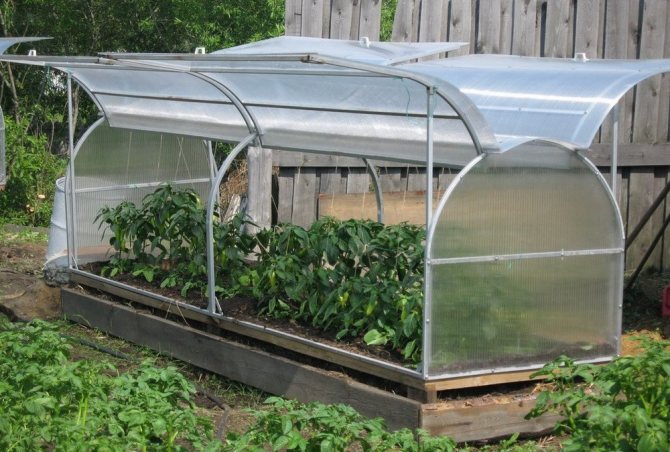
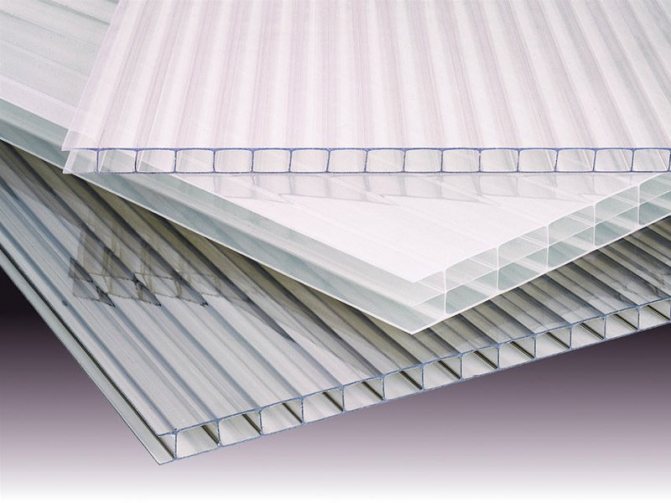
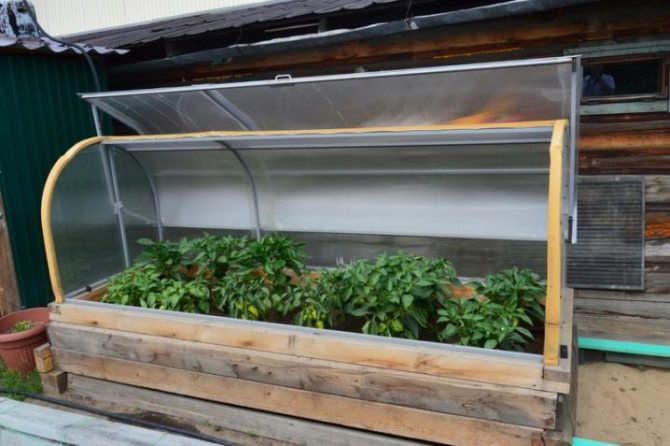
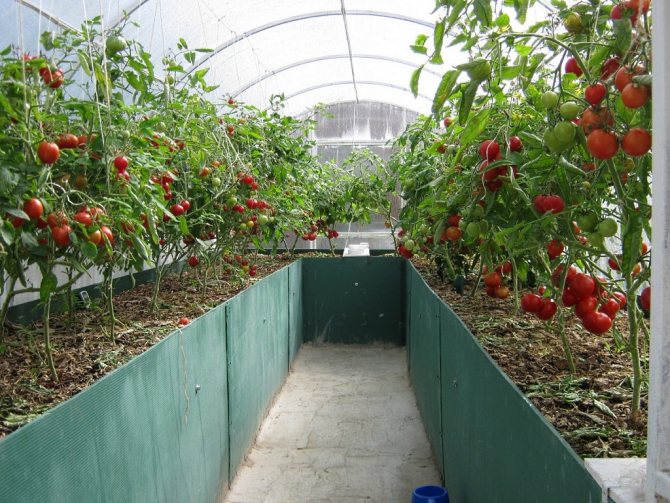
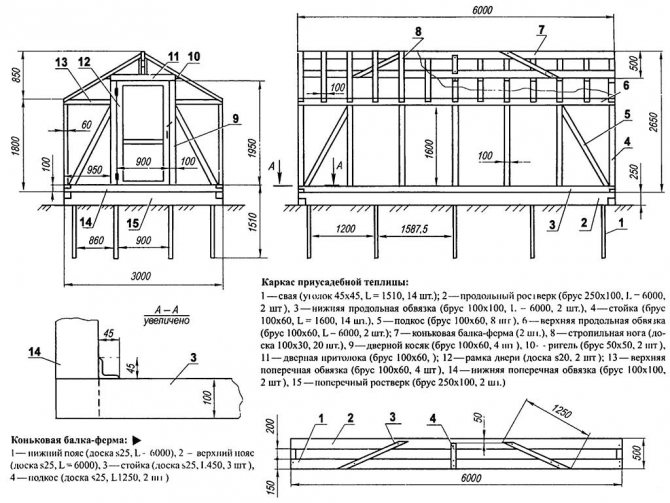
Building a greenhouse in your own summer cottage is the sacred dream of every gardener. A greenhouse is an opportunity to start growing different fruits and vegetables quite early, which means getting a fairly large and high-quality harvest for the entire season. If you build a winter greenhouse, then the freshest fruits and vegetables will be on the table all year round. Each gardener determines the best option for himself without the help of others. In addition to the fact that the structure can be purchased already in a finished version, it can still be built with your own hands.
Basic classical types of construction
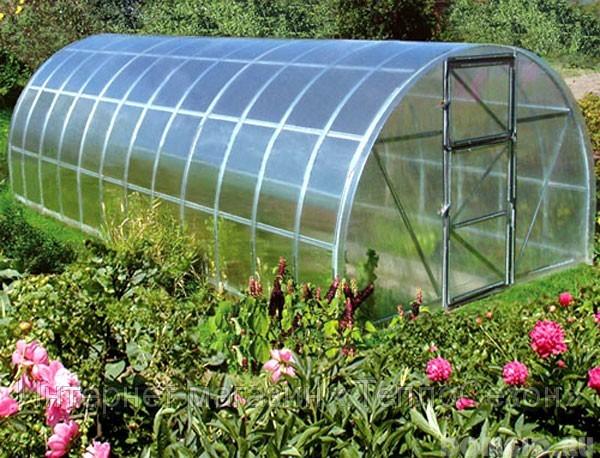

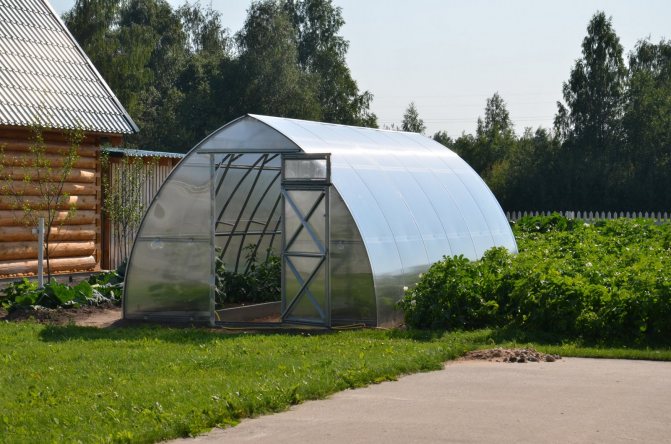
Traditional arched shape
Greenhouses differ from each other in shape, size, presence of a foundation, frame and coating materials. To find the best option for yourself, you need to consider all existing types of greenhouses and their designs. The difference lies not only in functionality, but also in ease of installation, cost and compactness. Only after evaluating all these parameters, you can proceed to the choice.
Greenhouse-arch - simplicity of construction and installation
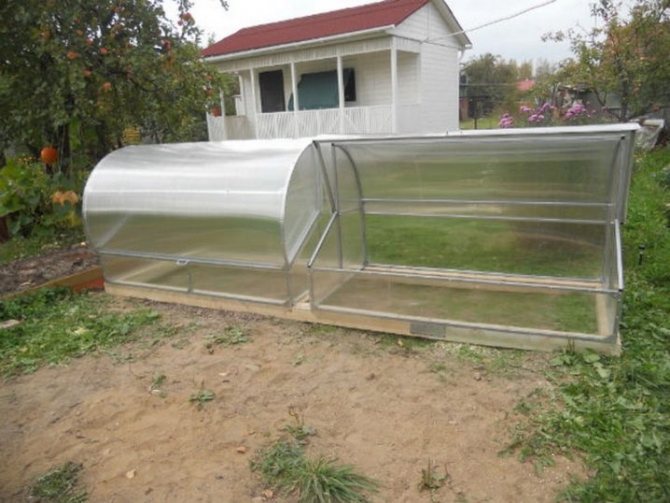
The most popular and easy-to-use option is an arched greenhouse, which is a lightweight frame of several arches connected by transverse elements. This type is economical, since the semicircular shape allows significant savings in coating material.
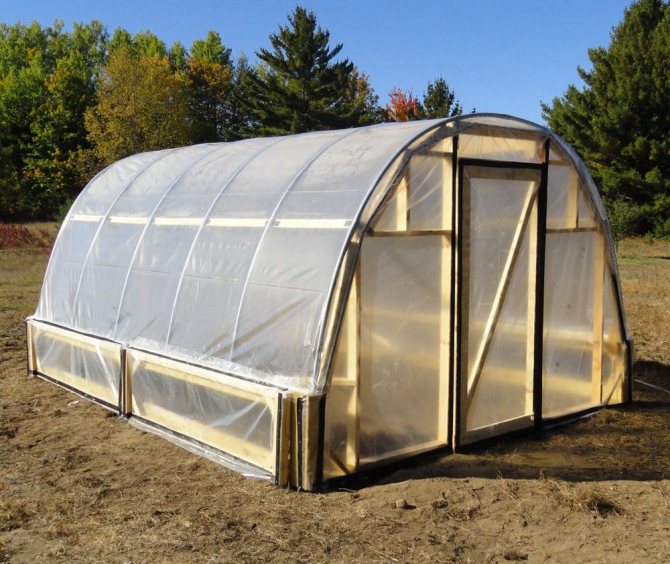


Small arch covered with foil
The versatility of this type of greenhouse lies in the fact that it is equally good both in a mini-format for a summer cottage and in an industrial version for growing vegetables in large volumes. The design is considered one of the most reliable and durable. The main advantages of a greenhouse-arch:
- the ability to add or remove any number of sections;
- snow does not linger on the surface;
- you can assemble a greenhouse-arch with your own hands without complicated calculations;
- low cost of materials.
This type of greenhouse also has disadvantages, which should not be forgotten either:
- it is impossible to use glass;
- the space inside can not always be used rationally.
The arched design does not allow racks or shelves to be placed on the walls. The height of the room is not the same, which does not allow growing plants of the same height over the entire area.
It is best suited for short and medium crops. In this case, the entire heated volume is not used. Thus, this type of greenhouse requires high heating costs.


Large arched greenhouse
For ventilation of the greenhouse-arch, an entrance door is used, and in large buildings, additional ventilation windows and transoms are installed. If the frame and covering are made of lightweight materials, and the greenhouse itself is not very large, you can do without a stationary foundation during installation.
At the ends of the arches, long reinforcement rods are installed, which are attached to the ground. Larger greenhouses require installation on a foundation.
Single slope or adjoining design
For home use, it is advisable to build greenhouses adjacent to another building. Another popular and simple greenhouse design is a lean-to. Such a model can be built near a house or any outbuilding. A lean-to greenhouse is one inclined plane adjacent to the supporting wall.Thanks to such a support, the costs of the greenhouse frame are significantly reduced.
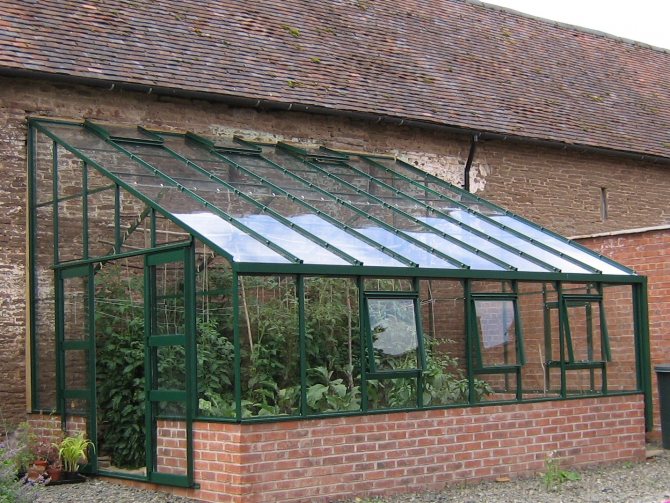


Location near a brick wall
Another advantage of the lean-to design is thermal insulation. Brick, wood, concrete wall - it doesn't matter. In any case, the thermal insulation properties of the wall material are better than those of plastic foil or glass. Thus, much less heat is lost in a heated adjoining greenhouse.
The disadvantages of a lean-to design are as follows:
- insufficient illumination;
- due to design features, snow often collects on the roof, which can damage the coating.
The main problem is low illumination. During construction, it is imperative to take into account the location of the building relative to the cardinal points. It is unacceptable to build an adjoining greenhouse on the north side of the building.
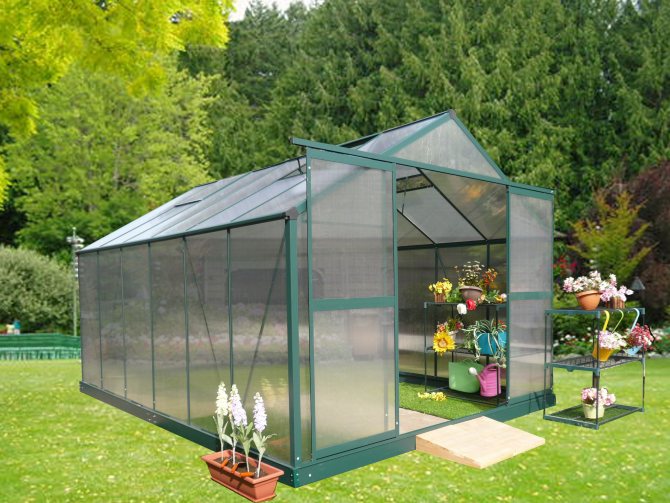
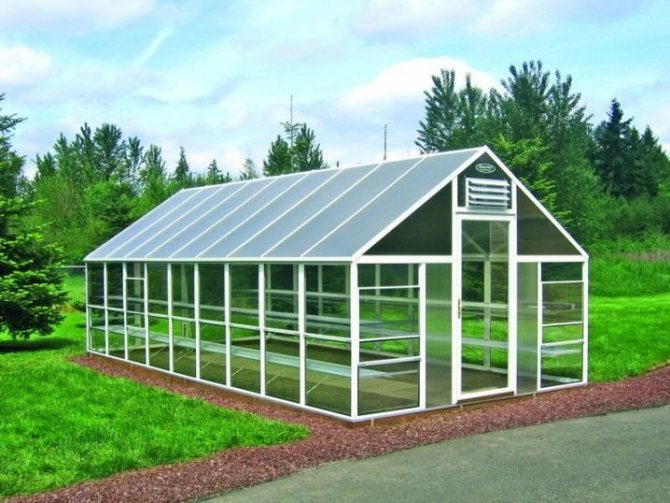
Greenhouse-house - vertical walls and a gable roof
A greenhouse with vertical walls and a gable roof is popularly called a "house". The structure consists of two lateral rectangular walls and two end walls - pentagonal. The roof is made of two inclined planes.
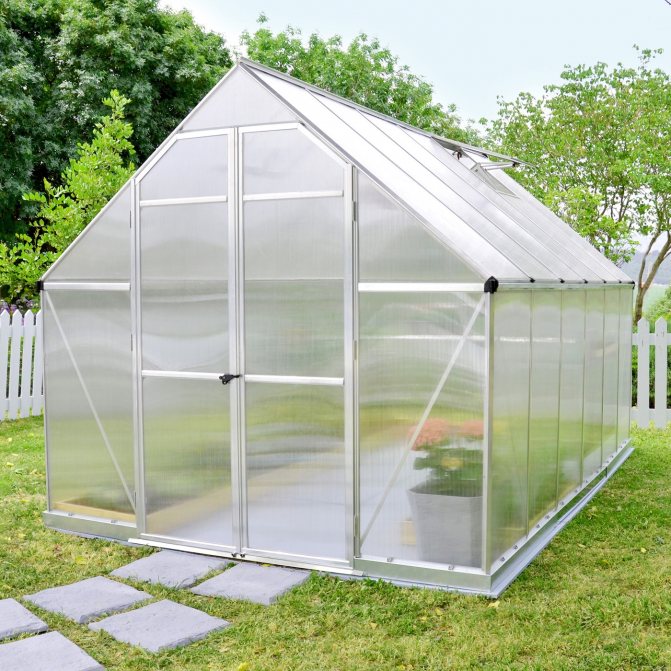


Classic "house" made of polycarbonate
The advantages of this configuration:
- a significantly larger usable area compared to a gable greenhouse;
- convenience of placing utility racks and shelves on vertical walls;
- ease of ventilation (it is very easy to place windows and vents in vertical walls).
The main disadvantage of this design is the complexity of installation. To build such a greenhouse, you will have to make a detailed calculation. The base is not very wide, therefore, in the absence of a foundation, the structure will not be stable enough.
A large number of joints suggests poor sealing. Because of this, gaps and, as a result, drafts can form. In order to prevent such miscalculations, you need to treat the greenhouse drawing with full responsibility.
The Dutch greenhouse is a kind of a gable "house". The difference is that the walls in such a model are not strictly vertical, but are located at a slight slope. This upgrade significantly increases the stability of this greenhouse design.
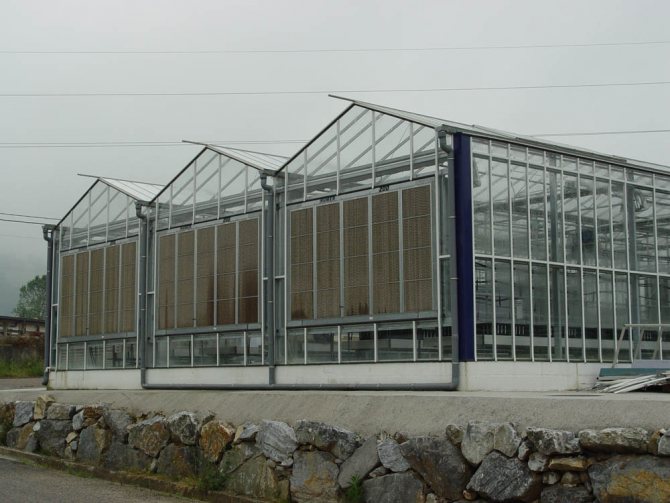


Dutch industrial greenhouse
Among the disadvantages is the difficulty of mounting shelves on inclined walls. However, when you consider the fact that the configuration has better light transmittance, this small disadvantage can be neglected.
A solution to the problem of a gable greenhouse is to use pots. Since the standard gable structure is more than 2.5 m high, it is very convenient to hang the planter with plants at the top.
Description and characteristics
A greenhouse is a small structure whose task is to protect garden crops and other plants from adverse weather conditions. This construction is not heated. The greenhouse consists of a side railing and a removable roof that allows sunlight to pass through. The covering material creates an isolated space with a certain microclimate inside the structure.
Did you know? In London's Hyde Park, there was a Crystal Palace of glass and metal. The structure was erected in 1851 under the patronage of Prince Albert for the World's Fair. It was destroyed by fire in 1936.
For the first time, designs similar to modern greenhouses began to be used in the era of Ancient Rome. They were stationary or mobile (fiddled on carts) and covered with caps. They were used to grow plants imported from hot countries. In the 13th century, the Italians figured out how to equip a greenhouse heating system, and thus turned it into a greenhouse. Tropical ornamental plants began to be grown in heated buildings - this is how greenhouses appeared.
When these structures became widespread among the Italian nobility, they became interested in other European countries as well. In the 18th century, the technology of growing plants in greenhouses came to Russia. Due to the harsh climate, greenhouses were initially used here, but soon popularity shifted to greenhouses due to the simplicity of their design.
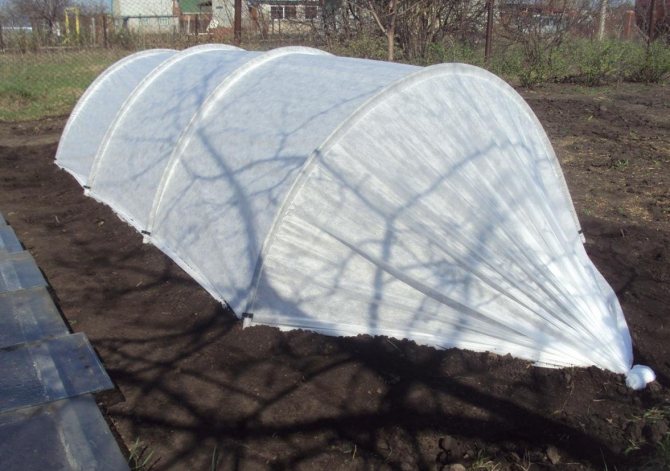


The main characteristics of the greenhouse:
- the structure is low - no more than 130 cm;
- heating is carried out at the expense of the sun and heat emitted by organic matter (manure, humus);
- suitable for growing seedlings, especially early varieties;
- has a mobile design that is easy to move around the site;
- the structure does not have doors, therefore, in order to gain access to the garden bed, you need to either raise the entire structure, or remove part of the covering material;
- you do not need to have special skills and abilities to build;
- a greenhouse is a seasonal thing, usually only for spring.
Also learn how to make a seedling greenhouse.
Mini greenhouses are ideal seedling greenhouses
At home, mini-greenhouses are most often used - hotbeds. They can be of different shapes and are made from different materials. You can see greenhouses covered with glazed window frames, which can be found on the farm of any summer resident.
Miniature greenhouses are installed not only on the site, but also in rooms, well-lit basements and even on the balcony. It is not necessary to heat such a greenhouse. Its main function is to extend the growing season of plants. That is, fruiting begins several weeks earlier and ends later.
There are several popular varieties of mini greenhouse designs. For example, a greenhouse pyramid is a pyramid with a square at the base. There is even an opinion that this form contributes to the concentration of positive cosmic energy with all the ensuing consequences for the harvest. Whether this is true or not is not known for sure, but the pyramid looks quite impressive.
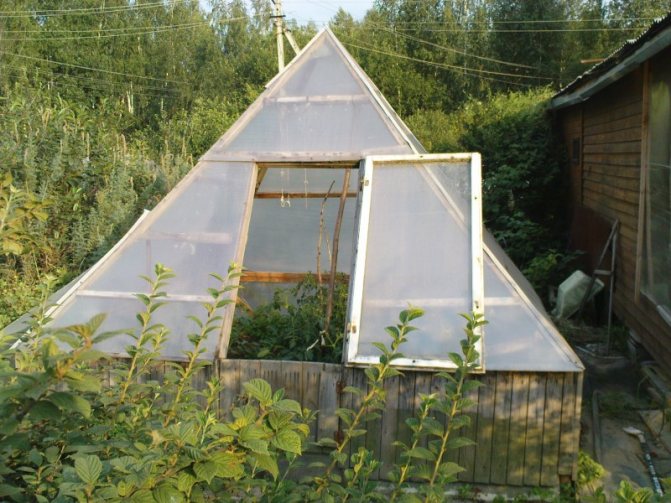


Rectangular pyramid for better harvest
Cloche is a glass greenhouse structure consisting of two panels. She is mobile and moves around the site depending on which plant needs protection at the moment. The greenhouse effect in this option is not very pronounced, but protection from the wind is provided. And this is also important for young shoots.
Most often, mini-greenhouses are a box of edged boards, which is covered with transparent material or a glazed frame. This type is convenient in that it can be placed anywhere on the site and even removed for the winter in a utility room.
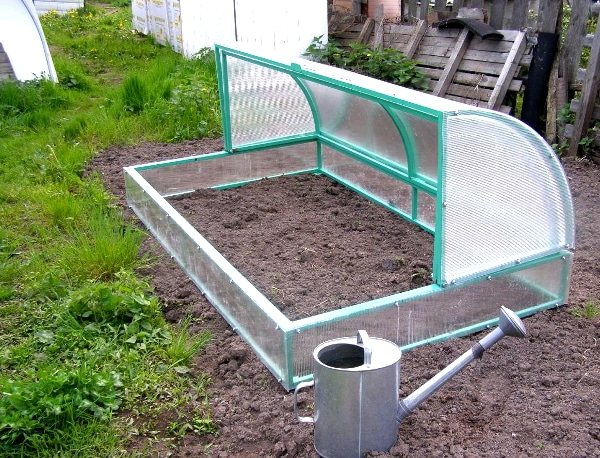


Mini greenhouse for summer cottages
Standard greenhouse 20 m
In summer, planting can be done in light greenhouses and greenhouses, and for winter time it is better to use solid greenhouse buildings with a heating function. Among the projects of greenhouses, different types and sizes of greenhouse and greenhouse structures can be distinguished, because some of them are used on the territory of the summer cottage, and others in large industrial areas, here it depends on the size of the territory, whether it is standard 4 ares or 10-20 ares, otherwise and more.
And yet, the arched square structure is an excellent greenhouse for any purpose.
Such a greenhouse can be found from manufacturing companies; it can also be installed at a summer cottage by specialists. Most often, a greenhouse is made from carbonate. In the standard form, such greenhouses are most often square in shape.
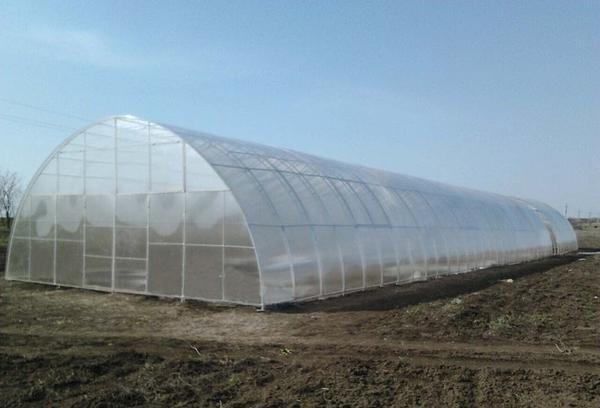


Moreover, they can be:
- With a pitched roof;
- With a gable roof;
- With the presence of a skate.
The shape of the roof is of greatest importance if a winter or year-round greenhouse is used. The types of such a greenhouse building can be anything you like, and they can be built according to your individual preferences. Everything will depend on the wishes of the customer.In addition, experts say that a 20 m greenhouse includes dimensions that are optimal for comfortable planting and plant care.
Underground or buried structure
It is known that the ground freezes slowly in winter. At an air temperature of ± 1 ° C, the soil temperature at a depth of 1 meter is about 10 ° C. In the device of the greenhouse, one cannot but take advantage of such a natural bonus. For construction, you must first dig a hole with a depth of 1 to 1.5 m, and install a transparent coating on top.
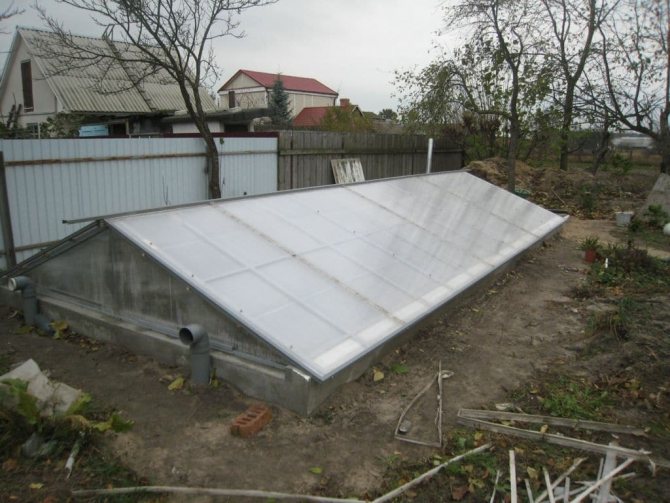


Greenhouse-thermos on the site
One of the options for a recessed greenhouse is an improved design - a thermos greenhouse, which provides even higher indoor temperature and illumination even in cloudy weather. For a thermos greenhouse, you need to arrange a reinforced concrete foundation. The coating is often two-layer. Inside, the walls are covered with reflective paint or other material that acts as a solar collector.


Free-standing "thermos" from the inside
The disadvantage of this type is that it is difficult to organize proper drainage in the underground part.
A large buried greenhouse takes a long time to build due to the need to dig a pit. In addition, you will have to take care of the steps at the entrance, waterproofing and protection from pests, which implies additional costs.
What is a greenhouse
This structure is small in size, the height of which usually does not exceed 1.3 meters. Heating in it is carried out by means of sunlight, artificial heating and lighting are not used. Additional heat is also provided by evaporation, which manure and humus release during decomposition. The greenhouse has no doors. Plants are accessed by opening its top.
Such designs are used for growing seedlings. They can be portable or stand in one place. To make a greenhouse, it is enough to cover the frame made of curved metal or plastic frames with foil. Usually, the greenhouse serves as a temporary shelter for immature plants, protecting them from the harmful effects of frosts in early spring. The air in it warms up quickly, and the heat remains for a long time.
Important! In a greenhouse, it is better to plant crops with the same requirements for thermal conditions and illumination.
Sophisticated advanced greenhouses
Considering the designs of greenhouses and their types, one cannot fail to mention such outstanding developments as the American greenhouse according to Meatlider, Ivanov's solar vegetarian or a greenhouse in the shape of a dome. These ideas became at one time simply innovative and served as an impetus for the development of farming and agriculture in general.
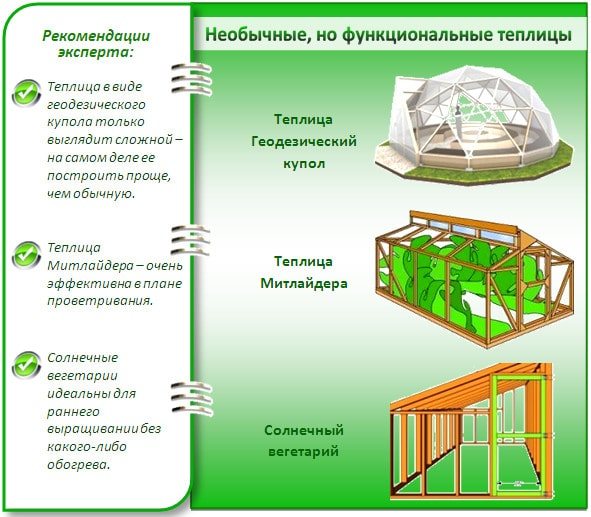

Unusual greenhouse designs
American greenhouse - J. Meatlider's developments
The main problem with large greenhouses is the lack of ventilation. Often, it is provided only by the front door, which is extremely insufficient. Plants get too hot, humid and literally can't breathe. The solution to this question turned out to be very simple. It was found by the American gardener J. Meatlider.
Its innovation lies in the fact that the greenhouse roof is arranged on two levels.
And at the junction of the two halves of the roof, a free space is formed, where transoms for ventilation fit perfectly. The structure can be arched or gable with vertical walls. In both cases, ventilation is very simple. The frame is traditionally made of wood.
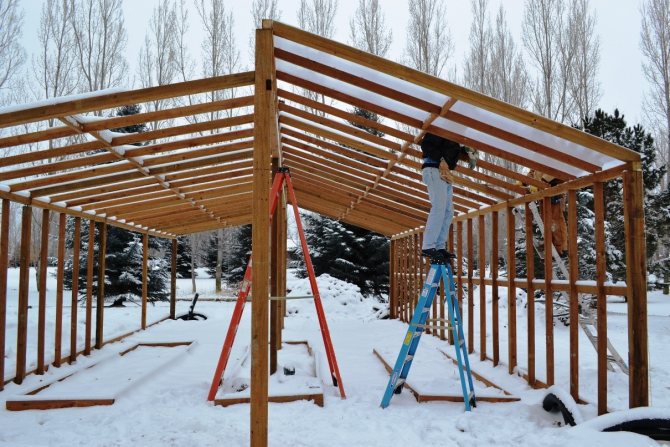


Classic version according to Meathlider - construction
In addition to good air exchange, the advantages of Meatlider development are as follows:
- simplicity of construction and installation;
- reliability due to cross beams and braces;
- the ability to build a collapsible version;
- no condensation due to the wooden frame.
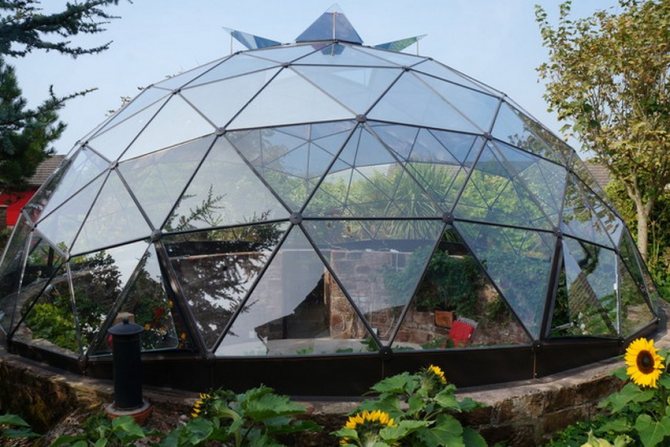
Geodesic sphere - dome on site
The greenhouse of the original spherical shape looks very unusual on the site.The structure itself is already a decoration of the garden and can serve as a striking element of landscape design. The greenhouse dome is assembled like a constructor from triangular elements. It is noteworthy that the coating is self-supporting and does not require any supports or frames, including a foundation.
The advantages of the geodetic sphere:
- light weight;
- the shape of the room ensures good air circulation;
- good illumination of the greenhouse from all sides;
- aerodynamic shape withstands even the strongest winds.
The disadvantages of this model are:
- the complexity of manufacturing and installation;
- the entire volume is not used, as in the arched version;
- hard to adapt curved walls for shelves and shelving.
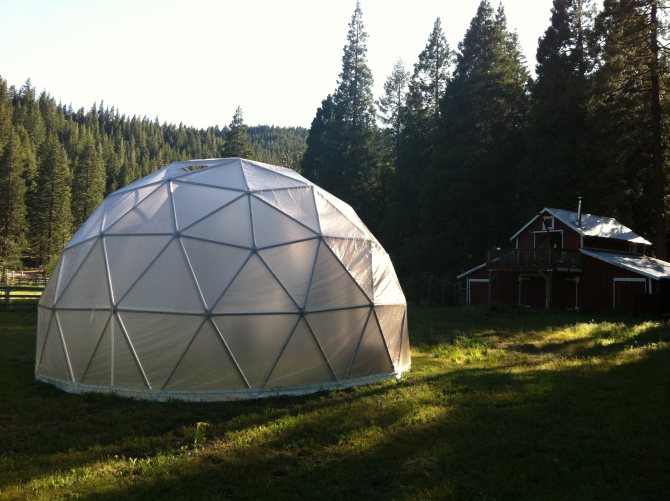


Geodesic sphere under polyethylene
Solar Vegetarian For Plants
The ingenious invention of the Soviet scientist Ivanov is the solar vegetarian. This building doubles the illumination of the greenhouse without additional lamps. In addition, the air temperature rises, without heating costs.
The veggie house can be a variant of an adjoining greenhouse, or it can be built separately. But in the latter case, you will have to build a capital wall. When building Ivanov's vegetarian, it is imperative to take into account the position of the compass needle. The blank wall must be north - this is a prerequisite.
In addition, the natural slope of the terrain is taken into account. Ideally, if the vegetarian will be located on a southern slope with a slope of 15 to 35 degrees. If there is no such bias, it will have to be arranged artificially. The greenhouse roof and floor must be parallel to each other. To ensure the stability of the greenhouse structure, a strong foundation must be built.
The main secret of this greenhouse is the reflective mirror coating on the north wall. The reflector will double the amount of sunlight. This innovation has a good effect on the harvest and does not require additional costs.
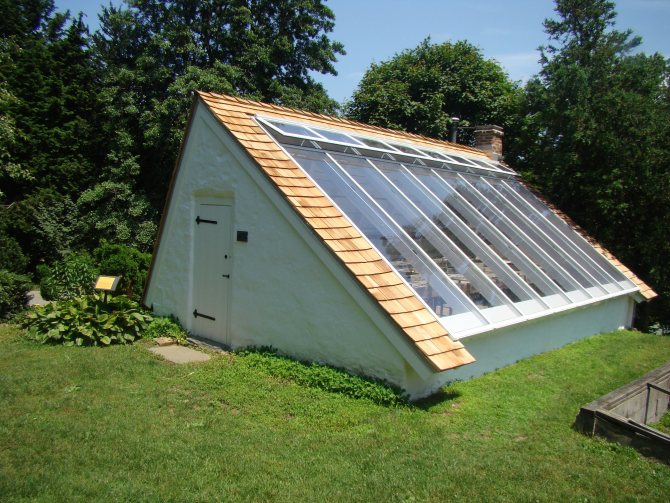


Freestanding vegetarian
Benefits of Ivanov's Solar Vegetarian:
- good illumination;
- good natural heating;
- saving on energy costs.
Disadvantages of the design:
- complexity of installation;
- high cost of building materials;
- stationarity.
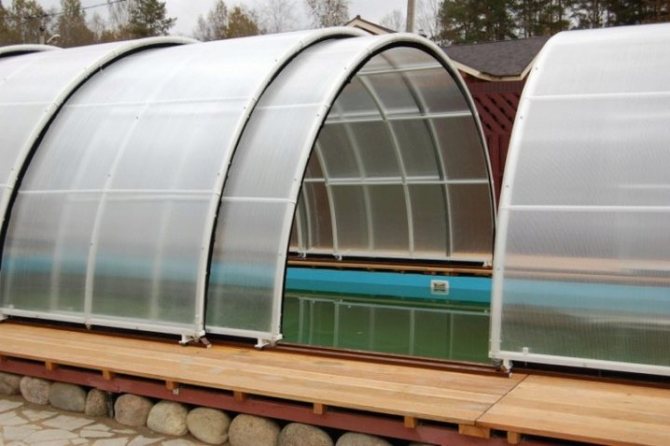
Sliding roof - ventilation without problems
Sliding roof greenhouses combine all the advantages of the arched type, but at the same time eliminate some of their disadvantages. The structure is a conventional greenhouse with a roof in two halves. A special sliding roller mechanism is used in the roofing device, which allows the greenhouse to be opened if necessary.


Great greenhouse solution
The advantages of the system are as follows:
- summer heat is not terrible for plants, especially in spring, when the temperature drops sharply at night;
- good ventilation is provided;
- easy cleaning of the greenhouse from snow, thanks to the opening mechanism.
Greenhouse types by material
When choosing a greenhouse, you need to consider not only its shape. The material from which it is made plays a very important role. This is reflected in the reliability of the greenhouse, and in its cost, and many other nuances. Consider the main types of building materials used in the construction of a greenhouse before making your final choice.


Wooden frame is a common option
What to choose


It is difficult to give an exact answer to this question. Everyone decides for himself. The choice depends on several factors: budget, climatic conditions of the region of residence, harvest requirements, etc. A greenhouse is much more expensive, it is easy to build a greenhouse on your own from scrap materials available on the site.


Mini greenhouse for seedlings: everything is ingenious - simple! Plastic transparent bottles of large capacity, along with the transportation and storage of water in them, are widely used in ...
In southern climates, there is no particular need for a greenhouse, vegetables there can be successfully grown in the open field, using a temporary greenhouse in the spring.But in more severe conditions, it allows you to get a yield that cannot be achieved in open beds. The greenhouse gives the gardener more opportunities, allowing even exotic plant species to be grown in the country. Large-sized structures are used in industrial crop production.
Greenhouses and greenhouses accelerate the development of plants, bringing the maturation of the crop closer. They protect plantings from adverse environmental factors - frost, hail and strong winds. Such an investment will pay off very quickly and significantly facilitate the work of any summer resident.
Varieties of frames depending on the material
The frame is the basis of the greenhouse. It is made from different materials and their combinations. It all depends on the place where the structure will be located, operating conditions, financial capabilities of the owner and the availability of a construction team for work.
Main frame materials:
- wood;
- metallic profile;
- galvanized pipe;
- polypropylene pipes;
- metal-plastic pipes.
Each of these options are good for certain situations. Wood is a cheap and easy-to-process material. But its durability is not the highest. The metal is very durable, but it promotes the formation of condensation droplets, which is very harmful to plants. The same applies to galvanized pipes, but they are better than steel pipes because they do not need anti-corrosion treatment.
It is cheaper and easier to make a greenhouse from plastic or metal-plastic pipes. The construction will turn out to be easy and will not require a capital reinforced concrete foundation, like a metal frame. But, unfortunately, reinforced-plastic pipes do not withstand difficult weather conditions very well.
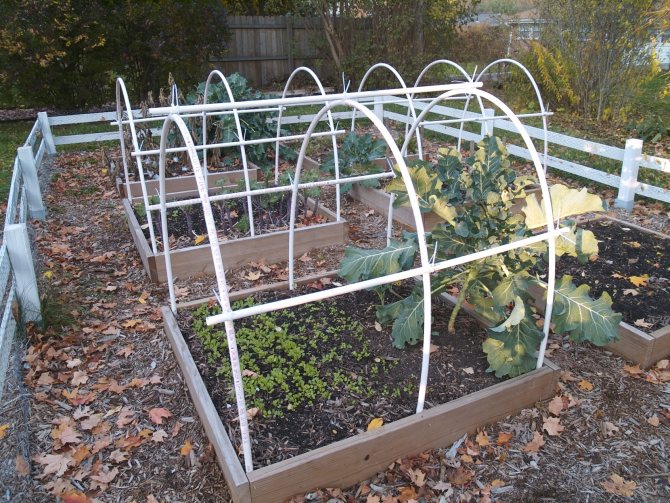


Greenhouse frame made of PVC pipes
Polypropylene pipes are a favorite greenhouse frame for many farmers. It is an affordable and lightweight material. By itself, polypropylene is warm, which is a guarantee against the appearance of unwanted condensation. You can even mount a small greenhouse from pipes alone.
The main enemy is reflection
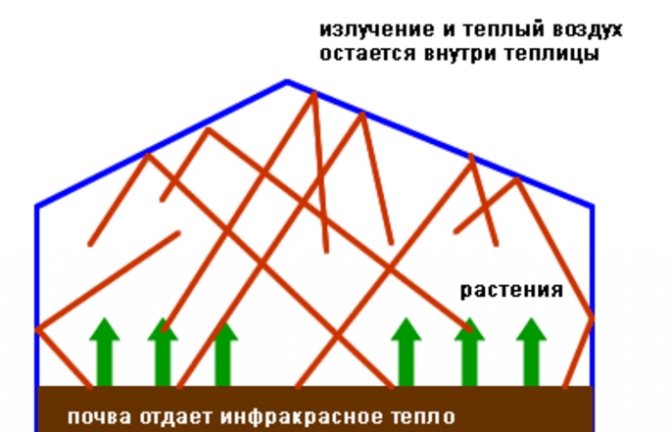
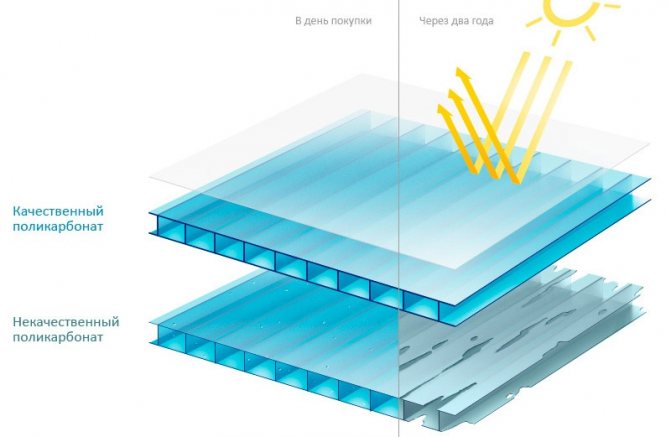
Yes, that's true, we said, but we talked about an ordinary, non-folded sheet. What is the difference? Let's figure it out.
Many people have probably noticed that reflections from the sun or other light source often appear on a curved surface.
What is it?
- This is a reflected beam of light that did not pass through the surface of the body and was reflected from it.
- In other words, a curved surface is much less likely to let light rays through itself, making every effort to reflect it.
- If for some buildings this does not matter, for the greenhouse it is a complete disaster.
- The sunlight so necessary for plants in cold weather is wasted without reaching the end point.
Our advice is to take a thin plate of any transparent plastic and direct a beam of light at it. After that, bend the plastic into an arc and repeat the operation, you will see that in the first and second cases, the light transmittance is significantly different.
- As you know, the sun does not stand still, changing the directional angle of illumination can only aggravate this situation, in which it will be lost up to 40% light and, accordingly, thermal energy of the sun.
Transparent doesn't mean good
From the above, it becomes clear that in relation to greenhouses, the arched structure is the most losing one. A straight surface is the best option in this case.


Greenhouse with straight walls.
Many consider a completely transparent greenhouse to be the best option for growing plants. A complete delusion inherent in the majority of the population. Don't believe me? Let's go deep again.


Completely transparent greenhouse.
Our reference is light, this is electromagnetic radiation emitted by an excited or heated substance.
Simply put, light is made up of a stream of photons. We will not delve further into the theory, so as not to frighten our readers, we will switch to a more accessible language.
- You have a completely transparent greenhouse with straight walls, everything is great. But watch what happens.
- Penetrating from the south side, photons of light, passing through the greenhouse space, abut against the northern transparent wall. What will happen to them next?
- You guessed it, they'll go through the wall and just fly out. Do you think this is correct?
Simple logic tells us that it is wrong to set up a greenhouse like that. Losses of light and heat are guaranteed in this case.
Sometimes, when it's opaque, it's better
- The most rational thing will be when only the walls facing the sun will be transparent, the rest should not let the sunlight through, they should absorb it.
- As a result, additional energy will be created inside the greenhouse space, ensuring the normal growth of plants (a lot has been written on our resource about what is profitable to grow in a greenhouse)
Our advice is to make the north side of the greenhouse from an opaque material. Be sure to arrange three layers, external, internal and insulation. Then the rays of light will begin to heat the inner layer, the insulation will not let the heat go outside and it will all completely remain in the greenhouse.
- Many people overlook this important detail when conceiving a greenhouse device.
- For any structure, including polycarbonate greenhouses, size and configuration are an important factor in its functional capabilities.
Industrial greenhouse for 5 hectares
Greenhouses can be of different shapes, even round and triangular. It is worth mentioning that home-made industrial greenhouses are almost impossible to find. They have a particularly strong welded frame. Industrial greenhouses always differ in their size.
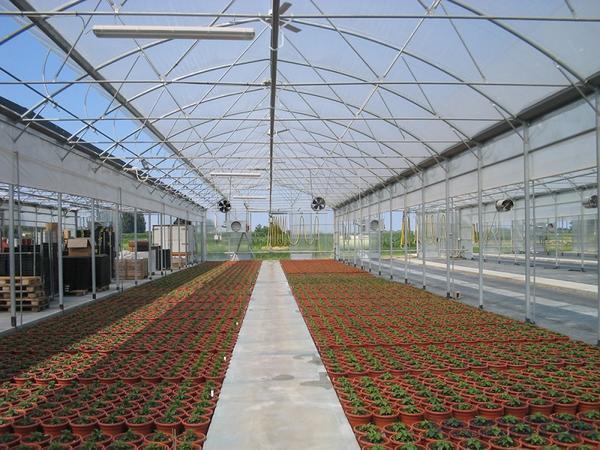


The most common are the following sizes of industrial greenhouses:
- 300 m is 0.3 hectares;
- 500 m - which is 0.5 hectares - is the ideal size for planting tomatoes and cucumbers;
- 1000 m - 1 hectare;
- 5000 m - 5 hectares.
Three greenhouses are enough for a small business to grow and supply fresh vegetables. It is better to buy large greenhouse buildings from trusted manufacturers. The supplier must have all the necessary quality certificates. Often, enlargers are included in the complete set of industrial greenhouses.
Greenhouse made of stretch foil with a wooden frame
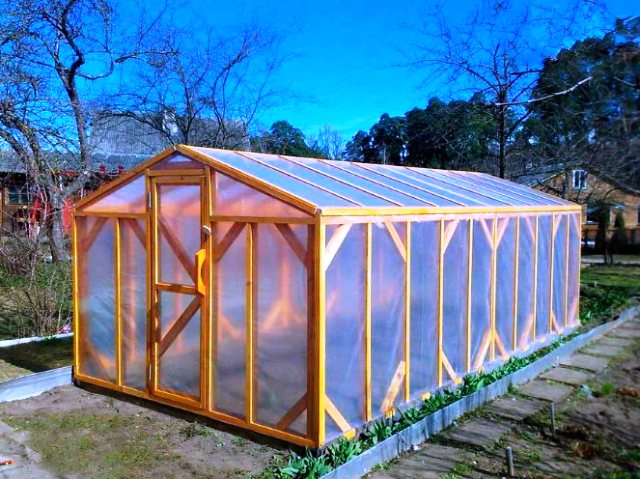


- Complexity of assembly: average.
- Foundation: not required.
- Cost: low.
Another quick way to build a greenhouse. A wooden beam is used as a frame, and a packing stretch film serves as a covering material. With a large number of layers, it transmits light a little worse than ordinary PVC film, but on hot days this is even a plus.
- The film is sold in rolls, so the size of the greenhouse is chosen according to the cutting of the timber and taking into account your wishes.
- For the base, steel corners 40 × 40 mm are used, in which holes are pre-drilled for fastening the frame racks. They can also be bitumen treated or painted to extend their service life.
- The corners are hammered into the ground, and pieces of timber are screwed to them with self-tapping screws. In turn, the lower frame is attached to the timber, on which the side walls and the roof are assembled. All corners are reinforced with additional inclined timber sections.
- The door is assembled on a wooden frame in one of the side walls and hinged.
- The film is wrapped in parts, and in several layers and with an overlap. First, the gables are installed, then the roof slopes and only then the walls. You need to start wrapping them from the bottom so that the flowing rainwater does not get inside the greenhouse.
- After wrapping with glazing bead or river, the door and its outer contour of the door are upholstered, and then the film around the frame is cut through. In the same way, you can make a window in the opposite wall.
Relationship with components
Consider the most important blocks that make up any greenhouse.
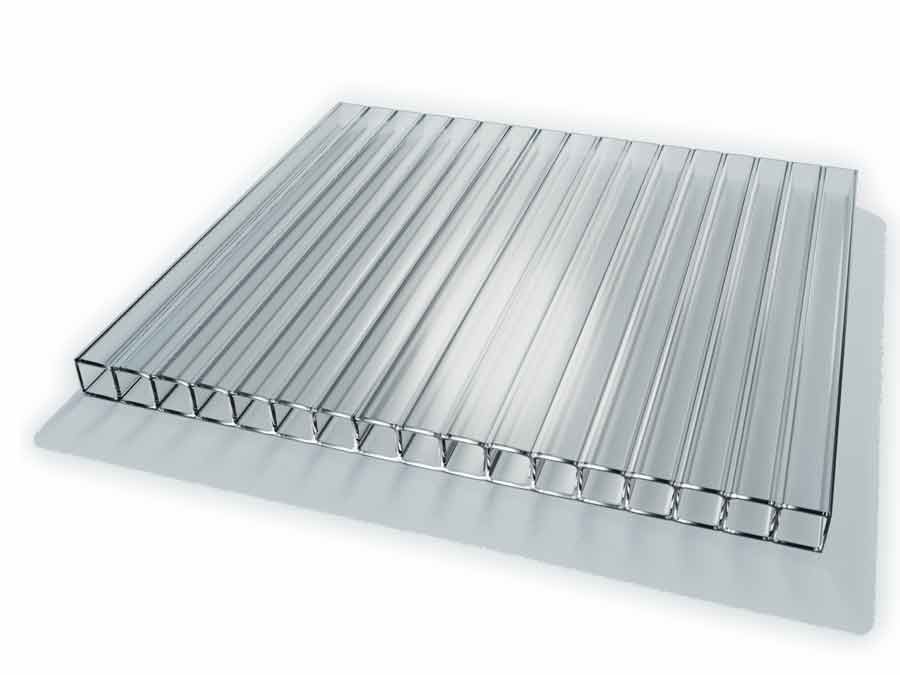
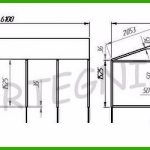
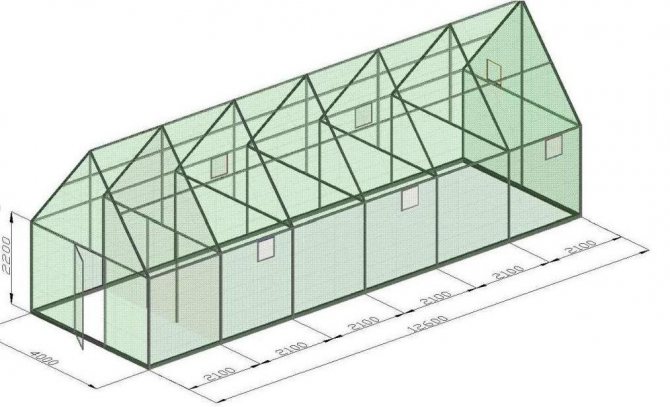
The length is usually a multiple of the dimensions of the polycarbonate sheets:


It is also important to take into account the parameter of the racks that will be in the greenhouse, the number of pallets. It should be borne in mind that the use of solid sheets is more preferable, this reduces the cost of creating a greenhouse and is a significant factor for strengthening the frame.
The thickness of the sheets should fluctuate between 3.6 and 6.2 mm, these are the optimal parameters that will meet the following indicators:


Frame material
The configuration of the greenhouse and its dimensions are determined by the customer. The material of the supporting structures is most often wood or metal. All elements must be treated with antiseptics and primers, nowadays there are effective formulations that allow you to ensure that there is no corrosion for a long time. It is necessary to do this, the microclimate of the greenhouse is humid, has a positive temperature; if you do not process the nodes of the structure, then after a few years it will hopelessly deteriorate.


PVC profiles have proven themselves well, they are not inferior in strength to steel, at the same time there is no risk that they will rust or rot. When making load-bearing structures from such profiles, it should be remembered that they must be located and mounted so that it is possible to withstand heavy loads in the cold season. There are tested patterns for the arrangement of PVC profiles, in which they realize their maximum potential.


The foundation
The massiveness of the foundation and its cost are interrelated with the weight of the structure. Often, for greenhouses of small mass, a foundation of timber or logs is used. But a foundation on screw piles is also quite acceptable. In terms of their characteristics, piles are not much inferior to strip foundations, at the same time they are installed quickly and are inexpensive.


The strip foundation is the most expensive and time consuming, it is able to withstand heavy loads. A trench should be dug under it, filled with concrete and reinforced. It will also take 4-6 months for the foundation to "shrink". If you analyze the practical side of the issue, then a strip foundation for greenhouses is not required. The weight of the greenhouse structure itself is small; this type of foundation is more suitable for a home.


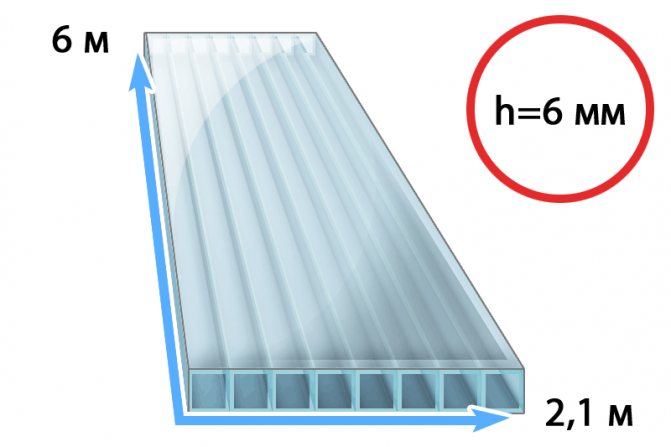
Length and width of sheets
Polycarbonate sheets are 6 meters long and 2.1 meters wide. When creating a drawing, one should proceed from these parameters. The sheet can be cut into pieces of 3x2.1 meters. And also a working format is considered to be a sheet size of 1.5x2.1 meters. Separating material in width is not easy, so you rarely see such things.


The roofs of greenhouses, like those of houses, can be pitched and gable. The angles of inclination of the roof vary, they can be from 19 to 32 ° or even up to 46 °. The greater the degree of inclination, the less snow will accumulate, the likelihood of roof destruction under the weight of the snow cover is noticeably reduced. Shed roofs often have different diagonal fasteners. Typically, the material is a metal corner 40x40 mm. Shed roofs are most often made when the greenhouse is an extension to the main building.


The distance between such supporting structures is slightly more than a meter (1.1 m), and the same applies to rafters, which are mounted on the same level with vertical wall structures.
Greenhouse shape
The configuration of the greenhouse is determined by the plants that are grown in it.
Examples include:
- cylinder;
- semicircle;
- classic rectangular elongated shapes with different roofs.
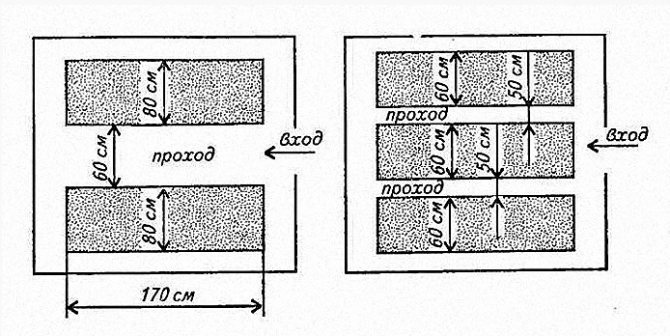
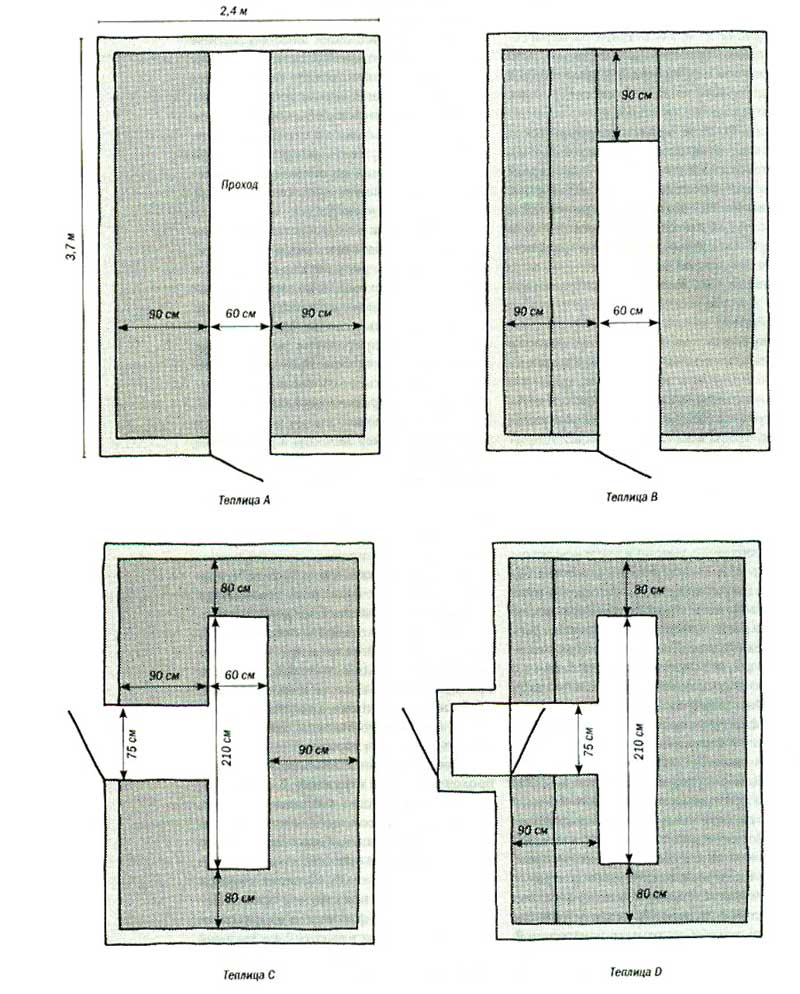
A classic greenhouse has a standard layout: different crops grow on the sides, and a walkway is located in the center. This arrangement is considered the most rational and therefore very widespread. A standard polycarbonate sheet panel is six meters long and 2.1 meters wide; it makes sense to take these parameters into account when designing.
In total, there are several main types of greenhouses, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages.
- An arch-shaped greenhouse has semicircular support nodes to which beams are attached. Polycarbonate sheets are bent and screwed to the frame. The advantage of this design is that it experiences a minimum snow load in winter, it is not difficult to assemble it. Among the disadvantages, it can be noted that the height of such structures has its own limitations, which often interferes with work. The classic version is an arched greenhouse with a gable roof. A little more material is needed for its creation, but at the same time it is possible to advantageously solve the problem of eliminating the problem of the low height of the structure. On the basis of an arched greenhouse, you can make the so-called Mitlider greenhouse, it is notable for the fact that it has a good air exchange system.
Types of greenhouses by design
So, first, just answer yourself these questions:
- What is a greenhouse for you, and what are you going to grow in it?
- Will you use it in winter, or do you only need it for the warm season?
- Are you going to install heating devices in it
- Is your goal to grow for yourself or for sale? Are you expecting a quick payback?
- What size greenhouse do you need?
- How smart and automatic will it be?
Have you answered? Now let's look at what the modern market offers us - domestic and foreign.

Greenhouse with a metal frame
If you want to build a greenhouse "for ages", make a frame of steel pipes or a corner. It can be welded (this is reliable, but it will no longer be possible to disassemble such a structure), but you can also make it collapsible.


The greenhouse doesn't have to be big.
Such a frame can be covered not only with foil, but also with cellular polycarbonate. A greenhouse made in this way is good for everyone: it can be quickly assembled and disassembled, easily rearranged to another place in the garden, it does not take up much space during storage.
Useful articles from the "Useful Tips" section:
- Preparing a vegetable garden for spring plantings: how to make beds
Save and Share:
Useful articles for the gardener:
- Red onions: planting, care, cultivation
- Nasturtium
- What flowers to sow for seedlings in February in 2020
- Sorrel: sowing, cultivation, care
- Planting eggplants for seedlings and greenhouses in 2020
- Planting raspberries in 2020: when to plant
- Planting corn in 2020: sowing time, cultivation and care
- Sowing calendar for March 2020: auspicious days
- Favorable days for planting beets in 2020: timing, cultivation and care
- The best tomato varieties for 2020: the tastiest and most productive