Disinfection of a polycarbonate greenhouse in autumn is a necessary preventive safety measure that helps to eliminate infections and harmful insects, which is a guarantee of a good harvest in the future. Correct disinfection is carried out in several stages.
In the article, we will tell you in detail why you need to treat the structure and soil, how to properly clean, wash the structure, and how to disinfect the greenhouse in the fall. Let's review preparations for disinfection against diseases, insects, infections.
Decontamination of the greenhouse in the fall contributes to a good harvest in the next season.
What pests and diseases can winter in a greenhouse
Not all greenhouse dwellers harm plants. Soil is a living organism, it contains billions of bacteria that work incessantly to process organic matter into chemical compounds that are consumed by plants for growth and development. In addition, worms and insects inhabit the soil, and only some of them are dangerous to plants. Do you need to kill everyone clean using potent chemicals?

Recommendations for disinfecting soil in a greenhouse
First you need to figure out which pests and pathogens can survive the winter in a greenhouse and what conditions contribute to this.
Aphid - a small insect that feeds on plant sap. Aphid colonies are able to grow rapidly in a greenhouse, which leads to damage to young shoots and a decrease in yield. In addition, aphids secrete a sweetish sticky liquid, creating conditions for the development of fungal diseases.


Aphid
Aphids overwinter in greenhouses and greenhouses in the egg stage, hiding in weeds and uncleared plant debris. In the spring, larvae emerge from the eggs, which soon turn into an adult insect that can harm young plants. In addition, ants hide aphids in their nests - they use this insect as a cash cow, feeding on sweet secretions, and even carry it around the garden in search of new "pastures".
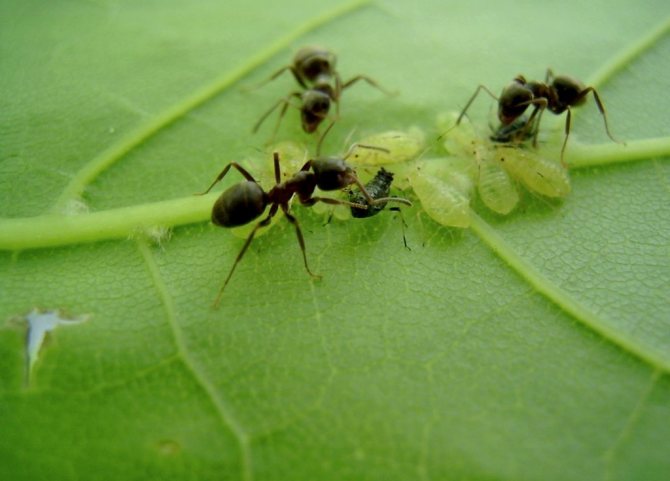


Ants carry aphids
To lime aphids in a greenhouse, it is necessary to carry out a thorough pre-winter cleaning of weeds, dead shoots and tops of plants. Experienced gardeners also recommend driving ants out of the greenhouse and destroying all anthills built in it.
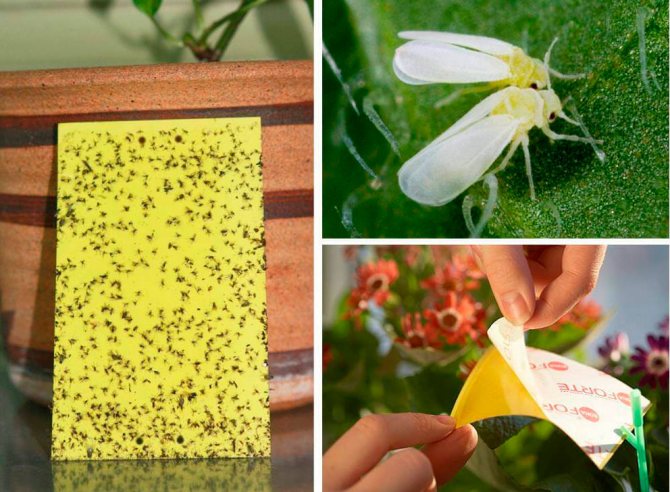
Whitefly - a flying sucking insect, similar to a moth. Whitefly colonies settle on plants and suck sap out of them. The plant gradually withers and dies, the yield is significantly reduced. In the greenhouse, the whitefly is able to overwinter, provided that the temperature does not drop below -5 ° C, in severe frosts, the pests freeze out.
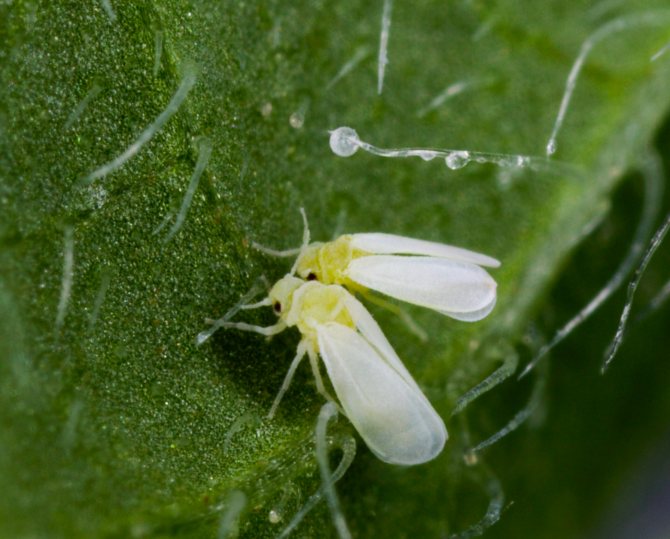


Whitefly
In the middle lane, to fight the whitefly, it is enough to open the windows in the greenhouse for the winter so that the temperature equals the street temperature. In more southern regions with mild winters, the greenhouse and the topsoil should be treated with one of the systemic preparations, which will be discussed below.
Spider mite - a fairly serious pest that can destroy all vegetation in the greenhouse in a matter of days. It can be identified by small dots on the back of leaves and a fine, disordered cobweb on plants.The spider mite hibernates in the cracks of the frame and base of the greenhouse and in wood debris. Natural and chemical preparations help against spider mites, but they should be used only after thorough cleaning.
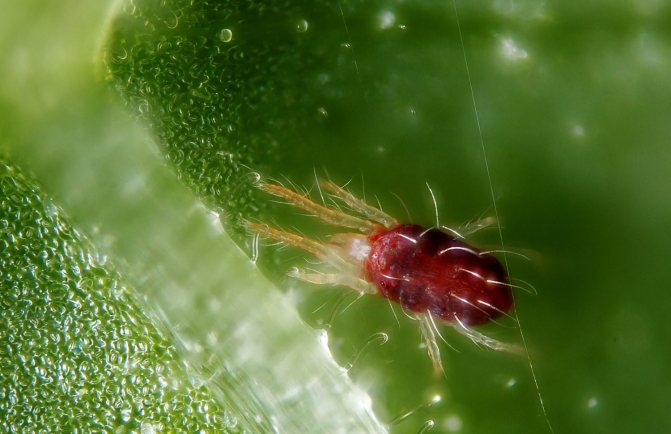


Spider mite
Slugs gardeners are also annoyed in the greenhouse. The fight against them is also complicated by the fact that they are active only in the dark, so it is sometimes difficult to understand who is eating shoots and fruits. The slug larvae hibernate in the ground, in the upper soil layer. You can kill them with boiling water or chemicals.
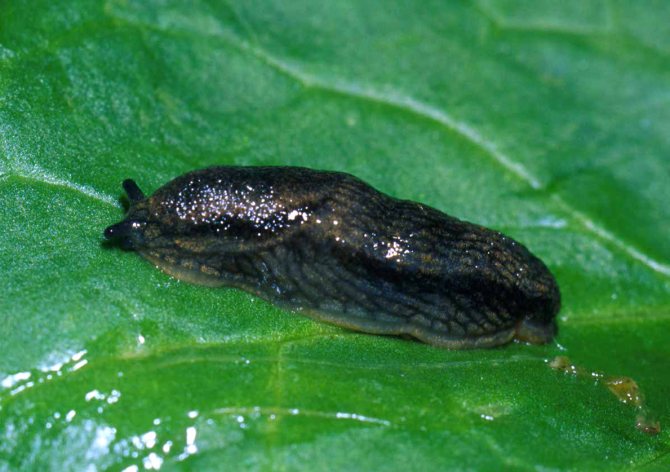


Slug
Nematode - small parasitic worms that live in the stems, roots or leaves of various vegetable crops. Nematoda is a real scourge of greenhouses, it is extremely difficult to remove it. Nematodes overwinter in the ground, at a depth of 20 cm, or in galls - thickenings on the roots of plants. Stem and leaf nematodes can also overwinter in plant debris.
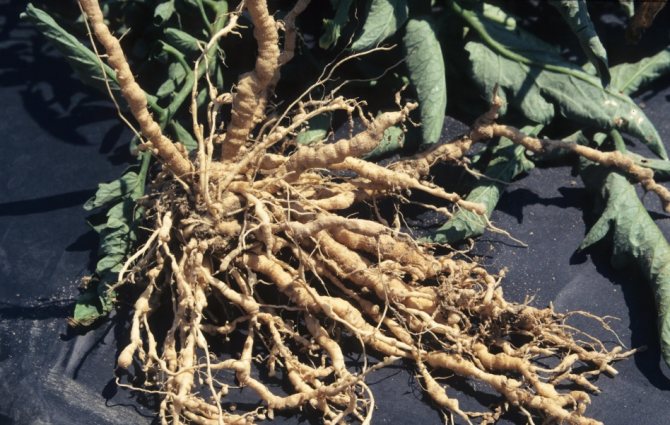


Nematoda - damaged roots
For the destruction of nematodes in the garden, crop rotation is most effective. In this case, plants of the same species are returned to their original place no earlier than after 3-4 years. However, in a capital greenhouse, this method is unacceptable. Replacing the soil is also of little help, since it is quite difficult to remove the soil to a depth of 20 cm.
To combat the nematode in industrial conditions, powerful chemical preparations are used - systemic nematicides. They are extremely toxic to humans and kill all useful microflora in the soil, so they are used with caution in a home greenhouse.
Warming up the soil up to 50-60 ° C using hot water, as well as the introduction of organic fertilizers and sugar can be beneficial. At the same time, saprophytes actively begin to multiply in the soil, attracting natural enemies of nematodes.
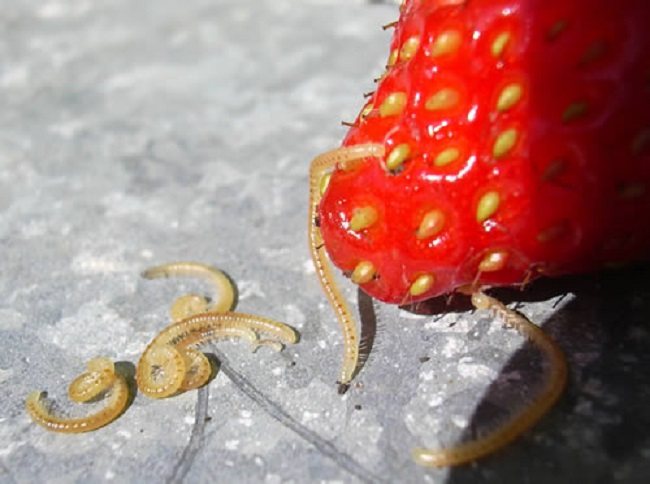


Strawberry nematode: pest photo
Another effective method is planting plants that oppress and scare away the nematode. These include marigolds and watercress. You can sow these cold-resistant plants immediately after harvesting vegetable crops, in two to three months they will have time to thoroughly clean the soil.
Fungal diseases - late blight, cladosporium, fusarium, powdery mildew and various rot - appear in the greenhouse in unfavorable conditions and quickly infect plants. It is difficult to cope with them, and sometimes it is completely impossible - most of the crop perishes.
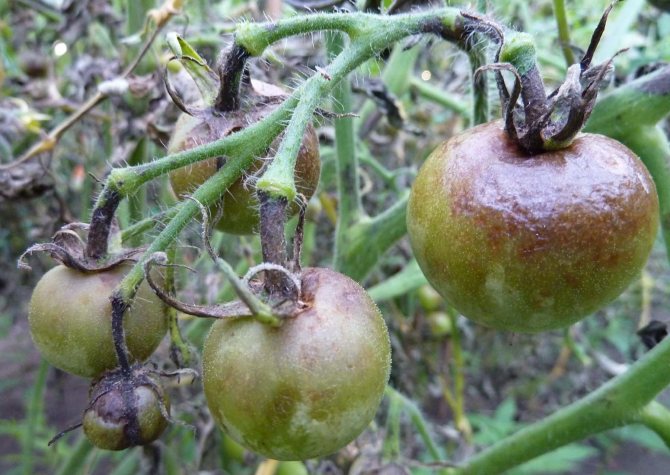


Phytophthora - a fungal disease of tomatoes
Fungi have great resistance to external conditions and winter well in closed ground, settling on the soil, the walls of the greenhouse and garden tools. To combat fungi, fungicides and copper-based preparations are used.
Viral and bacterial diseases can be introduced into the greenhouse with soil and planting material, they are also carried by sucking insects. Therefore, the prevention of viral and bacterial diseases in the greenhouse is reduced to cleaning, removal of harmful insects and preventive treatment of soil and structures with antibacterial drugs.
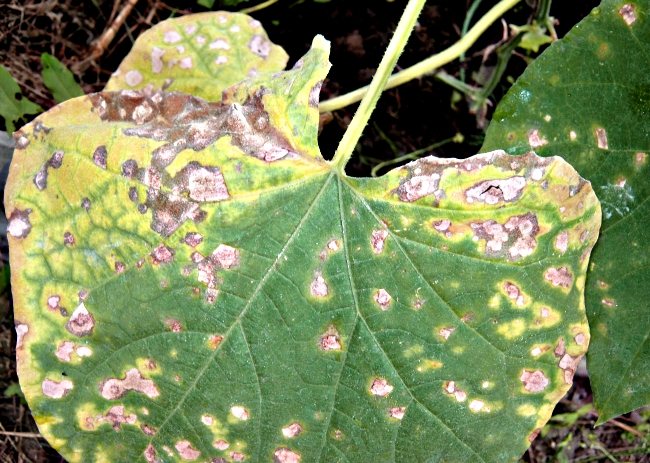


Bacteriosis - a disease of cucumber
Soil preparation
The greenhouse creates ideal conditions not only for the growth of plants (including weeds), but also for various pests that can ruin the standing crop if not dealt with. The processing of the greenhouse in the fall from pests and diseases should be complex. The use of chemistry - various insecticides during the growing season is not a very good idea. Chemicals accumulated in plants end up in our bodies.
Therefore, special attention should be paid to disinfection and other soil cultivation in the greenhouse in the fall.
Soil replacement
Quite a laborious and expensive process, but after it the number of pests decreases by several orders of magnitude. Such a procedure as preparing the soil in a greenhouse in the fall, with a complete replacement of the fertile layer, is recommended at least once every three years. The soil is removed to a depth of 7-10 cm.Then, in its place, peat, humus (manure) are introduced, sand and ash proportions are very different depending on the presence of one or another ingredient, but rarely exceed 1 bucket per 1 m2 of soil. The cultivation of the land in the greenhouse in the fall may include fluffing, for heavy and oily soils, using sawdust. However, with this method, you must be careful and, if possible, do not use sawdust of coniferous wood (spruce, pine, larch) and wood species with a large amount of tannins (oak, walnut).
The resulting mixture is dug up. Distribute evenly over the planting sites and cover on top with a thick layer of straw or fallen leaves. After the snow falls in winter, it is necessary to independently throw some of it into the greenhouse with a shovel (a layer of 15-20 cm) in order to prevent deep freezing of the soil and provide the earth with the necessary moisture in the spring. Some gardeners additionally water the enriched earthen mixture with a weak solution of potassium permanganate before adding fertilizers.


A thick layer of fallen leaves will help keep warm
Soil infected with pests and diseases can not be thrown away, but treated. How to treat the soil in a greenhouse in the fall in order to disinfect it qualitatively without resorting to strong chemicals. For this, a pile is formed with an area of 1-2 m2 and with a layer thickness of 20 cm.When it is arranged, each layer is generously sprinkled with lime at the rate of 250 g per 1 m2. It remains in this state the whole next year, having frozen out over the winter, the pile will need to be re-dug up next fall and used after the second winter.
Fertilizing the soil
How to fertilize the soil in the greenhouse in the fall depends not only on the type of soil, but also what crops are planned to be planted in the spring. To achieve the highest yield, not only special means are used, but also special methods of processing perennial plants:
- Strawberry. After the last harvest, at the end of August, all the greens are mowed so that the upper buds remain intact. The bed is watered abundantly and the soil is loosened. Potash and superphosphate fertilizers are introduced in the proportions recommended by the manufacturer. All this is sprinkled with a small layer of fertile soil so that new shoots do not dry out. Before the onset of cold weather, no later than October, the roots of strawberries are covered with peat. In winter, be sure to pretend to be a thick layer of snow to prevent freezing.
- Tomatoes. One of the most common greenhouse crops. They are very demanding on the quality of the soil and the composition of the dressings. For a tomato, soil preparation in a greenhouse in the fall consists in the introduction of organic, chemical or combined dressings, which must contain:
- Manganese - promotes faster ripening of fruits;
- Copper, boron - stimulate flowering and abundant fruiting;
- Potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, nitrogen - contribute to the rapid growth of the plant.
- Cucumbers. The most common "inhabitant" of greenhouses. There are many varieties available for greenhouse cultivation. However, the processing of a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall for planting cucumbers in it has its own specifics. First of all, you need to check the acidity of the soil. With an acidity of more than 6.5-7 pH in autumn, it is necessary to liming the soil. Also in the fall, the soil is fertilized with the following specialized mixture:
- Potassium salt - 10-25 gr.;
- Ammonium sulfate - 10-25gr.;
- Ammonium nitrate up to 25 gr.
Important! There is a very simple way to check the acidity of the soil at home. You need to pour a handful of dry earth with simple 9% table vinegar
If a reaction starts with the release of gas, then there is enough lime in the soil, and it is neutral.
Determination of soil acidity with 9% vinegar, reaction to neutral soil
Types of processing and disinfection of the greenhouse
Autumn processing of the greenhouse is carried out after harvesting cultivated crops before the onset of frost.
Processing includes:
- cleaning of plant residues, weeds;
- removal of garden tools, supports and garters;
- rinsing the frame and polycarbonate;
- soil preparation, fertilization;
- sowing biologically active plants;
- treatment with fungicides and systemic drugs;
- disinfection with smoke bombs;
- freezing.
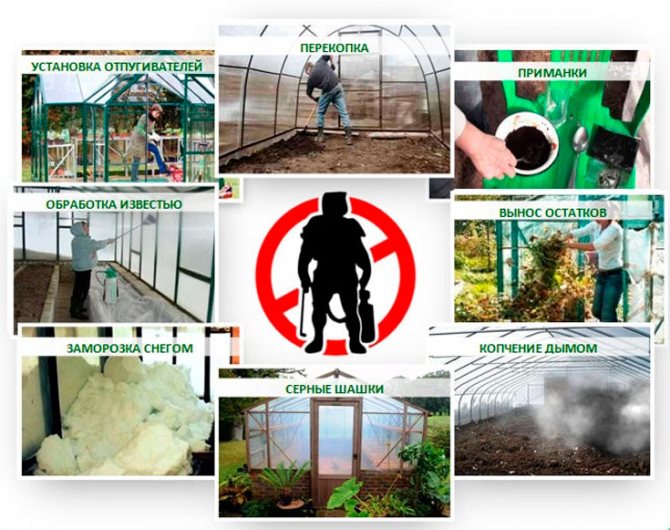
Processing a single greenhouse does not have to include all of the above stages - the list of works depends on the condition of the soil and the presence of pests and pathogens in the greenhouse. You can use the diagram to determine what treatment your greenhouse needs.
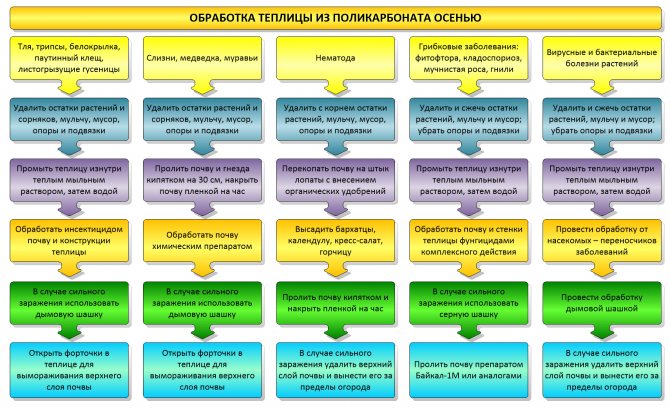

Scheme of disinfection of a polycarbonate greenhouse in autumn
Main steps
If you neglect the disinfection of a polycarbonate greenhouse, then harmful bacteria will again infect the planted crops in the new season. It is known that many pathogenic pathogens do not lose their activity for a long time. This applies to phytophthora spores, which kill tomatoes. Autumn processing of a polycarbonate greenhouse can effectively eliminate whiteflies, aphids, spider mites, nematodes and other parasites.


It is recommended that all work be performed in the following order:
- collect and remove all plant residues from the greenhouse;
- wash, clean the walls and roof of the greenhouse;
- to carry out processing and preparation of soil;
- disinfect;
- if necessary, make minor repairs to the structure.
Advice!
The best time to carry out disinfection work is when the air temperature is 10-15 ° C plus. It is necessary to take out all the pegs and garters from the greenhouse, as well as tools, racks. If polycarbonate is removed in the structure, then it is better to remove the coating.
Ready-made chemicals for greenhouse treatment
The list of chemicals is extremely wide, and most of them have a wide spectrum of action. For the treatment of the greenhouse, it is better to choose agents with a targeted action that do not disturb the balance of microorganisms in the soil. Descriptions of drugs are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Description of insecticides and fungicides for greenhouse treatment.
| Name of the drug | Application |
| Fufanon | The drug is used against aphids, whiteflies, thrips, spider mites. The drug is diluted at a dosage of 5 ml per 5 liters of water and the insect wintering sites (cracks in the frame, ridge fences) are sprayed, and the topsoil is shed. |
| Storm | Effective against slugs and snails. The drug is scattered over the soil surface at a dosage of 15 g per 5m2 immediately after harvesting the plants. Slugs after contact with him become dehydrated, lose mucus and die. After the onset of cold weather, treatment is useless. |
| Muracid | A preparation for the destruction of garden ants. A 1 ml ampoule is diluted in 10 liters of water and the nests are watered at a dosage of 1 liter per nest. As a result, the ants are trapped in the nest and die when trying to get out. Ant trails are also treated with a solution. |
| Thunder | The drug is effective against bear and ants. If bear burrows with a diameter of up to 2 cm are found on the soil surface, a slightly moistened preparation is laid in them (1 tsp per hole). To kill ants, the drug is sprinkled on the anthill. |
| Marshal | Effective against nematodes, aphids, thrips, spider mites. Dilute an ampoule of 7 ml in 7-10 liters of water and spill the soil over 10 m2. You cannot carry out more than one treatment per season! The drug is highly toxic to humans and animals! |
| Fitosporin | Biological product for the treatment and prevention of fungal diseases. Dilute 5 g of powder per 10 liters of water and spray the topsoil, walls and ceiling of the greenhouse. The treatment is carried out at a temperature not lower than + 10 ° C; at lower temperatures, the active substances of the drug do not work. |
| Copper sulfate | A preparation for complex treatment of greenhouses against diseases and pests. Dilute 1 tbsp. l. copper sulfate in 10 liters of water, spray the walls and water the soil until it is moistened. |
Note! When processing, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the dosage of the selected drug indicated on the package, and also follow all safety measures!
Preparing the greenhouse for winter: advice from summer residents
The experience of summer residents using similar structures on their plots is useful:
- Experienced owners of polycarbonate greenhouses, speaking about how to care for them in the fall, recommend using for washing the polycarbonate coating and frame elements, in addition to a solution of laundry soap, dishwashing detergent, soda or formalin in a ratio of 0.25 g per bucket of water.
- They also believe that it is not necessary to disassemble the polycarbonate structure for the winter. But in order to avoid its deformation during heavy snowfalls, it is recommended to strengthen the greenhouse roof with wooden supports in the shape of the letter "T".
- When asked whether it is necessary to bring snow into the greenhouse in winter, the answers are different. The absence of snow allows the soil to freeze as deep as possible in winter, which destroys the pests hiding in the ground. But, on the other hand, snow in a greenhouse turns into melt water in spring, which is an excellent stimulator of plant growth.
- The greenhouse frame should be cleaned of dirt and, if necessary, painted regularly to prevent the appearance of lichens and fungi on it, which are very difficult to get rid of later.


Autumn processing of polycarbonate greenhouses is troublesome and quite time consuming. But the friendly growth of greenhouse plants next spring, in the complete absence of diseases and pests on them, fully pays for the effort expended.
Polycarbonate greenhouse processing technology
Before starting processing, you need to assess the need for all stages. If no pests and signs of disease were noticed in the greenhouse over the summer, it will be enough to clean and process with gentle biological products. They do not disturb the balance of microorganisms in the soil and do not have a harmful effect on its composition.
You only need to use chemistry if plant diseases or a large number of pests have been noted in your greenhouse or neighbors over the summer. In this case, one should not exceed the consumption rate of drugs; it is better to carry out one more treatment in the spring.
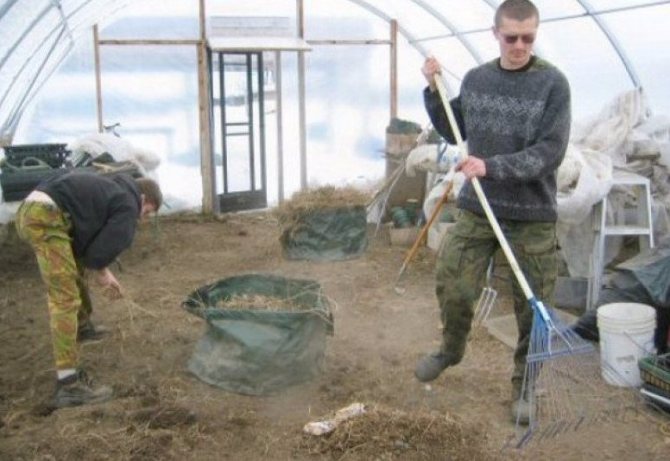
Cleaning
Processing must begin with the removal of all plant residues, weeds, mulch - various pests can hide and winter in them. The foliage affected by diseases and pests is burned. Healthy plants and weeds can be composted with organic fertilizers or spilled with urea solution. This technique promotes its rapid decomposition and composting.


Cleaning of crop residues and mulch
After removing the plants from the greenhouse, all supports and garters are removed: pathogens can remain on the twine. It is better to throw it outside the site or burn it. Reusable metal supports are processed together with the greenhouse structure.
Greenhouse cleaning
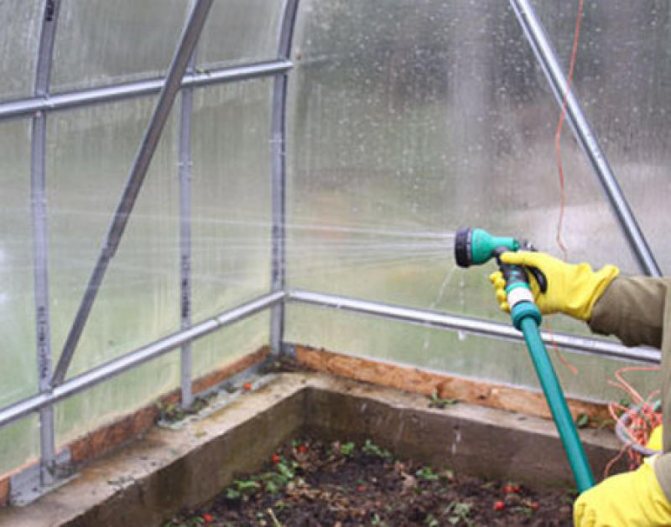
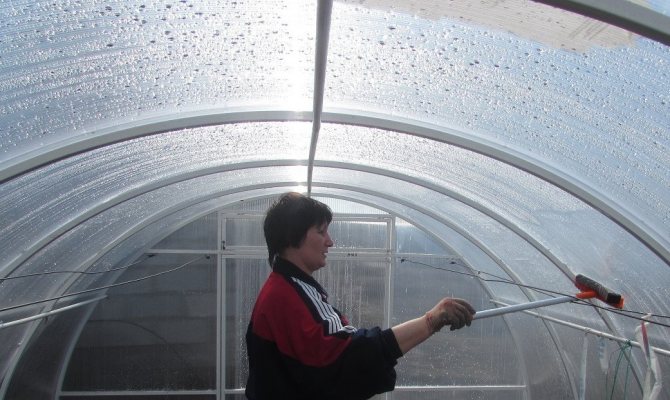
A polycarbonate greenhouse must be washed in the fall. Wet cleaning allows not only to remove dirt, but also to wash off viruses, spores and fungi that have settled on structures, as well as dust and chemical residues from spraying and fertilizing.
Polycarbonate is not scratch resistant, so only soft sponges or microfiber rags are used to clean the greenhouse. You can use the sponge mop on the handle to make the job easier.


Microfiber cloth
It is best to wash polycarbonate with warm water and laundry soap or liquid detergent. The soap foam is applied to the entire inner surface, paying special attention to the joints of the polycarbonate and the frame. Withstand 5-10 minutes and washed off by hand or from a hose with clean water.


Washing polycarbonate greenhouse
Note! The water pressure should be moderate so as not to damage the polycarbonate.
After rinsing the inside of the greenhouse, it is advisable to immediately rinse the outside to remove any dirt from it. It is easier to remove snow and ice from a clean surface in winter.
Soil preparation
If the soil in the greenhouse is heavily contaminated with bacteria, viruses or fungi, it is recommended to remove and remove it. Usually the top layer of soil is removed with a thickness of 7-10 cm. The soil cannot be used for other crops, it is best to take it outside the garden and spill it with a disinfectant. In place of the removed soil, after all treatments, fresh fertile is poured. In moderate fungal and bacterial infestations, the soil is treated with chemicals. Since spores of fungi and bacteria are located mainly on the surface of the soil, it should not be dug up before treatment with antibacterial compounds and fungicides.
The situation is different with insect pests. For hibernation, they usually hide in the most secluded places or bury themselves in the ground. To facilitate the access of chemicals to a sufficient depth, it is better to loosen or dig up the ground in the greenhouse before processing to 15-20 cm deep.


Digging and soil preparation
Simultaneously with the digging, fertilizers and copper-containing preparations can be added - they inhibit the development of fungal diseases.
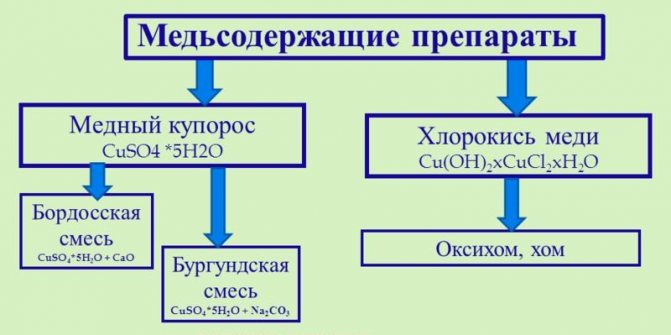

Copper preparations
Bordeaux mixture prices
bordeaux mix
Biological methods of nematode control
One of the ways to expel the nematode from the greenhouse without resorting to potent drugs is to plant biologically active plants, enemies of this parasite.
These include:
- undersized small-colored marigolds;
- calendula;
- mustard leaf;
- oil radish;
- watercress.
These plants also ward off most soil pests, including bear and wireworm. Marigolds can be sown even before harvesting the main crop for seedlings in a small area, and transplanted in early autumn. The rest of the plants sprout and grow quite quickly, during the autumn months they will have time to have a beneficial effect on the soil without suppressing its microflora.


Biological methods of nematode control
Note! Watercress, in addition to improving the soil, can be used in food as leafy greens for salads. It has a pungent mustard flavor and aroma.
Treatment with biologically active drugs
Healthy soil itself successfully fights against over-proliferation of pests due to the constant work of beneficial soil bacteria. By increasing the number of the latter, you can enhance the protective properties of the soil. Preparations containing beneficial soil bacteria are called bioactive.
These include:
- Baikal-EM1;
- Radiance;
- Phoenix;
- Fitop-Flora-S.


Baikal EM-1
The preparations are introduced into the soil by irrigation. To do this, they are bred in water with a temperature of about 25 ° C and the soil is watered. At the same time, the temperature in the greenhouse should be at least + 15 ° С, since microorganisms cannot multiply in the cold. It is best to carry out this treatment immediately after harvesting vegetables.
Prices for "Baikal EM-1"
baikal em 1
Once in the soil, bacteria begin to multiply actively, this is facilitated by moderate humidity and nitrogen, therefore, simultaneously with the introduction of biological products, complex fertilizers can be embedded in the soil - superphosphate, nitroammophoska or organic matter. Soil bacteria feed on pathogenic fungi and pathogenic bacteria, among other things, due to which they clean the soil in the greenhouse without the introduction of chemicals.
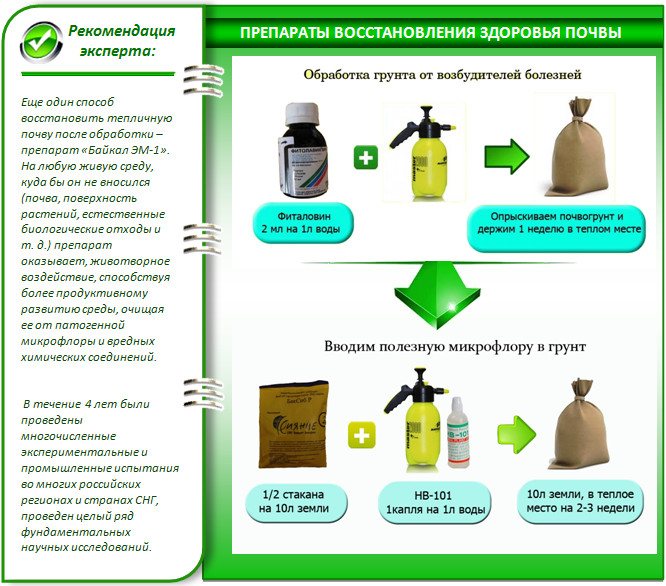

Soil cultivation in the greenhouse with biological products
Additionally, the greenhouse is treated with fungicides, for example, phytosporin. It is bred according to the instructions and sprayed on the walls, frame and soil surface. This drug does not harm soil bacteria, so it can be used prophylactically, even without signs of fungal diseases.It provides good protection against late blight, cladosporium disease, powdery mildew and fungal rot.
Treatment with chemicals from harmful insects
This method of disinfection is used if pests were observed in the greenhouse during the season, and measures for their destruction gave an unsatisfactory result. It should be remembered that chemicals rarely act selectively, in addition to harmful insects, they also kill useful ones. To reduce harm, you should strictly follow the instructions for the drug.


Systemic insecticides
Most of the preparations for soil cultivation are applied to the soil by irrigation. They take precautions: put on gloves, a respirator, and in the case of using strong poisons, a gas mask.
The drug is diluted in the required proportion, poured into an irrigation can or a sprayer, and all areas of the soil are processed, and in the case of spraying, the walls of the greenhouse. It is not necessary to wash off the preparations. After a while, they decompose and are removed from the soil with melt water.


Soil treatment with chemicals
Note! In order to flush the soil after the chemicals, it is recommended to throw at least half a meter of snow into the greenhouse at the beginning of spring. In this case, with melt water, non-decomposed chemical substances will leave the fertile soil layer.
Complex processing and disinfection
With the appearance of bacterial and viral diseases in the greenhouse, severe infection with fungal diseases and a large number of pests, it is necessary to sacrifice soil microflora and carry out complex processing with potent substances.
These include:
- copper sulfate;
- pharmaiod;
- bleaching powder;
- bordeaux liquid;
- formalin.
You can start processing with these compounds only after cleaning and washing the greenhouse. Processing is carried out in late autumn, before the conservation of the greenhouse for the winter.
Copper sulfate It is sold in the form of a blue-green or light blue powder. It is bred in the proportion of 1 tbsp. spoon on a bucket of water and spill the soil, and also spray the walls of the greenhouse and frame elements with it. The treatment acts on bacteria, fungi and insects, in addition, when the soil is saturated with copper compounds, the risk of developing fungal diseases is reduced.


Copper sulfate
Pharmayod - aqueous tincture of iodine. Diluted to a slightly brown color in warm water and treat the soil and the greenhouse itself from pathogenic bacteria. This measure is more likely a preventive measure, it is better to use it in combination with other drugs. Potassium permanganate, diluted to a bright pink color, has a similar effect.


Pharmayod
Bleach sold in powder form. It is scattered on the surface of the soil to fight bacteria and insects. Bleach well removes spider mites, against which other means may not be effective. In this case, lime is sprinkled not only on the soil, but also on the lower part of the walls of the greenhouse. In order for the drug to lay down better, the walls can be pre-moistened.


Bleaching powder
Bordeaux mixture Is a mixture of copper sulfate and slaked lime. It acts on almost all harmful insects, as well as bacteria and pathogenic fungi.


Bordeaux mixture
To use Bordeaux liquid, it is important to prepare it correctly.


Ingredients for Bordeaux liquid
- Dilute 100 g of copper sulfate in 1 liter of hot water until the crystals disappear, bring it to 5 liters with cold water.
- In a separate bowl, dissolve 100-120 g of quicklime in 1 liter of water, wait for repayment, after which the volume is also brought to 5 liters.
- Cool both solutions to room temperature.
- The milk of lime is stirred vigorously with a wooden lath until a funnel is formed and a solution of copper sulfate is poured into it in a thin stream.


Preparation of Bordeaux liquid
- The resulting mixture should be a sky blue hue.It is checked for copper sulfate with a new, non-rusty nail. The nail is dipped into the resulting liquid for a few seconds, removed and examined. There should be no reddish-brown plaque on the nail. If there is one, milk of lime is added to the solution.
Greenhouse elements and soil surface are sprayed with Bordeaux liquid. It is better to do this immediately after preparation, even after a short storage, the solution loses its properties.
Formalin used when the greenhouse is very infected - it kills all living things in it, including earthworms and beneficial bacteria. It is possible to process the greenhouse with formalin only in a protective suit, gloves and a mask, as it is poisonous.


Formalin
Formalin is poured along the furrows and covered with a cloth for uniform evaporation, after which the greenhouse is sealed for a day, the doors are closed and the cracks are sealed with masking tape. After a day, it is ventilated, after which a complete digging of the soil is performed on the bayonet of a shovel.
How to treat a greenhouse from a spider mite in the fall
To find out the answer to this question, we recommend that you read this article. In addition, you will probably be interested in learning about how to properly deal with whitefly in a greenhouse!
Using the sulfur checker
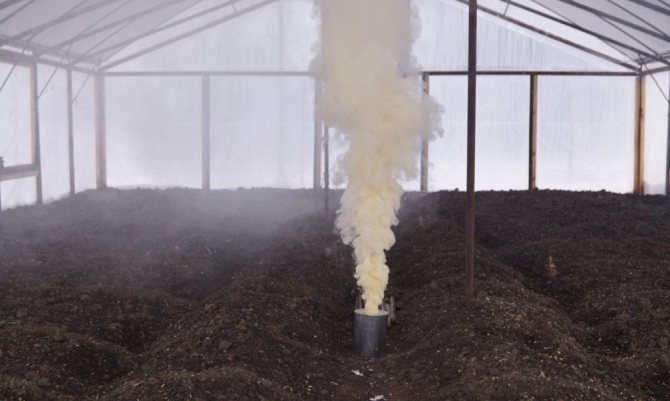
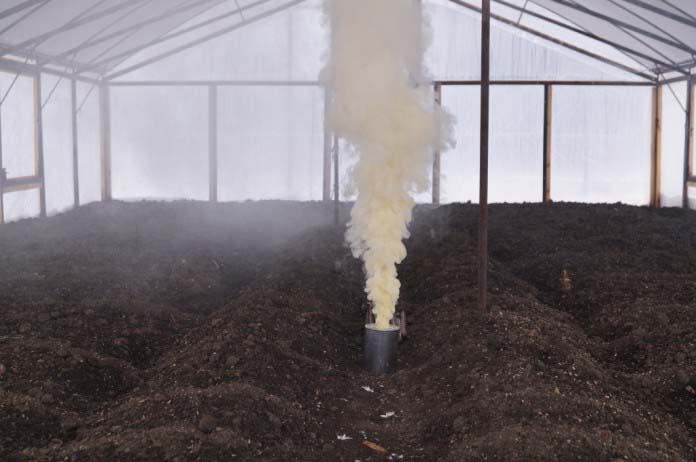
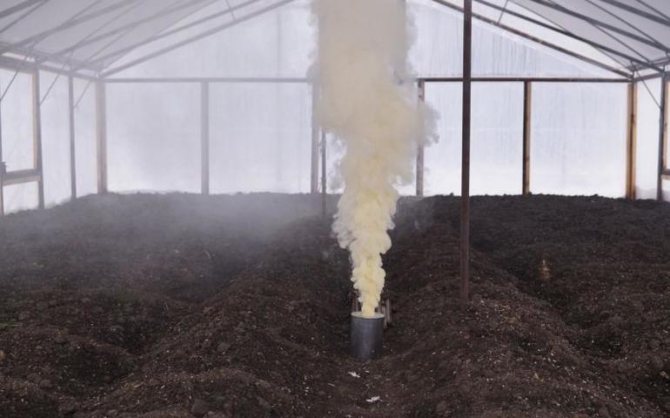
The sulfur checker is a radical method of pest and bacteria control. The smoke emitted by it contains sulfur dioxide, which gets into any crevice, as well as deep into the soil, while killing parasites, pests and microorganisms. The use of checkers requires preliminary preparation of the greenhouse and adherence to processing technology.


Sulfuric bulk checker PESHKA-S
Sulfur Smoke Bomb Prices
sulfuric smoke bomb
Step 1. The greenhouse is tidied up and washed, then dried. All unprotected metal elements are thoroughly lubricated with grease - corrosion will begin from sulfur compounds, which will be impossible to stop. If the paint has peeled off on the frame, it must be restored and dried.


Greenhouse cleaning
Step 2. The walls of the greenhouse are moistened with water, paying attention to the joints with the frame. Reacting with water, sulfur dioxide turns into a weak acid with disinfecting properties. This increases the efficiency of processing.


Moisturizing the walls
Step 3. Glue with tape or seal all the cracks in the greenhouse with sealant. If there are gaps on the door, scotch tape is prepared to quickly glue them after lighting the checkers.


Sealing cracks
Step 4. Wear a protective suit, gloves and a respirator, or better - a gas mask. Sulfur dioxide is a potent poisonous substance.


Protective equipment
Step 5. Prepare a metal sheet and paper for ignition, as well as the number of checkers required for the greenhouse area. The sheet is placed in the center of the greenhouse, paper and checkers are set on fire. They quickly leave the greenhouse and close the door, fill up the cracks if necessary.
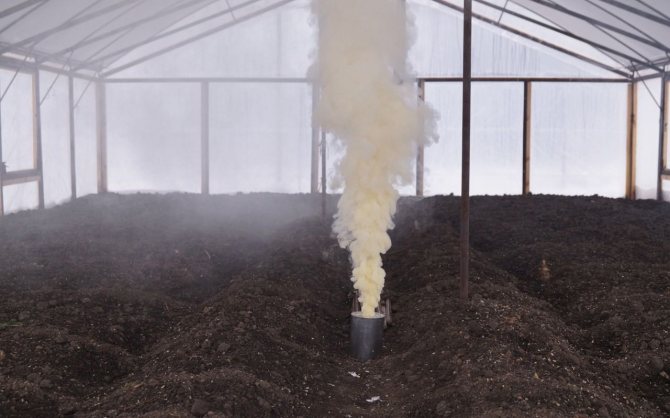


Sulfur checker
Step 6. Leave the greenhouse with the evolved gas closed for three days. Then the vents are opened and the greenhouse is thoroughly ventilated, only then can any work be carried out in it.


Airing
Note! A plaque may appear on the walls of the greenhouse and the frame, which is better to gently wash off with a sponge, being careful not to get it on the soil. On contact with water, it turns into acid and acidifies the soil.
Video - Fumigation of the greenhouse with a sulfur checker
Freezing the greenhouse
A clean method that doesn't cost you any money is to freeze the soil in your greenhouse. To do this, you just need to fix the vents or doors in a slightly open position. With the help of freezing, you can completely get rid of the whitefly, as well as other types of insects that winter in the soil.
In addition, the open window helps to equalize the temperature inside the greenhouse, as a result, condensation and ice will not form on its walls, and it will be much easier to remove snow from polycarbonate.In most cases, the snow simply slides off the smooth surface under its own weight.
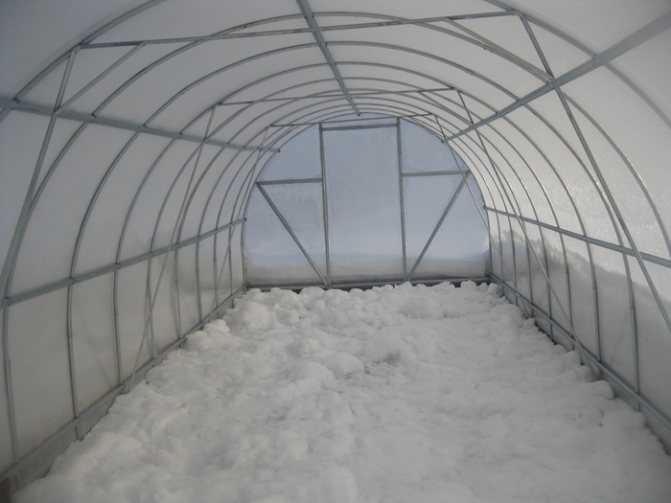


Snow in the greenhouse for the winter
At the end of winter, do not forget to throw snow into the greenhouse - the melt water will not only moisten the soil and make it easier for you to water when planting seedlings, but will also allow soil microorganisms to wake up earlier and start working on the fertility of your greenhouse.
Disinfection of greenhouse structures
After the greenhouse has been cleaned and part of the soil has been replaced, it is necessary to check the frame. Autumn is the time to tighten the fasteners of mechanisms and joints. At the same time, the concentration of microorganisms in the greenhouse reaches its maximum level. This is especially true among summer residents who grow one crop in a greenhouse, most often tomatoes.
The accumulation of microorganisms can be everywhere on windows, ceilings, walls, supports and shelves. Copper or iron vitriol, bleach, formalin are used as a disinfectant. If there are wooden parts in the greenhouse, then they are covered with lime. For the treatment of the greenhouse, sprayers and long-bristled brushes are used; it is important that all hard-to-reach meta are also disinfected.




























