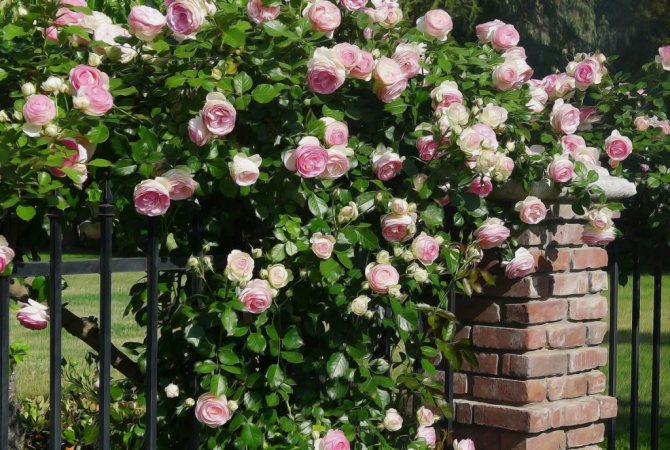

After planting, climbing roses of this group are cut to a height of 25-35 cm. In the second and subsequent years, pruning of these rose bushes is done after flowering. One or two old stems must be completely removed. They will be replaced by any root shoots that have begun to grow. If there are none, then one or two old stems are cut to 35-40 cm from their base.
With respect to old stems, pruning is carried out to the place where a new strong growth has appeared. He will become a guide. The plant continues to form in the horizontal plane. Short shoots that should bloom are shortened to 2-3 buds or up to 15 cm from their base. Weak shoots are shortened, leaving 2-3 buds from their base.
In summer, the rose blooms along last year's horizontally formed whips and on trimmed side shoots. During the growing season, the plant has young strong continuation branches.
Garden, vegetable garden and flower garden tips
Landing days in July 2019 in the Urals
Gooseberry care all season for large berries
Garden pests living in the ground photos and names
After the rose has finished blooming, it is pruned. This is done around August - September. Partially cut off old and all diseased shoots. One or two old lashes are shortened to 30-40 cm from their base. This stimulates the growth of replacing basal shoots. Important! If you want the rose to bloom constantly, cut off the wilted inflorescences.
Purpose and timing of pruning roses
In horticulture, it is customary to call roses the cultivated forms of plants belonging to the genus Rosehip of the pink family. With all the variety of types and varieties of roses, there are several general principles for pruning them.
Pruning is one of the most important agricultural activities. Timely pruning of roses is the key to the longevity of the bush, its decorative effect, good and long flowering.
To anyone who is just starting to master the features of pruning roses, this process will seem in many ways simply incomprehensible. And the point is not even in the variety of species and varieties that require an individual approach, but in a large number of types of pruning. Nevertheless, it is possible to single out the main tasks of pruning roses, on the basis of which one can determine the methods of its implementation.
So, pruning roses has the following goals:
- rejuvenation of the bush. By removing old shoots, the plant can spend all its energy on the formation of large, beautiful buds;
- giving the bush the most decorative look. By cutting off excess and unproductive shoots, you can give the bush the desired shape;
- lush and long flowering. Buds form only on strong young shoots;
- creating optimal conditions for wintering plants;
- reducing the risk of developing fungal diseases. The fact is that good ventilation, provided by removing excess branches inside the bush, prevents the occurrence of diseases;
- getting excellent cut specimens.
The basic rules for pruning roses are as follows:
- pruning is carried out to healthy wood;
- pruning is carried out on the bud located on the outside of the shoot;
- if after pruning 2-3 shoots develop from one bud, then only one should be left, the rest should be removed;
- it is necessary to remove all diseased, thin, dead, weak, intersecting shoots to healthy wood or to the level of the soil;
- so many shoots should be left so that there is normal air exchange and good illumination of the bush, this helps prevent the development of fungal diseases.
Pruning roses is a simple operation, but it requires knowledge.
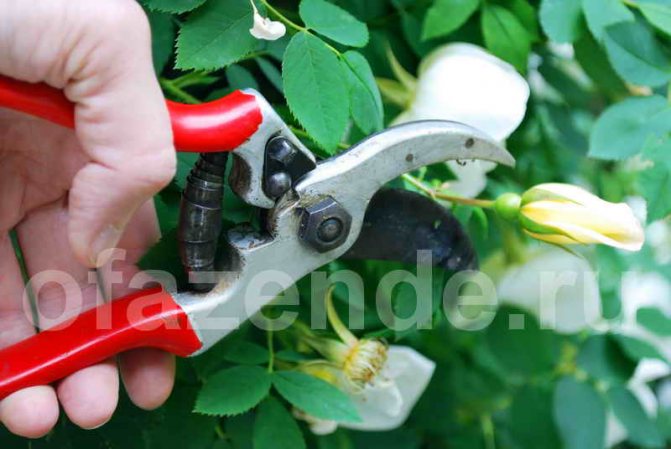
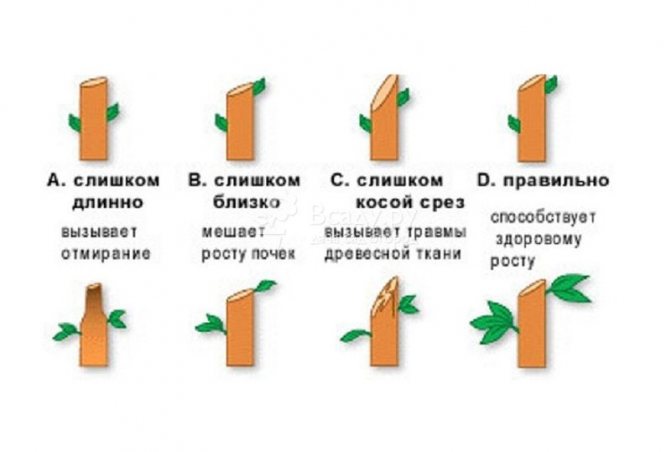
Shoots are cut with a sharp secateurs 5-6 mm above the developed bud and at an angle of 45 °. The cut surface must be smooth, free of cracks and burrs. It must be covered with garden pitch.
In the first summer after planting, special attention is paid to the formation of bushes. At this time, when pruning roses, all small, growing inward, thickening shoots, as well as growing from the graft site or root collar (in own-rooted ones) are cut into a ring, strongly growing ones are pinched. In July, the formative pruning is finished so as not to cause the growth of new shoots, which, not having time to ripen, freeze and often cause diseases of roses. In grafted roses, wild shoots are systematically cut out to the base, of which there are especially many in the first summer, with age it becomes less. In order not to weaken the plants, the buds that appear can be removed.
In subsequent years, summer pruning consists in shortening individual shoots that are too violently growing, especially in bushes of large-flowered roses and crowns of standard roses. However, the most important task of summer pruning is to induce the plant to bloom again. In order for the bush to give the maximum number of flowers that a particular variety is capable of producing, its correct summer pruning is necessary. You cannot just remove a faded rose flower by simply pinching, i.e. tore off one flower and that's it - this is a big mistake, because a new shoot with a flower will appear very high. It will be elongated, thin and easy to tilt, i.e. bend. It is necessary to remove the flower even before the petals completely fall off, i.e. as soon as the appearance has lost its appeal. You need to cut the flower lower, then the new shoot in this place will be strong and will hold on tightly (when cutting the flower, leave the stumps above the eye 6-8 mm). Probably, the disputes between gardeners about the need for pruning will never stop, because someone considers it a panacea for all ills, and someone perceives it as an act of vandalism over the very nature of the tree. Nevertheless, many years of experience show that pruning is necessary in many cases, contributing to more active growth and abundant flowering and fruiting, helping in the prevention and treatment of diseases and eliminating pests, and in addition, it prolongs the life of garden plants, allowing them to delight us with their fragrant fruits or beautiful flowers for much longer.
At the same time, one should not start pruning plants thoughtlessly, because each species or even variety requires an individual approach: someone needs a minimum of interference, and someone is unable to give a bountiful harvest without strong pruning in the spring.
However, remember: even observing the rules for pruning roses and performing this procedure in a timely manner, without proper care of the plant, it will still not bloom as expected. Therefore, take care of your garden, take care of the cultures, and they will surely thank you with lush flowers and delicious fruits.
General rules for caring for roses
Thanks to the work of breeders, modern varieties of this crop can grow almost everywhere.However, for abundant flowering, it is better to plant them in a sunny place in well-drained soil, and then feed them in a timely manner, water them regularly, carry out pruning and preventive treatments for diseases. There is a certain set of rules for caring for a plant:
- The correct planting of the seedling and the creation of conditions for its rooting are important. Better to give preference to a plant with a closed root system. When buying a seedling with open roots, you need to look at their condition. There should be a lot of roots and they should not have a dried out appearance.
- You should not immediately chase a large collection of varieties. It is better to start with buying 1-2 varieties and learn how to care for them. In the future, you can purchase other roses to decorate your site.
- Ideal for planting this flower will be a site where he can sunbathe for 6-8 hours daily. In the northern regions, it is better to plant the culture near the fence and walls of the house from the south or west side, providing them with protection from the cold wind. If the soil at the planting site is not very fertile in composition, it must be fertilized.


Planting roses
- Landing dates must be met. It is necessary to plant either in early spring, or in the fall one and a half months before the onset of frost, so that the plant has enough time for rooting. The event is best done on a cloudy day.
- For the flowering to be luxurious, the rose needs top dressing. It is recommended to apply organic fertilizers monthly, and mineral complexes twice a season, in spring and autumn. It is recommended to feed a newly planted plant with one organic matter until it blooms. At the time of flowering, granules with minerals can be added.
- The soil on which roses grow should always be moist. Watering is adjusted according to soil composition and weather conditions. On sandy soil, the rose requires more frequent moisture. During hot and dry periods, flowers should be watered daily, avoiding getting water on the leaves.
- The main pruning of roses should be done in early spring. During it, all damaged, weak and diseased shoots are removed, and healthy branches are shortened by half of last year's growth. It is also required to regularly remove faded buds to stimulate the emergence of new flowers. In grafted roses, you need to cut out wild shoots at zero.
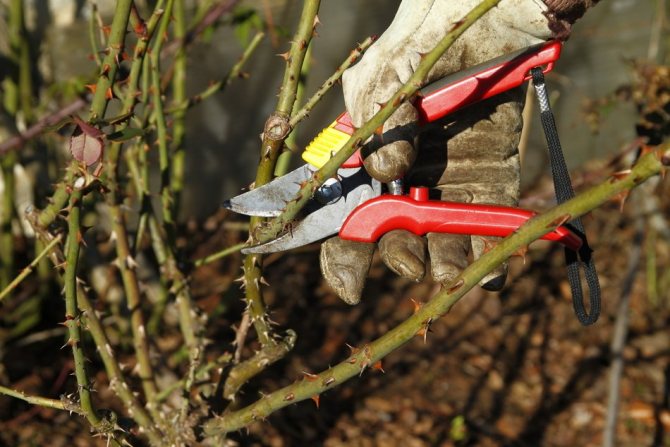


Main pruning of roses
- To keep the roses healthy, it is best to purchase disease-resistant varieties. To prevent the appearance of powdery mildew, thinning pruning should be carried out, which will ensure good air exchange within the bush. In order not to provoke the appearance of black spot, roses are watered at the root, preventing moisture from getting on the leaves. Insecticides are used to control pests.
Compliance with all the recommendations set forth will make it possible to enjoy a long luxurious flowering and aroma of roses on your site. Flowers grown with their own hands bring a special joy to the gardener.
Pruning roses to form a bush
A rose bush is formed in the first summer after planting. Small shoots growing inward and shoots coming from the root collar or grafting site are cut into a ring. Too long or intensively growing shoots are pinched. In June, the formation of a bush when pruning roses is completed. Otherwise, the rose will give new shoots that will not have time to ripen before winter.
Removing wild growth. Most often, roses are propagated by grafting: the varietal form of the rose is grafted onto the wild stock. Later, wild shoots grow from the site of inoculation. Their leaves are smaller, the stems are lighter, and they have more thorns. A part of the nutrients intended for the cultivated plant is spent on wild growth. Therefore, one must immediately get rid of such shoots, preventing them from growing. Wild shoots are cut in May.From the root collar of the bush, they rake off the earth to expose the place where the shoot grows. The sprout is cut off at the base with sharply sharpened scissors or a knife. A little bark is removed along with the shoot. Cutting off wild shoots near the soil surface is useless. Moreover, it will only enhance their growth.
Pruning by timing is divided into spring, summer and autumn.
Differences in the formation of a bush in spring and summer
Spring pruning of roses is considered basic. At this time, all the main activities are carried out to form and clean the bush from sick, dead and thickening shoots. The plant is given an open sun, vase-like shape with an empty center.
How to prune roses in summer? Pruning in July is done to remove buds that have begun to bloom. You need to cut off the shoot on an open bud so that the young twig grows outward. Blind shoots without flower buds are also removed at this time of the year. They are not cut at the root, but so that several developed five-leafed leaves remain on each.
Attention! Blind shoots should not be confused with basal branches growing from the neck and subsequently forming the basis of the bush, replacing old stems.
Without pruning, it is impossible to get a plant of the appearance that a gardener would like to have. When caring for roses, this technique should not be neglected. Removing shoots allows you to give the bush the desired shape, maintains its health, and rejuvenates. Pruning begins from the moment of planting and is periodically repeated throughout the life of the rose.
Pruning rose bushes in spring (with video)
After pruning, the roses are sprayed with a solution of copper sulfate at the rate of 100 g per 1 liter of water, then the bushes are spud and covered with film or lutrasil to create a shade.
If spring night frosts are no longer expected, then they remove the shelter from the roses and get rid of them.
Spring pruning is the main one, since the formation of a rose bush and its subsequent development are directly dependent on it. Each year the pruning time can be different due to the instability of weather conditions in central Russia. But in any case, it must be carried out on time. If the rose was cut too early, then during the first warm days, the buds will begin to swell and grow, but with repeated frosts, which also often happens in the middle lane, they die; if pruning is done late, the bush will spend too much energy on the formation of new shoots, which will later be removed.
Pruning rose bushes in the spring is carried out immediately after removing the shelter and breaking the bush. Roses are pruned in spring in March - April. It is advisable to wait for the awakening of the kidneys. Then it will be clear which stems are damaged by frost, and which survived the winter normally.
The rose is pruned, thereby creating the conditions for the beginning of the formation of the bush, which is characteristic of this garden group, and the most lush flowering.
The stems are shortened to a height of 20–25 cm. The exception is climbing and park species: they only cut off old shoots.
Growth buds of a rose are located in the leaf axils. The cut is made as close to the kidney as possible, but so as not to damage it. The cut is performed with a sharp pruner at an angle of 45 ° with an inclination from the kidney and at a distance of no more than 0.5 cm from it. The bud should be on the outside of the branch.
The shoot is cut to a healthy tissue. It is easy to determine the state of the branch: if the core is dark, brownish, then the tissues are damaged. The healthy core of the branch is white or greenish-white.
Sometimes several sprouts develop from strong buds at once. Of these, only one shoot is left, and all the rest are removed as soon as possible.
All varieties of roses need regular sanitary pruning.Broken, dry, diseased and damaged branches, as well as thin and weak growths, are cut to the level of the soil or to a healthy shoot.
To make it easier to care for the rose, before planting the bush, you need to check if there are any wild shoots on it. The found sprouts are cut with a sharp knife or scissors at the base, capturing a little bark.
The intersecting branches are cut so that one of them is below the intersection point.
The rose bush should not be thickened. So many shoots are left on it to ensure normal air exchange and sufficient illumination.
After pruning young roses, the soil under them is mulched with well-rotted manure or compost.
The video "Pruning rose bushes in spring" shows how this procedure is performed:
Help on Tele2, tariffs, questions
Using a clean pruning shear, cut the stems at an angle of approximately 45 degrees. A cut at this angle prevents the stems from completely resting on the bottom of the vase, which could prevent them from receiving the required amount of water and quickly fade. Cut the stems close to the ground so that the flower is long enough for later pruning.
Place the cut roses in a bucket of warm water.
Don't rush to put roses in a vase. Use a bucket that is wide enough for you to work comfortably in it. All further cuts are made in this bucket of water so that air bubbles or emboli do not end up inside the stems.
Cut the leaves below the water level.
Leaves immersed in standing water can develop bacteria and rot processes. Leaves must be left above the water, allowing them to occupy from the top third to half of the stem. Otherwise, roses simply won't be able to absorb water.
Pruning roses is essential primarily for regular rejuvenation and health maintenance. Pruning also achieves a good bush shape, lush and long flowering.
To many rose lovers, pruning seems like a complicated and mysterious process. To master the secrets of pruning roses, you need to stock up on a good tool, familiarize yourself with the basic principles common to all types of roses, and master the pruning technique.
Required set of tools: two types of pruning shears with sharp blades (for pruning thick and young shoots), garden shears with long handles for pruning in hard-to-reach places, garden saw for pruning very thick shoots and removing old hemp and a garden knife for stripping low-quality cuts ... To protect your hands from thorns, you will need thick gloves, and to protect the cut surface from possible infection, you need a garden var or a special paste called Rannet, which is easy to use.
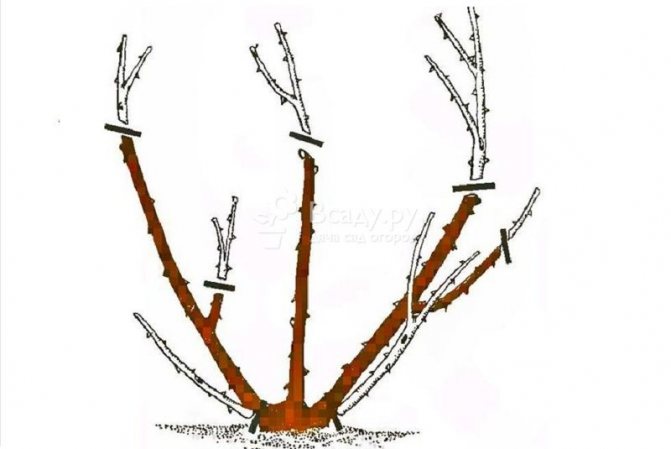
Basic principles and techniques for pruning roses Growth buds (eyes) are located in the axils of the leaves. After leaf fall, they are clearly visible above the leaf scars. The higher the buds are located, the faster they germinate. In the lower part of the shoot of the rose there are "dormant buds", which, before germinating, must go through several stages in their development. Pruning for immature buds delays the timing of flowering. Pruning should provide the ability to ventilate the crown and access the leaves and buds to light. The rose should, if possible, be cut to the outer buds and the center of the bush should not be thickened. The cut should be smooth, without torn edges, no closer than 0.5 cm from the bud and with a slight slope from it. Pruning should be done to a healthy (white) heart. If several shoots appear in the axil of one leaf, it is necessary to remove all but one at an early stage.
You need to start pruning all types of roses by removing dead, sick and frost-damaged stems, as well as thin and weak growths. Such pruning is called sanitary or thinning.
In order to avoid the spread of diseases, the removed parts of the plants should be burned. you can only work with a serviceable, clean and well-sharpened tool.
Types of rose pruning
Strong (short) pruning, at the level of 2-4 buds from the base of the shoots, is usually used when planting seedlings in spring, in case of rejuvenation of old bushes or as a last chance for weakened bushes of hybrid tea roses.
Medium (moderate) pruning, at the level of 5-7 buds, stimulates early flowering and provides maximum decorative effect.
Weak (long) pruning consists of lightly shortening the shoots and is used as a summer pruning to remove dead buds. For groundcover roses and some scrubs, this type of pruning is basic for at least a few years, after which heavy pruning may be needed to rejuvenate the shrub.
Combined trimming. Experienced rose growers often use various combinations of the listed types and achieve almost continuous flowering. Combined pruning is the best way to prolong the flowering of floribunda roses.
Dates of pruning roses
Distinguish between spring, summer and autumn pruning of roses.
Spring pruning is the most important and is sometimes referred to as primary pruning. It is held annually, although its scale for different garden groups and even varieties within the same group may differ significantly. After the opening of the roses, sanitary pruning is carried out, only live shoots are left. With the onset of swelling of the buds, the main pruning is carried out, the volume of which depends on the age and condition of the bush.
Summer pruning is carried out in a minimum volume, faded flowers and inflorescences are removed to the first developed bud. Hybrid tea roses are cut with part of the stem to the first true leaf. Timely removal of faded flowers prolongs the flowering period.
Autumn pruning is mainly associated with climatic risks and shelter techniques. In a warm climate, roses do not need pruning in autumn. In our conditions, almost all roses, to one degree or another, require winter protection. It is necessary to remove the unripe parts of the shoots and shorten the roses to the height of the shelter. It should be remembered that strong pruning harms climbing large-flowered roses and upright powerful scrubs, therefore, when covered, they are bent to the ground.
Pruning hybrid tea roses
Roses need strong pruning before planting in spring, and moderate pruning in fall. Hybrid tea roses bloom on the growth of the current year and need annual moderate pruning. This ensures good branching and the formation of young shoots. Powerful varieties do not tolerate heavy pruning, after which they can produce non-flowering shoots. At the same time, constant light pruning can inhibit shrub rejuvenation and reduce flowering. If the rose blooms only on the tops of tall shoots, the base of the bush is exposed and the number of young shoots is reduced, measures must be taken. Some of the older shoots that have reduced flowering need to be cut to the bottom, while others should be heavily pruned. Young shoots are pruned moderately. Experienced rose growers avoid such situations and use combined pruning.
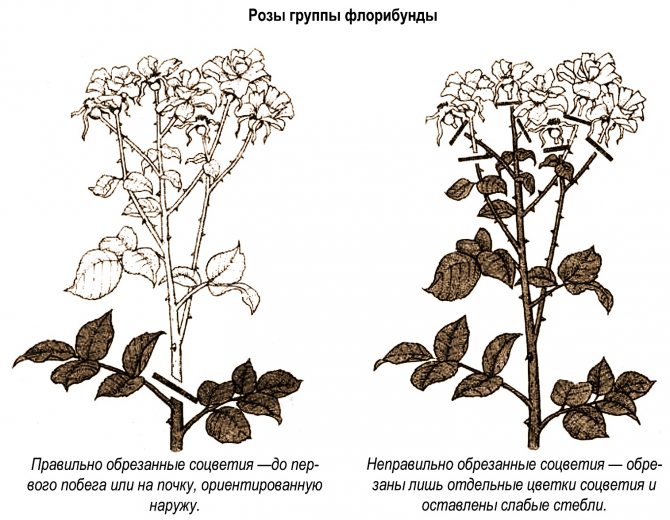
Floribunda rose pruning
These roses usually look more overgrown and more branchy despite being pruned annually. After sanitary pruning, shoots growing towards the center of the bush can be removed or pruned to the outer bud. Then one part of the remaining main shoots is cut strongly, the other - moderately. Lateral shoots on the main stems are shortened to 2-3 buds. Combined pruning for floribunda roses is the optimal solution. Some of the shoots are stimulated for early flowering, and the other for the growth of basal shoots and a later wave of flowering.
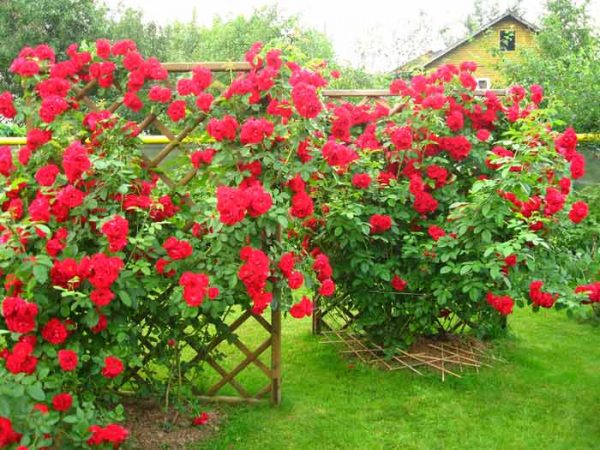
Pruning climbing large-flowered roses
The most difficult group of roses for conditions where they need serious winter protection. As a rule, during winter shelter, these roses suffer not so much from frost as from damage to powerful shoots when they bend down.For those who love roses of this group, it is better to choose varieties with relatively plastic shoots. In the spring, after the roses open, it is necessary to carry out sanitary pruning. After that, the main shoots should be cut to the upper overwintered bud, some too long shoots can be slightly shortened (to give the bush a neat shape). Lateral shoots need to be cut off, leaving 2-3 buds. In the summer, faded flowers and inflorescences are removed with part of the stem to the nearest leaf.
Pruning climbing roses like rambler


The main base for flowering next year for these once-blooming roses are young growing shoots of the current season. Old shoots drastically reduce flowering. A prerequisite for abundant flowering is that young replacement shoots should appear annually and ripen for a good overwintering. For this purpose, faded shoots older than two years of age are cut out immediately after flowering, and young growing shoots are pinched at 3-4 buds in early September. In the spring, after sanitary pruning, the degree of thickening of the bush should be assessed, since too overgrown bushes bloom weaker and are poorly ventilated. Too thickened bushes can suffer from powdery mildew and in some cases serve as a permanent focus of infection. It is enough to leave 5-7 young shoots and 3 biennial ones, the rest are completely removed. Lateral branches on two-year-old shoots should be shortened to 15 cm.
Pruning roses Modern Shrub
In Russia, the roses of this group are considered semi-climbing, in some countries they are called modern shrub roses, in others - landscape roses. Most roses of this large and complex group are voluminous and in warm climates they are undemanding to strong and frequent pruning. When pruning, one should take into account the strength of growth and the degree of development not only of the various varieties, but also of each plant. The main task of pruning is to achieve a uniform and compact bush shape. Under all conditions, diseased shoots and shoots directed inside the bush are removed. The main shoots in high varieties (from 1.3 m) should be shortened by no more than a third. If the height of the variety does not exceed 1.2 m, you can cut it in half. If there are many long side branches, they can be cut by two thirds. If the side shoots are short, then they are cut to 10 cm. In hedges from roses of this group, traditional pruning is not used. To achieve maximum decorativeness, only dead branches are removed in spring, and all shoots are cut exactly, about half the height. Subsequently, thinning (rejuvenating) pruning may be needed, the volume of which will depend on the age and condition of the bushes.
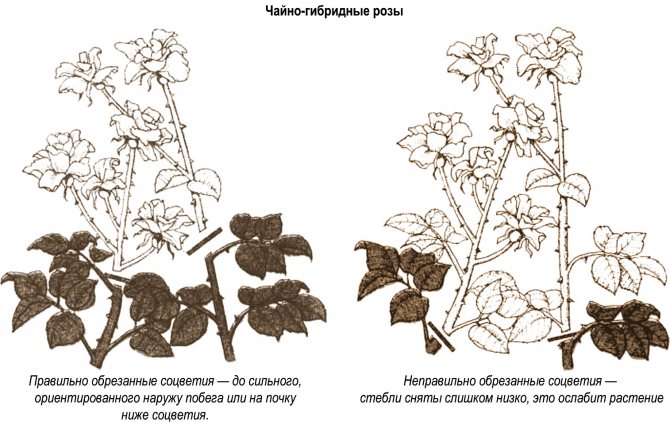
Correct pruning of roses in summer
Next, you can familiarize yourself with the photo, video and description of summer pruning of roses and the rules for forming a bush.
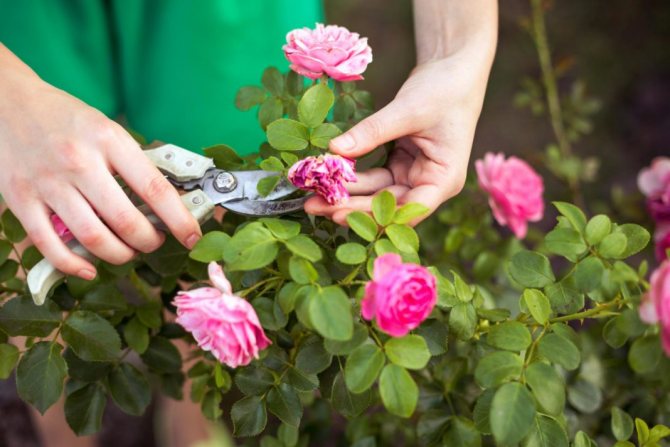
To maintain the decorative effect of the rose, sanitary pruning is carried out during the summer. Summer (sanitary) pruning is carried out from the beginning of the first flowering until the autumn. At the same time, flowers that have lost their attractive appearance are removed. There is no need to wait until all the petals fall off completely: this increases the risk of diseases.
As you can see in the photo, during the summer pruning of roses, the flowers are cut off as soon as the petals begin to wither:
Thus, they provide re-flowering, cut off sick, yellowed foliage and sluggish shoots.
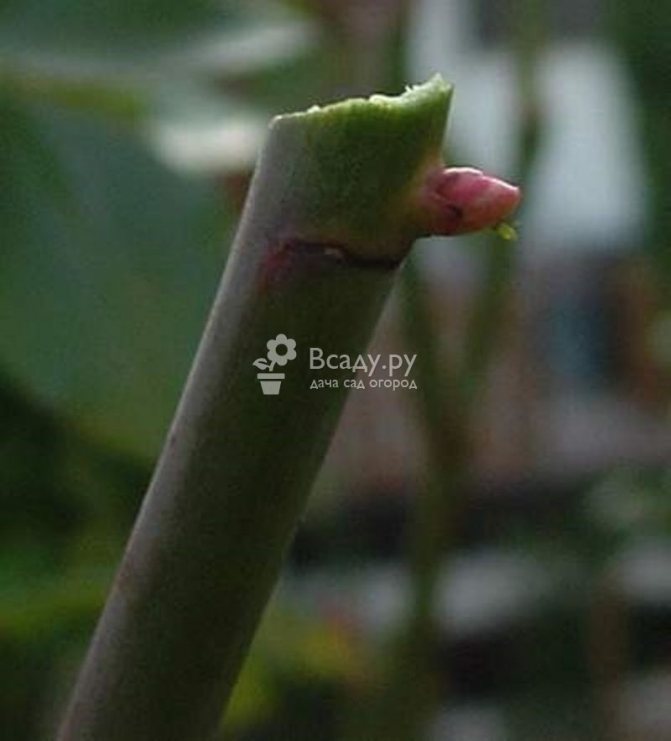
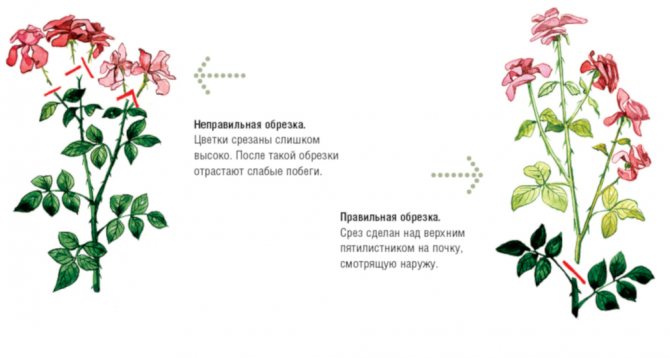
Pruning roses correctly in summer will help ensure continuous flowering and prevent nutrient depletion for seed formation. The cut is made on the 1st strong kidney. If you just cut a flower with a pedicel, buds will awaken on the remaining weak part of the stem. Stunted thin shoots will grow from them.
At the end of summer, inflorescences are no longer removed. Otherwise, shoots will still actively form on the bush. They will not have time to ripen by winter and will die from frost.
In order to prevent the development of diseases and pests, shoots that are too thick and growing inside the bush are removed.
The only exception is the small-flowered climbing rose of the Rambler subgroup that blooms once a year, which is cut off immediately after flowering so that replacement shoots appear that can bloom in a year.
Watch the video of pruning roses in summer to get a better understanding of how this agrotechnical technique is performed:
What elements does a rose need in summer
If in the springtime the priority substance is nitrogen, in order to awaken the flower, quickly form greens, then in the summer the rose requires increased doses:
- potassium - for the formation of flower buds, increasing their number, protecting the rose from diseases, preparing it for winter;
- phosphorus - splendor of flowering, bulky buds, ripening of new shoots;
- iron - for successful photosynthesis and prevention of chlorosis;
- calcium - creating a favorable soil microflora;
- magnesium - happy enzymatic processes, saturated color of the petals.
It will be useful: boron, manganese, zinc, molybdenum, selenium, sulfur, iodine, participating in metabolic processes, increasing the assimilation of the main components by the plant, increasing the defenses of the flower.
And the amount of nitrogen that promotes the emergence of new shoots should be reduced. Since August, the introduction of organic fertilizers into the soil, even in minimal doses, should be stopped altogether - fresh sprouts will not ripen by autumn and will not overwinter, they will only take away the strength of the plant. And the flowering will be weak, and the rose will not be prepared for winter.
Rules for pruning roses in autumn (with video)
Autumn pruning of roses is carried out in November. Pruning should be kept to a minimum so as not to cause vigorous shoot growth. Usually limited to the removal of flowers and frost-damaged fruits. According to the rules for pruning roses in the fall, the shoots of standard plants are cut by 1/3, then the crops are covered for the winter. In areas with strong winds, it is advisable to cut stems that are too long by 15–30 cm so that the wind does not sway and damage them.
Autumn pruning is mostly associated with the process of preparing the rose for the winter period and the implementation of the shelter. Before sheltering the plant for the winter, after a negative daytime temperature has established, it is recommended to remove all flowers, foliage, immature, defective, diseased and broken shoots. Pruning of the main shoots is carried out in accordance with the garden group of roses. All trimmed parts are removed from the site and burned, as they can become a source of infection.
Here you can watch a video of pruning roses in the fall to prepare plants for winter:
Timing of pruning. Removing buds after flowering
Pruning roses is required in autumn, spring and summer, taking into account the condition of the plants and their varietal affiliation. Trimming the bush can be strong, moderate, and light. In the spring, the procedure is carried out in order to form a bush and give it a decorative effect, in the summer, weak non-flowering shoots are cut, autumn pruning prepares the plant for winter before sheltering.
Pruning actinidia in spring
In the summer, dried flowers are regularly removed so that the bush does not waste energy on them. As a result, new buds soon appear. Pruning is done over a well-developed bud.
On a note! If you do not cut off the faded buds, fruits with seeds will form in their place and re-flowering on these shoots will not occur.
Pruning species and miniature roses
Pruning species (wild) and old roses. The species rose grows over time into a dense, strong bush. Most of these roses do not actually need pruning, and it is not recommended to touch them for about 4 years, so that the bush can build up a powerful base.
Long (light) pruning is necessary if the bush grows too large, if it comes into contact with neighboring bushes and damages its shoots if some branches have begun to die off.In the first place, the oldest shoots, at least 4 years old, located near the ground, need pruning in order to stimulate a young growth that gives abundant flowering. The surviving shoots of remontant varieties must be shortened by about a third (Fig. 60); in single-flowering plants, shoots cannot be cut off at all, since their flower bud is mainly laid in the top of the bush.
It is recommended to carry out this type of pruning in the spring or immediately after flowering, so that the rose bush has time to recover over the summer and tie many flower buds the next year.
Pruning patio and petite roses. The patio rose, as well as the true miniature rose, is a smaller version of the regular large-flowered and multi-flowered rose.
When planting a miniature rose, only the top and deformed shoots are cut off. In subsequent seasons, it is pruned in the same way as a hybrid tea.
Why do you need autumn pruning and is it worth touching plants before winter?


The main task of the autumn shearing of rose bushes is to give the plant a compact size, so that it is easier to insulate the bush for the winter. In most regions of our country, the rose garden is insulated for the winter with improvised materials: sawdust, peat, fallen leaves, agricultural fabric.
A small plant is more convenient to fall asleep "headlong" than a large bush, thereby reliably protecting it from frost.
Sanitary autumn haircut of roses consists in removing faded buds, weak and diseased branches, on which pathogens and pests can persist. In combination with the subsequent treatment of the bush with solutions of special preparations for diseases (Bordeaux mixture), the plant will leave completely protected during the dormant period.
Adjusting the number of branches in the rosebush will make it easier for the roots to supply the plant with nutrients. As a result, next year's flower buds will be large and vibrant. It is recommended to leave no more than 7 shoots on one rose bush.
Together with pruning, they remove all the foliage fallen from the bushes and other plant debris in the rose garden, depriving the insects - pests of the winter shelter.
After pruning, it is recommended to treat the rosary with antifungal drugs (fungicides):
- Abiga-Peak 50 g per 10 l of water,
- iron vitriol 300 g per 10 l
- or Bordeaux mixture.
The solutions are not only plentifully sprayed on the bushes, but also watered the soil under the plants.
Rejuvenating pruning is carried out in the fall, cutting off all branches older than 3 years of age. Older shoots grow more slowly and form flower buds poorly.
Pruning groundcover and climbing roses
Pruning a groundcover rose. In the spring, sanitary pruning is carried out, and the ends of the shoots are cut into 2-3 buds.
The ground cover rose does not need autumn pruning, only diseased, damaged branches that have not ripened are cut out, as well as shoots and branches that have lost their decorative effect, and all the foliage remaining on the bush. Once every 5-6 years, for the purpose of rejuvenation, the bush is cut short, by 5-7 buds.
Curly roses. Roses that bloom several times over the summer have flowers on both old and annual shoots. Withered inflorescences are also removed from plants, side shoots are cut into 2-4 eyes. Rejuvenating and thinning pruning is carried out as needed.
Roses that bloom once a summer have flowers on perennial shoots. Such plants need regular anti-aging pruning and thinning. Climbing roses are pruned immediately after flowering, so that young shoots have time to mature before the onset of frost.
In varieties with decorative fruits, wilted flowers are not cut off.
Wild roses. Virtually no pruning, with the exception of sanitary. If wild roses are grown as bush roses, pruning is done accordingly.
Cascading roses. They only need thinning.
Top dressing of roses in summer during flowering
Roses are one of the few plants that can bloom several times per season and therefore need more nutrition than other plants. In the summer, roses are fed several times and during this period they use more phosphorus and potash fertilizers. But it is better to refuse nitrogen fertilizers at this time, nitrogen affects the development of shoots. The danger is not only that nitrogen diminishes flowering. The big danger is that the shoots that begin to develop in summer do not have time to ripen before the onset of frost and simply freeze out.


In the summer, you can feed the roses with yeast and wood ash. At this time, a period of rapid flowering begins, and the plant needs various nutrients.
Garden, vegetable garden and flower garden tips
Plum fruits fall: what to do?
Top dressing of geraniums for flowering with iodine and peroxide
How to grow cauliflower outdoors
Pruning spray, flower bed and remontant roses
Shrub roses. Varieties that bloom once are not pruned, but only thinned out. Pruning will impair their flowering.
Constantly flowering varieties are pruned. Strong shoots are shortened only slightly, weak ones are cut into 3-4 buds. Every 3-5 years, the bush is thinned out and rejuvenating pruning is carried out. When pruning spray roses, the branches growing inside the bush are removed. Old unproductive shoots are cut off near the ground.
Flowerbed roses. Weak varieties are pruned into 3-4 buds (10-15 cm) to obtain strong stems.
Medium growing varieties are cut into 4–6 buds (15–25 cm).
Strong growing varieties are pruned into 8 buds. To rejuvenate the bush, pruning is carried out in the same way as pruning low-growing varieties.
Repaired roses. The roses of these varieties are pruned to stimulate the formation of strong basal shoots. Another goal is to form a globular bush. Its center should be open, and the peripheral stems should be evenly spaced.
Flowers of such roses appear on the growths of the current year. Therefore, they need annual moderate to heavy pruning. Thick stems are cut to 4-6 buds (about 20 cm from the ground). The rest of the stems are shortened to 2–4 buds (about 15 cm from the ground). In an adult plant, 2-3 stems are completely removed annually to rejuvenate the bush.
Why cut roses
Pruning red currants in spring
Roses are pruned annually. This is done for the following reasons:
- The shape of the bush needs correction. All twisted shoots, branches growing inside the bush and violating its geometry are cut out.
- According to the plan of the gardener, pruning is done so that many small buds or several large single flowers are formed.
- The bush needs rejuvenation. In this case, all the old shoots are cut off, and the rose releases many new shoots.


The bush needs rejuvenation
The procedure is carried out in the following sequence: first, the bush is thinned out, then dry and damaged shoots are removed, at the final stage, strong branches are shortened by one bud.
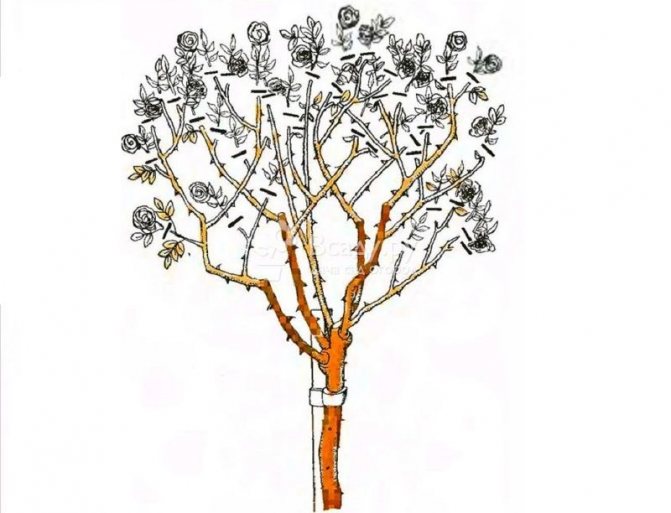
Correct pruning of standard roses
Pruning of standard roses is carried out in the same way as for spray roses, forming a symmetrical crown shape. Shoots that thicken the crown are especially carefully cut off, since many shoots do not contribute to an abundance of flowering.
For standard rosesstrong or light pruning is used, depending on the garden group. Strong pruning is used for hybrid tea crowns, floribunda, grand difflora, polyanthus and miniature roses, and light pruning for climbing and ground cover roses.
Trimming of climbing boles is carried out by strongly cleaning the crown. A few young, strong branches are left, pruning them to a powerful outer bud.
Their crown should be compact. The drooping varieties are thinned out. The rest are pruned in moderation.
In the spring, after planting, the crown of the trunk is cut short with an indent of 10-15 cm from the base of the bush.In subsequent seasons, pruning will depend on the growth potential of the grafted rose, on its group and on the general condition of the plant after overwintering. If the rose has survived this period well, it is pruned, leaving 2-3 more buds than the same varieties of bush roses. If the plant has undergone wintering poorly, it is pruned shorter, by 5–7 buds.
In summer, a hybrid tea rose, a floribunda rose and a miniature rose grafted onto a stem, a symmetrical crown is formed due to pinching of shoots by 2-3 buds.
Features of the formation of a rose bush in the first year of planting
In order for the bush to form correctly, in the first year, its shoots are pinched. Only ground cover, climbing and park roses should be pinched. Young developing shoots of seedlings should be pinched after the appearance of the 4th leaf. The buds that have just appeared are cut off - this technique stimulates the formation of many new shoots. Over the summer, the bush will get stronger and form a symmetrical crown. Such a plant will tolerate wintering more easily.
On a note! If you really want to admire the inflorescences of a young bush, in August you can stop cutting the buds and let them bloom. Blooming during this period will no longer have a negative effect on the formation of a rose.
How to prune a rose so that it grows roots
Rose planting usually takes place in the spring. It should be carried out at a time when the soil has already thawed, and the buds on the plant have not yet woken up. All non-viable areas of the root system should be cut out, and full roots should be shortened to 20 cm.
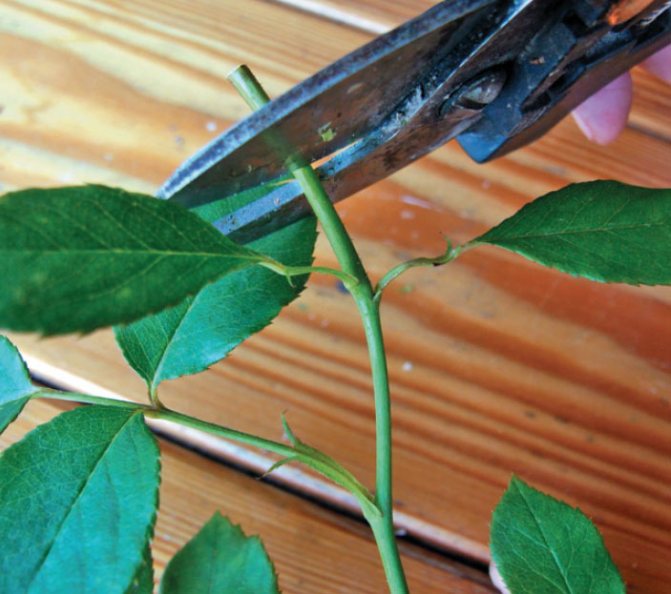


How to prune a rose so that it grows roots
Pruning a bush rose in this case should be as follows: strong branches are cut off to 6 buds, 3 points are left on medium stems, weak and dried branches are cut out completely. The fact that the rooting process was successful can be understood by the appearance of new leaves.
Pruning hybrid tea and polyanthus roses
The hybrid tea rose, as a result of the obligatory spring pruning, develops flower shoots that will bloom in the same year. In the year of planting, the plant is cut short, by 2-3 buds.
Subsequently, when pruning hybrid tea roses, it is imperative to take into account the varietal specifics:
- A vigorous variety needs long (light) pruning because short pruning often results in blind (non-flowering) shoots. With her, 5–7 buds are left on the shoot;
- when pruning other varieties, medium (moderate) pruning is used. Each one-year shoot is cut to 3-5 buds, and 2-3 buds are left in a strong mature 2-4-year-old shoot, depending on the growth rate.
A properly formed bush has a maximum of 5 strong shoots, all others are removed. The most valuable is the young shoot growing from the base of the bush. It should be carefully preserved, as it will rejuvenate the bush. During the formation of the shoot, a young root begins to germinate. The root system is growing. If such a shoot is removed, the root will not be able to form. Autumn pruning is carried out at a height of 20-30 cm from the base of the bush, leaving 5-7 buds.
Saplings with two or more shoots are cut in the spring immediately after planting, keeping 2-3 buds, weak shoots are cut more strongly. Thanks to this, flowers will appear in the first year. I also shorten the roots to about 30 cm (if they were cut back in the nursery, just refresh the cuts). If a rose is planted in the fall, then the roots are shortened to the same indicators, and the shoots are slightly reduced.
Further pruning is related to the variety of flowers. Thus, varieties that are characterized by active growth are poorly pruned, since otherwise you can get "blind" shoots, that is, shoots that do not give flowers. Other varieties respond well to moderate pruning.
The most valuable are the shoots that emerged from the root zone, since they contribute to the rejuvenation of the bush and an increase in the mass of the root system.If you cut them off, a new root will not develop either.
To obtain high-quality cutting material, hybrid tea roses are cut into 2-3 buds.
Polyanthus roses. When planting polyanthus roses, all weak shoots are cut off, and strong ones are shortened by about 4 buds. Varieties that are notable for their small height and weak growth are subjected to strong pruning in the spring, since due to this they give a lot of shoots that bloom in the same summer.
Actively growing varieties for early flowering are poorly pruned in the year of planting. The next spring, weak shoots are cut off, strong shoots are shortened to a third of their length, and the growths on them by 3 buds. Further care involves cutting out all old, weak and thickening shoots, pruning strong shoots also by a third of their length.
How to cover hybrid tea roses for the winter
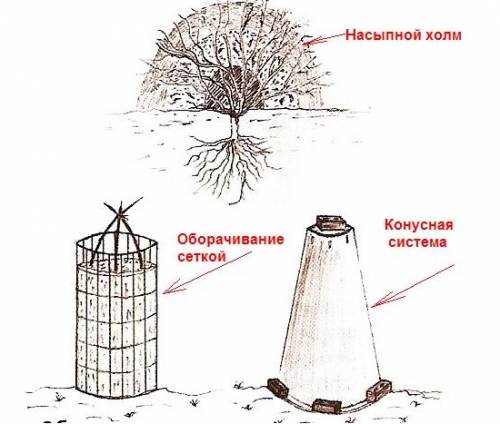
In order for the flowers to "survive" the winter well, the stems and roots remain intact, they need to make a shelter:
- The procedure is carried out when it becomes at least -7 degrees outside.
- Plants are pretreated with preparations containing copper, biofungicides (copper sulfate, Fitosporin, Baktofit, Kurzat). Carry out processing only on warm days in the morning. Next, the bushes are wrapped in foil and left to dry.
- From under the bushes, they remove the old mulch and put a new one - dry foliage, spruce branches, garden debris, plants plucked along with the roots in the garden, vegetable garden.
- The branches are attracted to each other with twine, they are insulated with burlap, agrofibre or thick paper.
- You can make a cover based on arcs. For this, the bushes need to be bent a little, but this should be started a month before, since hybrid tea varieties of roses do not bend well. The height of the arches should be 50–60 cm, and the distance from them to the flowers should be 10–20 cm. Geotextiles or any other nonwoven material are placed on top of the arches in 2-3 layers. It is fixed to arcs and soil. Some cover such a shelter on top with plastic wrap, but then you need to leave the ventilation holes below, and with the onset of frost, close them.
- In the northern regions, they use another method of shelter - they build a hut over the bushes of boards, cellular polycarbonate or plywood. From above, the structure is covered with lutrasil, the last layer is laid with the smooth side that does not allow moisture to pass through. At above-zero temperatures, the ends of such huts are left open, and with the onset of frost, they are closed.
Correct pruning of a floribunda rose
In the first season after planting, a strong pruning of floribunda roses is carried out for 3-4 buds. Subsequently, the most optimal pruning for a floribunda rose is a mixed spring pruning, during which:
- some shoots are slightly pruned to provoke early flowering of others, by 5-7 buds;
- other shoots are strongly pruned in order to stimulate the growth of renewed basal shoots and get a late flowering displaced by 2-3 buds.
A properly formed bush has no more than five strong shoots, all the rest must be removed. It is important to carry out autumn pruning at a height of 30–35 cm from the base of the bush.
Weak pruning does not allow preserving the decorative effect of the plant, although it promotes early flowering, a strong one depletes the bush, which is why the buds are tied at a later date, and a moderate one does not ensure constant flowering. Therefore, they resort to combined pruning, in which some of the shoots are cut strongly, while others are poorly cut. This will allow the bush to maintain its shape and bloom earlier.
With further care, all shoots directed deep into the bush are necessarily cut out, annual shoots are cut by a third, lateral growth on the shoots of the second year of life is cut off, old shoots are removed if a young growth is sufficient.
Care after pruning
8-10 days after cutting the rose, the bushes are treated with antifungal drugs, as indicated above, and prepared for wintering (covered).
The rose cover must be breathable; the foil is not suitable for this purpose. The plant is sensitive to high humidity and often suffers not from frost, but from the accumulation of moisture under shelter in a thaw. For warming roses are used:
- large wood shavings, and not small sawdust (they are pressed faster, not allowing air to flow to the plant);
- lutrasil, agrospan, spanboard - lightweight materials, but retaining heat;
- pieces of boards, bars for laying under the shoots of climbing roses so that they do not lie on the ground.

Option for sheltering roses from Yulia Minyaeva:
Do I need to remove the leaves from the rose if they have not flown around by themselves?
It is impossible to give an unambiguous answer to this question. Some growers prune leaves on the shoots of a rose, believing that diseases and pests can persist on them. Others are sure that plants treated with antifungal drugs are not afraid of diseases. From the leaves preserved on the bush, the outflow of nutrients to the roots continues for a long time. And for warming a rose, the presence of foliage plays a role.
The gardener should decide on the issue of leaving foliage on his own. If he decides to remove the leaves, this must be done carefully, trying not to damage the skin on the stem. It is better to cut the leaf with garden shears rather than pick it off.
Correct pruning of a climbing rose (with video)
Subgroup rambler (real climbing, climbing small-flowered). This group includes roses with long (up to 3-4 m) elastic shoots and miniature flowers in bulky inflorescences. They bloom in June - early July, once, for 30–35 days along the entire length of the shoot that survived the winter.
In the spring of next year, for proper pruning of the climbing rose, it will be possible to slightly shorten the tops of the shoots, but the main pruning falls on the period after the buds have faded. In the process, all faded shoots are completely removed. If this was not done in the summer, they must be cut in the spring. With proper and complete care, new shoots form on the bush, which will bloom this year.
As shown in the video of trimming climbing roses, in the first year after planting, the bush is cut 35-40 cm, due to which a huge number of basal shoots are formed:
There is no flowering in the first year. In all subsequent years, pruning is performed in the same way. In spring, it is recommended that only sanitary pruning is done.
The main pruning in this species is done immediately after flowering, in the summer. The rose of this group blooms on last year's shoots, so those that have faded are cut at the base of the bush into a ring. At the same time, many replacement shoots are formed, but only 5-10 of them are required to form a bush, the rest must be removed.
Look at the photo - when pruning climbing roses in the fall, only the very top with underdeveloped buds is removed and then sanitary molding is carried out:
This is done for the reason that the climbing rose blooms on last year's shoot, which must be preserved.
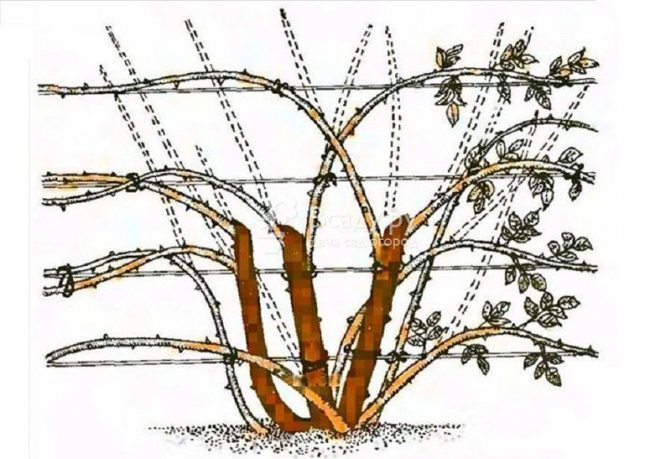
Cutting scheme for climbing varieties
Climbing plants' buds are formed only on last year's shoots. After flowering, old branches are cut only if there are new shoots.
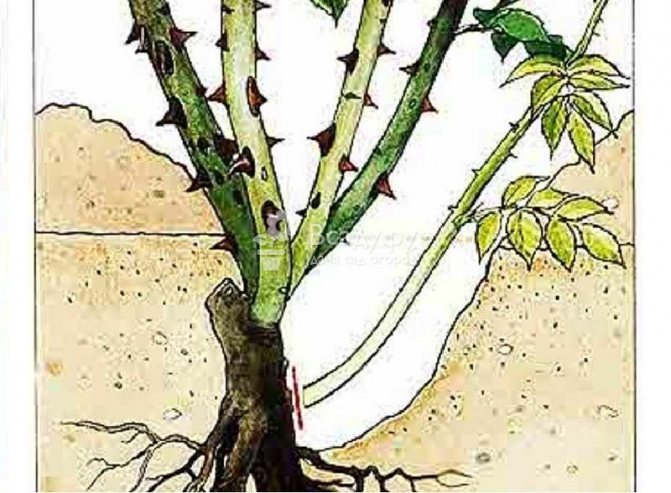
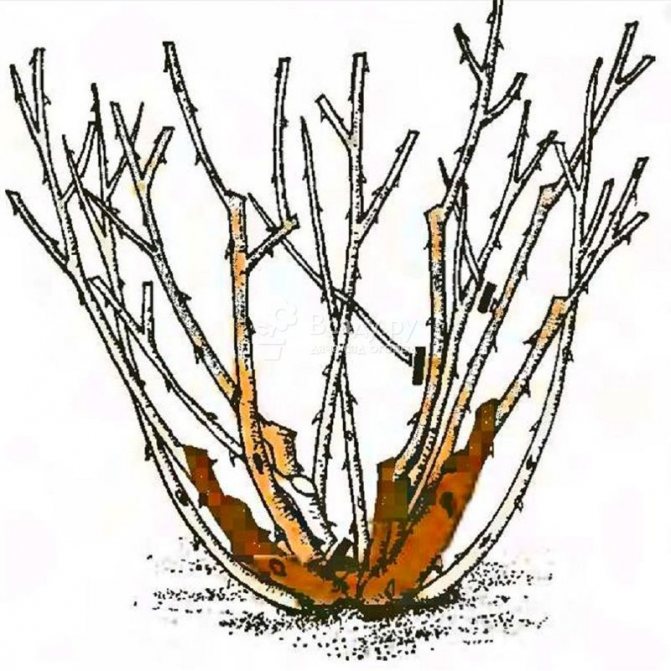
The formation of climbing bushes is carried out in the horizontal direction. Flowers and young branches appear along such branches in summer. Pruning after their flowering is carried out in late summer - early autumn. Old lashes are cut off, leaving 30-40 cm from the base.


Park rose pruning rules
Roses of this type need annual formative and sanitary pruning. Weak pruning of park roses activates the emergence of new shoots, contributing to the rejuvenation of the bush and the emergence of abundant long flowering. Due to the development of basal shoots, the mass of roots also increases, which has a positive effect on the vital activity of the entire plant.
In the first two years, it is necessary to create a strong skeleton of the bush, for which all weak shoots, faded flowers, etc. are cut out.n. In the fall, young shoots are cut by 5 cm, which will make it easier for them to cope with wintering.
The species of park roses, which bloom once in the middle of the season, are pruned in the spring, removing up to a third of the length of the basal shoots, since, due to the abundant flowering, the branches often break off under their own weight. In the fall, strongly grown shoots are also pruned so that they do not break during strong winds or heavy snowfall.
To prepare top dressing, you need to take yeast and ash
As a fertilizer for roses, shivers are used in combination with ash feeding; they contain a lot of vitamins, trace elements, minerals, and growth substances. All this stimulates the growth of plants and strengthens their resistance to various diseases. Root formation under the influence of the yeast solution is also accelerated.
In addition, yeast activates the activity of soil microorganisms. At the same time, the composition of the soil is significantly improved, nitrogen and phosphorus are formed from organic matter in it. True, yeast absorbs potassium, but in order to neutralize this effect, additional feeding with ash is used. It is applied directly to the ground in the form of an ash solution.
The main condition for the effectiveness of yeast feeding is warmth. In the cold, microorganisms are not able to continue their development and produce useful compounds, they either stop growing or die altogether.
loading ...
Pruning other types of roses
Climbing subgroup (climbing, climbing large-flowered rose). Flowers of this group reach 2-3 m in height, they have large flowers, collected in small inflorescences. It blooms profusely and for a long time, some varieties bloom again.
The flower is formed on the shoot of the 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th order, that is, it blooms for 4 or more years. At the same time, flowering becomes weaker year after year, therefore, growing roses of this group, it is required to leave 2-4 year old shoots.
Sanitary pruning is carried out in the spring. If possible, some lashes are formed horizontally or at an angle (this technique helps to avoid exposing the bottom of the bush).
During the summer, after removing flowers that have lost their decorative effect, the shoot is shortened by 3-4 buds, which stimulates re-flowering.
During the fall, only the top of the shoot is shortened, and rejuvenating pruning is carried out on the old bush. It is forbidden to prune all shoots: low pruning contributes to a return to the bush form, since most of the varieties of this group are any of the climbing varieties of the bush rose, and the plant may also stop blooming.
Semi-climbing and spray roses. Before planting, the tops of the shoots and roots are shortened, and non-viable growth is also removed. The next year, in the spring, weak shoots are completely cut out, and strong shoots are reduced by a third of their length.
Pruning shrub rose, scrub rose and English rose. Such a rose can only bloom on a two-year-old or more mature shoot. In the spring, it is necessary to carry out sanitary pruning and make the shoots 3-4 buds shorter, as well as remove the brushes with the fruits of the previous season, so that the bush can bloom earlier.
In the fall, you should also remove all thickened, old, lethargic, deformed, diseased shoots at the base of the bush on a ring so that they cannot grow back. After pruning, 3–7 stems will remain, half of which must be shortened by 2 times. Lateral shoots should be removed from all preserved stems, and the tops should be cut into 3-5 buds. The end result is a bush with shoots of varying lengths.
During the spring period, it should grow and continue its flowering from spring to autumn. They rejuvenate a park rose with the help of strong pruning to the base of the bush, save 3-4 buds to provoke the growth of "dormant buds".
Pruning roses depending on the type
The structural features of a bush of different types of roses also dictate the rules for pruning.
Hybrid tea, floribunda
Plants belong to the group of spray roses, forming bushes up to 100 cm in height.Perennial is characterized by unpretentiousness, rapid growth and formation of flowers on the shoots of the last year.
Autumn pruning of a rose bush consists of:
- in shortening the shoots by half;
- removing old branches;
- short pruning (up to 2 buds) of weak branches.
Park, miniature, polyanthus
This group of plants does not need to be shortened in the fall. Only the removal of damaged branches is carried out, the preserved unopened buds and dried flowers are pinched.
Climbing
These roses, like park roses, do not need to be shortened in autumn. Plants need only sanitary pruning and removal of faded buds.
Long shoots of a climbing rose are removed from the support and laid on the ground, placing boards on the soil. The plant is covered with agrotextile, wood shavings.
Groundcover, creeping
Roses that are placed on the surface of the earth or on horizontal structures (arches, trellises). Pruning this group of plants has its own characteristics.
How to prune roses in the fall:
- On a young plant in the fall, remove all the stems on which branches with flowers were located. Only young shoots are left, shortening them to 15-17 cm. The main stems are pinned to the ground.
Illustrated by Brickell. To "Pruning plants"
English
Bushes of English roses do not require special shaping. It is enough to carry out a standard sanitary haircut, and remove shoots older than 3 years.
Stamp
Capricious in growing and caring for a rose requires a careful attitude towards itself. In autumn, the plant needs to remove unnecessary and weak branches, as well as wild growth, if such begins to grow from the rootstock.
Rose pruning tools
Many growers do not like to prune roses because they have to deal with thorny stems. Nevertheless, if pruning is carried out correctly, the development of the plant will improve, it will become more abundant and more beautiful to bloom. In young seedlings, pruning improves the formation of the root system, which begins to develop faster.
Also, thanks to pruning, young shoots appear and grow more actively. Removing dry and old parts of the bushes helps to ensure the correct distribution of nutrients throughout the plant. Pruning also contributes to the flow of fresh air to all parts of the bush, which helps prevent the development of diseases, in particular black rot.
This operation is time-consuming and requires some practice and special tools.


To prune roses, first of all, you need to arm yourself with pruning shears and gloves, which will help avoid damage to your hands. In order to get to hard-to-reach stems, as well as to get rid of faded buds from climbing roses, use a long-handled lopper.
All tools must be kept clean and thoroughly washed and dried after each trimming. It is also recommended to wash the tools after cutting each individual bush: in this case, the spread of the disease can be prevented if one of them has been infected.
Storing rose cuttings until spring
Pruning healthy rose shoots can be used for propagation. In this way, you can get planting material from the Floribunda rose, climbing and miniature varieties.
Twigs 12 cm long and with 3 buds are suitable as cuttings for planting. Save cuttings:
- in sphagnum moss treated with hot steam or a solution of any fungicide;
- in sawdust scalded with boiling water.
The material is poured into a dense plastic bag. The twigs are immersed in moss or sawdust so that they do not come into contact with each other. The material is lightly sprayed with water, the bag is tied. Cuttings are removed in the refrigerator, in the vegetable compartment or in the cellar. Sprigs of roses are preserved at a temperature of +4 .. + 6 degrees.
Today we examined the rules for pruning roses in the fall for beginners, as well as the features of the procedure for different types of roses.We hope you find this information useful.
Adding an article to a new collection
Want your flower queens to look really royal next season? We will tell you how to prune roses for the winter so that they winter safely and without loss.
Roses are usually pruned in the fall in preparation for winter shelter. But inexperienced growers sometimes doubt whether it is necessary to do this at all or whether it is possible to do with spring pruning. Let's look at this controversial issue.
How to prune roses correctly in spring, summer and autumn?
Before starting the operation, you need to assess the condition of the bush and decide which pruning method to choose, because the latter depends on the type of rose and the purposes with which this manipulation is carried out. So, autumn pruning is carried out more rigidly, as a result of which the bush can be shortened up to 40 cm in height. Spring pruning is carried out to ensure the penetration of fresh air and sunlight to the stems and leaves.
It is recommended to cut at a 45 ° angle, and they should be neat, without torn or chewed edges. When pruning, you should remove dry, broken and affected parts of the bushes, as well as thin and weak shoots. If the seedlings have white and thin shoots after storage, they must also be cut off, otherwise the plant will die. On grafted roses, it is necessary to cut off the shoots that appear below the rootstock, since otherwise the cultivated part of the plant can die.
After cutting, the cut sites should be treated with an antiseptic, which will help prevent possible infection. As such an antiseptic, it is permissible to use a solution of brilliant green.
Types of pruning and their purpose
If roses are not cut for a long period, then they quickly lose their attractiveness. The aboveground part of the plants dies off literally after a few years and numerous shoots begin to appear from the buds at the base. If for wild specimens it is enough to cut off old and dried shoots so that they come to life again, then for cultivated varieties this is not enough. Almost all types of roses at the age of 3-5 years undergo annual pruning..


In order for roses to delight with their beauty all summer long, they need constant control.
Depending on the purpose, several trimming options are distinguished:
- sanitary;
- formative;
- anti-aging.
What does cropping give:
- Extends the life of the bush. If you do not resort to anti-aging pruning for 2-3 years, the plant becomes unkempt and subsequently dries up.
- Promotes abundant and beautiful flowering. This is possible provided that the plant receives adequate nutrition, and thinned, damaged and old shoots prevent this. In addition, they create a thickening of the bush, which provokes the development of fungal and infectious diseases. In such a case, sanitary pruning is used, which should be carried out in August.
- Stimulates roses to bloom again after a short period of time. This is the main function of summer pruning after the first wave of flowering. The procedure is carried out in cloudy weather.
- To form a beautiful crown at the bush. On young, obtained by budding (grafting with a kidney), during the summer, the shoots are pinched over the fourth leaf. Due to this, lateral branching is enhanced and more buds are formed in the future.
Pruning roses after flowering in the summer is especially necessary for standard and large-flowered hybrids. It is worth noting that there are varieties that are capable of blooming once during the summer season and even pruning them will not push them to do more. These include some varieties of climbing roses, of which there are not so many. Therefore, only wilted buds are removed from them.
In summer, grafted roses have to cut off the wild growth that forms on the rootstock. This usually happens after frosty winters.If you neglect this procedure, then the wilds begin to take away most of the nutrients from the plant and, as a result, will simply "clog" it. It is recommended to break off such processes (just do not cut them off) immediately, otherwise they will grow back again. And the shoots stretching from the base are cut off at the very root collar, having previously cleared it from the ground. If the cut is higher, then the wilds will start growing again.
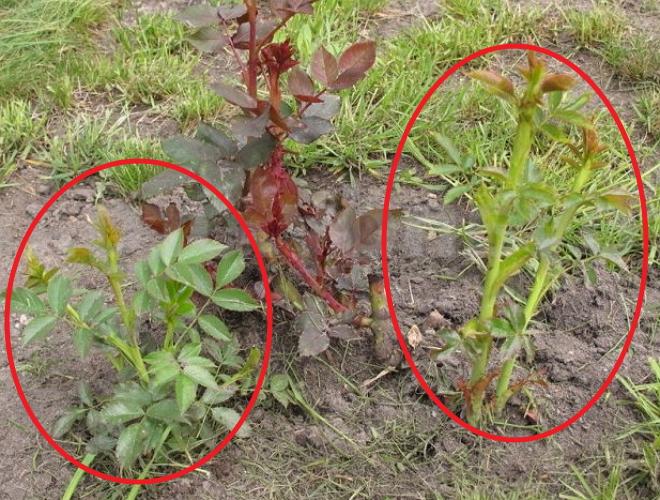


If the shoots are not removed in time from the roses grafted to the rosehip, then it will soon clog the bush
If roses do not bloom for a long time despite proper care, the reason for this is "blind" shoots. They differ from normal ones in the absence of a growth eye or fresh growth. They only have an underdeveloped kidney. The reason for this may be a lack of lighting or an unfortunate neighborhood with other decorative cultures. If you delete an empty node, then the shoots are activated.
Favorable days for trimming according to the lunar calendar 2019: August 9, 10, 19–22, 26–29.
Cropping rates
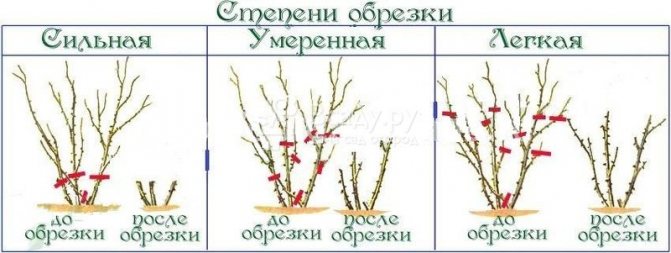
Gardeners conventionally divide pruning into several degrees:
- Strong - applied to overly thickened bushes at the level of 3-4 living buds from the bottom. Leave shoots no more than 15 cm long.
- Moderate - carried out for newly planted plants, the exception will be adult specimens of hybrid tea roses. Cut off the stems somewhere above the 5-7 eye, and cut the lateral shoots by half. In this way, all varieties of roses are pruned after the first flowering.
- Light - this is a kind of adjustment of the bush with cutting off the stems by 2/3 of the total length at the level of 8–12 buds. It is undesirable to resort to such a procedure often, which causes thickening of the plantings, deterioration of flowering and thinning of the shoots.


There are several trim levels: short, medium and high
When choosing the option for pruning a rose after flowering, they are guided by its age, size, growth rate and variety. At the end of the summer season, a strong "haircut" should not be done, so as not to cause intensive growth of young shoots on the eve of winter.
Removal of wilting blossoms of climbing roses
As with any other rose, for a claymer or rambler, the timely removal of fading flowers and prevention of fruiting is the main guarantee of the duration and splendor of flowering.
It is not worth waiting for the flowers to completely fade, because new shoots developing from replacement buds will be fragile and thin. It is better to remove flowers from any rose before its petals completely fall off or dry. Flowers are cut off not at the very base, but leaving short, up to 1 cm hemp above the eye. If a climbing rose has flowers located in dense inflorescences, the entire inflorescence is cut off after the last flower begins to wilt.
All flowers and inflorescences taken from climbing roses, as well as faded parts of the stems of abundantly flowering roses, must be destroyed.
Technique and features of the process of cutting roses
Work is carried out in dry weather, given that procedures during a prolonged damp period are fraught with infection of plants with fungal diseases due to infections from a humid environment entering open sections.
Instruments
For an even and clean cut of the shoots, a sharp pruner is used, which does not crush the stem and does not exfoliate the bark. Tool blades should be promptly sharpened and disinfected. Thick branches are trimmed with a lopper, and a garden saw is used to shorten old woody stems.
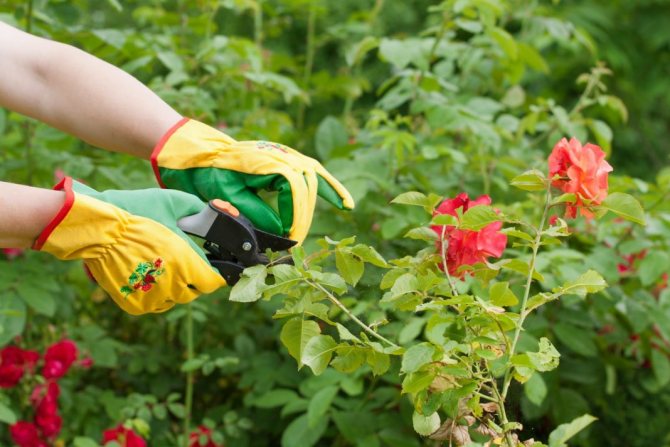


A sharp pruner is required for pruning roses in summer.
Pruning after flowering
Summer stimulating rose bush correction is carried out until the middle of the season. Later procedures are fraught with the fact that young shoots do not have time to prepare for winter, and the plant may not overwinter well. Cut to an external developed kidney, keeping a distance of 0.5 cm above the eye. Cuts at an angle of 45 °. It is not recommended to make a cut across, as moisture accumulates on the surface and the development of a focus of pathogenic microflora begins.A cut in the direction of the eye on the leaf axil is also not allowed. This is fraught with water rolling down to the growth bud, which leads to decay.
For the formation of spray roses
Pruning in order to form and rejuvenate the bush inhabitants of the rose garden is carried out in summer in dry weather immediately after flowering. Thick branches with darker bark are shortened. The cut is performed on a developed lateral shoot from the bottom of the stem or at soil level. The procedure should not be postponed until the end of summer or autumn, otherwise it is difficult to predict successful wintering when stimulating the growth of young shoots at a later date. To form a lush bush without thickening branches, pruning is done exclusively on the outer bud. The cut is processed with garden varnish or a special paste to exclude the formation of a focus of infection.


Pruning roses in summer is done to form spray roses
Climber pruning features
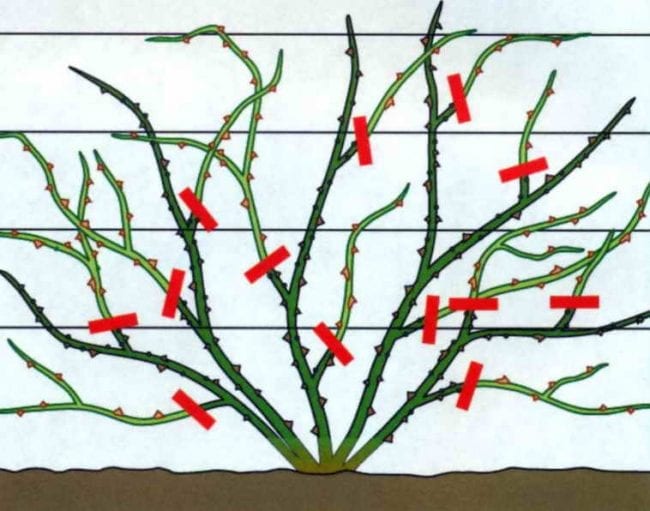

Pruning Climber roses
These varieties are large-flowered or climbing roses. They have tough, thick shoots, large, often beautifully shaped double flowers. Many side branches can develop within 5 years, after which they weaken. Based on this, you need to trim long lashes at the base at the end of the fourth year. You need to cut such curly roses for the winter, taking into account the following tips:
- The purpose of the work is to leave a limited number of the strongest, youngest, longest shoots.
- In the fall, you need to cut off the unripe parts of the shoots, faded inflorescences.
- If the branches are too long compared to the support, then feel free to prune them.
- Get rid of the lashes that interfere with the free development of the curly rose.
- The bush is given a neat shape: long lateral branches are removed, up to 4-5 buds are left.
- Remove last year's branches very carefully: you only need to cut off the tops with underdeveloped buds.
- To decorate the culture, cut off the tops of young shoots.
- To rejuvenate the climbing rose, remove 1-2 old shoots annually.
- In a mature, adult bush, leave 2-3 young shoots, the same number of last year's shoots, 1-2 shoots of three years of age.
The main differences between climbers and ramblers
Climbing roses are the most common type of garden vines and one of the favorite varieties of roses. The unusually lush flowering, large size, ease of growing in comparison with bush and park roses makes climbing princesses favorites of landscape design in the same way as the presence of countless options for their use.
Climbing roses are a conventional unifying name for all roses with creeping, arched or whip-like shoots, single or double long flowering. Flowers can be both single and collected in cluster inflorescences. In climbing roses, they are formed along the entire length, in the middle and upper parts or on the tops of the shoots in very large numbers.
But the main unifying feature, in addition to the growth form, is flowering on the shoots of last year's growth of the first or second order. Climbing roses are far from uniform in their qualities and characteristics. Determining the type or subspecies of a climbing rose is the key to success not only in growing it, but also in maximizing its decorative effect.
All climbing roses are usually divided into two categories - climbers and ramblers. But when it comes to plant selection, you have to deal with much more confusing classifications. Large, medium and small, curly, semi-climbing, real climbing, Cordes roses, large-flowered - it is very difficult to choose your ideal steeplejack among all not quite official and often similar categories.
But from a practical point of view, to provide roses with optimal care, it is not at all necessary to highlight the type of climbing rose: from pruning to watering in maintenance, all climbing roses are strikingly similar to each other.They need almost the same care, regardless of the size of the flowers or the length and type of shoots. The only thing you need to know is whether your climbing rose is capable of blooming only on last year's (most ramblers), or also on new shoots (mostly clammers).
In once-blooming roses, flowers are formed on last year's shoots. Bushes of climbing once flowering roses should be formed so that they consist of 6-10 shoots: 3-5 annual replacement branches and 3-5 biennial shoots, which will bloom in the current year. The main formation of these plants is carried out in the summer.
Repeated flowering roses are much more complex in structure and character. The flowering of their shoots weakens only by the fifth year, roses bloom on the branches of the second, third, fourth and even fifth order, which are formed on the main shoots. These roses do not need to remove the basal branches annually, allowing the main shoots to develop for three years and removing them to the base only after the fourth year.
Repeated flowering roses are formed so that 3 to 7 main flowering shoots remain in the bush and an annual growth of 1 to 3 annual branches intended to replace them in the future. The main pruning of re-blooming roses is always done in the spring.
There is a universal rule that helps not to get confused in the types of climbing roses and always regulate the number of shoots: remove from climbing roses during spring or summer pruning, you need as many old lashes as the rose has released new shoots at the base of the bush... This rule is applied when there is any doubt about the desired trimming degree.
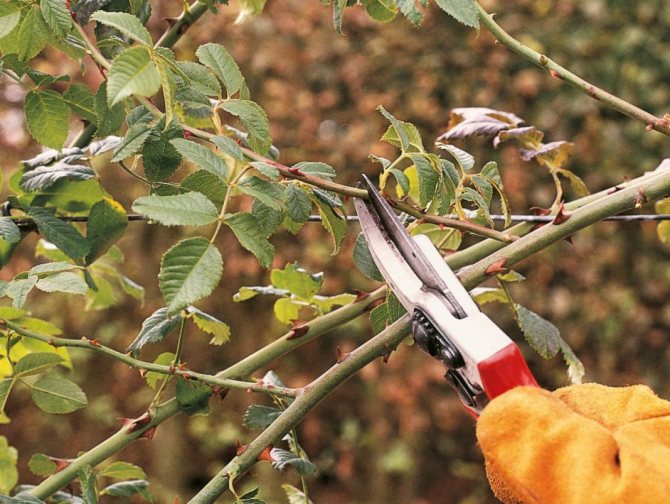


Pruning climbing roses.
When to prune
Autumn pruning of climbing roses can be started only when the air temperature at night stably stays at around minus three degrees - for the middle lane, this time coincides with the end of October. Pruning earlier can help promote bud development, leading to the death of the shoots in winter. Pruning should not be carried out even in August, since the shoots that have appeared will not have time to woody before frost and will die. The frozen branch will then thaw and become a breeding ground for fungi.
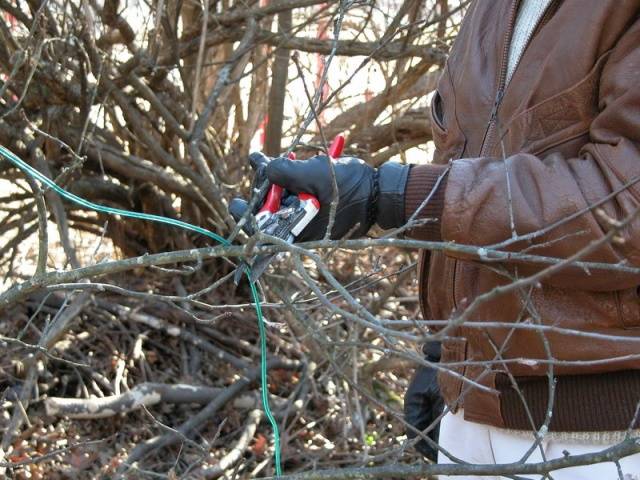


In order to prevent the emergence and subsequent freezing of shoots, preventive measures must be taken from the summer:
- at the end of July, stop feeding climbing roses with nitrogen compounds;
- increase the application of potash and phosphorus fertilizers - the former will help strengthen the root system of the plant and the faster ripening of existing shoots, and phosphorus will provide nutrition for future buds;
- after the last feeding, you need to stop removing flowers - this measure will help prevent the growth of new buds.
Important! So that the bushes have time to prepare for winter, the last feeding is carried out around the middle of September.
About pruning roses after flowering more
When starting to remove wilted buds, you need to wear gloves to protect your hands from sharp thorns. The cut is carried out with a sharp secateurs.
Caring for roses after flowering in summer
How to prune roses in the summer after flowering? Cut off those flowers in which the petals have become weak and began to crumble. At this time, the blossoming buds begin to wither and bend to the ground. At the same time, stems growing in the wrong direction can be removed. Excess shoots are removed to ensure the penetration of sunlight and air into the bush.
Before determining the location of the cut, carefully examine the leaves. They are combined on the handle into groups of several pieces. The correct cut is made over a sheet of at least 5 small sheets. It should be borne in mind that the new shoot will grow in the direction in which the leaf grows.
Note! When a shoot is cut, a non-flowering shoot may grow over a cuttings consisting of 3 leaves.The appearance of new flowers on them is possible only for the next season.
What are the consequences of doing something wrong?
With improper pruning, you can not only reduce or even not see the flowering on the plant, but also ruin the rose, greatly weakening it.
Attention! Using a poorly sharpened tool can lead to plant damage from diseases through poor-quality cuts.
For those who are just starting to master the features of pruning climbing roses, this process will seem difficult in many ways. But, following the instructions and recommendations, with due diligence, even a beginner can cope with it.
Frequent beginner mistakes
Experienced gardeners have no problem keeping roses in winter, but they do happen to newbies who have recently started growing these flowers.
Grooming mistakes that can interfere with a successful wintering:
- Intensive growth of shoots in the autumn... The problem arises with an overdose of nitrogen and complex fertilizers. Sometimes, in pursuit of decorativeness, gardeners too often feed the rose, as a result of which the shoots continue to grow, despite the fact that it is autumn in the yard.
- Cutting too early... Any pruning stimulates the growth of new buds, and on the eve of winter this is completely undesirable, so you need to wait for sub-zero temperatures, when the movement of juices slows down and the vegetative process stops.
Important! In most regions, roses are covered for the winter. If shelter follows after pruning, the rose and the soil in which it grows must be carefully treated with a copper-containing fungicide to prevent the development of fungi. - Pruning all shrunken buds... In climbing roses, it is recommended to cut off dried inflorescences partially and only at the beginning of the season to maintain decorativeness. Removing the buds at the end of flowering can help create new flower buds, making the shrub unable to survive the winter.
- Not all roses can be left with leaves... In regions with unstable temperatures and frequent thaws, foliage must be removed, as it is a source of pathogenic fungi, and can lead to decay of the bush. Leave the leaves only on roses wintering in mild climates without shelter.
- Inadequate sectioning... Sometimes gardeners do not immediately process the cuts, or completely ignore this procedure. Of course, you can take the risk and do without fungicides, but is it worth it if your favorite flowers can get sick and die from this.


Whatever varieties of climbing roses grow on the site, it is recommended to prune any of them for the winter, especially if the winter is long and frosty. Without this procedure, the bush may weaken and not survive the cold period, but if the pruning is done correctly, the rose will renew itself and by the spring will delight you with lush, long flowering.
How do I trim?
You can successfully trim by following a few simple tips. For this procedure, it is better to choose calm weather. When pruning a bush, you need to maintain its proportion: the size of the root system should be the same as the aerial part. You need to cut the bushes with well-sharpened tools.
Each cut should be treated with garden varnish. If the stem is too thick, it is best to use a hacksaw to trim it. The cut must be done so that the water can drain. You need to cut off the shoot above the outer bud. Moreover, the distance from the kidney should be 0.5 centimeters.


Gardening tips
Protecting bushes from the cold is a responsible procedure burdened with many nuances. Experienced gardeners have identified several important tricks of this process, which are also worth paying attention to before starting to cover hybrid tea roses:
- The lunar calendar will tell you the most accurate information about when the pruning and covering procedure should be performed. The action is recommended to be carried out only on the waning moon.
- When pruning, you should pay attention to the variety of hybrid tea roses, there are several of them. For example, in a flower with curly and large flowers, only 1/3 of the total length of the shoot can be cut off. Climbing flowers do not require prior release at all.
- Before covering this variety of flowers, it is recommended to first water it. But, before creating a structure, the bush must dry thoroughly.
- The ideal option as a heater specifically for a tea rose is spruce paws or straw.
If the plant is wrapped up in accordance with all the rules, then even the fiercest cold will not be afraid of it.
Actions after autumn pruning of climbing roses


Roses need not only be cut, but also covered for the winter. There are many frost-resistant varieties, but they are all afraid of temperature extremes. As soon as the stem of the thermometer drops to -5C, the branches of the bush are slightly twisted, bending to the soil, and covered with a structure in the form of frame arcs. From above, the frame is covered with a dense material that will retain heat and repel moisture. To do this, use durable polyethylene or spunbond.
On a note! Spruce branches or cardboard boxes can be used as insulation.
Bending the branches to the ground should not be done rudely. Over time, they themselves will bend to the ground. Before sheltering, you need to carefully examine the entire bush. There may be wounds or small cracks on it. They are treated with antifungal agents.
Pruning roses before sheltering for the winter is a necessary event. It will help save the shrub from the cold, and it will delight its owner with beautiful flowering in the coming spring.
Pruning on malformed and directed roses
If, as a result of carelessness or lack of knowledge, the clammer or other climbing rose ran wild, was directed incorrectly along the support, the branches were not tied horizontally or windingly, but strictly upward, as a result of which the flowers bloom only at the top and the plant does not look magnificent and impressive throughout the crown pruning for recovery is carried out in the spring and more radically.
The pruning procedure begins with the removal of all unproductive branches, damaged and dry shoots, the oldest branches. The remaining healthy shoots, which can no longer be guided correctly along the support, are cut in half in order to cause an active growth of young replacement branches. After installing a mesh or other guide support, to which it will be possible to redirect the rose, shoots are tied along it as it is recommended for any climbing roses - horizontally or almost horizontally.
Regional features
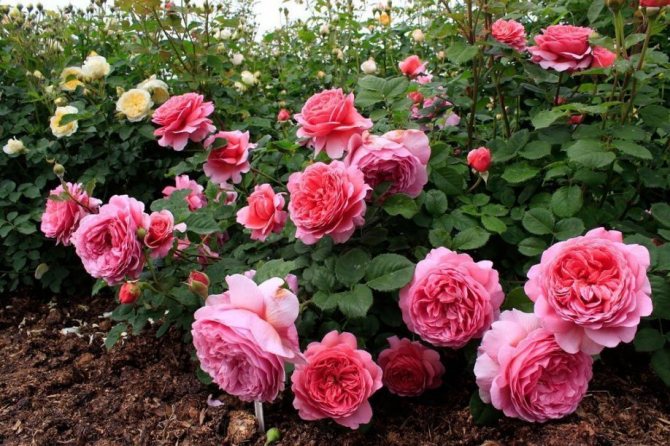


Early frosts can destroy both flowers and unripe young shoots.
Bush pruning is carried out in the middle of summer. In August, especially in the second half, the procedure is undesirable - the new flower will not have time to develop. During this period, it is better to remove only wilted flowers.
In the southern regions, re-flowering varieties are pruned up to three times per season.
Why do you need pruning?
A novice gardener may have a question: is it necessary to cut a climbing rose for the winter, and why do this if the main value of the plant is in the length of the shoots?
Did you know? Climbing roses hold the record for the intensity of shoot growth. In warm climates, their lashes can grow up to 10 m per season.
Firstly, after pruning, the shoots begin to grow more intensively, but besides this, a number of other problems are solved by correct pre-winter pruning:
- the process of sheltering a bush for the winter is simplified;
- shortening the tops of the lashes stimulates the growth of new shoots and flower buds;
- thinning out excess branches provides uniform lighting and airing of the bush;
- there is a more rational distribution of nutrients;
- the root system is strengthened, which contributes to better growth and abundant flowering of the rose;
- removal of damaged and diseased shoots increases winter hardiness and disease resistance of the bush;
- the plant is rejuvenated - the regular replacement of old branches with new shoots prolongs the life and productivity of the bush;
- as a result of pruning, high-quality material appears for further propagation of your favorite variety;
- pruning helps to shape the bush and direct the shoots in the right direction, resulting in maximum decorative effect.
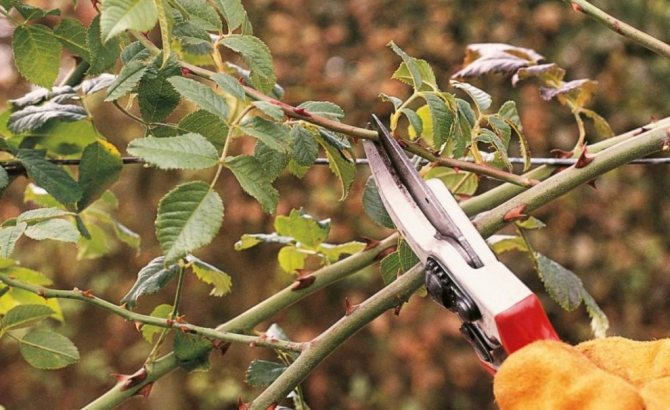


Procedure tips
Before the procedure, all instruments must be cleaned of rust and well sharpened. The cuts on the lashes should not be torn: this will bring pain to the bush and slow down its growth. Tools are disinfected with potassium permanganate so that dangerous fungal spores do not get into the cut sites. Each cut site is treated with a prophylactic solution. It can be potassium permanganate, copper sulfate, wood ash, activated carbon, or garden pitch.
On a note!
Garden var is prepared on the basis of yellow wax.
How to prepare a plant for pruning
In order to get the maximum effect from this procedure, from mid-August it is necessary to carry out activities aimed at slowing down and stopping the growing season. In this case, pruning will be the logical completion of the preparation of roses for the rest period.
What are these vegetation inhibition procedures?
- Reducing the number of waterings.
- Application of phosphorus-potassium fertilizers to the soil.
- Prevention of profuse flowering. To do this, in September, pinch young buds and new shoots.
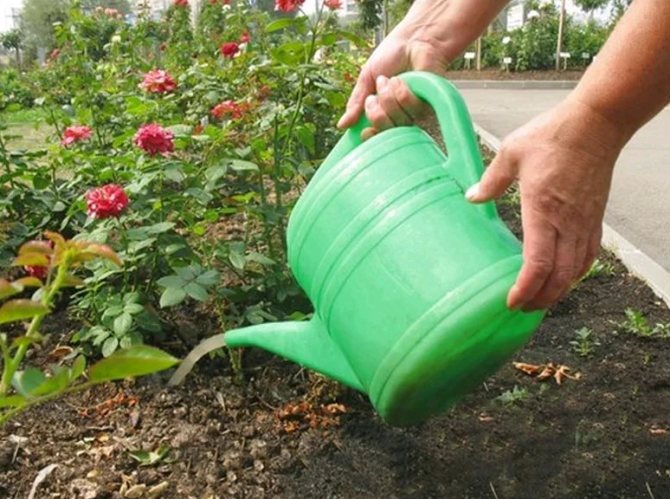


You can find out which type of roses a particular variety belongs to from the annotation upon purchase or from specialized classifiers. In most cases, gardeners know what kind of plants they are growing and what kind of care they need.
Tips from experienced florists
It is impossible to determine in advance when and how strong the frost will be. In order to be on the safe side, it is recommended to prepare roses for winter in two stages.


In early September, the leaves are removed from the bottom of the bush. This work is done with gloves. The leaves are collected and burned. In no case are they placed in the compost heap. Each bush at the root is sprinkled with earth.- With the onset of frost -5C ° - -6C °, all remaining leaves are cut off to the cutting line, which is performed, on average, at a height of 40-45 cm from the ground level. As in the first stage of preparation, the leaves are harvested and burned.
Next, proceed directly to the pruning procedure itself. But first they get acquainted with all its features.
Tool requirements
Climbing roses are pruned with a sharp, well-sharpened secateurs or a garden knife. Before the cutting procedure, the blade must be disinfected with any antiseptic or treated with a strong manganese solution.
You will also need a long-handled lopper with sharpened blades. You need to put on thick gloves on your hands that cannot damage the sharp thorns of a curly rose. The lopper is also decontaminated.
Important! If the shrub has not been cut for several years, and the branches are stiff, you will need a hacksaw. Its blade also needs to be disinfected.
Preparing roses for wintering
It is required to prepare lovely flowers with buds in mid-August-early September. This process consists of several main stages:
- Removal of nitrogen from soil. For this, fertilizing with potassium-phosphorus fertilizer is carried out. The performance of such an action is necessary to stop the active growth of the vegetative mass, aerial parts and strengthen the root system.
- Compression of shoots. After feeding, you should wait 5 to 7 days. As soon as this time has passed, it is required to carefully separate the shoots of the plant and lightly press the top of each of them. This is necessary to speed up the process of lignification of the stems.
- An obligatory step is pruning hybrid tea roses. Shorter flowers are easier to cover for the winter without harming them.
- At the final stage, it is required to cover the bushes, which will protect the stems from hypothermia.
Another important question is when to open the hybrid tea after winter. Early removal of the cover will lead to the premature appearance of the buds, later - to rotting and blackening of the bush. This must be done when a stable above zero temperature prevails during the day, but slight frosts will still be observed at night. The optimal time for opening plants for central Russia is from 10 to 20 April.
Pruning hybrid tea roses for the winter
To prune hybrid tea roses before winter, you will need a sharp tool - a knife, scissors or pruning shears. The sharper the blade, the better. First, it will be possible to cope with the task quickly. Secondly, the risk of harm to the plant is reduced. To carry out pruning, you need to do the following:
- Before you start covering the hybrid tea variety, you need to disinfect the instrument with potassium permanganate or Bordeaux liquid. This must be done to prevent infestation of the stems.
- Determine where the bud is located on the outside of the shoot.
- Place the secateurs over it at a 45-degree angle and make a cut. An acute angle must be created without fail. If you cut the stems at right angles, the plant sap will accumulate at the cut line. This will lead to rotting from excess moisture.
- Remove all damaged and dried stems, as well as unripe shoots from the bush of the hybrid tea rose.
- Treat the cut sites with an antiseptic in order to prevent the penetration of dangerous microorganisms. From folk remedies, you can use tree resin for this purpose.
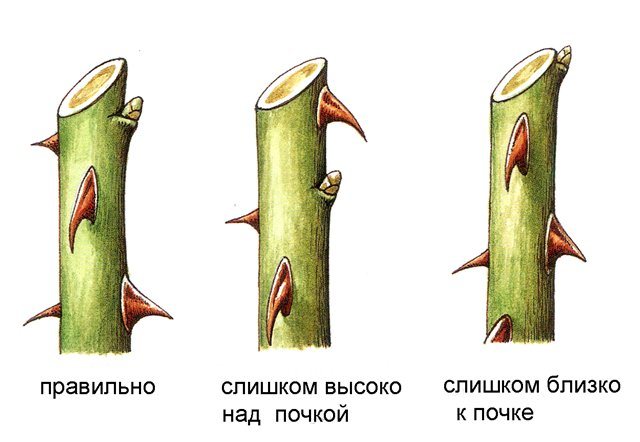

With proper pruning, it will be easier to cover the tea rose for the winter. In addition, the kidneys will not be affected, which will begin to actively develop.
Shelter rules for tea roses
Before you start covering, you should prepare hybrid tea roses for this process. To do this, you should slightly dig in them, approximately to the level of 20-40 cm from the base of the stems. All upper shoots must be carefully covered with a small amount of dry foliage and spruce branches. Then you need to make an air type of shelter, which can be built from geotextile fabric, thermal insulation material, plastic and even plywood.
In total, 3 options for creating a structure are known among gardeners:
- Frame - implies the installation of metal rods in the shape of a dome over a plant bush. On top of it, it is required to impose a fabric or heat-insulating material, which must be pressed to the base of the earth with boards or bricks. Depending on the climatic conditions, you can cover it in one or two layers. From time to time, you can open the fabric for a few minutes for airing.
- A fence with an embankment is the simplest option; you can create a shelter in a few seconds. This requires creating a small fence around the bush. To do this, you can use plywood, old cardboard boxes, metal mesh or plastic. Any insulation must be poured into the inside. You can use hay, foliage or sawdust as it. In case of severe frosts, it is necessary to additionally cover the structure with a plastic bag or thermal insulation material.
- Lutrasil cocoon is ideal for tall flowers. It is necessary to create a pyramid-shaped structure from metal rods around the bush. From the outside, it is required to wrap it with a special material - lutrasil. Additionally, insulation should be laid out along the lower border in order to prevent air penetration.
Every gardener should know how to cover roses before the onset of cold weather. This will not only save them from hypothermia, but also prevent the development of certain diseases, for example, the appearance of rot or blackening.
Optimal timing
You need to cut a climbing rose for the winter based on the climatic conditions of a particular region: in the middle lane, work is carried out at the end of October, in Siberia, in the Urals - in late September-early October. When choosing the time, be guided by the weather conditions. When the average daily temperature is about zero or slightly lower, get to work. It is not worth pruning a climbing rose early for the winter, because this will lead to untimely development of buds, death of shoots. When choosing the time of the procedure, keep in mind that the culture must have time to adapt to the cold weather, so plan an agrotechnical event a couple of weeks in advance: it is desirable that the branches become lignified before the onset of severe cold weather. If frosts promise in a few days, do not postpone the work, otherwise the plant will die without shelter: in the spring the frozen branches will thaw and become a favorable environment for the development of the fungus.


A number of preventive measures will help to protect the climbing rose from death in winter, to avoid early untimely emergence of shoots. Follow these guidelines:
- Stop adding nitrogen compounds in late July and early August.
- Before the onset of autumn, increase the introduction of phosphorus and potassium compounds, which will help strengthen the root system, quickly ripen existing shoots, and provide nutrition for future buds.
- After feeding, do not remove the flowers: with this approach, you will exclude the appearance of new buds.
- Fertilize for the last time in early to mid September.
Formation


The degree of pruning of the plant largely depends on what method of formation and placement was chosen for a climbing rose. If you decide to grow the variety with a scrub (a spreading bush without support), then spring and autumn sanitary cutting is carried out:
- wild growth is removed;
- the density of the plant is controlled by removing the shoots growing inside the bush.
The arrangement of the lashes on the support horizontally or in a wide fan will contribute to the appearance of many additional second-order shoots (see step-by-step instructions for making supports for climbing roses and tying plants to them here). This is especially true if the rose gives buds on the shoots of the current year. In this case pruning controls the number of main "skeletal" lashes and removes dry inflorescences.
Reference! If the rose is placed on an arch or a gazebo, and the buds appear on the shoots of the last year, then after the end of flowering, the shoots on which there were flowers are cut off (about 2/3 of the length), which contributes to the forcing and ripening of the lashes on which there will be flowers in the next season.
Step-by-step instructions on how to cover flowers


After the autumn pruning, climbing roses are prepared for wintering and covered.- The lashes are gathered together and gently bent to the ground.
- With the help of staples, they are pressed to the ground.
- From above, they are covered with spruce branches, film and agrofibre.
- If the lashes of roses do not bend tightly to the ground, then you need to tightly wrap them with spruce branches, and cover the roots separately.
We suggest you watch a video on how to cover a climbing rose:
Step-by-step instructions for pruning
- Peduncle... Removing dead and dry flowers and preventing fruit formation will promote longer, more lush flowering. The cut is made at a distance of 1 cm above the eye.
- Stem... Trimming the stem, like other parts of the plant, is carried out only with a sharp instrument. The cut should be smooth and neat. Dry shoots are removed at the very base. The same is done with wild growth and weak or excess shoots. When carrying out anti-aging pruning, the cut is made at a height of about 30 cm from the ground. This will allow the development of young shoots that will come from the awakened buds. When cutting the stems of climbing roses, a cut is made above the bud at a distance of about 1 cm. Slices of large stems are processed for faster healing.
- Leaves... If there is a need to remove damaged leaves from the plant, then the cut is made at the trunk itself.
- Arrows... In summer, you can see blind or fatty shoots on the rose bushes. Blind - this is when instead of a bud, a spike-shaped swelling forms, and fatty ones are shoots without a flower. They are cut to half their length, which will facilitate the emergence of several new flower shoots.