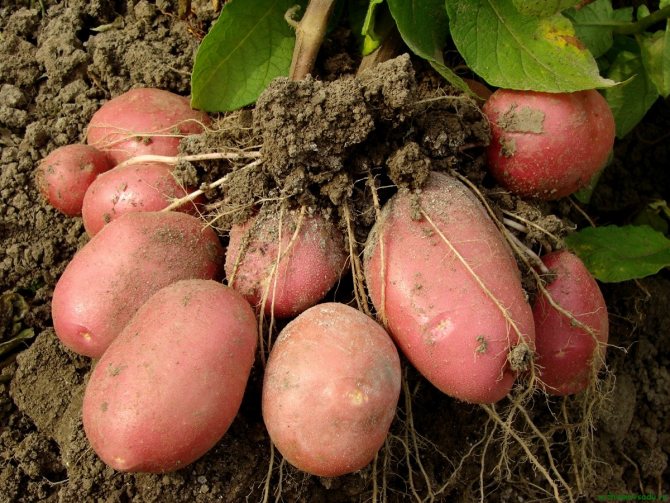
Each shoot of a potato bush is a separate plant with its own root system. The only common seedlings have is the “fodder base” - the maternal tuber. When it rots, the shoots begin to compete with each other for living space and access to light, moisture, and useful substances.
Plants spend a lot of energy on this struggle. The roots of the strongest of the shoots grow so that they occupy half of the entire area allotted for the bush, and large tubers are formed on the stolons. The root system of the second strongest shoot takes up less space, the tubers under it are slightly smaller. Other shoots have to huddle in the remaining area. If potatoes are formed under them, then they are very small.
And if you plant all the eyes separately, then the potato crop will be about 30-40% more than usual. When planting potatoes with eyes, plants do not have to reclaim living space, therefore, the leaves on the tops are exactly twice as many as when planting with whole tubers, and all potatoes grow large, have the correct shape, and are more resistant to diseases. Under one bush, 2–6 tubers are formed.
Advantages of the method of growing potatoes from eyes:
- high-quality varietal potatoes are expensive. Thanks to this method of planting, 2-3 times less seed is required;
- you can quickly multiply any rare variety;
- the leaves of potato bushes evenly cover the surface of the garden from the sun's rays, so moisture lingers in the soil longer;
- selected large tubers are used for planting;
- the yield and quality of tubers are much higher than with the usual method of planting;
- when the frosts are over, seedlings can be planted in the ground, in which tubers have already begun to form, having received early potatoes.
Disadvantages of the method: it takes more effort to plant potatoes and care for bushes than with the traditional method.
What are potatoes, botanical description
Our "second bread"
Novice gardeners often ask the question: “To which family are potatoes? " We answer: potatoes, like eggplants and tomatoes, are cultural "relatives" of the family nightshade.
Potatoes are a perennial tuberous plant, cultivated in agriculture as an annual. By the type of culinary processing, it belongs to the group of vegetables. Most often propagated by tubers, less often by sprouts and cuttings. Breeders grow seedlings from seeds.
Interesting fact! The name has Italian roots tartufolo - truffle, because the tubers are very similar to this outlandish mushroom.
The fruits of the nightshade are eaten, such as red tomatoes or purple eggplants. Potato berries, small green balls, poisonous... They contain a large amount of the alkaloid solanine, niacin. The plant produces these substances in order to protect itself from pests and diseases. Eating them can cause serious food poisoning.
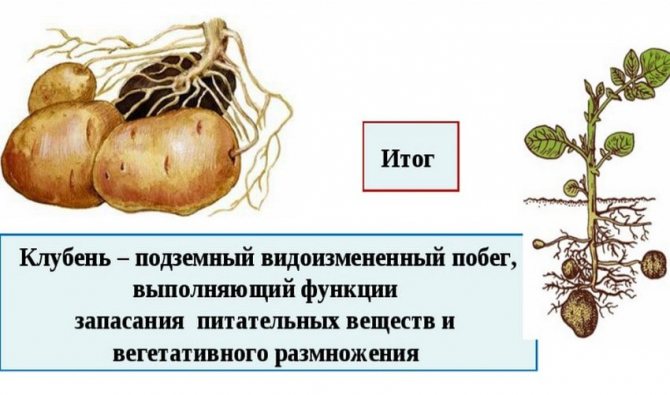
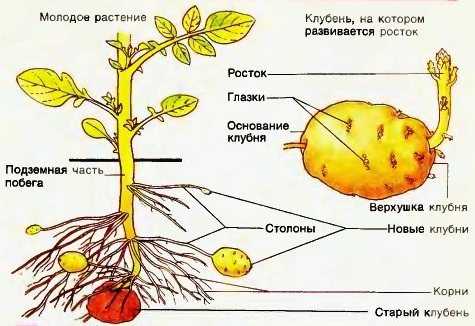
Tubers are ordinary buds, they only ripen underground. This is a reservoir of nutrients - starch, which is necessary for the successful life of a plant.
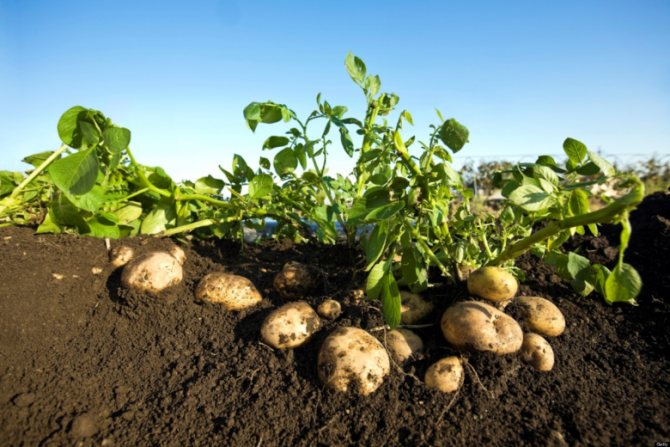


Potato bush
Root system
The properties of raw potatoes are numerous. The tuber itself has 75% water. The remaining 25% is rich mainly in starch, but also includes a huge range of nutrients.
- Starch. It is a plant reserve substance.In essence, this is the same glucose in a modified form. Such a large amount of glucose is useful for the pharmaceutical industry and for the production of alcohol. The productivity of potatoes in creating alcohol is several times higher than that of cereals. In folk medicine, it is used as a cholesterol-lowering agent.
- Another benefit is helping the stomach to absorb animal fats thanks to the presence of fiber and pectins in the vegetable. That is why potatoes are often used with meat. The vegetable has a beneficial effect on the digestive tract, normalizes the microflora of the stomach and intestines. The broth is used for cold inhalations, and the raw mass is used for making vitamin masks for the face, as well as for a speedy recovery after a burn or furunculosis.
- Potatoes are rich in vitamins of all groups, from B to C nutrient.
- Many elements of the Mendeleev system. And these are: K, Na, Fe, Mg, Mn and I. The vegetable is especially rich in potassium, which is necessary for arterial hypertension, as well as for disorders of the kidneys and heart.
The type of root system is not unambiguous. When a breeder grows a plant from seed, a rod type is formed in the first year. The next year, when new shoots are formed, it is fibrous. Usually a vegetable is grown from a tuber, so a fibrous root system develops immediately.
The potato root system includes:
- Maternal tuber.
- Stolons and near-stem roots are long, light and thickened structures, at the ends of which tubers develop.
- Fine root hairs called sprout hairs.
The root system occupies from 25 to 50 cm in depth. The tuber can form up to almost a meter if the arable layer is increased.
In the potato root system, the tuber is central. Its morphological structure includes:
- Scarring. These structures resemble curbs. These are atrophied scaly leaves that appear when tubers begin to form. It is in the sinuses of these leaves that kidneys are later formed.
- Eyes. They are located at the top of the tuber and are intended for stem growth. The eyes are often called the kidneys, the number of which ranges from 4 to 15.
- Lentils. They look like black dots. They perform the function of gas exchange. They form parallel to the formation of the rind. If the soil is clogged or there is little moisture, then loose white neoplasms appear on the lenticels, which help to absorb air. An increase in their size is a sign of illness or a violation of gas exchange.


Description of the fetus
The fruit of a potato is called a berry., in the common people of the bulb or shebolka. The size of a walnut (unlike the fruits of eggplant and tomatoes), it looks like a small dark green tomato. The juicy berry consists of two sections with a lot of seeds.
Fruit composition:
- Upper layer - dense, juicy tissue, protects seeds from damage and environmental influences. In the process of ripening, it changes color from green to purple or even black.
- Middle layer - juicy pulp. With insufficient watering, this layer gradually dries up in the heat.
- Internal partition, seeds are attached to it.
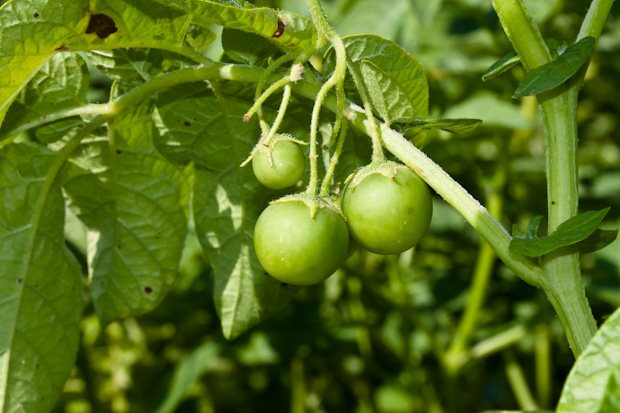


Potato berries
- One berry ripens from 100 to 300 small, round, flattened seeds. The size and number of seeds depends on the variety.
Sometimes in the bushes berries are not formed:
- The plant is grown in unsuitable conditions... Fertile, fertilized soil and abundant watering are important for potatoes.
- Pests eat leaves and buds of plants.
- Gardeners tear off the inflorescences, it is believed that this helps to form numerous, large tubers.
Why should a potato tuber be considered a modified shoot?
If you carefully study the botanical description of potatoes, then it is not at all difficult to answer this question.All underground shoots with forming tuberous thickenings in the apical part are a continuation of the aerial stem, since they originate from its base.


However, the tissues of the tubers differ in many respects from the tissues of the aerial part, therefore, the presence of underdeveloped, scaly leaf plates on the young potatoes testifies to their vegetative origin. Dying off, they leave arched marks on the surface of the future crop, with 2-3 buds inside. Together with the edges, such traces form a tap hole.
Additional evidence that the tuber can be regarded as a modified shoot is its ability to change color when exposed to solar radiation. Despite the absence of chlorophyll in the fruits of potatoes, they can turn green no worse than foliage and the aerial part of the stem.
What is a tuber
Tuber, this is a kind of thickening of the stem, modified the escape round shape near potatoes... Part of a large root system. Serves as a storage of nutrients, is a support and nutrition for future shoots. With the help of a tuber, the plant is fixed in the soil.


What are potato stolons? Stolon - an elongated lateral shoot. Tuber - shortened shoot. Tuber grows on stolon.
Internal and external structure
The potato tuber has a peculiar appearance. A fairly large adult tuber is juicy (80% water), dense and covered with skin (epidermis).
The external structure of the tuber is arranged as follows:
- On a smooth surface, there are buds - eyes, from which stems then sprout.
- Near the main kidney, there are always a few additional ones. This is insurance, if the main one is damaged, additional ones will sprout. About fifteen eyes can nest on the tuber, they are in the upper part.
- There are also lentils on the surface, small dots due to which gas exchange takes place.
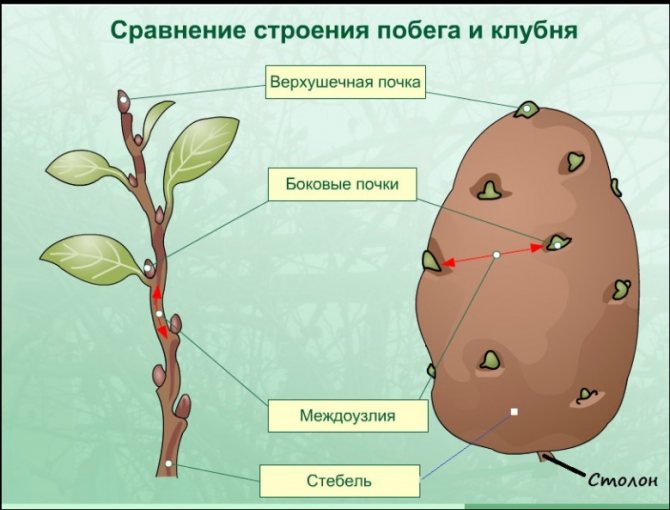

The appearance of the tuber indicates its condition, if it is too humid or the soil does not loosen well, neoplasms appear on it, which help to absorb oxygen. Large lentils speak of a potato bush disease.
The thickness of the peel depends on the variety, weather conditions, care, application of fertilizers.
- Phosphoric fertilizers thicken epidermis,
- Potash make the peel thin.
Shortly before harvest, the tops are cut and the tubers are left in dry soil to thicken the skin. Such vegetables are stored better and longer, without losing their beneficial qualities.
The internal structure of the potato tuber: under the skin is the bark, vascular bundles and pith.
Remember! The fruit of a potato is a berry, and a tuber of a potato is a modified shoot
Biological features
The biological characteristics of development depend primarily on the variety. On average, a full harvest requires a period of 90 days. Abundant tuber ovary is characterized by flowering (sometimes it is absent). Gradually, carbohydrates and proteins (starch) accumulate in young potato tubers. The share of starch reaches 18-20% of the total mass. At the end of the growing season, the tops darken and gradually dry out. So it's time to harvest. Young potatoes are often dug up, they are considered a "delicacy", they are consumed together with a delicate peel. The ripening period of early and mid-early harvest is 60 days from the day of planting.
Stages of development
1st stage of development this is emergence of seedlings 20-25 days after planting. The higher the soil temperature, the faster the process goes. During this period, the field is not watered until the first stems with leaves appear, the plant does not require moisture. Sandy, loamy soils are more suitable for growing this vegetable. The planting depth is 10-15 cm, for small tubers, the depth is chosen less by 2-5 cm.
Stage 2-4 budding, flowering, maximum tuber growth... During this period, potatoes are actively formed.Their total number may be about 30 pieces, but only half, at best, will fully ripen.
Nurturing care is especially important at this stage.
- Abundant (but not excessive) watering,
- fertilizing with mineral and organic fertilizers,
- regular loosening of the soil and removal of weeds.
The first time they huddle small bushes 5-7 cm in height, moreover, it is protection in case of small frosts. Second hilling after 2-3 weeks.
This is the main period for the formation of the future harvest and it lasts 40-60 days. Pests and various diseases at this stage directly affect the yield.
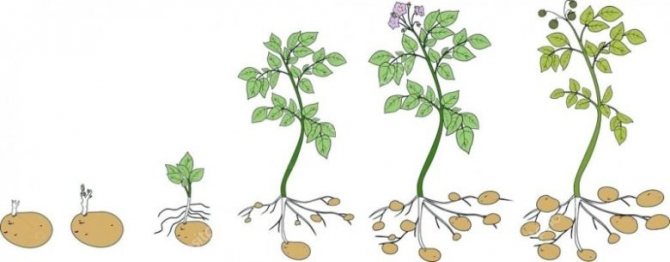

Stages of development of a potato bush
5th stage dying off of tops bushes, harvesting and storage... Tubers are dug 90-100 days after planting. The tops are removed and, if there is a suspicion of the presence of any pathogen, they are destroyed outside the garden. Everything is thoroughly dried indoors or outdoors if the air temperature is below + 6-8 degrees. Further calibration, transportation and storage.
How potato tuber develops
Taking into account the biological characteristics of potato fruits, it is possible to clearly define all stages of its development.
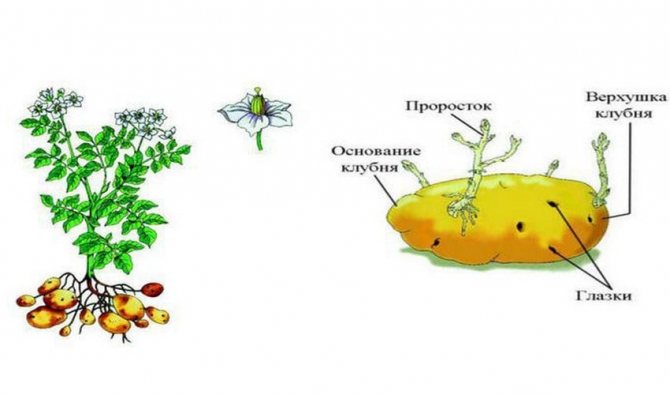

As you know, potatoes are formed by thickening of rhizomes (underground stem part), developing in the lower leaf axils, therefore, several main stages are distinguished in the life cycle of a potato:
- Initiation and active growth of tubers.
- Dormant period without significant changes in the characteristics of the main part of the plant.
- Germination, which ultimately leads to subsequent vegetative generation (under the influence of increased cellular metabolism, seedlings begin to appear from the eyes).
- After germination of potatoes, the formation of all plant parts of the culture begins, photosynthesis occurs.
The formation of new tubers (future harvest) requires at least 30-60 days from the moment of planting the seed, after which, over the next 1-2 months, new fruits will grow and develop to a state of full maturity.
It is noteworthy that the formation of underground parts of many potato varieties is completed when the soil warms up to a temperature of + 25 ... + 27 ° C.
Did you know? Contrary to popular belief, not all potatoes on Earth grow in soil. In the tropical regions of our planet, there are plant species that grow from trees. There is even a 15-meter potato tree, but apart from year-round flowering, it no longer pleases a person.
Ground parts of the plant
The bush grows up to 1 m, depending on the variety. The stem is ribbed, the leaf of the potato is dark green, consists of several lobes. Potato leaves are located along the entire length of the stem, like wing-like appendages. On the underside of the leaves, relief veins are visible, the color of which coincides with the color of the tuber of this variety. Each variety has a different number and shape of leaves. The veins on the leaves are arranged in a grid, like in most dicotyledonous plants. The cells of the leaf skin are alive, different in size and transparent, which allows sunlight to penetrate into the leaf.
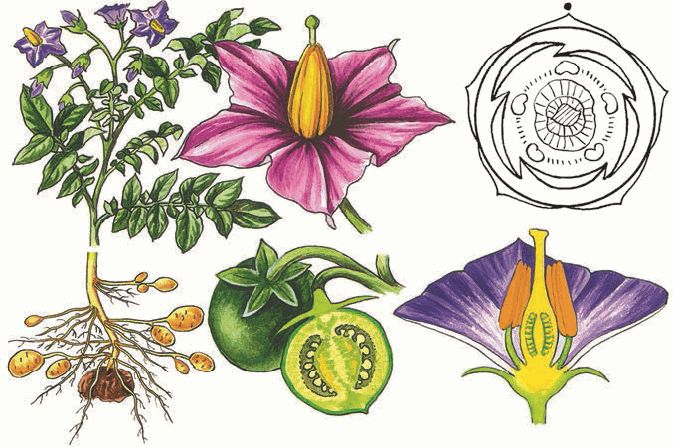


Flowers, fruits and general appearance of potatoes
The flowers are pink, white, or purple, clustered in an inflorescence at the top of the stem. The fruit ripens by autumn, it is poisonous and not edible.
Signs of toxicity
So, first sign toxicity of potatoes are green spots under the skin. They appear if the tubers are stored in direct sunlight - at this time photosynthesis occurs, which increases the concentration of the poison in the vegetable.
Second sign - eyes and sprouts on the surface of the root crop, which are caused by long-term storage of potatoes. And the most dangerous for us is spring sprouted potatoes - according to statistics, they contain three times more solanine than autumn ones.


Finally, third sign - these are lesions on the peel.The fact is that the plant independently tries to "heal wounds" on the surface of the root crop and directs all biologically active substances there. Needless to say, solanine is one such substance?
Potato propagation
The fruits
Seed propagation of potatoes is not a very popular method, but it has its advantages. As a rule, potatoes are the vegetable that takes up the most space in the garden, so it is difficult to ensure regular crop rotation. The land is depleted, the quality of the planting material deteriorates, even replacing the tubers with a new species does not help. Exit: growing potatoes from seeds.
Benefits:
- The seeds from the store have been pre-processed and have a strong immunity to diseases.
- Seeds are much cheaper than sown tubers.
- The shelf life of seeds is 4-6 years.
there is limitations a method like this:
- Seedlings require careful maintenance, time and patience.
- The term for growing a full-fledged crop is 2 years. The first harvest is set, nodules 30-40 gr. The table harvest is obtained only in the second year from sevka crops.
On a note! When potatoes are propagated by seeds, planting material should be renewed after 6-7 years.
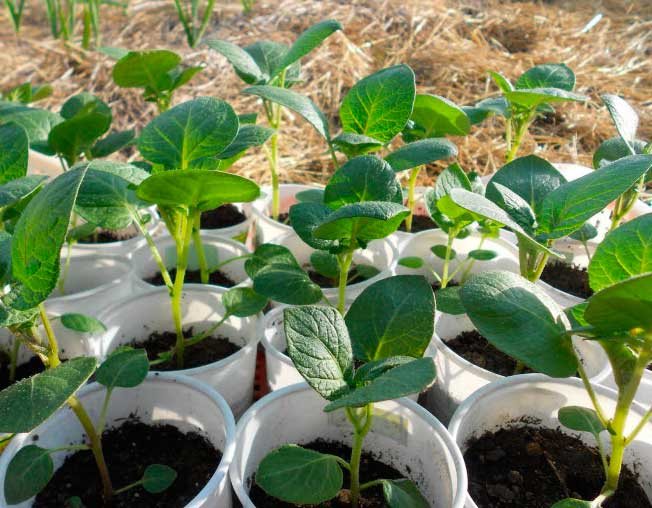


Seedling potatoes
Tubers
In gardening practice, the main method of planting potatoes is tubers. Such reproduction is called vegetative. They choose medium-sized fruits up to 100 grams, important conditions:
- healthy appearance,
- several eyes.
To get the harvest faster, the potatoes are sprouted. This stage is called vernalization. It is carried out 30-40 days before planting in the ground.
In the same period, tubers are treated against diseases and pests:
- "Fitosporin" helps against various fungal diseases,
- "Prestige" from the Colorado potato beetle.
Large tubers are cut into several parts, each one should have several eyes. Cutting should be done not earlier than two days before planting in the ground. The cut is sprinkled with activated carbon or ash.
Potatoes love sunny areas, in the shade, the bushes stretch out, the tubers will turn out to be small. Best predecessors: legumes, cucumbers, green salad.


Well-groomed potato beds
Potato classification by purpose
Based on the content of nutrients in tubers, potatoes are conventionally divided into 4 groups: table, technical, fodder and universal.
- Dining room
Root crops in this category are characterized by large or medium sizes. They are round in shape, covered with a thin skin, the eyes in which are not set too deep.
For reference! Breeders make sure that these varieties contain enough vitamin C, and the starch level is in the range of 12-18%.
- Technical
This potato serves as a raw material for the production of alcohol and starch, therefore it is characterized by a content of the latter from 16%.
The amount of protein doesn't matter.
- Stern
Potatoes used as livestock feed are distinguished by large tubers saturated with protein.
Particular emphasis is placed on increasing the yield of varieties in this category. But breeders do not really care about taste.
- Universal
The varieties of this class combine the properties of the other groups. They can be equally suitable for human and farm animal consumption, as well as for industrial purposes.


Technical potatoes
Chemical composition and nutritional value
The chemical composition of potatoes is a mini-periodic table. It is present in large numbers potassium 421 mg per 100 g, it is useful for the heart, blood vessels and the nervous system. The maximum is contained in the pulp under the peel and in the peel itself. Therefore, baked potatoes with peels or boiled in "uniforms" are the most useful. What else?
- iron 0.78 mg per 100 g
- zinc 0.29 mg
- magnesium 23 mg
- phosphorus 57 mg
- manganese 0.153 mg
- copper 0.108 mg
- sodium 6 mg
- calcium 12 mg.
By content vitamin C potatoes are almost as good as orange (19.7 mg per 100 g).
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) 0.08 mg - protects the body from the effects of toxins,
- B2 Riboflavin 0.032 mg - gives health and beauty to hair, nails and skin.
- B6 Pyridoxine 0.295 mg - increases the efficiency of the brain, improves memory and mood.
The chemical composition of potatoes contains acids that are irreplaceable for the human body:
- apple - improves blood circulation, fights inflammation;
- folic - regulates metabolism, normalizes the digestive tract;
- lemon - has antioxidant properties;
- oxalic - fights against many diseases, incl. with tuberculosis.


Everything you need to know about potatoes
What glycemic index? This is the rate at which carbohydrates are absorbed by the body. Nutritionists recommend eating foods with a low or medium index. Buckwheat, oatmeal, eggplant, beans have a low index, but the potato rating depends on the cooking method.
- Fried potatoes in vegetable or, God forbid, in margarine or butter, has a maximum glycemic index, the same as that of chocolates.
- Boiled potatoes without peels are in the middle of the glycemic line.
- The "jacket" potato has an index of 30 units less than that of fried in oil.
Output: don't get fat from potatoes! Potato dishes are low in calories, but only boiled or baked. They should be consumed no more than once a day without butter and sour cream, without meat or fish. It is useful to pour the finished dish with unrefined vegetable oil or sprinkle with natural vinegar (wine, apple).
How to get healthy planting material
We are all used to plant potatoes with seed tubers, selected from the harvest of the past years. But the tubers annually accumulate diseases and it so happens that we harvest potatoes only a little more than the planted amount.
In this case, it is necessary renew potato seeds... At the lowest cost, you can get a healthier seed materialgrowing tubers from botanical seeds. Only now you will have to part with the variety, because during seed reproduction, seedlings will grow that differ not only from the original variety, but also different from each other. But you can bring your own variety if you're lucky)))
Interesting Facts
- In the list essential products for humanity, potatoes in 4th place. After wheat, rice and corn.
- The worst enemies potatoes - Colorado potato beetle and late blight. During the epiphytotic period of this dangerous fungal disease, potato yield losses can be up to 50-60%. The Colorado potato beetle in 1859 completely destroyed the potato plantations in the state of Colorado (USA), perhaps because of this it got its name. Very tenacious, cunning and resistant to many methods of struggle against him.
- Most expensive grade potatoes "La Bonnotte" cost 500 euros per 1 kg. It grows only on the island of Noirmoutier (France). Potato beds are fertilized with seaweed using a special technology. They are planted and harvested by hand. Has a unique, delicate taste. Harvest only 100 tons per year.
- In the 19th century, during the gold rush in Alaska, potatoes were literally worth their weight in gold. It's great scurvy medicine.
- Exists fries museum in Belgian Bruges. Here is the whole history of this plant from obscurity to deafening success.
Van Gogh "The Potato Eaters"
- Pomidofel - a hybrid of potatoes and tomatoes. Gives two harvests, tomatoes on top, potato tubers below. This species was developed by the Soviet agronomist N.V. Brusentsov in the 30s of the twentieth century.


Pomidofel

Tomato harvest
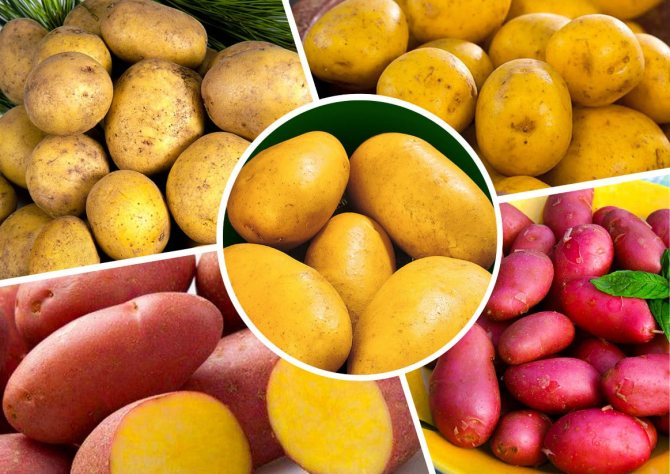
The most popular table potato varieties for growing in Russia
There are a number of varieties that have proven themselves in cultivation in various regions of the country:
- Luck. An early maturing variety with a high yield. Tuber weight 90-120 g. Tubers are round, oblong, white, pleasant to the taste. Resistant to late blight and black leg.
- Red Scarlett. Early ripe table variety. The skin is red, the flesh is white.Tuber weight up to 100 g. Resistant to potato cancer, nematode. Stored for a relatively long time.
- Rosara. Early maturing, high-yielding table variety. Red rind and yellow flesh. Weight 80-115 g. Resistant to cancer, scab, nematode.
- Adretta. Medium early, high-yielding table potatoes. Tubers with yellow skin and a light yellow core. Resistant to viruses, persists for a long time.


Varieties of potatoes
- Gala. Medium early table variety, resistant to cancer and nematodes. The skin is smooth, yellow, the core is dark yellow. Tuber weight is slightly more than 100 g.
- Karatop. An early maturing table variety, gives a good harvest, is resistant to viruses and nematodes. The skin is yellow, the core is light yellow. Tuber weight up to 105 g.
- Nevsky. Medium early grade. Bushes quickly bounce back after attacks of the Colorado potato beetle. Resistant to Rhizoctonia, Alternaria and Blackleg. tubers weighing 90-130 g, beige skin, white pulp.
- Tuleyevsky. Medium early table variety. Resistant to viruses, late blight and scab. The skin and flesh are yellowish.
Knowing the main classifications of potatoes and the key characteristics of the crop helps to choose the right type of vegetable for growing in your area. Having received the basic information and understanding what it is - potatoes, you can proceed to choosing the right variety.
Method 4: grow potatoes from sprouts
We have already introduced you to the easiest way to update potatoes, and now we want to share the fastest. With its help, up to 40 young plants can be obtained from one potato tuber. For this you need sprouted tubers.
For sprouting, it is best to use mid-season potato tubers. They are planted in boxes with universal soil, buried 3/4 of the length. Soon, sprouts will begin to grow, which are broken off and planted in separate pots. The sprouts can be separated from the tubers when they reach a length of 5-7 cm. When planting, they are also buried 3/4 of their length.
You can break off the sprouts for rooting from one tuber 2-3 times, and in some cases even more. When young plants take root, they can be planted in a garden bed, where they begin to build up the root system and form tubers.
Method advantages
- The method is good when you need to quickly multiply potatoes of some valuable variety.
- The yield of potatoes grown from sprouts is not inferior in volume to the yield obtained by planting tubers.
Disadvantages of the method
- The only drawback is that a large area will be required for planting sprouts of several orders, which is not feasible in all situations.
Method 2: grow potatoes from seeds
It is customary to propagate potatoes with tubers, so many summer residents do not even think that after flowering, fruits and seeds can be removed from the bushes. That is why this method of growing potatoes is not so popular. Meanwhile, good quality planting potatoes can be obtained from seeds. How?
To collect potato seeds, you first need to remove green balls from the faded bushes, very similar to unripe cherry tomatoes. These fruits should be stored in a warm room until they lighten and become soft. It is not difficult to extract seeds from such fruits. The seed must be rinsed under running water and dried, after which it can be sown in the ground.
You can also buy potato seeds at a specialty store. Remember, however, that only varieties should be selected, not hybrids.
Method advantages
- After harvest, potato seeds can be stored for up to 10 years without losing their qualities. This means that at one time you can collect seed for several seasons in advance.
- Potatoes grown from seeds are quite resistant to many diseases inherent in this culture.
Disadvantages of the method
- The process of collecting seeds and growing potatoes is very long, and therefore requires patience from the gardener.