Despite the fact that orchids are considered finicky sissies, they are quite viable plants. The more extensive the damage, the stronger the craving for life manifests itself. Often, a dying orchid will develop side shoots or try to bloom to reproduce. Even with the loss of almost all of the root system and most of the leaves, there is a chance to save the plant... Most likely, the recovery process will be long - from 3-4 months to a year or more. But if everything is done correctly, the orchid will come to life and grow.
If there is at least one living bud on a dying plant, it makes sense to fight for its salvation.
Symptoms of the disease
It is not difficult to understand that something is wrong with the orchid. It is enough just to take a close look at the "behavior" and the state of the plant. The main symptoms of feeling unwell are:
- wilting and drying of leaves;
- poor or even stalled growth;
- lack of flowering.
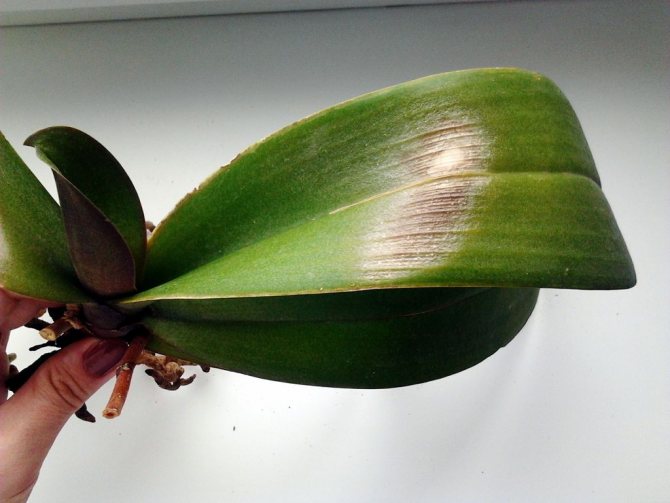
The main indicator of negative changes is foliage. When an orchid does not feel well, the leaves wither, turn yellow, curl, become stained, fall off. It is impossible not to notice this.
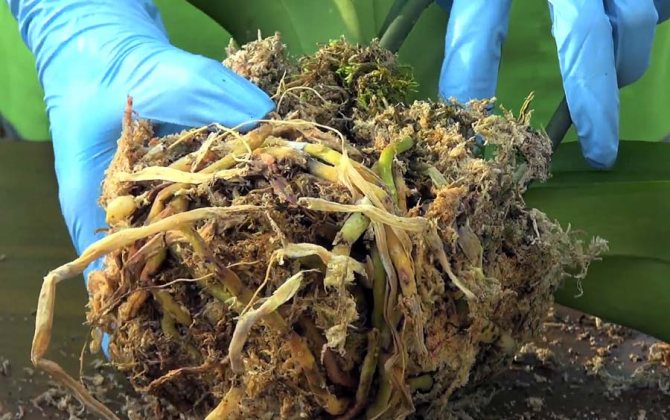
It is necessary to start reanimating the plant immediately. The sooner you start treating the flower, the higher the likelihood of a successful outcome. The first step is to check the roots: in a healthy state, they are white, slightly greenish. If the roots start to rot, they acquire a dark shade and an unpleasant, musty smell.
How to prevent rotting
It is recommended to grow orchids in transparent containers. Experts associate this with the peculiarities of the existence of a plant in nature. Phalaenopsis roots are visible in glass or plastic transparent containers. They should be light green when healthy and moist. If the roots become pale green or white, and the leaves wither, then phalaenopsis needs moderate and regular watering. Contrary to popular belief, orchids are quite tenacious, so that minor flaws in the care are unlikely to cause rapid rotting of the root system.
As a rule, orchid diseases are associated with improperly selected soil or a pot that is too loose for transplanting. There should be no dense particles of earth in the soil, because this can cause stagnation of water, leading to the death of roots and preventing the flow of oxygen. It is best to use a substrate for transplanting phalaenopsis, which consists of sphagnum moss and dry pine bark. You can prepare such a composition yourself.

Yellow foliage


This is the most common problem when growing orchids. The yellowing of the leaves can be caused by various reasons, but usually this is a banal improper care or not the most suitable conditions of detention.
Due to decay of roots
To rule out the possibility of root rot, check them right away. It is easy to distinguish rotten parts from healthy ones: they are dark, brown, lethargic, slightly soaked, wrinkled. If the problem is precisely in the roots, the plant needs an urgent transplant with the removal of rotten parts.
Due to overheating
The foliage can also turn yellow due to too high room temperature. Most often, this happens if the pot is near the batteries in winter.
Move the container with the plant away from the battery and leave it alone for a while.After 3-4 days, the flower usually recovers on its own. And to avoid a repetition of this problem, do not place the pot near radiators or other heat sources. And you just need to keep the orchid on the windowsill, shading it from direct rays.
Lack of light
Sometimes it affects the disease of the plant and its maintenance in low light. If the orchid does not have enough light, it will react to this with wrinkled leaves, their small size and dull color. In general, the appearance of the flower will be unhealthy, drooping.
How to treat rotting at home?
To help an exotic plant and choose the right treatment, you should first determine the cause of rot, and only then use this or that remedy.
Chemical
If it turns out that pests (whiteflies, midges, scale insects, thrips) or viral diseases are the cause of root decay, then acaricide or insecticide preparations are useful, such as:
- Aktara;
- "Tsvetofos";
- "Fufan";
- Inta-vir;
- Vermitek.
With fungal infections, fungicides are indispensable. The drugs that are most effective for prevention and treatment are considered fungicides, which destroy the causative agents of fungal diseases in representatives of the flora. They are of different spectrum of action. The main active substances of fungicides are: aldehydes, mercury, copper, manganese, organic substances.
- Oxyhom;
- Fundazol;
- "Immunotitofit";
- Fitosporin;
- "Topas".
Folk


What can you do at home to save rotting roots? Homemade recipes are proven over the years. Yes, they do not have the same degree of damage as industrial ones, but they are more affordable and environmentally friendly.
- A decoction of cyclamen tubers. For cooking, you will need finely chopped flower tubers. It is advised to boil them over low heat for 30-40 minutes. Leave for a day. After the broth, strain, and lower the diseased roots of the orchid into it for 5-10 minutes.
- Soap solution. Dissolve 1 bar of laundry soap in 3 liters of clean warm water. Then immerse the roots in soapy water for a few minutes.
- Oil solution. Dissolve 2 tablespoons of olive oil in 1 liter of water. Orchid roots can be immersed in the resulting mixture.
- Onion infusion. Cook 3-4 small onions for 30 minutes. Then cool the broth and leave for a day. The pure roots of the flower should be left in the healing liquid for 7-10 minutes.
Important. Folk remedies can only help in the early stages of the disease.
Root rot
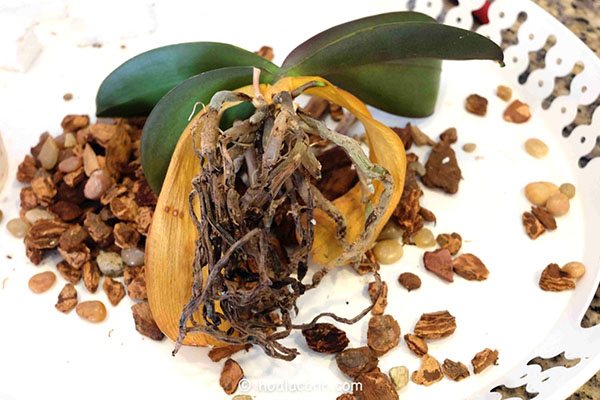


A very dangerous condition that can lead to the death of a flower. Most often, three reasons lead to root decay:
- fine, crumbling substrate;
- lack of light;
- high humidity.
Let's consider all of the above reasons in more detail.
Substrate
All growers know that orchid substrate has a special composition: it is fibrous, consists of separate fragments. Therefore, it is important to choose high-quality soil, with elastic particles that do not lose their shape.
Fragments should not quickly disintegrate into fibers, crumble strongly. When this happens, small particles of the substrate begin to rot, decompose, and mold: as a result, instead of a soil that absorbs moisture well, a mushy substance is formed in the pot. The roots of the orchid, being in such a substrate, rot. Soon the flower may remain without roots at all.
To cope with the problem, you need to fill the container with a fresh substrate, consisting of whole fragments that have not lost their elasticity. It is important that the substrate is well permeable to both moisture and air.
Lighting
Keeping an orchid warm requires a lot of light. Moreover, the higher the air temperature, the more lighting the flower needs.For wintering, choose the lightest window sills in the house, since when the batteries are running, the plant's need for light is especially great.
If the orchid is kept warm, but in partial shade, this will inhibit the development of its root system, lead to decay, yellowing of the leaves.
Humidity
The orchid should be grown in a very high humidity environment - as much as possible. It is clear that in an apartment it is not always possible to provide tropical conditions, but whenever possible, at least carry out regular spraying. The spray should be fine, better dispersed. It is important to take care during the procedure so that water does not enter the deciduous sinuses. Otherwise, decay is also possible on the leaves of the plant.
Keep a distance between waterings: it is important to avoid stagnation of moisture in the soil. Between moisturizing procedures, the substrate should have time to dry well and ventilate. Moisture stagnation can be identified by the musty smell coming from the pot.
The main causes of decay
In an orchid, like all epiphytes, the root system is built in such a way that the flower does not absorb water and nutrients through the small roots. All nutrition occurs through the spongy part of the rhizome. If this process fails, then the orchid begins to hurt.


Another cause of decay is compacted soil that has not been changed for a long time. It becomes heavy and dense. Water begins to stagnate, and the root system rots. To prevent this from happening, the land for cultivation is prepared independently from disinfected pine bark and sphagnum moss. Deficiency of sunlight can also provoke rotting. Part of the moisture does not evaporate and is not absorbed, which negatively affects the state of the root system.
Popular: Fast and maximum tomato yield by pinching
It can rot due to improper feeding of the orchid. The roots are easily burned when using phosphorus and potassium compounds. The orchid receives similar damage with a careless transplant. An infection that weakens the plant gets into the "wound". The roots of the flower can feed on pests such as click beetles. Waterlogging of the substrate in winter and autumn is provoking. Florists do not always adjust the intensity of watering in different seasons.
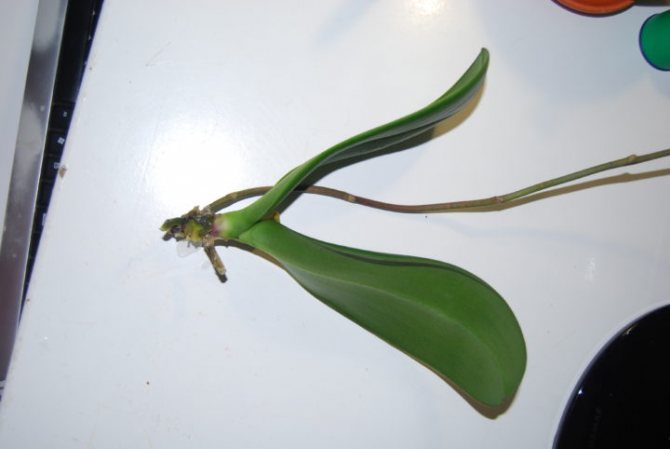
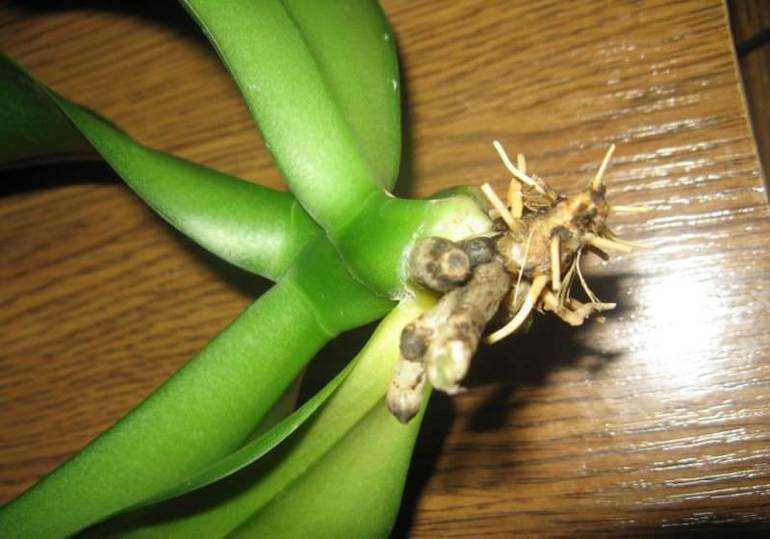
What to do with the roots


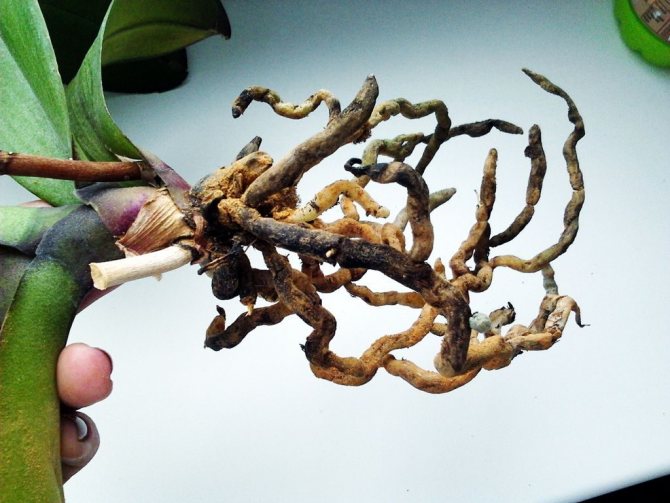
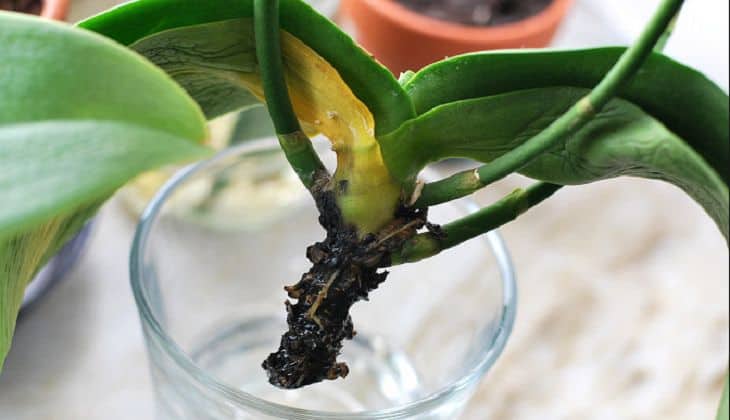
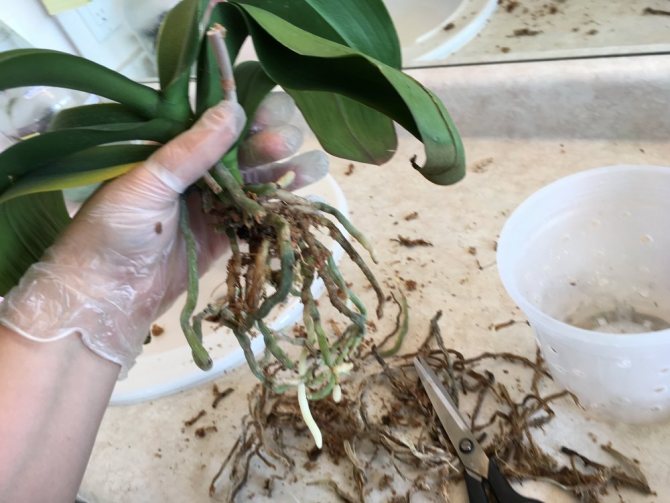
Rinse the root system of the plant and inspect it carefully. Removal of the substrate and rinsing will show a clear picture of the lesion. Symptoms of diseased, rotten roots are the following:
- darkening of individual or even all roots;
- the appearance on the surface of the roots of weeping, slimy areas;
- when you press on the root, liquid oozes out of it;
- large roots disintegrate into separate filamentous fibers.
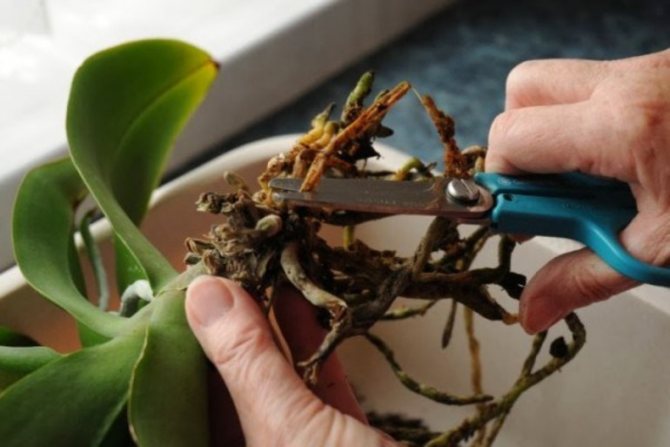
It is impossible to reanimate the areas already covered by decay: they only need to be amputated, cut off. The tissue of the putrefactive roots is already dead. If the roots are dry, remove them too.
Drying and processing
- After all decaying parts have been removed, the cut sites should be treated with ground activated carbon or cinnamon powder. This recommendation is related to the need to disinfect the cut areas.
- Dry the roots and immerse them in the fungicide solution for 15 minutes. This will help rid the plant of pathogenic microbes and fungi parasitizing on it.
- After fungicidal treatment, soak the roots in the growth stimulant solution. Such a thorough reanimation care will increase the plant's immunity and activate the formation of new healthy rhizomes.
After all the above preparatory stages, you can proceed to resuscitation closely.
Withering plant care


An orchid after resuscitation and in a sluggish state requires careful care. We must not forget that the flower tolerates a slight drought better than overflow.Another important point is quality light (12-14 hours). They make him absent-minded.
In order for the rooted roots to recover faster, the pot is chosen transparent with holes for air intake.
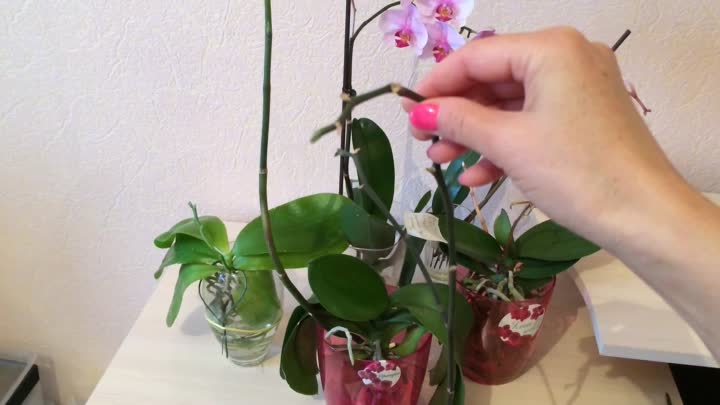


Orchid resuscitation methods
Let's get acquainted with the most effective ways to save a plant at home.
Method 1
Check the roots of the plant and if there are enough of them left alive, clean them of the old substrate, then transplant the plant into a new pot. Rotted roots must be cut off before transplanting. It is advisable for the first time to strengthen the orchid in a new pot, since due to the absence of all the roots, the plant will be unstable.
After transplanting the flower, it is necessary to create favorable conditions for recovery. Place the pot in a well-lit place, protected from direct sunlight. It is also very important to normalize watering of the plant, avoiding excess moisture.
Since the affected roots cannot yet fully absorb moisture, it is necessary to water evenly from a spray bottle and very carefully, only slightly moistening the soil. You can also water the plants from below by pouring water into the pan of the pot.
Method 2
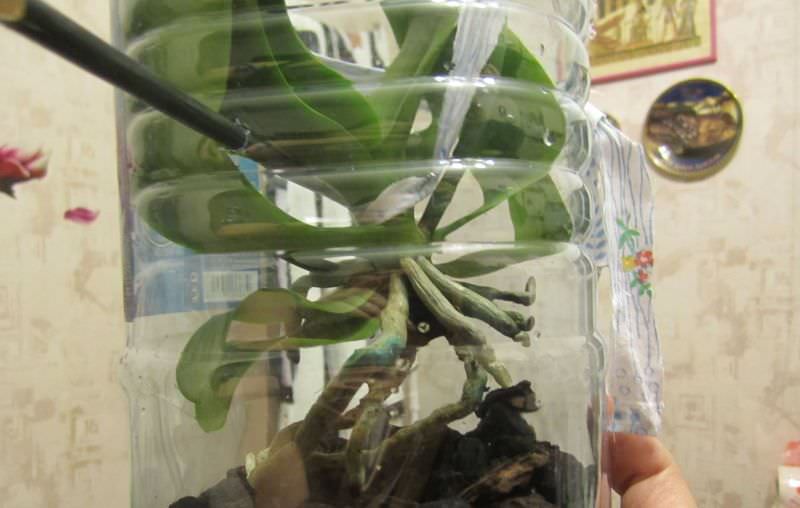
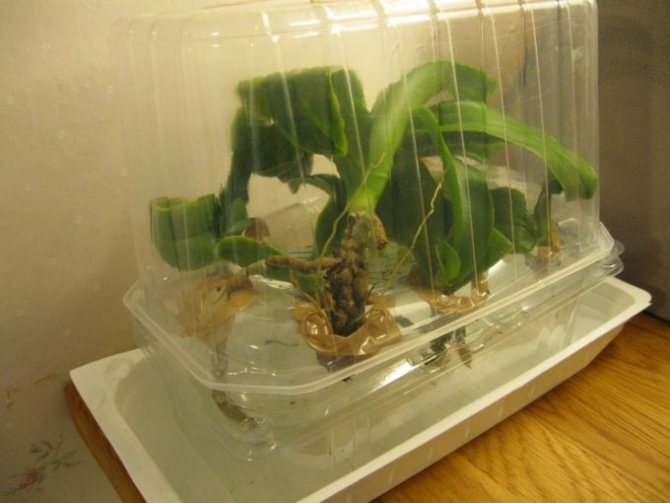
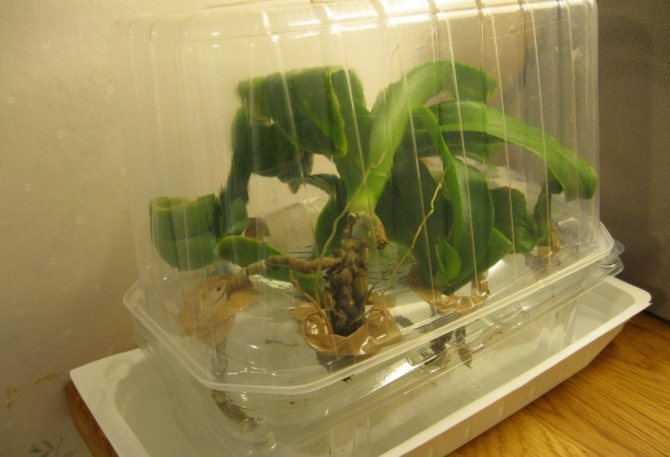
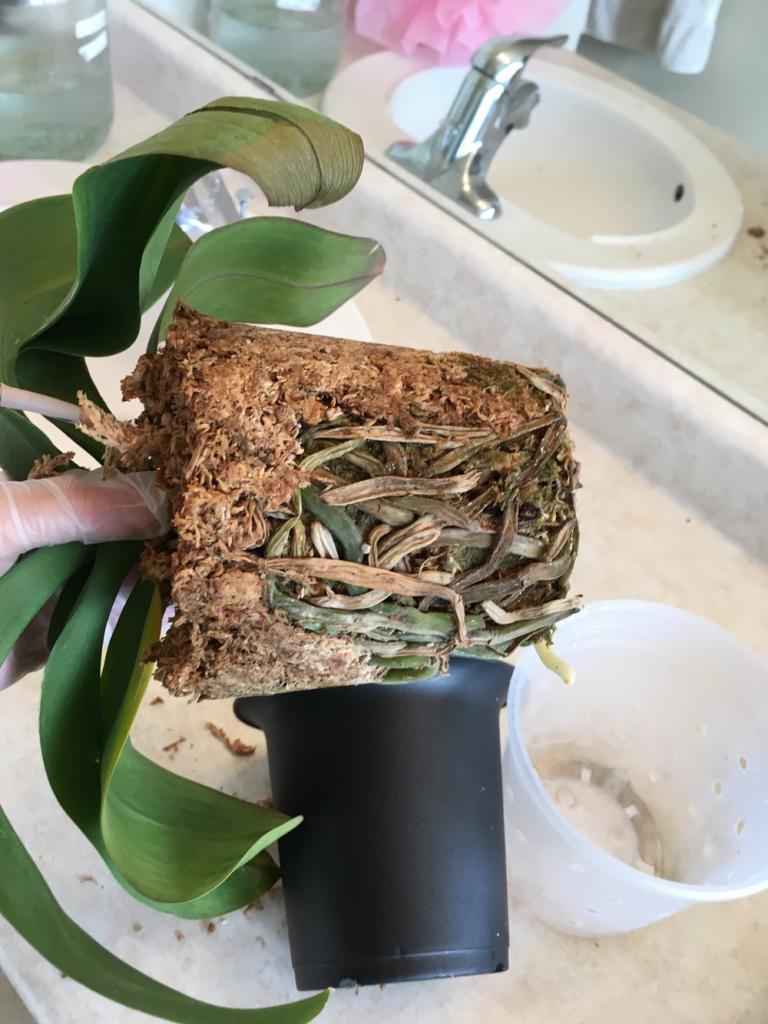
This method is suitable if the plant has no living roots left: they all either dried out or rotted. Sometimes it happens. In this case, resuscitation procedures must be carried out using a greenhouse.
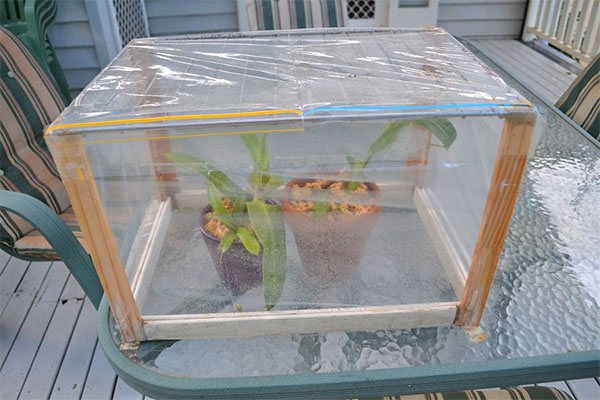


The device can be made simply: a layer of expanded clay drainage should be poured into a spacious container, on which a layer of moist moss should be laid. It is better to purchase a moss layer in a specialized store, as wild moss can be contaminated with harmful microorganisms.
Attention: A five-liter water bottle is often used as a suitable container for greenhouse equipment.
The orchid must be placed on the moss and the container must be covered with a plastic, glass or polyethylene cap. Thanks to such a cap, greenhouse conditions are created inside the container, favorable for the growth of new ones with the root of the orchid.
Important: the moss must be constantly wet, and the lower part of the orchid must be literally immersed in it.
Vermiculite can be used instead of moss. This free-flowing substance contains many useful substances in its composition, so its use in resuscitation of an orchid may even be preferable.
The air temperature inside the greenhouse should be from +22 to +28 degrees. However, do not forget to ventilate the container daily so that the plant does not suffocate in it. The humidity inside should be very high: 70 to 10%. After about 10-14 days, the roots appear. And when they reach 3-4 cm, the flower can be planted in a pot.
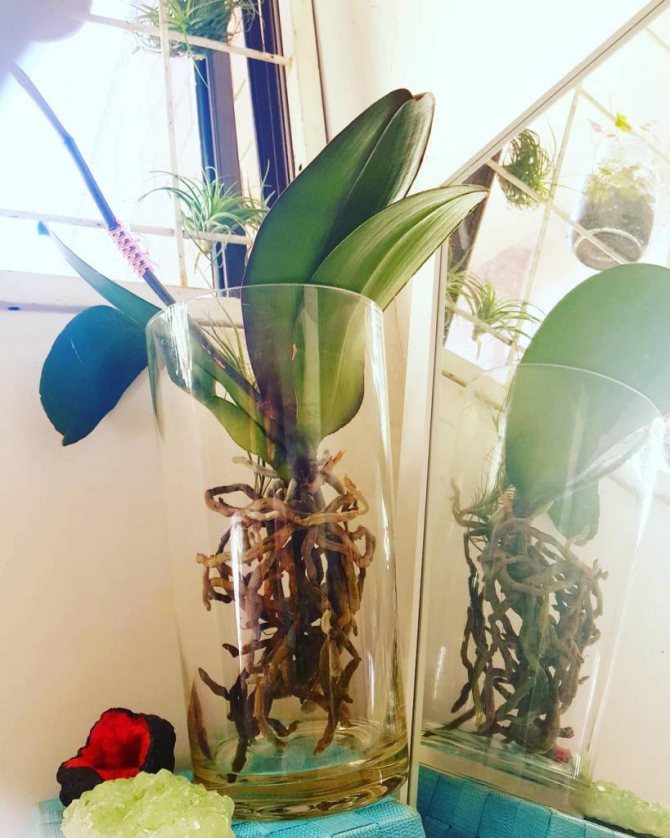
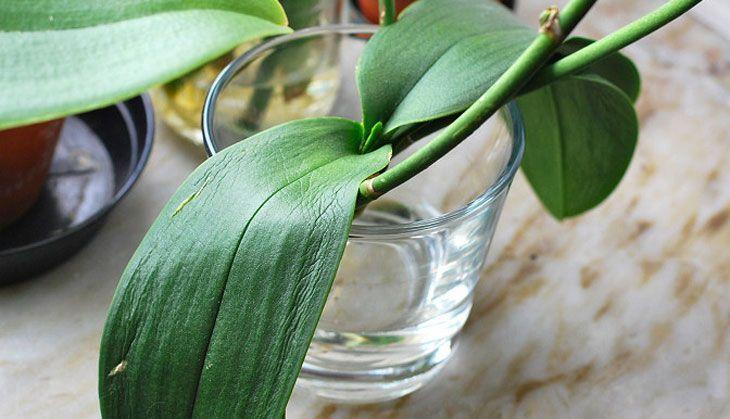
Method 3
This resuscitation involves the use of regular water. The diseased plant is placed in water, but so that only the lowest part of the flower is in contact with the liquid. After half a day, the water is poured out, and after the same time a new one is added.
All these manipulations should take place at a very warm temperature - at least +25 degrees. Roots after "water resuscitation" appear at 6-10 weeks, but sometimes only after six months.
How to disinfect a plant
Actually, in order to save your orchid from poor care, you first need to get rid of the rotten parts of the plant. For this operation you need to have with you:
- Activated carbon.
- Charcoal.
- Fungicides.
Orchid owners often have problems with weeping or rotting roots. This is due to improperly selected soil or excessive watering, plus a low temperature in the room where the flower lives.
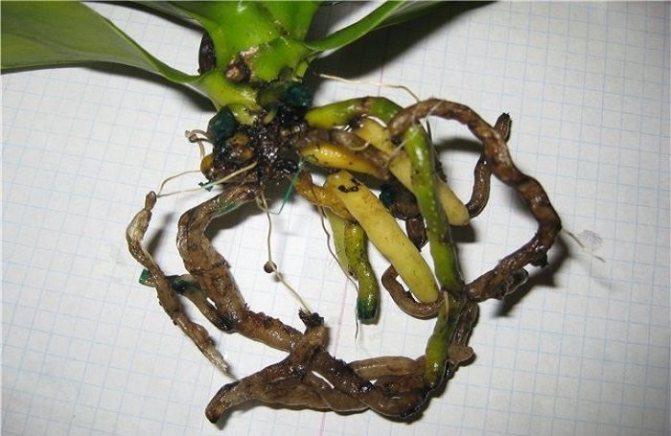
To determine whether the roots are rotten or not, just look at them through a transparent pot. If they are green or grayish in color and their tip grows, then everything is in order with the root system. If they are brown or black, then the roots must be immediately saved from their complete withering away. Therefore, the roots are shortened to healthy green tissue.
Pruning is done with sharp scissors disinfected in alcohol. The cut sites are sprinkled with charcoal or, if it is not there, then activated charcoal purchased in a human pharmacy.
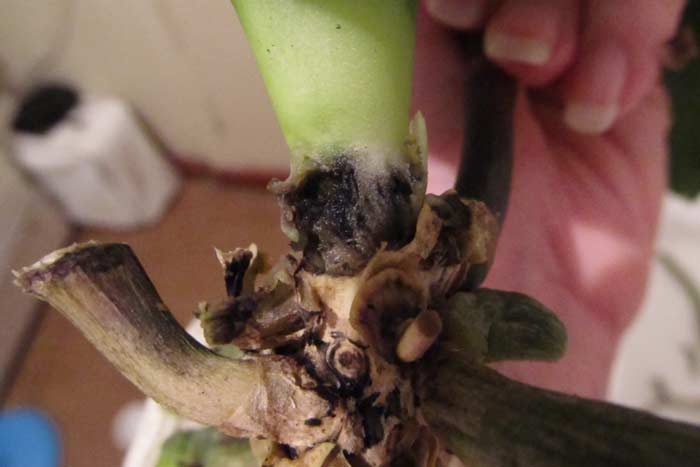
If, after removing the root system of the orchid from the pot, a fungus was noticed in the form of sooty (black) accumulations, then the whole flower is bathed in warm water and the cut points are treated, as written above, and then soaked in any fungicide from the following:
- Tolclofosmethyl.
- Boscalid.
- Pencycuron.
Fungicides are treated twice, so do not rush to plant the flower directly into the ground. Take a week break and re-process. To prevent the roots from drying out too much, they are sprayed with a spray bottle and covered with a cotton cloth.
How to grow roots
If the roots have all rotted away, without a trace, you can get out of the situation if you remove all the processes, and then build them up again. To do this, select the highest quality substrate with a suitable density and structure, place the plant in it and keep it warm, rarely watering, mainly in the morning.
After completing all the rescue work, the plant will not immediately begin to recover. It may bounce back in a month, and sometimes it takes about a year. With the revival of Pholenopsis in the spring or autumn months, the chances of its salvation are much greater than in winter.
How to replace the greenhouse
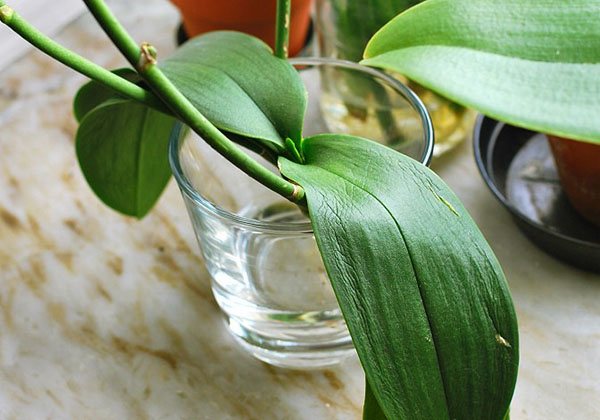


If it is not possible to equip a comfortable greenhouse, you can do without it. With the right approach, the result can be no worse. Instead of a greenhouse, you will have to use a glass vessel: it should be quite deep. Usually a vase of a suitable size is used.
The roots are processed in a standard way, after which the rosette with the surviving roots (or without them) is placed in this vessel. Every day in the morning, a little water is poured into the bottom of the vase: so that only the lower part of the plant comes into contact with the liquid.
The flower is left in water for six hours, then the liquid is drained, and the orchid is left dry until the next morning. The procedure is repeated daily.
To make the roots grow faster, growers are advised to add honey to the water (1 tsp per liter). You can also make your water healthier by adding:
- a weak solution of complex fertilizers;
- iron;
- sugar syrup;
- root stimulant.
All supplements should not be used every day but periodically. This is especially true for fertilizers.
Step-by-step resuscitation: preparation
So, your pet needs reanimation. Considering that the concept of "resuscitation" is combined exclusively with the degree of "urgent", then the procedure should be started immediately. Resuscitation of an orchid without roots occurs in several stages:
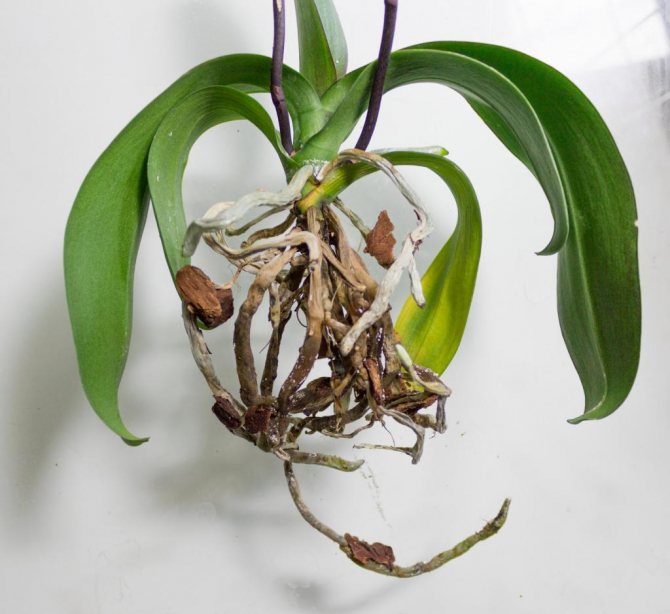


- remove the flower from the pot;
- to inspect the roots, pre-rinse them from the soil;
- spread the roots on a horizontal dry surface and dry them for at least 2 hours;
- inspect the condition of the roots;
- remove damaged roots, leaving only dense green;
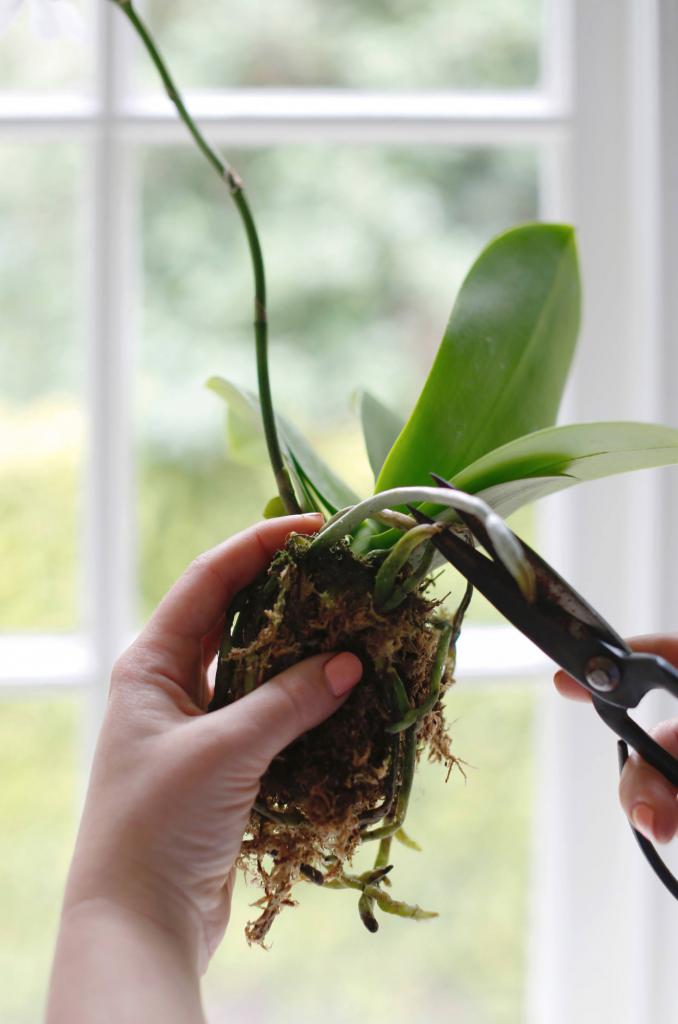


- estimate the percentage of damage to the root system: in case of losses from 75 to 90%, we will urgently revive the orchid.
Use of growth stimulants
In order for the roots of the orchid to grow faster, experienced flower growers use growth stimulants when resuscitating a plant. These drugs not only activate root growth, but also increase the plant's immunity, which is also important.
Epin and Zircon
The popular Epin is most often used as a suitable stimulant, and many people also like Zircon. Epin is diluted in the following proportion: 1 drop of the drug per liter of water. The flower is soaked in the resulting solution for 20 minutes if the root damage is insignificant. If there are almost no roots left, the stimulation time should be increased to 1.5-2 hours.
succinic acid


In addition to Epin and Zircon, succinic acid is also very popular.The tool helps well to activate root formation, regrowth of green mass. The proportion in this case is as follows: a tablet of the drug per liter of water. Apply the agent for spraying plants and watering, but not more than once a month.
Kornevin
The tool is well known to flower growers. It is usually used when it is necessary to reanimate the phalaenopsis orchid. Kornevin is diluted according to the instructions in water, after which the lower part of the plant is placed in the solution. The drug has a wonderful effect on the immunity of the flower, activates its vitality, and promotes early recovery.
Fitosporin
The drug is indispensable when it is necessary to reanimate the orchid after fungal diseases. In this case, the plant is soaked in a solution of the drug for 15-20 minutes, after which it is planted in a vase, greenhouse or pot.
Greenhouse and wet moss
A greenhouse is easy to build from a regular plastic bottle. At the bottom you need to put sphagnum and moisten it in sufficient quantity with water. The orchid is fixed in the bottle so that it does not touch the moss and is above it at a distance of about 4-5 cm. Such a greenhouse should be placed in a warm, with diffused light, place.
It is very good that there is no need to constantly check the moss for moisture - the necessary microclimate will always be maintained in the greenhouse. Young shoots of roots will appear in about a month. Only when the roots are about 5 cm long can the plant be transplanted into the substrate.
With succinic acid
Succinic acid is the second name for dibasic carboxylic acid. It is sold in drugstores in pill form and can be used to preserve the leaves during root growth in orchids. The acid is diluted in a ratio of 1 tablet to 200 g of water and the leaves are wiped with this mixture once a day. You can also soak the roots of the plant in solution, but then 1 tablet is taken for 1 liter of water.
How to care after resuscitation procedures


Consider the main nuances of caring for an orchid after the flower has been revived.
Top dressing
Be careful with this procedure after resuscitation. While the orchid has not yet fully recovered, it should not be fed: the plant may react poorly to additional nutrition.
After a month has passed after resuscitation, you can start feeding, but carefully, in moderation. An excess of nutrients leads to darkening of the roots of the plant, tarnishing of its leaves, and wilting of flowers. A banal root burn with a large amount of fertilizers provokes these negative changes.
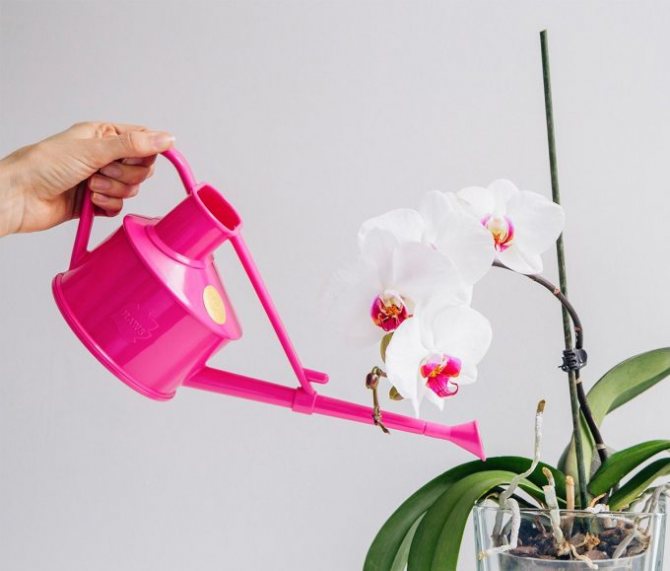
Watering
The procedure should also be carried out with caution. It is recommended to use the method of spraying or pouring water into the pan.
Protection against parasites and fungi
When only the orchid was brought into the house from the store, it is necessary to immediately check for pests on the plant. Finding out about the presence of parasites is simple: you need to put a pot with a plant in water. If there are pests, they will begin to crawl up the flower from the water. If insects are found, you need to change the soil in the pot, washing and treating the roots of the orchid with a fungicide.
To prevent the appearance and spread of the fungus, you should be careful about watering the plant, avoiding waterlogging of the soil. A regular examination of the roots will also help in order to have time to stop the onset of the disease at an early stage.
Why do roots rot
The main reason - excessive watering, insufficient drainage (stagnant water). The orchid becomes ill with the fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia. It appears as brown spots on the roots, the leaves turn yellow and wrinkle.
Important! The plant is watered when the soil is completely dry. You can insert a thin wooden stick into the substrate. When it is taken out of the ground and it is dry, it is time to moisturize the orchid. Pay attention to the quality of the water: they use filtered or thawed water, since tap water contains impurities harmful to the flower.
Algae can form in the root system. The reasons are an excess of mineral fertilizers or lighting. This "neighborhood" leads to a lack of oxygen for the orchid, the formation of toxic substances. The roots will darken, begin to rot, the leaves will wither.
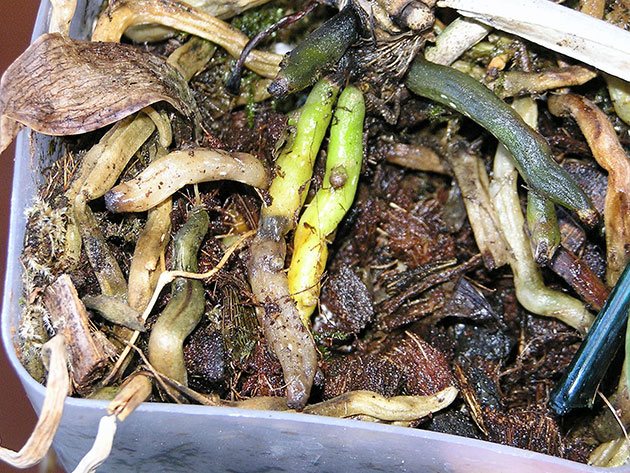


Rotting can be a consequence of diseases:
- Fusarium - rot of the trunk, orchid roots, yellowing, wilting and dropping of leaves, buds, flowers. The disease is caused by Fusarium molds when non-sterile tools or a work surface have been used. Leaves become thinner, turn yellow and wrinkle. The cross section of the rhizome becomes purple in color. The orchid may die.
- Late blight (crown or pith rot) - appears as wet brown spots on the entire surface of the plant. It affects the vascular system of the trunk, bulb, etc.
- Black rot caused by late blight. It spreads quickly. The leaves soften and turn black, the roots become black or reddish, the growth points die off. The orchid must be isolated from other plants.
- Soft bacterial rot manifests itself as wet brown spots throughout the plant: on aerial roots, bulbs, trunk and leaves.
The orchid must be transplanted every 2-3 years, changing the pot to a larger one, and filling in a fresh substrate. The soil becomes compacted over time, which causes rotting of the roots due to lack of oxygen, drainage. In addition, the orchid is not getting enough nutrients.
Overfeeding, hypothermia, too large or small pot cause root rot. When there is a lot of fertilizer in the soil, they get burned. Another important rule: you should only feed the orchid after watering. In case of frostbite, damaged leaves are also removed.
Care should be taken when transplanting. The delicate roots are easily damaged, which can cause infection and rot.
Orchid pests are click beetles. Their larvae, deposited in the soil, eat the roots of the plant. Leaves, buds become lethargic due to lack of water. Revive an orchid can be done like this. The roots are washed in warm water. Fresh soil is placed in a new, disinfected flowerpot and the orchid is transplanted. Watering is stopped for 10 days, the plant is not fed and no chemicals are added. The flower is being watched. If he began to build up the root system, the leaves become elastic, - Phalaenopsis is saved.
Soil composition and pests
In many ways, the health and well-being of an orchid depends on the composition of the soil in which it grows. No matter how initially good and loose substrate is in the pot, over time and with watering it inevitably becomes denser, loses its permeable ability.
Dense soil is a serious obstacle to normal ventilation of the orchid root system. To avoid such a problem, it is necessary to regularly change the substrate in the plant pot. Take care that the soil included pine bark - this is the best baking powder for a tropical flower.
Pests
The most dangerous pest for an orchid, which can even lead to the death of a plant, is the clicker beetle. The insect feeds on the roots of the flower, gradually suppressing the plant's immunity, leading to its wilting and drying.
If the click beetle is wound up, you need to take the following actions:
- get the orchid out of the pot and rinse its roots thoroughly;
- remove sluggish, damaged roots;
- replace the substrate in the container, it is advisable to replace the container itself;
- transplant the orchid into new soil.
Water the plant after transplanting in 10-12 days, not earlier.
Causes of plant death
Cases when an orchid loses its root system are quite frequent. It is important not to miss this moment in order to start building it up in time. The main causes of root death in orchids include:
- Transplant carried out in violation of the rules.
- Excessive watering of the plant.
- Insufficient watering and, as a result, strong overdrying of the substrate.
- Watering with very cold or hard water.
- Mechanical injury, such as falling a flower pot.
Improper watering and its consequences
When an orchid is watered too hard, it can lead to decay of plant roots, wilting of leaves, and other unpleasant problems, including the development of fungal pathology.
To avoid such problems, the soil should be moistened only when it is noticeably dry. If you water the orchid without waiting for the soil to dry out, this will inevitably lead to plant disease. And it will be difficult to rehabilitate the flower.
The time that elapses between waterings is difficult to pinpoint. It depends on many factors: external conditions, temperature, humidity level, lighting, soil composition, even the type of flower.
The size of the pot also matters: in a large container, the soil will dry out more slowly. Therefore, it is recommended to initially plant a tropical flower in a tall and rather narrow container.
It is also important not to allow the roots to dry out, since this fact will undoubtedly negatively affect the health of the orchid. And it can even lead to her complete death.
Freezing and sunburn


A delicate tropical orchid may well be overcooled - in our climate, this is not surprising. If only leaves and peduncles were frozen, then, without any doubt, the plant will survive and recover, although not quickly.
If the roots have suffered, resuscitation will be more protracted, but, however, in most cases, it will also be successful. However, if the growth point is caught by frost, and the latter has become watery, translucent, unfortunately, the orchid cannot be restored.
In case of sunburn, the affected leaves and flowers should be cut off, since it is no longer possible to restore their beauty. Then, be sure to move the orchid to a shaded area.
Leaf problems
The plant often suffers from foliar problems. Orchid greens can:
- turn yellow, and completely;
- wither, sink;
- "Decorate" with spots and holes, other suspicious artifacts.
The likely cause of foliar ailments is overheating of the plant. An orchid can suffer from heat only when it is located near the radiators, but also when it is in direct sunlight.
The first step is to eliminate the likely cause of the problem and wait a few hours. During the waiting period, do not water the plant, only spraying is permissible not earlier than after three hours.
Quickly, however, after overheating, it is unlikely that it will be possible to restore the orchid. With the most favorable development of events, the first positive changes should be expected no earlier than in 4 days.
Natural aging
Inexperienced growers often mistake the natural dying off of orchid leaves for a plant disease. You should know that the leaves tend to grow old and sooner or later, but wither, die off and give place to young growth.
In the case of this completely natural process, the foliage will wilt slightly, and only in the lower part of the stem. You should not try to speed up the process by cutting off the withering leaves - such an intervention will negatively affect the well-being of the orchid. The leaves should die off on their own.
Recovery methods
Further actions depend on which part of the plant has remained intact.
| Plant condition | Recovery prospects | Resuscitation methods | |
| Saved parts | Lost (perished) parts | ||
| The lower part of the stem (stump) with a root collar and at least 5% rhizome | Leaves, growth point | From dormant buds on the surface of the stem, lateral shoots are formed (children) | Plant in fresh soil and take care of it as usual, reducing watering and eliminating spraying, or in a mini-greenhouse |
| Roots (at least 2-3 3 cm long roots), rhizome or stem with a growing point | Leaves (partially or completely) | After growing the root system, new leaves are formed from the growing point. | Plant in fresh soil and take care of it as usual, using spraying of the substrate surface instead of watering |
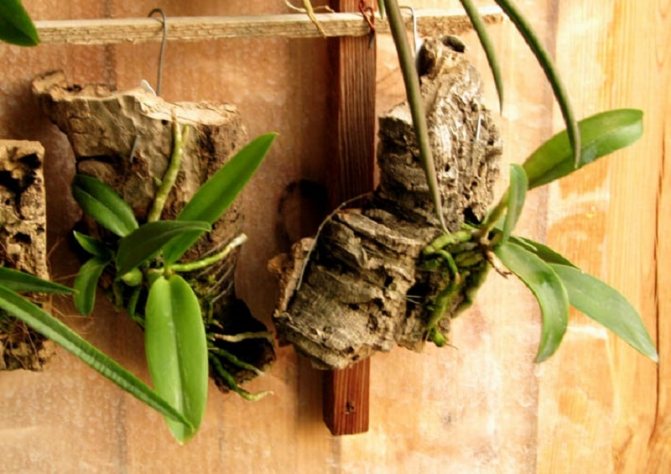
| At least one leaf with part of the stem | Roots (partially or completely) | New roots are formed from the lower part of the stem, after which the growth of the vegetative part will begin | Place for rooting in a closed system, in a greenhouse on a damp substrate, secure in a vessel above water |
| Peduncle | Growth point, leaves, roots | Children are formed from the sleeping buds of the peduncle | Place the cut peduncle in a container of water |
| Divide the peduncle into 2-3 cm segments with a dormant bud and place on the surface of a wet substrate (sphagnum moss) | |||
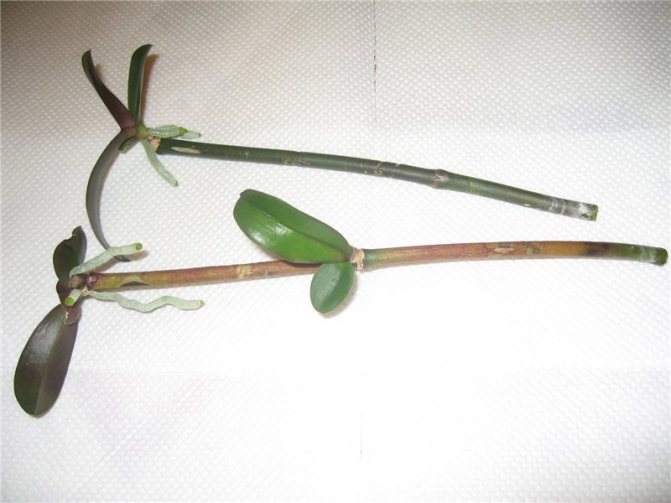


On a faded peduncle, you can get a full-fledged baby.
Important! An orchid can survive by losing its entire root system and leaves, but without a basic, vital organ, it is doomed. In monopodial orchids, such an organ is the stem, and in sympodial orchids, the rhizome. The stem of many orchid species is short, hidden among densely-sitting leaves. The rhizome is also often almost invisible due to closely growing leaves and bulbs, or, conversely, can be thick and long. But regardless of size, it is this part of the plant that is considered its heart, without which all resuscitation measures are meaningless.
Drying of peduncles


A similar problem happens with an orchid if:
- it is not watered enough;
- overfeed.
Depending on the cause, the negative factor that caused, take appropriate measures:
- make watering more abundant and frequent;
- minimize feeding.
In the latter case, in order to save the orchid, a transplant may be necessary: if too much fertilizer has been applied.
General recommendations
Do not throw your orchid away, even if it is completely rootless. And in this case, there is an opportunity to reanimate the plant - you just need to make a little effort and be patient. In general, this flower is very life-loving, and if given a chance for salvation, it will not delay this opportunity to seize it. Watch a video on simple orchid resuscitation measures.
Before choosing the desired method, first examine the plant and realistically assess the condition of its leaves and roots. If about 60% of the roots of an orchid have rotted, it is usually possible to return it to its previous healthy state in a month. But if the roots are completely lost, resuscitation is sometimes delayed for a year, or even longer.
So, we learned how to reanimate an orchid at home. There are enough ways: thanks to them, you can restore the plant, even when not a single root has survived. Closely monitor the condition of your pet and take action as soon as the orchid looks worse.
How to reanimate an orchid without roots?
Flower lovers who grow orchids know that the plant can live in 2 modes. The most interesting and useful for the resuscitation of the orchid is the one that leads to the release and exchange of carbon dioxide. It is also called C3C4. With him, the plant begins to develop at a rapid pace. For a month, the orchid grows a few centimeters and throws out a couple of leaves. This mode is indispensable when you are thinking about how to save an orchid without roots.
In order for the plant to pass into it, it is necessary to create the desired humidity and maintain the temperature at 25-28 °. Therefore, after resuscitation, it is worth placing a flower in a mini-greenhouse. You can buy it at flower shops or make it yourself. Do not throw out the transparent boxes from large cakes - they may be needed. You can simply define the plant in a round pot and cover it with this package. Another option for reanimating an orchid is to place a box with an orchid under a sheet of glass.
If you decide to keep a flower in a greenhouse, then it is allowed to plant it close to a special type of moss - sphagnum. It is sold in the same place where aquariums are sold. Drainage is poured at the bottom of the box, wet moss is placed, and an orchid is placed on it. Make sure that the sphagnum is not wet. Otherwise, the roots will begin to die again. It is also worth ventilating our greenhouse from time to time.
On a note! The average time it takes to resuscitate an orchid using this method is from 1 to 12 months. It all depends on its initial state, but in the end you can achieve the same brilliant results: